Table “Cervical length during pregnancy by week”
The organ matures rapidly during the last two prenatal weeks. Its length is reduced to one centimeter, and the cervical canal, closed by a mucous plug throughout the entire gestation period to protect the fetus from various infections, opens and forms an exit from the uterus to the vagina. This is how the body should prepare for the birth process; all deviations have their own reasons and require mandatory correction.
As can be seen from the table, the average length of the cervix at 36 weeks of pregnancy is 28.6 mm.
The normal course of pregnancy depends on the condition of both the uterus itself and its lower segment - the cervix. By holding the baby in the uterine cavity and ensuring its connection with the vagina, it directly affects the development of labor. It is important to promptly monitor its length in order to prevent problems that may arise due to various violations.
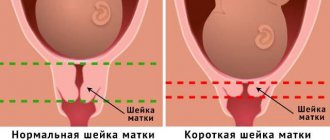
Normal cervical length during pregnancy
A pregnant woman will have to undergo many examinations, during which abnormalities may be detected. What is undesirable in this condition is shortening the length of the cervix. Timely diagnosis of this pathology will allow you to avoid risks, including miscarriage and premature birth.
The cervix performs an important function. It closes the entrance, securely holds the baby in the womb, and prevents the penetration of vaginal secretions and pathogenic microflora.
A short cervix is a serious threat
The length of the cervix during pregnancy is an important indicator for assessing the condition of the pregnant woman. It is not permanent. Closer to childbirth, the cervix becomes smaller and this is normal, since the tissues stretch. But in the early stages, the length of the canal should be within normal limits; this is the key to a pregnancy without complications.
How is the length of the cervix measured?
Pregnant women may not even be aware of the measurements taken, because if there are no deviations, the woman is not notified. This examination is called cervicometry.
It is an ultrasound of the reproductive system and is carried out at 20-24 weeks.
If the first routine ultrasound examination showed abnormalities, the length of the cervical canal can be measured at an earlier date with a break of 1-2 weeks.

External ultrasound to measure the length of the cervix during pregnancy, preferably in later stages
No special preparation is required for the ultrasound; you should empty your bladder before the procedure. This is necessary for greater comfort for the pregnant woman herself. The examination is painless, there is no need to worry.
During cervicometry, not only the length is studied, but also the density and degree of dilatation of the cervix, its readiness for the maternity process. Normally, it should gradually soften and shorten closer to childbirth.
The length of the cervix can be measured on ultrasound in 2 ways: externally or transvaginally, that is, using a special sensor that is inserted into the vagina.
There is also a manual method. The examination is carried out on a gynecological chair, but it is impossible to determine the exact length. Thanks to this technique, it is possible to assess the degree of opening, density and condition of the pharynx.
Norm and pathology
A woman needs to know when to be wary. Until the 27th week, there should be no shortening or opening of the pharynx. If at this stage the length is less than 25 mm, then a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is made. This condition is a threat of miscarriage.
A long cervix in the later stages, like a short one in the early stages, is not the norm.
The norms for the length of the cervical canal are as follows:
- 10-14 weeks – 35 mm;
- 15-19 weeks – 36.2 mm;
- 20-24 weeks – 40.3 mm;
- 25-29 weeks – 41 mm;
- 30-34 weeks – 36.4 mm;
- 35-40 weeks – 28.6 mm.
These are average values. In the first and second trimester, the length is maximum, as the fetus rises. In the last stages, the cervix shortens due to its maturation and lowering of the abdomen.
The minimum acceptable value in the early stages, which does not indicate isthmic-cervical insufficiency, is 30 mm. The minimum cervical length in the third trimester is 25 mm.
If the cervical canal is shortened even further, then surgical intervention is performed to apply a ring. This is the only way to save the baby.
Starting from the 37th week, the cervix is actively ripening. It softens, is located in the center of the small pelvis, and opens. Its length can even reach 15 mm, and this is not a pathology.
The cervical canal becomes the shortest at the time of childbirth, as it opens and stretches in breadth.
There are differences in the length of the cervix between first-time mothers and women who have given birth more than once, so you should not draw conclusions on your own with the results in hand. Only a specialist can identify the pathology.
In multiparous women, the cervix may be slightly shortened compared to women who give birth for the first time. However, during the second pregnancy, the decrease in its length closer to the date of birth is not so pronounced, since dilatation occurs rapidly. The cervix dilates and shortens rapidly during the birthing process.
Multiparous women sometimes have problems with the length of the cervical canal, although this pathology was absent in the past. Previous births may be to blame.
Why is a shortened neck dangerous?
A shortened neck is unable to perform its intended functions. There is a risk of premature dilatation and miscarriage. If the pregnancy can be maintained, there will still be threats. When the neck shortens, the throat does not close tightly. There is a possibility of infections, and this is another reason for premature birth.
Why is the neck short?
This pathology occurs for the following reasons:
- lack of progesterone;
- abortions, cervical injuries during previous births, for example, the application of obstetric forceps, ruptures;
- hormonal changes;
- inflammatory or infectious processes that lead to shape deformation and scarring;
- cauterization of erosion, cervical surgery, circumcision;
- uterine bleeding leading to unfavorable changes;
- physiological structural features.
Why is medical supervision needed?
It is advisable to conduct an examination of the cervical canal before conception. If it is shortened or there is another pathology, this will allow maintenance therapy to be started in advance and will minimize the likelihood of miscarriage.
Medical supervision is mandatory throughout pregnancy so that a specialist can monitor the condition of the cervix and fundus of the uterus and, if necessary, can quickly respond and select effective therapy.
Normal indicators
Until week 20, the size remains virtually unchanged, and there is no need for observation, however, further changes should be monitored. Although the length of the cervical canal is slightly different for all women, there are certain standards that allow you to control the process and make it possible to detect deviations. Standard indicators are determined based on medical research. To continue the pregnancy, if something goes wrong, urgent treatment or hospitalization may be required.
At the beginning of the article there is a table indicating the normal length of the cervix at 36 weeks.
cervical dilatation during pregnancy
1. Uterus, size and shape.
Average dimensions of the uterus: body length of the uterus - 4.4-5.6 cm,
thickness of the uterine body - 3.2-4.3 cm,
The width of the uterine body is 3.2-5.5 cm.
Cervical dimensions: cervical length - 2.8-3.7 cm,
cervical thickness - 2.6-3.3 cm, cervical width - 2.9-5.3 cm.
2. Endometrium.
Ultrasound anatomy of the endometrium is considered in relation to the various phases of the menstrual cycle with the so-called “ideal” cycle lasting 28 days, with ovulation on the 14th day. During menstruation, a thin hyperechoic stripe or hyperechoic echostructures (blood clots) are detected in the uterine cavity. Sometimes the cavity appears slightly dilated due to echo-negative contents (liquid blood).
On days 5-7 of the cycle (early proliferation phase), the endometrium has a relatively low echogenicity and a homogeneous echostructure. The thickness ranges from 3-6 mm, averaging 5 mm.
In the center of the M-echo, already during this period, a hyperechoic thin line can be detected, representing the border of contact of the anterior and posterior layers of the endometrium. On days 8-10 of the cycle (medium proliferation phase), the endometrium thickens somewhat - on average up to 8 mm (fluctuations 5-10 mm). The echo structure remains virtually unchanged compared to the previous period.
On days 11-14 of the cycle (late proliferation phase) - in addition to further thickening, on average up to 11 mm (fluctuations 7-14 mm), the echogenicity of the endometrium begins to increase slightly - at this stage it can be called average.
On days 15-18 of the cycle (early secretion phase), a slower growth rate of the endometrium is characteristic, but the latter still continues to thicken, reaching an average of 12 mm (fluctuations 10-16 mm). The echogenicity continues to increase, and this occurs from the periphery to the center, as a result of which the hypoechoic central fragment of the endometrium takes on a teardrop-shaped appearance (the wide part in the area of the uterine fundus, tapering towards the cervix). During this phase, the hyperechoic line in the center is no longer clearly visible.
On days 19-23 of the cycle (medium secretion phase), the endometrium reaches its maximum thickness - an average of 14 mm (fluctuations 10-18 mm). The echogenicity increases even more; the hyperechoic line in the center is poorly visualized.
On days 24-27 of the cycle (late secretion phase) - the thickness of the endometrium decreases slightly - on average 12 mm (fluctuations 10-17 mm). An essential feature of this period is the high echogenicity of the endometrium in combination with a heterogeneous internal echostructure, due to which the line of closure of the layers ceases to be visualized.
The uterine cavity in postmenopause is an M-echo in the form of a thin hyperechoic line 1-2 mm thick. The acceptable upper limit of normal in postmenopause should be considered an M-echo thickness of no more than 4-5 mm.
When Dopplerography of the uterus, attention is paid to changes in indicators of both the speed and resistance of blood flow, depending not only on the caliber of the vessel, but also on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Doppler assessment of the endometrium is of particular importance when searching for gynecological pathology and should be performed in the early proliferative phase. It is important to emphasize the lack of visualization of intraendometrial blood flow during this period.
During Doppler examination in postmenopausal women, intraendometrial blood flow is normally not visualized.
3. Ovaries Sizes of ovaries:
Length - 20-37 mm,
Thickness - 16-22 mm,
Width - 18-30 mm,
Volume - 4.0-10.0 cm3.
On days 5-7 of the cycle (early proliferation phase or early follicular phase), the visualized part of the follicular apparatus consists mainly of 5-10 tertiary, or antral follicles. The latter have the appearance of round echo-negative inclusions with a diameter of 2-6 mm, located mainly along the periphery of the ovary. A network of spiral vessels around the developing follicle appears already at the beginning of the antral phase. In this case, the blood flow is visualized in the form of a few color loci in the stroma and along the periphery of the antral follicles.
On days 8-10 of the cycle (middle proliferation or middle follicular phase), a dominant follicle usually appears, the diameter of which is already 12-15 mm and continues to increase, while the growth of other follicles stops, and they reach 8-10 mm in diameter, undergo atresia (which is sonographically determined by a gradual decrease and disappearance towards the end of the menstrual cycle).
The blood supply to the dominant follicle usually occurs through two or three stromal arteries, usually visualized along the periphery, or even in the wall of the latter. At the same time, Doppler indicators of the stromal arteries and arteries of the dominant follicle do not differ significantly.
On days 11-14 of the cycle (late proliferation phase or late follicular phase), the dominant follicle increases by 2-3 mm per day, reaching 18-25 mm (average 20 mm) by the time of ovulation.
Prognostic signs of ovulation, indicating that the latter will occur in the next few hours, include: the diameter of the dominant follicle is 18 mm, a double contour around the latter, as well as fragmented thickening and unevenness of the internal contour of the dominant follicle.
The vascularization of the dominant follicle becomes subjectively more noticeable compared to other follicular structures only on the eve of ovulation. The occurrence of ovulation can be judged echographically by the disappearance of the dominant follicle or a decrease in its size with deformation of the walls and the appearance of echogenic contents in the cavity, as well as the appearance of fluid in the pouch of Douglas.
On days 15-18 of the cycle (early secretion phase or early luteal phase), a corpus luteum with a diameter of 15-20 mm (usually smaller than the dominant follicle) appears at the site of ovulation, having an irregular shape, uneven contours, and an extremely diverse internal echostructure of varying degrees of echogenicity.
This peculiar echographic polymorphism is easily explained by the morphological substrate of the nucleus of the corpus luteum, which is a blood clot in varying degrees of thrombus formation and lysis.
On days 19-23 of the cycle (mid-secretion phase or mid-luteal phase), the “blooming” corpus luteum is characterized by a slight increase in diameter (up to 25-27 mm), as well as the appearance of an unevenly thickened echo-positive ridge.
The echogenicity of the contents due to lysis can gradually decrease until the formation of a “cystic” corpus luteum. During the first days after ovulation, a dense, multilayered vascular network is formed around the corpus luteum, especially pronounced during the flowering phase. On color Dopplerograms, a pronounced color ring appears around the corpus luteum, the blood flow in which is characterized by high speed values and low impedance. This is typical of rapid physiological neovascularization.
On days 24-27 of the cycle (late secretion phase or late luteal phase), the “fading” corpus luteum decreases in size (10-15 mm), its echogenicity increases slightly, and the echostructure becomes more homogeneous. In this case, the corpus luteum often begins to be poorly visualized echographically.
In the absence of pregnancy, the blood supply to the corpus luteum begins to change approximately 9 days after ovulation.
The tissue of the corpus luteum begins to undergo luteolysis, the capillaries contract and are reduced, which is characterized by a noticeable depletion of local blood flow.
During menstruation, the corpus luteum, as a rule, is no longer defined, or in its place a fuzzy echostructure of increased echogenicity with a diameter of 2-5 mm (corpus alba) remains, which usually disappears without a trace during the next menstrual cycle. It has been proven that the non-passing white body in the form of a scar is preserved only after the gravidar corpus luteum.
Blood circulation in the vessels of the disappearing corpus luteum stops, and the vessels themselves disappear during the first three days of menstruation.
Diagnostic methods
The condition of the uterus and all its elements is assessed using two methods:
- When examined in a chair by a gynecologist. The doctor determines the approximate density and length of the cervix, its location in relation to the pelvic axis, and the condition of the external pharynx.
- Through ultrasound. The examination allows you to determine the structure of the external and internal pharynx and calculate the length of the lower segment.
At mid-term, the fetus begins to grow faster, which puts more strain on the muscles, so regular examinations become especially important. Also at this stage, a second screening ultrasound is performed, in which special attention is paid to the cervical canal. If there is a suspicion that it is shortened, a transvaginal examination is auxiliary, which involves inserting a sensor into the vagina, making it possible to measure the length more accurately.
Causes of soft cervix during pregnancy
In addition to indicating the onset of labor, a soft cervix develops at different stages of pregnancy for the following reasons:
- pathological decrease in muscle tone in the organ (due to softening of the walls, the muscles of the organ cannot fully hold the fetus inside), which leads to an increase in pressure inside the uterus and the occurrence of premature birth. This condition is typical from 20 to 30 weeks;
- inflammatory processes in the cervical canal or vagina;
- gynecological diseases associated with a violation of the ratio of connective and muscle tissue (endometriosis, ectopia, etc.);
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- previous births with severe trauma (a large number of ruptures, scar formation, etc.);
- taking medications that affect the condition of the uterus (prostaglandins, etc.);
- a large number of scrapings, which were accompanied by constant mechanical damage.
Also, the cervix shortens and becomes soft before menstruation. This happens to make it easier for sperm to enter the cavity and fertilize the mature egg.
If fertilization does not occur, then the woman experiences abundant mucous discharge from the cervical canal. Next, the uterus begins to gradually descend, returning to its original place, the cervix expands, and so-called uterine bleeding appears, which contains unfertilized eggs. This causes the cervix to become very soft.
But if pregnancy does occur, then the cervix acquires a solid structure and, as it were, closes the entire organ. This is created so that the fetus can develop calmly and not leave the organ area. The softening of its walls should occur immediately before childbirth. Shortening of the walls and changes in their density in the early stages indicates a serious pathology.
Short cervix during pregnancy, what to do?
The cervix is of great importance for a woman, especially during pregnancy. Usually, its normal length is from three to four centimeters, but if it turns out to be short, then its size does not exceed two centimeters. A short neck is a fairly common occurrence.
It may cause ICI (isthmic-cervical insufficiency). With this disease, the cervix is not able to hold the constantly enlarging fetus in the uterine cavity.
As a result, it can shorten even more and open under the pressing weight of the child, which often provokes the risk of miscarriage, miscarriage, pathological or premature birth.
Causes of pathology
- The problem can be triggered by injuries received during an abortion, cervical rupture during unsuccessful previous births, or labor using obstetric forceps.
- The genetic predisposition of the body is a common cause of pathology, but still, this applies more to acquired anomalies than to congenital ones.
- Hormonal disturbances during the restructuring of the body of a pregnant woman are another reason for a short cervix.
- When a woman has undergone many surgeries on the genitourinary organs or has had an infection, this could provoke a problem.
- A large child makes it difficult to eliminate the problem if a woman has polyhydramnios or multiple pregnancies.
- If the expectant mother has been diagnosed with this, she will have to see a doctor for the entire period of pregnancy.
Diagnostics
That a woman has a short uterus can be noticed in the twenty-first week of pregnancy; the signs are: shortening of the cervix, softening, and sometimes the cervix opens early and premature labor begins. Typically, these signs appear when the child suddenly begins to gain weight and increasing pressure is placed on the cervix.
A woman may experience colorless or slightly bloody vaginal discharge, feel heaviness in the lower abdomen, and later may begin to experience severe pain.
Don't wait, go to the gynecologist right away! The doctor examines the patient (vaginal examination) and, to confirm the diagnosis, sends her for an ultrasound examination. An ultrasound can confirm or refute the diagnosis.
To measure the length of the cervix, a transvaginal ultrasound is added to the usual one. This study is carried out with a transvaginal sensor, which accurately shows the size of the cervix.
What is the danger?
A short cervix detected at 20-22 weeks can cause spontaneous abortion or stillbirth. This means that the female body cannot overcome the load placed on it. Also a risk factor is the 34th week, when the fetus has already formed, and the patient’s body begins to prepare for childbirth with redoubled force.
Cervical pathology between 14 and 24 weeks indicates premature onset of labor:
- if the length is less than one centimeter, then the baby can be born at 32 weeks;
- if the length is less than 1.5 cm, then the baby’s gestational age is 33 weeks;
- less than two centimeters, then 34 weeks;
- less than 2.5 cm, then 36 weeks.
A short cervix at a period of 28-32 weeks can provoke the introduction of various infections, because the shortened organ cannot prevent harmful microorganisms from entering the uterus. The fetus at this time becomes completely defenseless. Such a cervix can speed up the process of labor itself. During rapid labor, numerous ruptures occur.
Treatment
If a pathology is detected, treatment is prescribed after a thorough examination, and the gestational age of the child must be taken into account. The doctor must determine whether the cervix is already dilated.
If the abnormal length is determined at 18 weeks, the doctor may prescribe medications (glucocorticoids) that will slightly equalize hormone metabolism. But if the problem arose before 12 weeks, then you need to be very careful with medications so as not to harm the unborn baby. After all, at this time his main organs are just being formed.
The doctor tries to use different courses of therapy. If the pathology is discovered before 27 weeks of pregnancy, the specialist may apply stitches. This method will be effective even if the opening of the cervix has already begun. The sooner this procedure is done, the better the result will be.
Cerclage or suturing prevents preterm labor. The sutures are removed when the woman’s amniotic fluid breaks, labor begins, or bleeding begins. If the pregnant woman is in normal condition, the sutures are removed at 38 weeks of pregnancy.
During a caesarean section, the stitches are not removed at all.
The second method involves the use of a silicone pessary - a ring. Sometimes it is worn for prophylactic purposes, when there is no shortening of the cervix yet, but the doctor suspects that the patient has isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
Preventive measures
- Medical examinations that a woman should undergo with a gynecologist at least once a year will help identify this pathological disorder. And in order not to provoke it, you need to use reliable contraceptives and try to avoid abortions.
- If a woman is planning a pregnancy and has previously had miscarriages, especially at longer periods, then she should take care of treating her problem in advance.
- Every expectant mother should understand that her condition is not a disease, so you should not give up special fitness and try to wear a bandage.
- Try to avoid a state where the uterus is in good shape, because this can cause the cervix to ripen ahead of time.
Thus, if you detect cervical pathology in time and take the necessary measures, prevent premature dilatation and follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the woman will not feel that she has abnormalities and will be able to calmly give life to her baby!
Source: https://medportal.su/korotkaya-shejka-matki-pri-beremennosti-chto-delat/
Soft cervix as a harbinger of labor
Starting from the 37th week of pregnancy, a woman begins to prepare for the onset of labor. This is a very exciting moment; it requires increased attention, both from the expectant mother and from doctors.
Important! Normally, the cervix is located quite high from the vagina; as the child grows, it approaches it. If, upon examination at 37-39 weeks of pregnancy, the cervix has a very soft structure and opens wide, then the woman is immediately sent to the delivery room.
Among the harbingers of labor include the release of the mucus plug, which covers the lower part of the cervix and the entrance to the vagina. This is followed by the release of amniotic fluid and the onset of labor pains. In this case, the cervix should be located very low, almost in the very center of the vagina.
Cervix by week during pregnancy
Measuring the length of the cervix by week of pregnancy is an important diagnostic sign that can be used to determine various health problems of the woman and the fetus. In addition, the condition of the cervix allows you to predict the date of the upcoming birth. In the article we will talk about what the length of this organ should be and what deviations may occur in this area.
The significance of this indicator during pregnancy
Cervix uteri is the Latin name for the lower part of a woman's reproductive organ. Inside the cervix is the cervical canal. Its upper part is icy with the body of the uterus itself, and the lower part descends into the vagina. The functions of Cervix uteri are as follows:
- Protection of the reproductive organ from various pathogenic microorganisms.
- The cervical canal is tightly closed with mucus, so it does not allow even sperm to enter the vagina at the wrong time.
- On the day of ovulation, the cervix opens and allows male reproductive cells to pass through. Thanks to this, pregnancy occurs.
After conception occurs, the Cervix uteri is again tightly closed with a mucus plug, reliably protecting the fetus from infection and other pathogenic microorganisms that can enter the reproductive organ through the vagina. Another important function of the cervix is to hold the baby as it develops in the womb.
If the Cervix uteri is weak, the woman is at risk of miscarriage or premature birth. That is why it is so important to monitor the condition of the cervix of the uterus throughout the entire period of gestation.
How does the measurement work?
These parameters are measured in medical practice in two ways. The first method is examination on a gynecological chair using a mirror and a colposcope. The second way is to conduct an ultrasound examination.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor determines the condition of the external pharynx, the density of the cervix and the presence of dilation of the cervical canal.
Ultrasound helps measure the length and obtain more accurate information about the condition of the internal pharynx.
The length of the cervix is usually measured after the 20th week of pregnancy. In the first weeks, this indicator, as a rule, is not checked. This is explained by the fact that it is during this period that the baby’s active growth is observed.
Features of measurement in early and late stages
Normally, in a woman in the absence of various diseases, the length of the cervix should be approximately 3-4 cm and the width about 2.5 cm.
These indicators are not absolute and may be less or more depending on the individual characteristics of the girl’s body. If pregnancy has not occurred, Cervix uteri has a pink tint, a smooth structure and a somewhat shiny surface.
After conception, the organ undergoes changes. Due to increased blood circulation in this area, its color becomes bluish or purple.
In addition, the process of maturation of the CMM begins. It will last all 9 months. At the same time, this part of the organ grows, becomes thicker and more elastic. This is necessary for normal labor.
It is worth noting that in the early stages of pregnancy the Cervix uteri should deviate slightly towards the anus and close tightly. In the later stages, the doctor can assess by the condition of the cervix how close the woman is to giving birth. At the same time, this part of the uterus becomes softer, and the length of the cervix gradually shortens.
On an ultrasound examination, you can see that the internal os is expanding, which indicates the imminent onset of labor.
You may be interested in reading an article on the topic of hCG in early pregnancy. All the necessary information is in this article.
Normal organ length by week
Timely diagnosis of abnormalities in the cervix allows you to take all measures to prevent negative consequences. In modern medical practice, various treatment methods are used to treat cervical cancer pathologies.
These include both medications and special fixing devices to support the cervix. That is why doctors recommend that expectant mothers register in a timely manner and undergo Cervix uteri measurement at least four times.
You might be interested in: 5th week of pregnancy
A routine examination of this indicator is carried out approximately at 20, 26-27 weeks, and then at 32-34 and 37-39 weeks of pregnancy. In the table you can see what the length of the cervix should be at different stages of gestation.
| Gestational age in weeks | Average values in mm | First pregnancy | Second and subsequent pregnancies | Standard size in mm | Deviation from the norm |
| 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 35 | 35,2 | 35,7 | 23-45 | 5 |
| 17, 18, 19, 20 | 36 | 36,7 | 36,8 | 30-49 | 5,8 |
| 21, 22, 23, 24 | 40,4 | 40,6 | 40,7 | 33-45 | 4,8 |
| 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | 42 | 40,7 | 42,5 | 33-46 | 4,8 |
| 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35 | 36,7 | 35,9 | 36,4 | 36-43 | 3,9 |
| 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42 | 28,7 | 28,3 | 28,7 | 21-37 | 4,5 |
If in the first and second trimester the cervix is shortened or short, this indicates a threat of miscarriage or premature birth. In this case, the patient requires hormonal or other types of therapy.
The prognosis for a woman is not very good even if the cervix is too long before the upcoming birth.
In addition, it should be noted that in primiparous girls, the length of the Cervix uteri increases more slowly than in multiparous girls.
In case of twins, the length of the cervix may differ slightly from the indicators discussed above. However, it may be slightly shorter than with a singleton pregnancy.
By what indicators does the doctor judge the maturity of the cervix?
During a medical examination, not only the size of the cervix, its shortening or, conversely, lengthening are taken into account. Other criteria also indicate the degree of maturity of the organ. Let's look at them:
- Consistency of CMM. It is rated in points - dense - 0, soft - 1, soft - 2.
- Length. From 2 cm – 0, 1-2 cm – 1, less than 1 cm – 2.
- Location relative to other organs. Tilt back – 0, tilted forward – 1, in the center – 2.
- The degree of opening of the cervical canal. The doctor's finger does not pass - 0, one finger passes - 1, passes 2 fingers - 2 points.
Cervix uteri should be more dense to the touch in the early stages. In the second and third trimester, it becomes softer and smoother, which indicates that it is almost ready for childbirth. If any abnormalities are detected in the expectant mother, the doctor is obliged to inform the patient of the diagnosis and explain what to do to prevent dangerous complications.
You might be interested in: How to tell if your water has broken during pregnancy
A soft cervix, for example, at 38-39 weeks does not mean that the expectant mother has some kind of pathology. This is a completely normal phenomenon before childbirth. It is much worse if the cervix is dense and immature at this stage.
Possible deviations from this body
Measuring the length of the cervix during pregnancy makes it possible to timely suspect various pathologies in a woman. These disorders can cause serious problems, including fetal death and premature birth. Let's take a closer look at common problems.
Ectopic pregnancy in the cervix
It happens that in the early stages of pregnancy the cervix is too enlarged. In this case, the doctor may suspect such a dangerous condition as the attachment of a fertilized fertilized egg in this part of the genital organ. Under such conditions, the embryo lives for approximately 5-6 weeks, less often 6-7, after which it dies and is rejected.
This type of pathology is considered quite rare and occurs no more often than in 0.01% of cases. Read more about ectopic pregnancy here.
Short neck
Shortening of this part of the organ can be either a congenital or acquired condition. In addition, it often happens that such parameters are observed in a woman due to the anatomical features of her body.
Normally, the length of the cervix increases in the first and second trimester and shortens immediately before childbirth. If the length of the organ is too short, it will be difficult for it to support the growing fetus, which often leads to premature birth.
If such a condition is detected, the woman is subject to stricter medical supervision. Often, the expectant mother is offered to go to a hospital for preservation and completely limit physical activity. In addition, methods of treating this pathology include the installation of a pessary - a special ring that prevents the pharynx from opening prematurely. This device is removed before childbirth.
Extended neck
This disorder in women can also be a congenital feature of the body or develop as a result of various medical manipulations in this area, for example, after undergoing operations.
This feature may cause some problems during conception.
We can talk about, for example, improper attachment of the fertilized egg when it is implanted too low to the exit from the reproductive organ.
Childbirth is also complicated for women with this deviation. They are usually painful and protracted, and the risk of rupture increases.
Erosion
Sometimes the length of a woman’s cervix during pregnancy is normal, but a disease such as erosion may be detected. This disorder occurs among the fair half quite often, in approximately 60% of cases. Factors that provoke pathology include a wide variety of causes.
These could be hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes in this area, and much more. Treatment of the disease is carried out using minimally invasive techniques such as cauterization and laser treatment. If erosion is diagnosed in a nulliparous woman, treatment is postponed to rule out problems with the resulting scar.
At the same time, the expectant mother faces the threat of organ rupture and other dangerous complications.
For many girls, after childbirth, erosion goes away on its own. The pathology does not affect the course of pregnancy itself.
Dysplasia
During colposcopy, another problem may be discovered in the patient - dysplasia. Pathology involves processes of change in the epithelium, which indicates precancerous conditions.
In most cases, the disease is diagnosed in women aged 25 to 35 years. Timely treatment of pathology in the early stages allows you to cope with the disease without developing dangerous complications.
You may be interested in: Foley catheter for cervical dilatation
The causes of dysplasia include human papillomavirus. The risk group includes girls suffering from bad habits, as well as patients with weakened immunity and the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases. Another reason is the start of sexual activity too early and frequent changes of sexual partners. Treatment of the disease is carried out with medication or surgery.
A mild degree of dysplasia rarely degenerates into oncology, so this condition requires only medical supervision.
Ectopia
This concept means the same erosion, but with it part of the columnar epithelium is displaced into the vaginal area. During the examination, the gynecologist may see a red round spot that looks very similar to erosion.
In this case, the patient may experience discharge with an unpleasant odor and uncharacteristic color.
The causes of this pathology include mechanical damage to the reproductive organ, as well as various infectious diseases suffered by a woman in the past.
After bearing the baby and giving birth, changes in the form of ectopia observed in the patient, as a rule, go away on their own.
Recommendations for the expectant mother during pregnancy
The period of bearing a baby is a very important and responsible time in the life of every woman. At this stage of life, the expectant mother should be very attentive to her body, since now she has double responsibility. To prevent various complications and miscarriage, a girl should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Sleep and relax more.
- Properly organize working conditions and daily routine.
- Eat right, saturate your body with all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
- To refuse from bad habits. Smoking and alcohol negatively affect the health of the mother and fetus.
- Register in a timely manner and follow all recommendations of the specialist.
- Avoid heavy lifting and heavy physical work.
- Try to eliminate stress and excessive emotional disturbances.
- Devote more time to communicating with loved ones, read books, watch calm films.
If any alarming symptoms occur, you should contact your doctor immediately. All this will help maintain the health of mother and child, as well as prevent such dangerous pathologies as miscarriage, placental abruption and premature birth.
Do you want to know how to register during pregnancy? Then you should definitely read this article.
Shortened cervix during pregnancy at 36 weeks
This deviation is dangerous, as it not only threatens the normal course of pregnancy, but can also provoke a miscarriage.
Causes and consequences
Factors that can cause excessive shortening in the early stages include:
- anatomical and physiological characteristics of the body as such and the reproductive system in particular;
- scars left after an abortion or other surgical interventions, or as a result of muscle rupture during a previous birth;
- pelvic diseases of an inflammatory nature;
- infections suffered during pregnancy;
- complications caused by bleeding;
- progesterone deficiency and other hormonal disorders;
- psychogenic factors such as stress and fear.
IMPORTANT! Most often, shortening of the organ indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Its danger lies in the fact that the cervix with this pathology cannot hold the child in the uterine cavity: it opens prematurely, unable to withstand the load, which entails premature birth.
Cervical length during pregnancy: norm by week, how to increase?
Pregnancy is a special period in life for every girl. The female body has an interesting and complex structure. During gestation, many organs begin to change. A fairly large number of changes occur in the body.

The uterus is one of the most important organs that performs reproductive functions. During gestation, this organ may change. What do expectant mothers need to know and what should they be prepared for?
What is a uterus?
This is a sexual organ with a smooth muscle structure. The organ is unpaired. Inside the organ, the development of the embryo and the gestation of the fetus itself occurs.
The location of the organ is concentrated in the pelvic area, in the middle. The uterus has a cervix, located in the lower part and has a round shape.
The size of the organ changes during pregnancy and after childbirth. This is explained by the process of muscle hypertrophy that occurs during the period of bearing a child.
This organ is one of the mobile organs, capable of occupying different positions in the environment. In shape, this organ resembles a pear.
There are women with different shapes of the uterus and are not always pear-shaped. This does not always indicate the presence of pathology. This is just an individual feature.
The walls of the organ consist of three types of tissues:
- endometrium;
- myometrium;
- perimetry.
In general, the organ itself consists of three parts:
Each part of the uterus plays an important role in the life of women and during pregnancy.
What is the cervix?
Now it has become clear what such an organ is. As mentioned earlier, this organ consists of three parts, one of which is the neck.
The cervix refers, let's say, to the lower segment of the uterus. Accordingly, this is one of the components of the entire organ.
- In the center of the cervix is the canal of the cervix itself.
- One of the ends of the canal passes into the cavity of the uterus itself, and the second end passes into the vaginal cavity.
- The length of the neck reaches approximately three to four centimeters.
Cervical length measurement
As already mentioned, the pelvic organs are quite important organs, the condition of which is under special supervision during gestation.
Why is it important? During the period of bearing a baby, it is important to preserve and hold the fetus in the uterine cavity. If the baby is not kept in the uterine cavity, this threatens to disrupt the course of pregnancy.
It is extremely important to determine the condition of the cervix. This is done by measuring the cervix. There are normal standards that you can follow and monitor the condition during gestation.
Research methods
Women who have never given birth are often frightened by procedures such as cervical length testing. Few people imagine the measurement procedure. How does this happen?
There are two methods by which research is carried out:
- When examined by a gynecologist. When examined by a doctor in the chair, a specialist analyzes the entire cavity of the cervix and the length that needs to be known and controlled. Particular attention is paid to the location of the uterus relative to the pelvic axis.
- Using ultrasound. Another method that is in demand in gynecology. Using ultrasound, it is possible to estimate the length of the cervix.
Control of cervical length begins around the twentieth week. This is explained primarily by the variability of the cervix until the second trimester.
Being, so to speak, at the equator of pregnancy, it is necessary to more regularly monitor the uterus and the cervix itself. This is required for the purpose of prompt detection of pathology. The fetus grows, and accordingly the load increases, which can lead to some health problems.
At the stage of the second ultrasound examination, the condition of the uterus and cervix is assessed. During this period, an ultrasound is performed using a sensor that is moved across the expectant mother’s abdomen.
If a shortened cervical size is suspected, doctors often prescribe a repeat examination. In such cases, the sensor is inserted vaginally. This method will allow you to determine the most accurate dimensions.
Measuring cervical length by week
The following indicators are considered normal:
However, doctors determine the condition of the cervix according to established standards:
- From 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy, the normal size of the uterus should reach from 40 to 45 mm;
- From 25 to 28 weeks, the size should reach from 35 to 40 mm;
- From 32 to 36 weeks the size should reach from 30 to 35 mm.
That is, as you can see, the longer the gestation period, the shorter the length of the cervix.
Short cervix
Short length is one of the most dangerous pathologies in pregnant women. This fact can interfere with a healthy pregnancy.
If the length of the cervix reaches up to 25 mm, then pregnancy is at risk. In such cases, there is a high risk of premature birth or miscarriage. To avoid such problems, doctors place such patients under increased control. After all, the main task of the doctor is to prevent premature birth, after which the likelihood of the child’s survival is low.
Most often, this condition occurs without any associated symptoms and the woman does not feel anything at all. For this reason, it is important to control this process and prevent such gross mistakes.
Causes:
- hormonal imbalance;
- scars formed due to surgical interventions;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- infectious diseases;
- anatomical features that prevent the normal course of pregnancy.
Dangers with this pathology
The danger lies, first of all, in the formation of a diagnosis - isthmic-circvical insufficiency (ICI).
With such a diagnosis, there is a great danger of losing the child.
The entire organ is unable to hold the fetus. Under the weight of the baby, dilatation occurs and this entails premature birth, ending in the death of the child.
The survival rate in this case is low.
As a rule, ICI occurs without symptoms, and the problem can be noticed when examined by a doctor. Sometimes pregnant women suffer from bursting pain in the vaginal area. Pain can spread not only throughout the vagina, but also into the lumbar area and even into the groin area.
Treatment
If a problem such as ICI is diagnosed, doctors offer several solutions:
- courses of therapy using hormonal drugs;
- installation of a pessary;
- installation and suturing of the cervix to avoid problems.
Of course, only the doctor determines which treatment path to choose.
It all depends on how high the probability of miscarriage is, and what the threat may be for the child and mother.
Such measures help prevent uterine dilatation. The sutures placed to hold the cervix in place, as well as the installed pessary, are removed at 38 weeks. It is at this stage that the baby is already full-term and his life is not in danger.
Long cervix
There may be not only a short cervical length, but also an exceeding normal cervical length. Is it dangerous? This will not affect the pregnancy process in any way. If the length of the cervix does not change by the time the baby is born, this may complicate the birth process.
In this case, dilatation during the prenatal period is very difficult and causes difficulties in the process of giving birth to a child. As a rule, in such cases, the doctor decides on an emergency caesarean section.
Causes:
- Features of the anatomical structure. This happens due to circumstances beyond our control. From birth, a woman has an individual formation of all organs and it is not possible to influence this process.
- Surgical interventions. Surgical interventions can provoke problems in the future, both during childbirth and during pregnancy.
- Violation of generic dominance. This happens when a woman is afraid of childbirth, her psycho-emotional state is disturbed, stress and depression occur.
Consequences during childbirth
- The consequences may not be as dire as with a short cervix.
- In the case of a large length, the hardness of the organ increases, it becomes oaky and there is a need to soften it.
- Moreover, for these reasons, poor dilatation occurs and this interferes with the process of giving birth to a child.
- If during the prenatal period it was not possible to smooth the cervix and eliminate the problem of cervical structuring, then in this case a caesarean section is promptly performed.
Symptoms of ICN
The diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is determined on the basis of medical studies, however, there are signs by which a pregnant woman can identify a possible problem before undergoing an ultrasound. The pathology is often accompanied by bursting pain in the vagina, which also spreads to the lumbar region and groin.
However, you cannot rely only on the absence or presence of pain. The course of ICI can be asymptomatic, and the woman will not feel anything suspicious until the very moment when it is no longer possible to save the situation. This is why observation by a gynecologist is necessary.
Treatment
What therapeutic measures need to be taken in each specific case is decided by the doctor, based on the cause of the pathology. So, the following can be used:
- Hormonal drugs. They are prescribed in cases where INC is caused by endocrine disorders and restoration of hormonal levels can still return the size of the organ to normal.
- Installation of a pessary. It is a ring made of silicone or plastic and is installed directly in front of the canal through the vagina. The procedure takes only a few minutes and does not require painkillers. The pessary supports and is used in combination with medications. A pregnant woman with an obstetric pessary should remain in bed most of the time and avoid any stress to ensure that the device does not become dislodged and performs its function properly.
- Cervical cerclage. This procedure is also known under a simpler name, which immediately reveals its essence - suturing the cervix. There are two main methods by which cerclage can be performed: Shirodkar and MacDonald. The latter involves the application of temporary circular sutures, which temporarily narrow the canal and are removed at approximately 37 weeks of pregnancy. If cerclage is carried out according to the first method, then the suture will be permanent, and childbirth will require a cesarean section. Being a surgical intervention, cerclage is performed under anesthesia - epidural or spinal, less often general.
Regardless of what kind of treatment was prescribed, constant medical supervision is a prerequisite for therapy. The specialist must keep the process under control in order to correct it in time if necessary.
Medical supervision is especially important in the first time after cerclage has been performed, since the procedure is associated with certain risks. To make sure that the surgical intervention does not provoke premature onset of labor, doctors monitor the pregnant woman’s condition for several hours. During the first week, it is advisable to move as little as possible and observe bed rest, and you also need to mentally prepare for the fact that after suturing, cramps and minor bleeding are possible for several days.
Elongated cervix
Not only a short, but also a long neck is possible. This situation may be due to the following reasons:
- atypical structure of the patient’s organ;
- previous operations;
- an unformed or disturbed generic dominant, which manifests itself in a depressed state of mind, fear of the upcoming birth.
The elongated canal does not affect the course of pregnancy at all and does not pose a danger to the development of the fetus, but it can complicate the birth itself. The long neck usually has a compacted structure - obstetricians sometimes call it “oak” - and does not open well during contractions, and in some cases does not open at all, which will require an emergency caesarean section.
In order for the birth to take place naturally and without complications with an elongated organ, the woman is prescribed medications that are designed to soften and smooth out the structure. As a rule, such therapy is carried out in preparation for childbirth.
Prenatal changes
The lower segment of the uterus is a hollow ring-shaped muscle, the length of which in non-pregnant women is mainly from 4.5 to 3 cm. During pregnancy, it gradually contracts, this process begins to take place actively from the 37th week (the rates of changes at earlier stages are shown in the table above).
The organ becomes not only shorter, but also softer and centered in relation to the pelvis. The period during which these changes occur varies depending on the characteristics of the reproductive system of the woman in labor. So, in some women, the cervix smoothes out to the final state (1-1.5 cm) and opens properly over several days or even weeks, while in others this process takes place within a day or just a couple of hours before the onset of contractions.
Whether a woman gives birth for the first time or the second time does not have much influence on the course of changes. The process sometimes differs only in that in pregnant women who have given birth before, the contraction during the early stages will be less pronounced, but will pass quickly immediately before childbirth.
From the moment of conception to childbirth, the cervix undergoes various changes, the most important of which is shortening in length. This indicator affects whether the expectant mother will be able to carry the child for the entire prescribed period or not, and deviations from the norm are fraught with such serious consequences as miscarriage and premature onset of labor.
A short cervical canal, however, is not a categorical contraindication to motherhood, and the negative impact of the pathology can be balanced by various therapeutic measures, in particular the use of a pessary or cerclage. In order to identify the problem in time and eliminate it, you need to be observed by a gynecologist and take his recommendations responsibly.
Cervical length during pregnancy: norms for cervical length by week
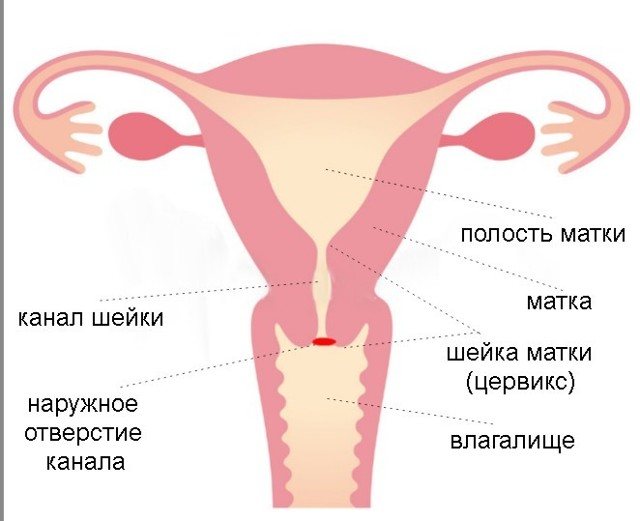
The cervix is the lower segment of the uterus itself, where a canal is located in the center and the first end of the canal opens into the uterine cavity, and the other end of the canal opens into the vagina. The length of the cervix is 30-40 mm, while the cervical canal is closed.
What is considered normal
The correct anatomical structure of the cervix consists of a vaginal part, which doctors examine using a gynecological speculum. The cervix is connected to the vagina using fornixes: the anterior, posterior fornix and two more lateral ones. The cervical canal runs along the entire cervix.
This canal is completely clogged with special mucus, which prevents pathological microbes from entering the uterine cavity. Also, this mucus can prevent sperm from entering. Mucus changes during the menstrual cycle.
For example, in the middle of the cycle, mucus has the property of liquefying, which allows sperm to penetrate into the uterine cavity, where they enter directly into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal.
During pregnancy, the cervix is tightly closed with mucus, due to which the protection against fungi and microbes becomes stronger.
The cervix itself is also capable of changing its size. For example, during childbirth, the cervix dilates by an average of 10 cm.
The cervix has a special function during pregnancy - to directly hold the developing fetus in the uterine cavity.
How to measure and why
The size of the cervix is usually determined in two ways:
- Manual examination using a speculum: assesses the external os (closed or open), the cervical canal and the density of the cervix.
- Ultrasound examination of the cervix: this study helps to reliably determine the size of the cervix and shows the condition of the internal os.
When registering a woman for pregnancy, the doctor examines the cervix manually, and then the size of the cervix is monitored from the 16th week of pregnancy until delivery.
From the second trimester of pregnancy, ultrasound examination is performed transabdominally. During this examination, if the doctor notices a suspicion of deviation from the norm in the size of the cervix, then in this case an intravaginal ultrasound examination is prescribed. Because only with this study can you accurately see the length of the cervix, as well as measure it.
All measurements of the cervix are necessary to exclude premature birth.
Normally, during pregnancy, cervical length testing is prescribed 4 times.
Changes during pregnancy
In the early stages, when pregnancy occurs, the cervix changes. Normally, a healthy woman’s neck is pink, slightly shiny, and has a smooth surface. During pregnancy, the color of the cervix becomes bluish, cyanotic. This is a consequence of a rich blood supply.
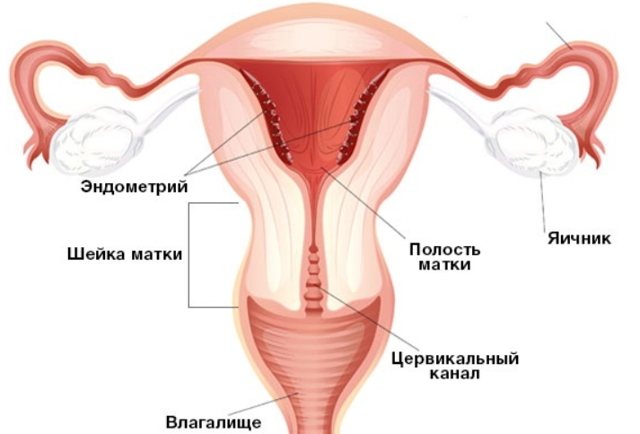
Diagram of the cervix
Early changes
In the early stages, the cervix undergoes strong internal changes, for example, it becomes denser and more elastic.
At the beginning of pregnancy, the cervix can predict an upcoming miscarriage. If, upon examination, the doctor noticed a loose surface of the cervix and the cervix is slightly open by 1 finger, then this is the first sign that the body is preparing for a miscarriage.
Also, if the cervical canal is not completely closed during pregnancy, this poses a great threat to the fetus. Firstly, this may be one of the reasons for a miscarriage. Secondly, this is the cause of infection, microbes, fungi, which leads to infection of the fetus and its possible death.
Initially, the cervix changes during pregnancy at the 4th week, so it changes its usual position.
Late changes
Towards the end of pregnancy, obstetricians may learn that labor is approaching when examining the cervix. The size of the neck, or rather the length, gradually decreases. An ultrasound examination allows you to see how the internal os begins to expand. All this does not happen in a few hours or days, but lasts for several months.
At a period of 37 weeks or more, when examining the cervix, you can determine readiness for the start of the birth process if the cervical canal allows 1 finger of the doctor to pass freely.
So, not long before the upcoming birth, a woman notices the release of a mucus plug. It is this plug that serves as protection against the penetration of microbes into the fetus.
A woman who is preparing to give birth for the first time, the process of modification of the cervix is quite slow. Changes occur much faster if the woman is multiparous.

Normal cervical length by week of pregnancy
Any deviation from the norm, which is recognized in time, in 95% of cases contributes to the successful maintenance of pregnancy. That is why the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes cervical examinations 4 times throughout the pregnancy. Such an examination is prescribed at the following stages: 20, 28, 32, 36 weeks of pregnancy.
But, if there is even the slightest suspicion of a deviation from the norm, then the doctor has the right to prescribe an additional examination at any stage of pregnancy.
Standards for cervical length vary. There are average norms. These indicators are the sum of factors such as pregnancy count and gestational age.
Table of normal cervical length during pregnancy
| Gestational age | Cervical length (normal) |
| 16-20 weeks | from 40 to 45 mm |
| 25-28 weeks | from 35 to 40 mm |
| 32-36 weeks | from 30 to 35 mm |