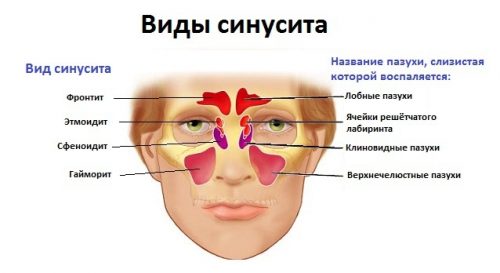
Types of sinusitis. Acute and chronic forms
Varieties of sinusitis are related to the location where the inflammation occurs. There are 4 types of paranasal sinuses, which give the disease a second, more local name:
- maxillary, or paired maxillary (sinusitis);
- paired wedge-shaped (sphenoiditis);
- paired frontal (frontitis);
- ethmoid sinuses (ethmoiditis).
There is also pansinusitis, a disease in which all the paranasal sinuses become inflamed at the same time.
Sinusitis can have 2 forms - acute and chronic. As soon as the disease occurs, it has an acute form, and if treatment is insufficient or untimely, it quickly becomes chronic.
Important! Do not delay treatment for sinusitis even for a day. Any delay can cause serious complications.
Features of the course of the disease in a child
Children are highly susceptible to all forms of sinusitis. So, sinusitis can occur in a one-year-old child, and ethmoiditis even earlier. Children who have reached the age of 5 often experience frontal sinusitis, and sphenoiditis often occurs after 10 years. This is due to the stage of a child’s life at which particular sinuses develop.
An additional danger to children's health is the small width of the drainage and ventilation holes between the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses (they are called anastomoses). The narrower the hole, the faster it closes during swelling of the mucous membrane. This contributes to the rapid accumulation of inflammatory fluid in the sinus and the onset of sinusitis.
Remember that a child's pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids) can also contribute to sinusitis. It is better to remove hypertrophied adenoids immediately, even if they do not interfere with the child’s breathing.
Causes
Typically, sinusitis is caused by a runny nose that remains untreated or a respiratory infection suffered on the legs. A risk factor may be a chronic runny nose or a deviated nasal septum, that is, conditions leading to impaired nasal breathing. Often, sinusitis can be provoked by diseased adenoids or dental diseases.
At the initial stage, pathogenic bacteria appear in the nasal sinuses, and the child’s body, due to reduced immunity, hypothermia or an allergic reaction, is not able to resist the infection. Due to edema, sinus ventilation is impaired. They lose connection with the nasal cavity. At this time, mucous contents accumulate in the sinuses, which eventually fills them. This creates greenhouse conditions for microbes to multiply. The sinuses begin to fill with pus, which then ends up in the blood, leading to intoxication of the body.
Causes and factors of occurrence
The chance of getting sinusitis increases if the child already has a sore throat or a group of
The disease may have a viral or bacteriological basis. Sometimes fungal sinusitis occurs, but due to the similarity of symptoms it is also considered bacteriological. Sinusitis that occurs due to viruses is called catarrhal, and due to bacteria and fungi - purulent. The origin of the disease has virtually no effect on its treatment. The principle of treatment (both traditional and folk) remains unchanged.
What is the treatment for maxillary sinusitis is indicated in this article.
What are the reviews about Albucid for runny nose in children, indicated in the article.
How to quickly cure colds and runny nose is indicated here: https://prolor.ru/n/lechenie-n/kak-vylechit-nasmork-za-odin-den.html
The chance of developing the disease greatly increases if a person suffers from a sore throat, flu or other diseases from the ARVI group. This is especially true for children, but adults also need to be extremely careful.
First signs and symptoms
The main signs of sinusitis, which allow diagnosing the disease at an early stage:
- constant nasal congestion;
- yellowish/greenish mucus in the nose and throat;
- painful appearance of the nose, eyes, forehead and cheeks;
- cough, especially at night.
These signs alone do not guarantee the occurrence of sinusitis. A child may have trouble breathing, look sick and cough at night even with a simple sore throat, as well as with a number of other diseases from the ARVI group. But you shouldn’t hesitate and hope for the best. As soon as you see that your child has symptoms similar to sinusitis, take him to the doctor. In any case, the doctor will suggest the correct course of treatment, even if the disease turns out to be much less serious than you expected.
Other symptoms of sinusitis are more rare, but also cannot be ignored:
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- increased body temperature;
- unpleasant odor when breathing;
- state of constant fatigue;
- a sore throat.
All these symptoms are equally characteristic of both children and adults. There are no specific signs of sinusitis that would be characteristic only of a certain age group. Moreover, the symptoms of all types of disease look approximately the same. Even if the frontal sinuses are inflamed, the throat will hurt first.
Important! Even if there are no main symptoms of the disease, it is worth carefully assessing the child’s general health. He may have more rare symptoms that also signal the onset of sinusitis.
Symptoms of sinusitis in children
Often, sinusitis occurs as a result of an untreated cold or as a complication after a flu infection. The manifestation of this disease directly depends on the form of the disease and the age of the baby. It is believed that sinusitis cannot appear in a child until the age of three, since the paranasal sinuses are not yet fully developed. In children from three to six years of age, the disease occurs as a result of private infectious diseases or enlarged adenoids. In this case, the symptoms do not manifest themselves very clearly. Often sinusitis is accompanied by otitis media, since the nasal and auditory tube cavities are located next to each other.
In children older than seven or eight years, the paranasal sinuses are already fully formed. Therefore, the inflammatory process can occur in any of them. The main symptoms of sinusitis in children are characterized.
- Congestion of the nasal passages. At the same time, it may block one nostril, then the other.
- A runny nose that lasts more than two weeks. This sign is the most important in determining sinusitis.
- The presence of yellowish or greenish discharge.
- Painful sensations in the paranasal sinuses.
- Manifestation of headaches.
- Changing your voice. Nasality appears.
- Decreased olfactory function.
- An increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees. In the chronic course of the disease, a febrile state is extremely rare.
- Deterioration of general condition in the form of fatigue, lethargy, sleep disturbances and lack of appetite.
- A feeling of dryness in the throat, resulting in a dry cough.
- Swelling of the eyelids and cheeks.
Diagnosis of the disease
Sinusitis can be diagnosed at home. If a child constantly has a stuffy nose and an unhealthy-colored discharge that does not resemble normal nasal mucus, this may be sinusitis. In adults, before the onset of the disease, there is usually a prolonged runny nose (at least a week), and only then pain appears.
In children, a similar picture is not observed very often, because Their sinusitis tends to be sudden. Often, an illness is signaled by the fact that a child who has almost recovered from ARVI suddenly becomes ill with renewed vigor. When such a “second wave” appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. And in general, as soon as you notice symptoms similar to sinusitis, immediately take your child to the clinic. What to do when a runny nose does not go away after an acute respiratory viral infection is indicated in the article.
If a doctor diagnoses sinusitis in an adult, he will most often perform a puncture of nasal mucus. This method is not recommended for children. Most often, doctors diagnose childhood sinusitis using ordinary external examinations. Sometimes an x-ray may be needed to determine the disease.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
Signs of sinusitis correspond to other infectious and colds. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, in addition to the survey, the doctor prescribes additional studies.
1. An x-ray of the paranasal sinuses is performed. In this case, the doctor will find out the thickness of the nasal mucosa. And where exactly did the inflammation occur?
2. They take blood for a general analysis to find out about the presence of inflammation in the body. When you have sinusitis, the number of white blood cells increases.
3. A computed tomography scan of the nasal cavity is performed. Tomography reveals the surface of the paranasal sinuses more clearly. The presence of polyps, cysts, and deviated nasal septum are detected.
4. Sometimes you should show the child's handkerchief to the pediatrician.
If a patient with sinusitis or a child has a swollen cheek or red eyelids, then you should immediately go to the hospital.
Treatment
Treatment options

As a rule, with sinusitis, a sick child is not hospitalized. The necessary care can be provided at home
Sinusitis, like most inflammatory diseases, can be effectively cured using folk remedies. But you should not rely only on alternative medicine. It is best to combine it with the treatment prescribed by the doctor. This is the best option for getting rid of sinusitis in a short time. So, how to treat sinusitis at home?
Most often, quick treatment of a runny nose in children involves the use of antibiotics. But if the disease has a viral basis, then antimicrobial drugs are not required. The main goal is to remove the causative agent of the disease. Drugs such as amoxiclav and amoxicillin can help with this. Azithromycin, doxycycline and clarithromycin are often used instead.
This treatment can be used both in a hospital and at home. As a rule, the patient does not require professional care, but if you want to constantly learn about changes in the child’s health, an inpatient course of treatment will not be amiss.
Important! Preschool children should take antibiotics in the form of syrups or suspensions.
Treatment with folk remedies
Plants such as Kalanchoe and eucalyptus are best suited for the treatment and prevention of sinusitis. But before using folk recipes found on the Internet for a runny nose, consult your doctor. They may not be best suited for the child or for a particular type of illness.
You can also use cotton swabs soaked in a decoction of eucalyptus and string leaves, as well as St. John's wort and violet flowers. The composition of herbs in different recipes may vary, but these are the main ingredients.
Many people believe that to get rid of sinusitis you need to rinse your mouth or nose with a decoction of some herbs. This is not entirely true, because, for example, this method is not suitable for treating the symptoms of sinusitis in children, since the affected sinuses are not involved in rinsing at all. You should not experiment with folk remedies. They, of course, will not harm, but they will not bring much benefit either (at least until the doctor approves them).
Possible consequences and complications
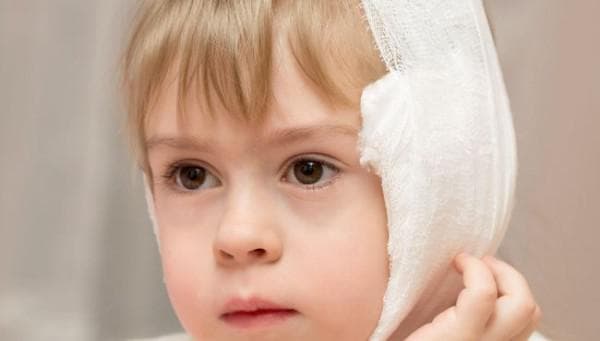
Ear inflammation is one of the possible unpleasant complications of sinusitis.
If you let sinusitis become chronic or simply delay treatment, a number of unpleasant complications may arise. Here are the most basic of them:
- various ear infections; But how to treat ears and what means you can find out by reading the article about drops in the ears for otitis Otipax
- blurred vision;
- inflammation of the lining of the brain (meningitis).
Bacteria and viruses that cause sinusitis can often cause other illnesses in a child. They are not as dangerous as meningitis, but can threaten the health of the entire body. So sinusitis needs to be treated immediately, before it reaches the stage of complications.
Other unpleasant consequences are associated with the eyes and skull. This may be a subperiosteal abscess, orbital periostitis, optic neuritis, swelling of the tissue, meningeal abscesses, and even brain abscesses. Sometimes such complications lead to death. Complications themselves occur in approximately 10% of cases, usually due to inappropriate or untimely treatment. But the chance of death with them is quite significant.
Possible complications of childhood sinusitis
Without timely treatment, the condition takes dangerous forms. Infectious agents pass from the inflamed cavity to soft tissues and nearby organs. Purulent phlegmons form inside the orbital tissue.

Blockage of the ethmoid sinus can lead to loss of eye muscle movement and severe vision impairment.
The development of infection on the bone walls of the sinuses causes osteoperiostitis. Advanced suppuration of the frontal and sphenoid sinuses leads to brain abscess and meningitis. Young children (from birth to 3 years) may develop a rapid course of a purulent-necrotic disease, sepsis.
Severe consequences rarely occur. In 70% of cases, acute sinusitis in children is cured without becoming chronic. The task of parents is to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.

Video
You will find tips on the proper treatment of a runny nose in a child in this video:
Any inflammation inside the head is dangerous, but sinusitis is especially dangerous. In addition to painful sensations, it can cause a number of unpleasant consequences, which will be very difficult to cope with. When treating, you should trust the doctor and the antibiotics he prescribes, and traditional medicine can only be used for prevention, in combination with traditional methods of treatment.
Remember! Sinusitis is not fatal. But there is no need to push it to the stage where complications may arise that are several times more serious than the disease itself. Treat your child right away and everything will be fine!
Treatment
The first task that is set in treating the disease is to relieve swelling of the anastomosis. It is necessary to ensure that the mucus has the opportunity to exit naturally. For this purpose, drops that have a vasoconstrictor effect are instilled into the child several times a day. These can be galazolin, naphthyzine. The nasal drops should reach the middle nasal passage. To do this, you need to lay the child horizontally so that the head is thrown back. When the sinuses are inflamed on one side, it is necessary to tilt the head to the side that is affected.

Along with vasoconstrictor medications, anti-inflammatory medications and anti-allergy medications are used. If the disease is advanced and the inflammation of the sinuses has turned purulent, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
At the resorption stage and in the treatment of chronic sinusitis, special massage and breathing exercises are recommended.
The massage comes down to gentle tapping on the bridge of the nose for 2-3 minutes using the phalanx of the thumb. It makes sense to do drainage tapping twice an hour. You should also massage the following places: the point between the eyebrows, the place below near the eye socket. These areas may be painful. The massage is carried out in a clockwise direction.