Causes of allergies in infants
An allergic reaction can develop in a young child for various reasons.
- Lack of maturity of the gastrointestinal tract. It is because of this that babies so often have a negative reaction to food, in particular to proteins, carbohydrates and fats. The newborn’s body does not yet produce enzymes that break them down. Hence the negative reaction.
- Incomplete composition of microflora. Therefore, children up to a certain age are fed formula or breast milk and only gradually introduce new products upon reaching six months.
- Mom's diet during pregnancy and breastfeeding. If a woman consumed allergenic foods before the birth of her child, he may already have signs of allergies immediately after birth. If during lactation, then allergens reach the baby through mother's milk.
- Unsuitable mixtures. Breastfed babies are more susceptible to allergic reactions than breastfed babies. Especially those fed cow's milk based formulas.
- Immune system response. It protects the body from viruses and infections. But sometimes she can perceive even harmless substances as foreign and dangerous. And he begins to fight them. We see this as allergic reactions.
The listed reasons are more related to food allergies. But it also occurs most often in infants.
Types of allergies in infants
Various elements and factors can act as irritants.
Depending on what exactly acts as the main “harmful” element, there are four main types of allergies in infants:
- Food allergies. The main food for children under six months is mother's milk or special formulas, so it is in them that you need to look for the cause of the allergy. Feeding formulas are usually selected through trial and error, but the quality of breast milk must be monitored by the mother. Also, young children often have an allergy to cow's milk, then you will have to select other possible alternatives;
- Respiratory allergies. This type of allergic reaction occurs when a child’s mucous membranes come into contact with pollen, dust, or animal hair. It manifests itself in the form of nasal congestion, lacrimation, shortness of breath and some signs of suffocation;
- Contact allergy. Occurs when the protective function of the skin in a newborn is impaired. Allergies can be caused by washing powder and personal hygiene products. Manifests itself in the form of dermatitis and urticaria;
- Cold allergy. This type of allergy is very rare and occurs when the skin comes into contact with cold air and water. When exposed to frosty air, redness and then blisters develop on exposed areas of the child's body. This allergy is practically untreatable, so parents should completely eliminate contact with the cold. When walking in winter, it is recommended to leave as little exposed areas of the body as possible and not give a pacifier.
How do allergies manifest in babies?
Symptoms depend on the allergen, the baby's immune system and overall health, and other factors. We will tell you further what manifestations there may be.
Skin reactions
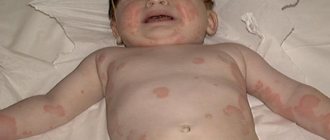
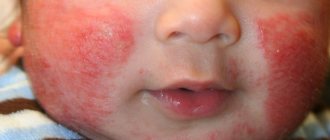
More often than not, allergy symptoms first appear through the skin. You may notice a rash, peeling, blisters, redness, and hives on the baby's body. Children who can speak complain of itching.
Another symptom is atopic dermatitis. Localized on the cheeks, elbows, under the knees, on the buttocks, neck, around the mouth and anus. The skin on the body in these places turns red and peels, and then begins to get wet and crusts appear.
Against the background of skin rashes and itching, the mood of the newborn also changes: from a cheerful baby, he turns into a capricious, nervous and irritable one. He sleeps and eats poorly, constantly cries and itches.
Gastrointestinal disorders
If parents have not taken measures to eliminate skin reactions, allergies can also cause problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Constipation or diarrhea, bloating, reflux, colic - this is a list of problems that a baby may encounter.
How the eyes, nose and throat react
As a rule, a reaction from the respiratory and visual organs occurs to pollen, chemicals (paint, cosmetics), dust, fluff, and wool.
If a baby develops an atypical runny nose, watery eyes, or swollen mucous membranes, this may indicate an allergic reaction.

Also, from the respiratory system, a reaction may occur in the form of allergic bronchitis or asthma, sore throat, wheezing, noisy breathing.
Systemic reactions and critical conditions
An allergen can cause a fever.
In particularly severe cases, angioedema or anaphylactic shock are possible. These are critical conditions, they are rapidly getting worse. Require immediate medical attention.
These are the symptoms that are a reason to urgently call an ambulance: the skin turns pale, becomes locally tense, the newborn cannot breathe, and loses consciousness. In this case, time is counted in minutes, since there is a high risk of asphyxia - suffocation, as a result of which death occurs very quickly if help is not provided. To save the baby's life, parents will need to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
What can a baby be allergic to?
Newborn babies experience allergies to various substances.
This could be breast milk, formula, washing powder, clothing, hygiene products, house dust, animal hair. Young children do not have stable immunity. Therefore, new substances can cause an aggressive reaction. Most often, food allergies occur in infants.
The irritant can enter the child's body through breast milk. Therefore, during lactation it is recommended to follow a hypoallergenic diet. Allergies to gluten and lactose often occur at this age. Vegetable and milk protein are strong allergens. Sometimes it is very difficult to identify a reaction to them.
Interesting! Recently, even safe foods have caused allergies in infants. Rarely, a reaction to buckwheat, oatmeal, and cottage cheese occurs.
Causes of an allergic reaction
Every mother should understand what her baby may be allergic to. Therefore, it is important to know for what reasons pathology may develop. Among the main reasons are:
- individual reaction to a specific component;
- genetic predisposition to allergies;
- decreased activity of the immune system;
- the presence of chronic, viral, infectious diseases.
The allergen can be hidden in foods, medications, and animals. In most cases, the pathology is inherited. If parents suffer from any form of allergy, then the child’s risk of developing it increases by 50%.
Contact allergy
This type of pathology occurs due to contact with external irritants. It is a delayed type allergy. Symptoms are localized on the skin at the site where contact with the irritant occurred. The manifestation of this allergy is caused by the following factors:
- pet fur;
- flowering of indoor plants;
- synthetic clothing;
- products for children's hygiene;
- household chemicals.
Within 15-64 hours, the first symptom of the pathology may appear. The speed in this case depends on the strength of the stimulus’ influence on the child’s body. This causes certain symptoms:
- skin redness;
- swelling;
- the appearance of bubbles, in their place after bursting weeping spots appear.
It is very important to identify the irritant in time and limit its contact with the child. Otherwise, the treatment will not be effective. With prolonged contact with the allergen, the following skin symptoms may develop:
- redness;
- itching;
- peeling;
- wounds;
- crusts;
- vesicles:
- thickening.
If the irritant is not eliminated in time, cross-allergy may occur. In addition, there is an increased risk that the child will remain allergic for life.
Food allergic reaction
A food allergy is an aggressive reaction of the immune system to a food product. It can even appear in a newborn baby. In this case, absolutely any product can cause a reaction.
Children are more likely to be allergic to milk, eggs, cereals, nuts, and fish. With age, tolerance to certain allergens can develop. For this reason, reactions to such products are rarely observed in adulthood.
There are characteristic symptoms of food allergies:
- rash, redness, itching;
- allergic cough, rhinitis;
- Quincke's edema;
- labored breathing.
Treatment usually consists of eliminating the irritant from the baby's diet. Drug therapy is rarely used.
What are the most common allergies?
Babies are most likely to suffer from reactions to certain foods. A newborn baby does not have stable immunity. In addition, the digestive system is not formed.
As a result, the baby suffers from gluten and lactose intolerance. These complex proteins and carbohydrates are found in infant formula and cereals. Lactose is the sugar in cow's milk. Therefore, a child may develop an allergy to dairy and fermented milk products.
Often a newborn baby reacts negatively to pets. This pathology is observed less frequently, but it cannot be excluded. The allergen can be the fur of dogs and cats.
Diapers can cause contact allergies. Most of them are the cause of diaper dermatitis. Sometimes, in order to select a quality manufacturer, parents have to spend a lot of time. It is difficult to identify the irritant in this case.
Important! It is impossible to independently determine the allergen. To do this, you need to undergo several laboratory tests and consult a doctor.
Food allergies in infants. Diathesis in a baby. Treatment of childhood allergies and diathesis. Baby care
List of allergenic foods
The list of certain products has been created in order to introduce them into complementary foods with caution. Also, a woman who is breastfeeding should limit her diet to allergens.
- food fusion for kids;
- cow's milk;
- egg yolk;
- red fish, seafood;
- cereals (wheat, semolina, rye);
- red vegetables (carrots, beets, tomatoes);
- citrus;
- red and exotic fruits, berries;
- nuts;
- honey;
- chocolate, cocoa.
A baby usually encounters such allergens through breast milk. Therefore, during lactation it is recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet.
Household products
There may be these:
- washing powders;
- detergents;
- shampoos, bathing gels;
- oils to moisturize the skin.
If a child is allergic, then he may have such a reaction against the background of other pathologies.
Danger of complications
All parents are interested in the question: what are babies most often allergic to?
Considering that newborn children can react negatively to everything new, it is difficult to determine the irritant. This causes the development of complications:
- lifelong allergies, development of cross-reactions;
- anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema;
- development of skin diseases;
- decreased immunity.
A dangerous complication is Quincke's edema. If a sign of this appears, you should immediately call an ambulance. Otherwise, the child will suffer from suffocation.
Approaches to diagnosis and treatment
If you suspect an allergy, take your baby to an allergist. The doctor will examine the little patient and collect anamnesis. He will assess the general state of health, find out whether there is a heredity (if the baby has one of the blood relatives with allergies, he is also at risk), and conduct a diagnosis.
Methods for identifying an allergen
- Parents analyze what new foods their baby has eaten recently or what else could trigger the reaction (for example, pets or apartment renovations).
- Allergy tests. Carried out if the provocateur could not be identified in a simple way. Performed only in a doctor's office.
- Provocative test. Performed if none of the tests helped identify the allergen. The procedure is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor.
On an individual basis, the doctor can also refer you for other examinations - a coprogram, an analysis for lactase deficiency, etc.
General treatment regimen
Treatment depends on the triggering factor. Here's the general diagram:
- Eliminating the allergen. Excluding trigger foods from the diet (or from the mother’s diet if the baby is breastfed), eliminating the sting of an insect (after its bite), stopping contact with a pet (in case of a reaction to fur), etc.
- Nutrition correction. In the case of food allergies, the baby is prescribed a hypoallergenic diet (if complementary foods have already been introduced). For bottle-fed babies, the formula is changed.
- Prescribing antihistamines. They are prescribed only by a doctor. Medicines are produced in the form of tablets, drops, syrups - the doctor will select the medicine that is right for your baby. He will also prescribe the dosage and course of treatment.
- Local therapy. For skin reactions, ointments, creams, lotions, and emulsions are prescribed. They can be aimed at moisturizing and restoring the skin (emollients) or eliminating allergic symptoms (hormonal agents).
Remember that the treatment regimen is prescribed only by the doctor after examination and examination of the small patient.
Prevention of future relapses
If the provocateur is a food product, it is excluded. It is advisable to temporarily exclude any allergenic foods - gluten cereals, milk and dairy products, fish, citrus fruits, tomatoes and others.
If your baby has a reaction to insect bites, dress him in clothes with long sleeves and pants. Cover the stroller with a light cloth.
If your skin is hypersensitive to synthetics and other artificial fabrics, choose clothes for your child made from natural materials - ideally cotton.
If the reaction is to dust, do daily wet cleaning. Reduce the number of stuffed toys - these are known dust collectors. Monitor air humidity. Optimal - 40 - 60%. Buy a humidifier and hygrometer.

If you react to animal fur, limit your baby’s contact with your pet, keep the house clean—fur should not fly in the air or settle on the floor or furniture.
If you have a reaction to pollen, walk in cloudy, windless weather, ideally after rain. The sun, wind and dry air are your child’s enemies.