From the moment the baby is born, his parents watch him closely. They monitor his behavior, but, unfortunately, not everyone knows what in the baby’s behavior should alarm parents, and what is the norm and is not a cause for concern. Experts also have mixed opinions about the phenomenon when a child rolls his eyes.
If a child periodically rolls his eyes, then parents should pay attention to this. Although only a specialist can determine a disturbance in the body from a normal state, this phenomenon is always alarming. A one-year-old child does not always roll his eyes because of play or simply because he is so comfortable in a certain environment; sometimes this indicates a serious illness.
In the first 30 days of their life, children still cannot control the work of their muscles, and, accordingly, do not control. They do not yet know how to focus their eyes, and if a small child rolls his eyes, then this is considered the norm. If a one-month-old baby rolls his eyes, this is not always a normal condition. By this time, children can already focus their gaze and control the work of their muscles. And this means the presence of problems.
If a child rolls his eyes, the reasons may be the following:
- uneven muscle tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- epilepsy;
- Gröff's syndrome.
The latter may be indicated if the child rolls his eyes down when he has already fallen asleep. If a child rolls his eyes up when falling asleep, then this is just his peculiarity, and there is nothing to worry about. This state indicates that the baby is almost asleep.
It is very rare to find the listed diseases that have such a symptom as eye rolling. And for the sake of children’s health, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician and neurologist if the child begins to roll his eyes. If a specialist detects some deviations, he will prescribe timely and effective treatment, which will help avoid more severe consequences.
For example, with uneven tone, in which the child rolls his eyes when falling asleep, the doctor prescribes physical therapy for the baby. Often, such measures very quickly restore muscle tone and the baby recovers. The situation is more complicated with more serious diseases, the occurrence of which requires complex treatment.
Many experts tell parents that if a child rolls his eyes when falling asleep, and otherwise his behavior does not change, then there is no need to worry. It’s just so convenient for the baby, and if he’s a little older, he can play like that. If other behavioral disorders occur, it is worth going to the hospital.
What to do in this case?
To find out exactly why a child rolls his eyes upward, you need to consult a specialist. Otherwise, it is impossible to determine the cause and make a diagnosis at home. If small children under one month old roll their eyes, then there is no cause for concern, but if a child of 6 months rolls his eyes, this may indicate a disease.
Specialists conduct an examination and use it to determine an accurate diagnosis. You cannot delay time if you have discovered other disturbances in the functioning of the child’s nervous system. It is necessary to contact immediately after symptoms appear.
If a child rolls his eyes to the side, this may also indicate a disease or its peculiarity if the baby falls asleep at the same time. There is no need to panic in this case, but you need to contact a neurologist. Only a specialist will adequately assess the baby’s condition and be able to answer your question about why the child rolls his eyes to the side.
Some experts recommend doing this for those who suffer from impaired functioning of the visual organs. However, under the age of one year this is difficult to do. But in older age, this technique works effectively.
Thus, we can say that the reasons for eye rolling in young children are very different. This phenomenon may be a symptom of a disease, or may not mean any disorder. Since rolling up can be a sign of serious illness, if such a behavior pattern is detected, you should contact a pediatrician and a neurologist. This will help to detect the problem in a timely manner and eliminate it.
If a child rolls his eyes in his sleep, then often this behavior does not go beyond the norm; this indicates that the baby is practically asleep. In conclusion, I would like to reassure parents by emphasizing the fact that rolling eyes is extremely rarely a symptom of serious disorders in the baby’s body. Therefore, in most cases there is no need to panic.
Date: 03/03/2016
- Physical therapy exercises
If a child older than 1 month rolls his eyes, this should alert parents. At first, any baby cannot control the system of muscles that controls the eyes, but if he is more than a month old, he should be able to concentrate his gaze on one object.
Causes of eye rolling in newborns, older children and adults
During the first month of life, children cannot control the work of their muscles and the eye muscles are no exception. Such babes do not know how to focus their eyes, so rolling up can be regarded as a variant of the norm. When the baby turns one month old, but this sign does not disappear, a diagnosis is necessary, as a serious disorder may occur.
Starting from the age of one month, children can already control their muscles, but if this does not happen, pathology occurs.
The reasons may be hidden in conditions such as:
- Epilepsy;
- Graefe syndrome;
- Uneven muscle tone;
- The phenomenon is observed with increased intracranial pressure.
For example, Graefe's syndrome is indicated by rolling the eyes downward when the baby has already fallen asleep. If the eyes go up, then this is just a feature of the body and there is no need to worry about anything - this indicates that the baby is almost asleep.
The listed diseases, accompanied by a similar symptom, are quite rare, but pose a great danger.
Therefore, for the sake of the child’s health, parents should immediately visit a pediatrician or pediatric neurologist. Deviations noticed in a timely manner allow treatment to begin at the earliest stages of pathology development, which increases the chances of a successful and rapid recovery.
If uneven tone of the eye muscles is detected, which is accompanied by rolling while falling asleep, physical therapy (PT) is prescribed. Diligently following the doctor’s prescriptions will allow you to quickly restore muscle tone, which, accordingly, will lead to a speedy recovery. The situation is much more complicated with other pathologies that require complex treatment.
Some pediatricians say that eye rolling that is not accompanied by changes in the baby's behavior is not dangerous. Perhaps it’s just more convenient for him, or when the child is already big enough, he plays like this. But if accompanying disorders appear, you must seek medical help.
What to do when you roll your eyes?
First you need to visit a pediatrician or pediatric neurologist. Many parents put off making a visit, but at home it is impossible to determine the cause of the disorder and make a diagnosis. In newborns, this condition does not pose a threat, but after a month, parents and doctors should take it more seriously.
A diagnostic test is required. You should not delay it if disturbances are detected in the functioning of the nervous system. Parents should remember that contacting a specialist should be urgent, that is, immediately after symptoms are detected.
Rolling the eyes to the side when falling asleep can be a physiological feature or a symptom indicating the presence of pathology. Special exercises for the eyes help well with disorders of the visual system, but under the age of one year it is almost impossible to perform it.
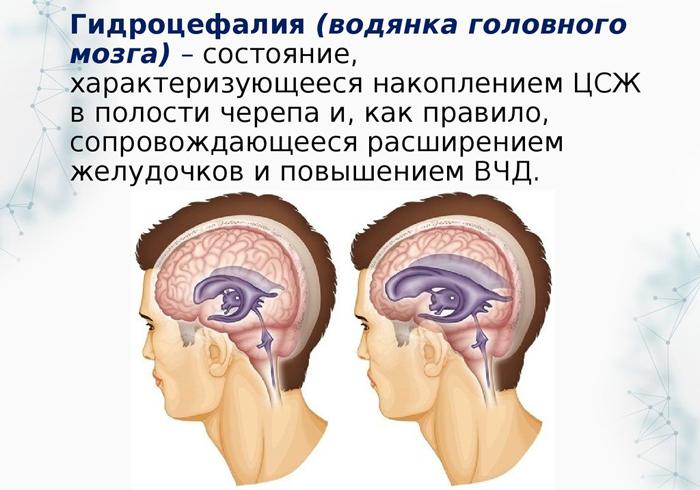
Eye rolling in children and adults as a sign of hydrocephalus
This pathology is manifested by the accumulation of an excessive amount of fluid in the brain, resulting in damage to the brain. Hydrocephalus is also called hydrocephalus. This pathology without timely treatment can lead to death.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the age of the patient and the degree of progression of the pathology. For example, in newborns, the roundness of the head exceeds the norm and then quickly increases, and on the parietal part of the head there is a convex fontanel. Sick children vomit, become irritable, and have trouble sleeping. Eye rolling with convulsions also occurs periodically in newborns. Very often, babies with hydrocephalus develop delayed.
Older children and adults experience headaches accompanied by vomiting. As for the visual system, they experience attacks with double vision, inability to focus vision, and rolling of the eyes.
During movement, poor balance, fatigue, and poor coordination may be present. With hydrocephalus, urinary incontinence, memory loss, severe irritability and personality changes periodically occur.
In addition, the symptoms are influenced by the cause that provoked the accumulation of fluid. For example, in old age the normotensive form is most often diagnosed, which manifests itself primarily in problems with walking, urinary incontinence, and dementia.
The cause of hydrocephalus may be a primary disease (meningitis, intoxication, meningoencephalitis) or an injury that disrupts the outflow of fluid from the brain. In newborns, it is triggered by an infectious disease that the mother suffered during pregnancy. It is worth noting that congenital hydrocephalus can make itself felt not in the first days of life, but even after several months.
Treatment methods for hydrocephalus in children and adults
In the early stages of the disease, conservative treatment (medication) is possible, but with rapid progression, surgical intervention is indicated. The most common method previously was ventriculoperitoneal shunting.
The patient was implanted with special shunts that ensured the outflow of fluid from the brain into the abdominal cavity. A significant disadvantage of this method is the imperfection of the shunts, so they need to be changed every few years.
One of the methods of surgical intervention is the ETV operation. During the procedure, a hole is made in the ventricle of the brain through which excess fluid drains. This method is used for blockage between the ventricles of the brain. It is also used for the congenital form of the disease, if shunting does not help or infection occurs. Now this method is used only when the child is over 6 months old.
One of the most effective methods is neuroendoscopic. It is the most gentle of the above. During the operation, neuroendoscopes with a mini-camera are used, which allows you to visualize the entire process and restore normal fluid outflow.
Monitor your symptoms and do not delay your visit to the doctor, as the consequences of delay can be disastrous!
The child rolls his eyes
From the moment the baby is born, all the attention of the household is focused on the new family member. Parents constantly watch their baby. But you need to understand that you need to observe not from the point of view of simple admiration, but still strive to understand whether everything is in order in the behavior of the little man. Not everyone understands what in a child’s behavior should alert his parents and what is normal. Sometimes a phenomenon occurs that the child begins to roll his eyes, and the opinion of experts on this issue is ambiguous.
If you notice that your child is rolling his eyes, then you should be wary and watch. how often does this happen, and then consult a doctor. Only a specialist can determine whether such specific behavior is a sign of a disorder in the body. Of course, a child can do this while playing or when for some reason it is convenient for him, but when this is repeated several times, this may be a symptom of a disease.
Causes of eye rolling symptoms
Loving parents closely monitor any, even small, changes in the baby’s behavior. Many people are frightened when a baby suddenly rolls his eyes, although there is no reason for this.
You need to contact a specialist if:
- the child behaves restlessly, cries, screams, twitches and rolls his eyes;
- The baby is more than 3 months old and the problem does not go away.
The causes of unpleasant symptoms are:
- uneven muscle tone and weakness;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- epilepsy;
- Graefe's symptom.
Return to contents
Why does the disorder occur in adults?
An adult may roll his eyes when talking or while sleeping. Usually such movements are observed in emotional people. This is also considered normal and does not require treatment. If such a symptom occurs constantly and is accompanied by other disorders, you need to see a doctor. The reason may lie in neurological diseases. The most common cause of eye rolling in adults is epilepsy and increased intracranial pressure.
Hydrocephalus can also provoke this symptom in an adult. This disease is characterized by the presence of excess fluid in parts of the brain. The disease can develop both as a result of head trauma and previous infections. Symptoms of this disease include frequent headaches, which are accompanied by nausea, blurred vision and impaired balance. Some people experience memory loss and severe irritability.
If you experience a deterioration in your health for no apparent reason, you should definitely visit a doctor and, if necessary, undergo an examination.
Peculiarities of infant behavior
The human eye is a complex organ with which it sees the world. The eyes are controlled by a group of muscles, and in a newborn this process is still imperfect, and only at the age of more than 1 month does he begin to focus his gaze on bright objects and toys. A premature baby often rolls his eyes.
A newborn baby may roll his eyes when falling asleep, and this behavior of the baby is associated with the peculiarities of his development. At this moment, he is in a borderline state between sleep and wakefulness, so this phenomenon does not pose a health hazard. Gradually this problem will go away on its own.
If this phenomenon does not disappear as the baby grows older, you should immediately consult a doctor for advice.
A baby may roll his eyes downward before going to sleep, which indicates a disorder, Graefe's symptom. This diagnosis is given to children in whom a white stripe of the white of the eye is visible between the eyelid and the iris when the eye moves downwards.
A newborn baby cannot control eye movement, and parents must distinguish between what is normal and where pathology begins.
Be careful if, in addition to abnormal eye movements, the baby has other symptoms: throwing back the head, squinting, excessive regurgitation, prolonged crying.
After the examination, the neurologist and ophthalmologist will prescribe an examination, a course of special physical therapy, or recommend simply monitoring the child’s further development.
Attentive parents are always wary if they see that the baby is making some uncharacteristic movements, including with the eyes. It is difficult to determine on your own what it is - a harmless individual feature or a manifestation of some kind of disease? For example, why does a child roll his eyes?
Firstly, it must be said that if you are concerned about some feature of your child, never hesitate to ask for advice from a pediatrician, who, if necessary, will refer you to a specialist for consultation. The same applies to eye rolling, which can occasionally actually be a symptom of a disease. But to do this, you need to describe in detail how often the baby’s eyes roll (for example, several times a day), whether this happens in a dream or while awake, and in what state the baby is at this time.
When to worry and why
You should sound the alarm and, as a result, contact an ophthalmologist or neurologist if:
- the child turned 3 months old, but he did not stop rolling his eyes;
- when falling asleep, his eyeballs go down, not up;
- during periods of wakefulness, the mother also observes how the newborn baby rolls his eyes;
- at such moments he becomes capricious, expressing concern with his whole appearance.
All these symptoms may indicate the presence of serious developmental pathologies in the newborn, namely:
A child rolls his eyes: reasons
If your baby is still very young and has only recently been discharged from the maternity hospital, then for up to a month this condition does not cause concern to doctors. The fact is that a baby up to a month old does not know how to focus his eyes. Why does a child roll his eyes at this age?
Several eye muscles are responsible for the movements of our eyes - levator, depressor, adductor and abductor. They influence the movements of the eyeballs up, down and to the sides. All parents notice that the gaze of a newborn baby is not focused: the eyes look up, then down, then scatter in different directions, then squint. Rolling the eyeballs relates to the same issues of coordination and tone of the eye muscles, which are imperfect in the baby. But after a month, the gaze begins to focus and the baby looks at his parents and bright toys, thus training his eyes. In some cases, the process lasts up to three months, but consultation with an ophthalmologist is necessary in this case.
If a child rolls his eyes when falling asleep, this does not belong to the category of pathologies. In fact, in the initial phase of sleep, adults also roll their eyes, eliminating the possibility of light entering the retina. Remember how we determine that the person sitting next to us is falling asleep? We only see the white of his eye. But the eyeballs always rise up during sleep, and if you notice that the baby’s eyeballs go down, on the contrary, this cannot be considered normal.
If a child rolls his eyes, the reasons in some cases can be much more serious:
- Epilepsy;
- Increased intracranial pressure;
- Other neurological disorders.
Of course, any of these reasons requires a thorough neurological examination. Epilepsy poses a particular danger: most parents have the vaguest idea about this disease, believing that it is invariably accompanied by convulsive attacks with falling and foam at the mouth. This is not so, and eye rolling may well be a symptom of so-called absence seizures - small seizures that can be very short, and parents do not even notice at first that the child has “passed out.” Childhood absence epilepsy is more common at ages 4 years and older.
Reasons why children under one year old roll their eyes
During the neonatal period, the child is unable to control his muscles. A newborn is not able to concentrate his gaze, so if at this age a child rolls his eyes, his family should not be afraid for his health.
Children from one month to one year
After one month of life, the baby learned to focus his gaze on objects and control his oculomotor muscles. And if a baby over a month old begins to roll his eyes, then sometimes this indicates the following problems:
- uneven muscle tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- epileptic seizure;
- Graefe's syndrome.
A sign of Graefe's syndrome (another name is "setting sun" syndrome) can be a situation when a baby begins to roll his eyes downward in his sleep. If a child rolls his eyes up or to the side when falling asleep, there is no need to worry: this state only confirms that the baby is almost asleep.
Pathologies whose symptom is eye rolling are extremely rare. But if your baby begins to roll his eyes, in order not to miss a serious illness and to prevent the serious consequences that it can cause, you should immediately contact your pediatrician and neurologist. If deviations from the norm are detected in the baby’s health, the specialist will promptly prescribe effective therapy with a good prognosis.
For example, if a child begins to roll his eyes due to uneven tone of the extraocular muscles, the doctor prescribes physical exercises for therapeutic purposes, which quite quickly helps to tone the extraocular muscles.
Serious pathologies require complex treatment.
Experts agree that if a child begins to roll his eyes when he falls asleep, and otherwise his behavior is within normal limits, then there is no need to be afraid. You should consult a doctor if you have other warning symptoms.
What treatment should you undergo?
If a child rolls his eyes when he falls asleep, or is less than a month old, no treatment is required, since this is not a disease. If the doctor diagnoses uneven muscle tone, the eyes should be trained. This can be done with the help of bright toys and rotating devices - mobiles. The baby will follow their movements above his crib, and his eye muscles will strengthen. In addition, there are massage therapy and physiotherapy treatments that will help restore muscle tone and improve eye coordination. This happens quite quickly if the parents consult a doctor on time.
In cases where a baby or child rolls his eyes and cries a lot or becomes hysterical, parents should visit a neurologist with him - after all, these symptoms themselves are a sufficient reason for concern. If parents notice that from time to time the child has a blank look, and at the same time the eyeballs go up, this is also an absolute reason for an urgent consultation. To establish a neurological diagnosis, you need to undergo a series of special examinations. The sooner the problem is identified, the faster doctors will be able to begin treatment, so in such cases there is no point in delaying a visit to the clinic.
When is treatment required?
If a child less than a month old rolls his eyes, this is a physiological norm. No treatment is required here. However, training the eye muscles will not be superfluous. You can show your baby bright objects. The child will follow them with his gaze, strengthening the eye apparatus.
If the problem does not go away, you need to visit an ophthalmologist, who can prescribe special gymnastics for the eyes and physiotherapy to strengthen the eye muscles.
If the pathology is not associated with weakness of the eye muscles, you will need to consult a neurologist. After all, a blank look accompanied by rolling of the eyes may be evidence of serious neurological diseases. In this case, the child or adult will need to undergo a series of examinations, only after which treatment can begin.
So, we found out that eye rolling is considered normal for infants. However, if we are talking about older children or adults, then this phenomenon may indicate the presence of serious health problems that require immediate treatment.
As soon as a baby appears in the family, all the attention of the household is focused on him. Parents worry about their baby every second and not only admire him, but also watch to make sure nothing bad happens to their child. It is not surprising that a mother or father begins to panic if they notice that the child is rolling his eyes upward for no apparent reason.
Experts have different opinions on this matter, but there are several common reasons for the appearance of such symptoms. To determine them, you need to observe the baby.
Video: What to do when a child is capricious and throwing tantrums - advice from a family psychologist
4.6666666666667 4.7 out of 5 (6 votes)
11.10.2016
Parents who treat their children with love and attention always notice even the slightest changes in their behavior. They rejoice in the successes of their children and experience failures with them. And they completely lose their heads when children get sick. Unfortunately, there are plenty of reasons to worry while children are growing up.
Many mothers panic at the sight of a small child rolling his eyes upward so that the whites are visible. Most often this happens at the moment of falling asleep. Today we will try to explain why a child rolls his eyes and in what cases you should worry.
In newborn children, this can be explained by the imperfection of the brain, which is still at the beginning of extrauterine development, and cannot fully control the muscles responsible for eye motility. There are only seven such muscles, and the child will learn to control them, fix his gaze on an object and follow its movement, only after reaching 1 month. Until the age of one month, you can safely observe the baby’s development. If a child rolls his eyes even at 3 months, he needs to be shown to a neurologist, having first selected a good specialist.
Only a qualified neurologist can ask the question why a child rolls his eyes. The doctor may order an ultrasound examination of the head to rule out any pathologies.
Although most often the reason that a child rolls his eyes upward is low tone of the head muscles, including the eye muscles. If the doctor has made such a diagnosis, regular physiotherapy and massage will restore normal coordination and stabilize the muscle tone of the eyes.
It is useful if the baby performs exercises that are based on alternately moving the eyeballs down, up and to the sides. You can hang rotating rattles and bright toys above the crib, then the baby will very soon learn to control the movement of his eyes. After a massage and a set of therapeutic exercises in the clinic and at home, the problem will disappear.
Sometimes the doctor may give the child Graefe's symptom. This pathology of the eye muscles and poorly developed nervous system in children usually goes away on its own with age. Swimming in the pool, prescribed by a doctor, will help. All the deviations described above are explained by the immaturity of the child’s brain and require not so much treatment as simply observation by a specialist.
In rare cases, the problem may be more serious if the child rolls his eyes when falling asleep. He may have increased intracranial pressure. The most accessible method of diagnosing this disease is to have the fundus checked by an ophthalmologist.
What to do and who to contact if your child blinks frequently
Ophthalmic causes
- Foreign body. If a speck gets into your child’s eye, you can try to gently rinse the eyes and pull it out, and then consult an ophthalmologist. Use a cotton swab dipped in water. Do not allow your baby to rub his eyes, do not try to pull out the speck with your fingers, much less with tweezers. This will cause injury.
- Drying of the cornea. This occurs in children who often watch TV or play computer games for a long time. In this case, limit the time or completely remove activities from the child’s daily routine. Go see an ophthalmologist. The doctor will prescribe moisturizing drops to relieve dryness and restore comfort to the baby.
- If vision deteriorates, the child will not only blink, but also squint. If you observe both symptoms for several days, take your baby to an ophthalmologist.
- Another reason for frequent blinking is microtrauma of the eye. Ask the baby if he was hit or if he got a bump under his eye. Examine the child yourself and, if scratches, ulcers and broken blood vessels are found, consult a doctor.
- Fatigue. It is observed in many schoolchildren. As school begins, the strain on the eyes increases and the body does not always have time to adapt to it. It is better if the child spends most of his free time outdoors, walking and playing sports.
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the eyelid and the front of the eye. Causes discomfort and a feeling of sand in the eyes. Occurs due to hypothermia, injury or disease of the nasopharynx. The baby begins not only to blink frequently, but also to rub his eyes, complain of headaches and increased lacrimation. In some cases, pus may leak from the eye. Conjunctivitis is usually treated with medication. Medicines are prescribed only by an ophthalmologist.
Neurological causes
- Severe fear often causes nervous tics in children. In this case, the child squeezes his eyelids tightly. May also flinch at loud noises. You cannot cope with such a problem on your own. You will need the help of a neurologist and, possibly, a psychologist.
- Long-term stress, for example, when entering kindergarten or changing residence, can trigger a tic. If there are no problems with the eyes that we wrote about above, then you should consult a pediatric neurologist. The doctor will recommend soothing teas, reflexology or sessions with a psychologist.
- Concussions and other traumatic brain injuries can cause frequent blinking of either one or both eyes. You need to immediately call an ambulance, doctors will examine the baby and take you to the hospital. There they will conduct a full examination and prescribe treatment.
- In various forms of epilepsy (Encephalopathy, West syndrome, partial epilepsy), frequent blinking and involuntary contractions of the facial muscles are observed during attacks. In this case, blinking is accompanied by impaired consciousness, cramps of the arms and legs, involuntary urination, etc. Only a neurologist can make a diagnosis after the child has had an electroencephalogram. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will be able to select the correct anticonvulsant therapy.
- If relatives have a similar illness, then we can talk about a genetic predisposition. The child should be shown to a neurologist and consulted about how to combat the problem.
- After suffering from severe infectious diseases, for example: sore throat, influenza, acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections, some disorders of the nervous system, including tics, may be observed. They can also be triggered by antipyretics or nootropic drugs. If such a reaction occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor to change therapy.
- In infants, frequent blinking is a consequence of complications during childbirth. Hypoxia leads to damage to the nervous system.
The danger still exists
But the situation when a child rolls his eyes up after 3 years should alert parents. Especially if it manifested itself after the child suffered a severe infectious disease with a high fever.
This may turn out to be a rare inherited pathology - paroxysmal tonic upward gaze. The disease itself does not pose a danger to the child’s body, but sometimes such children suffer from poor coordination of movements and may lag behind in development.
Many parents begin to panic when they see uncharacteristic movements in their child, especially with their eyes. After all, it is very difficult to understand whether a disease is a harmless feature inherent in the baby. For example, why does a child roll his eyes?
First, we note that parents should not hesitate to ask for advice from a pediatrician, who, if necessary, will refer the child to the appropriate specialist. Tell the doctor in detail about how often the eyes roll, whether this happens in a dream or while awake, and how the child is feeling at this moment. The phenomenon in which a child rolls his eyes can be either pathological or characteristic of a certain childhood age. Only rarely does it indicate a serious illness.
Up
For a full-term infant up to one month old, the phenomenon of rolling the eyes upward is a variant of the norm. This happens especially often before bedtime, when the newborn is not yet sleeping and is at the borderline level between sleep and wakefulness.
Infants rolling their eyes upward can also be a sign of illness. Especially if this condition appeared after the baby suffered an infection, accompanied by an elevated temperature.
For example, an infection can trigger the appearance of a rare hereditary disease - paroxysmal tonic upward gaze. Although the disease does not have a strong impact on the child's body, it can cause slow development and impaired coordination of movements.
During illness, parents should surround their baby with special care, protect him from stress, infections and nervous shock, and ensure comfortable and sound sleep. By the age of five, children usually outgrow the condition.
Down
When a baby rolls his eyes downward, this may be a manifestation of a disease, so you need to see a neurologist. Very often, this condition may indicate high blood pressure.
Other causes may include: Tourette's syndrome, nervous tics, obsessive-compulsive neurosis (an attempt to reduce nervous tension by repeating certain actions) and Graefe's symptom, which will be discussed later.
Graefe's symptom
Back in the 19th century, scientists discovered Graefe syndrome, which is informally called “setting sun” syndrome.
Often newborns are diagnosed with Graefe's symptom. It manifests itself in the following: the child’s upper eyelid peels off from the iris, which becomes noticeable when the eyes are lowered; Between the iris of the eye and the eyelid, a white stripe of sclera is clearly visible. The eyes roll down like the setting sun.
Graefe's symptom usually goes away with adulthood without additional treatment. But the baby should be under the supervision of a pediatric neurologist for several years.
Sometimes, to relieve symptoms, the doctor prescribes diuretics and recommends swimming and massage. In severe cases, surgery or bypass surgery may be required.
In children over one year of age
Up
Why does a child roll his eyes? For example, if he has diseases of the hearing organs and upper respiratory tract (inflammation of the sinuses, tonsils, tonsils), pain in the soft tissues of the face. This condition can then be considered an expression of the fact that the child is uncomfortable with pain. Accordingly, the rolling of the eyes will stop as soon as it passes.
Sometimes parents of children aged four to ten years suddenly see that the child has begun to close his eyes, roll them to the side and up, and blink frequently.
Everyone reacts to this differently. Some people don’t attach any importance, thinking that the child is grimacing, others begin to scold the child, control his behavior, believing that he has some kind of pathology.
Usually, such “blind man’s buff” and rolling of the eyes to the side can be a manifestation of a nervous tic. You cannot ignore such behavior or scold the child, because this is a signal that not everything is in order with the child’s psyche.
Nervous tic
It can appear in absolutely every child, but not all parents know how to help him in this case so that he can get rid of the disease on his own. But if mom and dad behave correctly, in 80% of children the nervous tic disappears without a trace by the age of ten.
Note that children who sometimes have twitches and tics cannot be called mentally ill.
The following are the causes of tics in a child:
- Nervous tension. Typically, children begin to get nervous when there is a change in home environment, for example, to kindergarten or school. It is at this time that the first symptoms of a nervous tic are possible. The causes of the disease may be conflicts with children, communication problems, a strict teacher or educator. The trigger for the development of tics is quarrels between parents in front of the child, as well as too strict upbringing, fear, loss of a loved one or other nervous shocks.
- Heredity. If relatives even had this deviation several generations ago, then there is a high probability that it will manifest itself in the baby.
- Eye rolling to the side and involuntary blinking can also appear after taking medications due to illness.
- Child head injuries.
- Uncontrolled watching TV, sitting at the computer for a long time.
- Poor nutrition.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Although nervous tics are usually not a serious illness, the child should be registered with a neurologist and undergo a timely examination.
Down
If parents notice a child over one year old's eyes rolling downwards, this may mean that his blood pressure has increased.
If intracranial pressure is very high, the child will vomit, the eyes will roll down or squint strongly. In this case, the baby may fall into a coma, as well as briefly or permanently lose vision.
Epilepsy
You should pay close attention to the fact that a child over 5 years old begins to roll his eyes when falling asleep. Especially if this happens with his head thrown back and he does not react to anything at that moment. At this age, such symptoms may indicate the development of epilepsy in the child.
It is accompanied by seizures. Absence - a weak epileptic seizure - manifests itself in rolling the eyes upward and in a short “slowdown”, suspension of all higher processes of the child’s psyche. The baby “freezes”, his eyes begin to roll back, after which he “dies away” and behaves as if nothing had happened.
Sometimes absence seizure turns into a severe epileptic attack. In this case, the child first rolls his eyes, twitches, shakes his head, after which a convulsive seizure occurs. This is the most severe degree of epilepsy.
Epileptic seizure
What does an epileptic seizure look like? Before the child begins to shake his head and shake convulsively, he develops a prodrome - irritability and anxiety.
The beginning of the attack is indicated by the child's cry, then he loses consciousness, and involuntary contraction of the body muscles begins. The child rolls his eyes upward and clenches his teeth tightly. At the same time, he begins to breathe less often, his pupils dilate. Afterwards clonic convulsions, defecation and urination occur.
As a result, the child falls asleep and then does not remember anything. Note that epileptic seizures usually recur periodically, and at the same time of day.
What to do in case of an epileptic seizure?
- Do not panic. Parents need to track the course of the seizure, measure its duration in order to tell the doctor about it in detail.
- Turn the child's head to the side to prevent the tongue from retracting and to ensure easy flow of saliva.
- Under no circumstances should you open your child’s jaws with a spoon, finger or other object!
- Do not put medications in his mouth.
- If the baby starts vomiting, make sure that he does not roll over, but lies on his side.
- Be with the child all the time until the end of the attack.
- If a child falls asleep after a seizure, there is no need to wake him up.
It is important to note that epilepsy must be treated without fail, since with each new attack the disease only gets worse. This is fraught with a slowdown in mental and psychomotor development. Only timely therapy ensures a speedy recovery, so do not delay your visit to the doctor.
What to do and how to help your child
If your baby rolls his eyes in the first weeks of his life without showing concern, there is no need to worry. It’s enough just to wait until he grows up, and the problem will disappear on its own.
Once he reaches the age of one month, it makes sense to purchase a mobile phone.
A small funny toy, its appearance reminiscent of a carousel with funny animals and insects, actually performs the most important function - it teaches the baby to focus and train its eye muscles.
By the way, similar therapy is also prescribed if a child is diagnosed with weakness of the eye muscles. True, the function of the mobile is now performed by special gymnastics for the eyes. Its basics are taught in a children's clinic, but usually it all comes down to:
In addition to therapeutic exercises, specialists can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. They will be carried out both at home and in a medical facility. Taken together, regular exercise will help not only improve the muscle tone of the eyes, but also improve vision in general.
If your baby rolls his eyes and is capricious, cries, or becomes hysterical, you should immediately visit a neurologist. The worst thing is when he periodically has a blank look. All this may indicate the presence of serious neurological diseases.
In order to confirm or not confirm them, you should undergo a number of special examinations, which only a qualified specialist can prescribe. The main thing is not to delay and contact him as early as possible, before the problem becomes chronic. Moreover, in infancy, most of these ailments can be successfully corrected.
In a dream
- Breastfed babies can sleep as if with their eyes open. In fact, the eyes roll back in sleep due to weakness of the eye muscles. Keep it quiet while your baby is sleeping, because the noise may cause him to open his eyes slightly and then fall asleep in this state.
- In an older child, eye rolling in a dream can be observed when he has not yet fallen asleep, or, on the contrary, is preparing to wake up.
To prevent eye rolling, you should:
- Train your baby with colorful toys and objects. They will help the child develop normal vision. Frequent exercises will help adjust and focus the baby’s vision, which will have a beneficial effect on his visual system in the future.
- Do eye exercises: rotate your eyes in different directions, blink frequently, close your eyes tightly.
- Exercise in the pool and give your child a massage.
- Choose bright rattles for your newborn: they will help not only in the development of normal vision and hearing, but also in concentration.
- If your baby's eyes roll back in his head due to physical muscle weakness, then he needs to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures, massage and perform a set of exercises.
What to do if your baby starts rolling his eyes
One thing can be said absolutely for sure: under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Even if we are talking about traditional medicine, it is very important to understand that the baby’s internal organs have not yet fully developed, and those drugs that are considered harmless for an adult can harm a newborn.
Only a doctor can distinguish pathology from minor deviations. Most often, specialists do not resort to aggressive treatment, limiting themselves to gymnastics and exercises, so you don’t have to worry that your baby will have to be stuffed with pills.
Summary
If a child rolls his eyes upward, this is usually not a pathology or a symptom of any disease. This is especially true for newborns, because they have not yet learned to control their eyes. Older children may simply have fun with this behavior.
Do not forget that as the child grows, such manifestations should disappear.
If this does not happen, or you think that eye rolling is not just a childish prank and a phenomenon characteristic of a certain age, then contact a pediatric neurologist. He will examine your child and tell you if there is any cause for concern. We recommend reading: .
When should you see a doctor?
Note! Sometimes eye rolling occurs due to a serious illness when urgent medical attention is needed.
This series includes pathologies such as:
- Epilepsy.
- Intracranial pressure.
- Mental retardation.
- Other nervous system disorders.
Another dangerous disease when a newborn’s eyes roll back can be hydrocephalic syndrome, when excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the head.
This condition develops in the womb. In this case, an in-depth examination and careful treatment will be required.
Since hydrocephalic syndrome left unattended further causes an increase in intracranial pressure and a lag in physical development.
In this case, you will not be able to help the baby at home.
In addition, parents without proper medical education will not be able to determine the seriousness of the situation.
If your baby is more than one month old, is whiny, often throws his head back, and you notice other abnormalities besides rolling his eyes, do not delay going to the doctor.









