Tears of grief and pain
In the vast majority of cases when young children receive thermal injuries, the parents are to blame; we are confident in the thermal injuries department of the main regional clinic, where a team of various specialists fights for the lives of patients - orthopedic traumatologists, surgeons, anesthesiologist-resuscitator, therapists, pediatricians, pulmonologists. After all, adults and children are brought here with a variety of burns: chemical, thermal, electrical, radiation.
“It’s a pity for all patients when you see how they, poor things, suffer, and especially little children,” say experienced nurses. And all the trouble is due to my mother’s oversight. And there are more than enough sad examples.
“I am constantly with my son. We’ve been waiting for him,” the mother of a one-and-a-half-year-old baby justified herself, remembering the day when the accident happened. — My husband called that he was already on his way home. I heated up dinner and boiled the kettle. I always do this. Sasha was right there in a walker. Literally for a minute I turned to the stove and heard a sharp scream. I turn around - the kettle is lying on the countertop and boiling water is pouring from it onto my son - there are tears in the woman’s eyes. “I grabbed him, took off my T-shirt and ran into the room. There I thought of taking off my diaper and socks. Unfortunately, I didn’t know that I should have poured cold water on the baby.”
350
operations per year are performed in the burn department of the regional hospital. Surgeons operate on 10-15 burn patients per week
According to the Amur resident, she was so confused that she could not even remember how to call an ambulance. It’s good that the husband arrived quickly and the child was taken to the hospital by car. “My husband remembered a folk recipe: if you get burns, you need to lubricate the wound with butter or egg white,” continued the mother of the injured baby. “He had already moistened his hands with sunflower oil, but was afraid to touch his son. His skin peeled off right before our eyes...”
“And it’s good that the parents did not have time to self-medicate their burned child,” says Andrei Bregadze. “If they had smeared the burn site with oil or egg white, as they wanted, they would only have caused harm.” In this case, a greenhouse effect occurs, the wounds become deeper, which significantly worsens the victim’s condition.
What people sometimes use to try to alleviate the situation. They put toothpaste on the burn site, sprinkle it with soda, lubricate it with anti-inflammatory cream, goose fat, sea buckthorn oil... You absolutely cannot do any of this! This all only deepens the burn and aggravates the course of the disease.
The smaller the child, the more severely he suffers the burn.
According to doctors, I-II degree burns can be treated at home. If everything is clear with the first one - it’s soreness and redness, but how to figure out whether it’s still the second degree or already the third?
- With first-degree burns, only the superficial layers of the skin are damaged and recovery is usually quick - from a week to 10 days. If there is no violation of the baby’s general condition, then you can get by with home remedies. For example, a small burn with an iron with redness of the skin without blisters should be washed under cold running water, then treated with a cooling gel (Panthenol, Pantestin) to reduce pain and speed up skin healing, advises Andrei Anatolyevich. — In the second degree, blisters appear on the skin because the upper layer of the epidermis peels off. The pain is very strong.
150
children are annually treated at the burn center, of which about forty percent of children have deep burns and have to undergo several operations
First and second degree burns often occur on the skin if we overdo it on vacation, forgetting to cover our backs and shoulders when the sun is at its zenith. The most dangerous time is between 12 and 16 hours, when infrared rays predominate in the sun's rays. And there is no tan as such, but a burn. Skin damage in the first and second degrees is reversible.
“If the color of the damaged skin is dark red or pale gray, then this is the third degree, at which skin necrosis occurs,” explained an experienced combustiologist. “Therefore, the child feels almost no pain. In this case, you cannot hesitate. We need to go to the hospital urgently! In childhood, not only the depth, but also the area of the burn is important. The higher it is, the worse the injury prognosis.
The danger of burns in children is not only the subsequent cosmetic defect, but also the development of severe dysfunction of all organs and tissues.
— This condition is called “burn shock.” The child’s body quickly loses fluid, the composition of the blood changes, and its coagulability is impaired... In infants, the body’s reserve capabilities are much less, so in infancy, burn shock occurs often and quickly - even with second-degree burns, states Dr. Bregadze. — For a one-year-old baby to get a burn from boiling water at a temperature of 60 ° C, 10 seconds of exposure is enough, and for a newborn - only 3-4 seconds. The higher the temperature of the damaging object, the deeper and more extensive the child’s burn will be.
What to do and what to apply?
Many accidents involve medications, chemical solutions, burns, when children fall into a fire or are doused with flammable liquid. The success of treatment largely depends on correctly and quickly provided first aid.
— A burn is the death of tissue to a certain depth, and it is impossible to revive the cells by any means. Therefore, the most effective first aid is to stop the action of the damaging object, advises surgeon Bregadze. - You need to remove the hot object or discard the electrical wire, and then take off your clothes. If the burn is severe, then you need to cut off the tissue around the injury - do not remove it from the surface of the burn yourself! The third step is to urgently cool the burned area to prevent the burn from deepening, because subcutaneous tissue has a high heat capacity and the damaging factor continues to have a destructive effect for a long time. Run cold water over the burn area. This will relieve pain and reduce the damaging factor, that is, the depth of the burn by a whole degree! In case of extensive injury, give the child any painkiller - analgin, ibuprofen, paracetamol - and quickly transport it to the burn center by any available means.
1. Boiling water or any other hot liquid - overturning a pot of soup, bathing in too hot water;
2. Hot objects - electric stove burner, curling iron, iron and other turned on electrical appliances (in this case, the burn is often combined with electrical injury);
3. Flame, when older children experiment with fire, flammable liquids, lighters, firecrackers;
4. Chemical reagents - solvents, paints and mineral fertilizers, which cause not only thermal damage, but also poisoning of the entire body. Burn damage develops not only when exposed to the skin, but also to mucous membranes (swallowing hot or aggressive liquid). As a result, there is a burn of the tongue or the entire oral cavity; the worst option is a chemical burn of the esophagus.
DO: Cool the burned area with cool water for 5-15 minutes, but do not use strong water pressure from the tap. Then cover the burn site with a gauze bandage soaked in cold water. If you don't have gauze on hand, you can use a bactericidal patch. This will protect the wound from infection.
DON'T : Do not use ice, snow, or frozen foods to cool a burn. Low temperatures can quickly cause frostbite, since the skin at the burn site is already damaged and does not fulfill its protective function.
DO: First degree burns or minor second degree burns after cooling with water can be treated with certified burn sprays. But such products must be strictly water-based. You can use Panthenol, Levisol, Levian aerosols or gel wipes, especially for second degree burns.
DON'T: Never lubricate burns with vegetable oil, badger or goose fat, bear lard or any other fat, including fatty creams. The oil film traps heat inside the skin and makes the burn deeper.
YOU CAN: Be sure to give your child water in small portions. You can make a solution: per liter of water, a teaspoon of salt and a spoon of soda. Give the child this solution or mineral water.
DON'T : Do not open the blisters left from the burn yourself - you risk getting an infection. Burns are prone to inflammation and the development of suppuration more often than other injuries.
NECESSARY:
Give a painkiller. If the burn causes severe pain, chills or fever, call a doctor immediately.
- Irina Voroshilova
- Amurskaya Pravda from 06/08/2017
Degrees
There are 4 degrees of injury based on the depth of damage.
- Superficial damage is accompanied by minor pain, redness and swelling of the tissue. Heals within a few days even without special treatment.
- Pathological processes spread into deeper skin structures, which is manifested by severe pain, redness and swelling of the skin, and the formation of blisters.
- Damage to deep tissues, involvement of muscle and nerve fibers in pathological processes. The injury is accompanied by the formation of a scab (dry hard crust) or wet necrosis, non-infectious purulent inflammation.
- If, after a burn with boiling water, the skin darkens, becomes charred, and pathological processes reach the bone tissue, doctors diagnose a 4th degree burn. The injury is accompanied by the development of burn disease: in the first 3 days the patient experiences a state of shock, then disturbances occur in the functioning of the internal organs (kidneys, liver, hematopoietic system).
The most dangerous are 3rd-4th degree burns, even if the area of the wound surface is insignificant. But at home it is almost impossible to get such damage. Injuries of 1st and 2nd degrees pose a serious threat if they occupy a large area (30% of the skin or more).
Features of thermal injuries in children
In childhood, burns appear on any part of the body, it depends on where the child spilled, for example, just boiled water. Statistics show that the arms and lower legs are most often affected. Less commonly exposed to hot temperatures are the face, neck, thighs and inner shoulders, but it is in these areas that the deepest and longest-healing damage occurs.
The most dangerous burn to the face with boiling water is that it simultaneously injures the eyes and mucous membranes of the mouth and causes a thermal burn of the respiratory tract.
Burns from boiling water in children occur even with short-term exposure to hot water, despite the fact that after boiling it has had time to cool slightly. Adults should be aware of the high sensitivity of a child's skin. So, for children in the first months of life, a four-minute exposure to water at a temperature of 60°C is enough to get a burn; up to 1-1.5 years old - 10 seconds; older children require a little more time, but they will also have a mark from this temperature. The higher the water temperature, the less time it takes for a burn to form, and the larger the affected area.
To assess the child’s condition, they use the well-known classification based on the depth and symptoms of skin damage:
- First, only the top layer of skin suffers. There is redness and pain in the burned area. Parents can cure this condition on their own in 7-10 days.
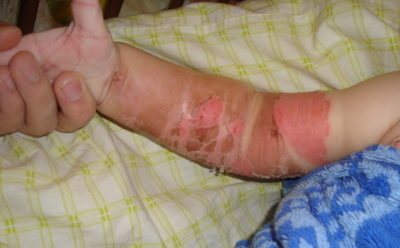
The second is that the upper epithelium and part of the inner layer are affected. Initially, the skin turns red and a slight swelling forms. Over time, bubbles form, which, filling with liquid, burst and cause even more pain to the child. The inner layer of the epidermis takes a long time to recover and treatment may take about 3 weeks. Treatment can be carried out at home, but after consulting a specialist.- The third one leaves deep damage, often affecting blood vessels and nerve endings. The child suffers severe pain and extensive swelling of the adjacent tissues occurs, and the burn itself becomes covered with blisters filled with blood. Treatment of this degree requires a long time.
- Fourth, under the influence of high temperature, not only skin cells are destroyed, but also muscles, tendons, joints and even bones. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting and surgery is often required.
To diagnose childhood burns, information not only about the depth, but also the area of the lesion is important. The larger the area, the worse the child’s condition, even with a mild burn.
Localization
In everyday life, it is easiest to get a burn on your arm or leg by accidentally spilling boiling liquid. Such burns (with the exception of damage to the hand and fingers) are usually mild and heal fairly quickly.
Burns to the torso are more dangerous, since with deep damage, pathological processes can spread to internal organs.
Damage from boiling water, localized on the face and neck, is quite rare. The skin here is more sensitive, so even short-term contact with hot water leads to deep damage. Burns on the face threaten not only health, but also life, since they are often combined with damage to the eyes, upper respiratory tract, mouth, and hearing organs.
First aid
First aid for burns with boiling water includes:
- freeing affected areas of the body from wet clothing;
- prolonged (at least 15-20 minutes) rinsing the damaged area with cool water (this will reduce pain and stop the spread of pathological processes);
- treating the damaged area with an anti-burn agent, if no blisters appear at the burn site (it is advisable to have Panthenol, Bepanten, Pantoderm in your home medicine cabinet);
- applying a sterile bandage to the damaged area (if burn remedies are not at hand);
- relief of pain with any painkiller (you can give the victim Ketanov, Ketorol, Analgin, Baralgin);
- providing plenty of warm drinks (helps reduce the manifestations of intoxication in case of deep and extensive injuries);
- calling an ambulance.
Damage from boiling water, like other thermal injuries (burns from steam, molten metal, a hot object, open flame) requires mandatory medical attention in the following cases:
- deep damage;
- extensive trauma occupying a significant area of the skin;
- getting burned by a child, a pregnant woman, an elderly person;
- injuries to the face, hand, foot, groin area.
If the hand is burned with boiling water, apply a bandage so that the material does not compress the damaged tissue. If not only the hand, but also the fingers are damaged, a bandage is applied to each finger separately. If your face is burned, do not apply a bandage.
It is strictly forbidden to:
What to do if a child burns his hand and blisters appear?
The appearance of blisters on the skin is a sign that the burn is deep enough (2nd degree). It is best to consult a doctor in this case. If you decide to treat such a burn at home, it is important to understand that the liquid accumulated in the bladder is absolutely sterile. This is blood plasma, there are no microbes in it. If such a blister is opened, it can cause an infection. In addition, the exposed surface is very painful.
The burn will heal faster if you do not open the blister. This results in less pain and lower risk of infection. But what to do if a child burns his hand, and the bubble at the burn site is very disturbing? Then it is best to pierce it on the side with a sterile syringe needle, wait for the liquid to drain out, and apply a dry sterile bandage on top, which should be changed every 2-3 days. The top layer of the bladder (thin skin) should not be removed; it should act as a natural dressing and protection from injury.
Treatment
Therapy for deep and extensive grade 3-4 injuries is carried out only in a hospital setting and includes the use of:
- antiseptic solutions for treating wound surfaces;
- painkillers;
- infusion solutions;
- anti-shock therapy (for deep injuries);
- broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Local burn therapy is carried out in one of 2 ways:
- open - ointments or creams with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and regenerating effects are applied to damaged tissues (to prevent infection, the patient is placed in a special aseptic room);
- closed - medications are applied under a bandage, bandages are changed once a day, and for purulent inflammation - every 2-3 hours.
Mild 1st-2nd degree burns can be quickly treated at home with the help of local pharmacological preparations and folk remedies.
Drugs
Treatment of burns with boiling water at home is carried out with local remedies that have a regenerating, antibacterial and healing effect.
The healing process of burns occurs in 3 stages:
- inflammation (rejection of damaged tissue);
- granulation (disappearance of inflammation, beginning of skin regeneration);
- epithelization (restoration of healthy skin).
Antibacterial drugs are used in the first phase of a burn injury to prevent the development of infectious inflammation. Treatment of a 2nd degree burn after opening the bladder is carried out with ointments with pronounced regenerating properties.
There is a wide range of remedies for burns from boiling water in the pharmacy. The following drugs have proven themselves to be effective:
- Panthenol. A product based on dexpanthenol stimulates metabolic processes in tissues and has a pronounced regenerating effect. Panthenol for burns with boiling water in the form of a spray is best used immediately after injury. It is advisable to use an ointment based on dexpanthenol in the later stages of healing, after the inflammatory processes have stopped.
- Olazol. Burn spray contains sea buckthorn oil, benzocaine, boric acid and chloramphenicol. The presence of a local anesthetic and pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, regenerating properties of the components ensure the high effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of burns.
- Sulfargin. Ointment for burns with boiling water with blisters based on silver ions and the sulfonamide component has a pronounced bactericidal effect. It can be used at all three stages of pathological processes, as well as for treating wounds immediately after injury.
- Syntomycin. Syntomycin ointment for burns with boiling water is used to prevent infectious processes or treat existing bacterial inflammation and purulent wounds. The pronounced antimicrobial effect of the drug is due to the presence of chloramphenicol, an antibacterial component, in the composition.
- Levomekol. The ointment has a complex effect on burns: chloramphenicol, which is part of the product, suppresses the development of infectious inflammation, and methyluracil stimulates the regeneration of damaged tissues.
- Zinc oxide. Zinc ointment for burns with boiling water has an anti-inflammatory and regenerative effect, and is used in the treatment of 1st degree injuries that are not accompanied by the formation of blisters. In case of severe burns and the development of purulent processes, the drug is contraindicated.
- Actovegin. The ointment improves blood circulation and metabolic processes, saturates cells with oxygen, thereby stimulating regeneration processes. It is used at the stage of healing of the wound surface.
The child has
The principles of first aid and treatment for burns in children are identical to those for treating adults. The only difference is in the calculation of the dose of the drug, frequency and duration of therapy. And of course, when choosing a drug, the age of the child is taken into account. For example, dexpanthenol-based products are used even in the treatment of newborns, Sulfargin is used in the treatment of children older than one year, Olazol is prescribed from 2 years of age, and Levomekol - from the age of three.
A child’s skin is much thinner and more sensitive, so children’s bodies always tolerate burns more severely than adults. And in the case where a child has been burned by boiling water, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a doctor, even if the injury, at first glance, is insignificant. Only a specialist will be able to correctly assess the degree of tissue damage and select an effective ointment for burns with boiling water for children that is optimally suitable in a particular case.
The main causes of hand burns in children
Children's hand burns are a type of injury that a child receives most often in everyday life due to damage from thermal radiation, chemicals, electrical energy, etc. Depending on the degree of clinical exposure, the degree of burns the child receives changes, as well as the depth of damage to hand tissue, general manifestations, and shock in particular. When determining the causes of burns and diagnosing them, special attention should be paid to the nature of the injury received by the child, determining the depth and extent of the affected area. For this purpose, various measurement techniques, thermography, and other methods are used. Treatment of hand burns in children of all ages involves performing therapy aimed at eliminating the consequences of the resulting shock, as well as treating the surface of the resulting burn and applying a bandage.
Iron burn on hand
If a child receives a burn from an iron, the first step is to stop exposure to the traumatic factor and remove the child from the household appliance. After this, it is recommended to place the child’s hand under a stream of cold water in order to cool the affected surface. You should hold your hand under running water for about five minutes, and you can also apply a cold compress. The pain will decrease and the area of damage will be reduced.
If blisters appear on the burned area, it is recommended to treat the surface of the skin with Panthenol or another product, and then apply a bandage to the child’s hand. If a child suffers severe pain from a burn, it is recommended to place him at rest and give him plenty of fluids.
A child burned his hand with boiling water
In such a case, first of all, it is necessary to remove clothes in the place where the boiling water came into contact with the child’s hand. This is done as quickly and carefully as possible, in order to avoid additional injury to the child’s hand. It is best not to pick off burned skin or blisters on it. Tight clothing is best cut with scissors.
After this, it is best to treat the injured area as soon as possible. You can immerse your burned hand in a pan of cold water for about 15 minutes. It is best to hold the burned hand vertically upward to avoid swelling.
After this, a sterile bandage should be applied to the child’s hand. To avoid worsening the situation, it is better not to use alcohol, various oils and iodine.
Child's finger burn
In any case, first of all, it is necessary to stop the impact of the traumatic factor on the child’s fingers. It should be taken away from the heat source and the burned fingers should be cooled as much as possible. With a small degree of burn damage, this is enough, but if the burn injury is accompanied by severe pain, the child must be calmed down, a compressive bandage applied to his fingers and placed in a state of rest. If we are talking about a high degree of damage, it is necessary to call an ambulance and place the child in hospital treatment.
Forecast
The speed of recovery after a burn with boiling water depends on many factors, including the depth of the damage, the area of the wound, the state of the immune system, the presence/absence of purulent complications, the patient’s age, and existing concomitant pathologies (with diabetes, wounds take much longer to heal).
On average, 1st degree burns heal in 3-5 days. It takes about 2 weeks for the skin to recover after a 2nd degree burn. With a 3rd degree burn, the first weeks after the injury are accompanied by inflammatory processes, rejection of necrotic tissue, and regeneration begins a month later.
4th degree burns are the most difficult to treat and often lead to disability. For 1-1.5 months after the injury, tissue death and rejection continue. Then the skin is gradually covered with loose granulation tissue and scars over time. With a small burn area, the skin is completely restored after 2 months; with extensive damage, healing takes longer. The resulting scars greatly tighten the skin. Subsequently, because of this, if an arm or leg is burned, motor activity is impaired.
Burns from boiling water are the most common household injury. Even short-term exposure to hot liquid on the skin can lead to serious complications, especially if a child is injured. However, high-quality and timely first aid significantly reduces the risk of developing unpleasant consequences. And competent drug treatment ensures rapid recovery.