Reasons for the appearance of a lump
Hematoma cones form in children after hitting a hard surface
The formation of a lump is based on a mechanism associated with the accumulation of blood in the tissue layers. This happens due to rupture of blood vessels. The condition is also complicated by swelling, which necessarily forms at the site of the bruise. However, bumps and falls are not the only reason why a large lump may appear on a child’s forehead:
- A congenital disorder in the structure of the skull - such a bulge cannot be treated and does not pose a danger; it is detected in the first months after birth.
- The formation of a wen due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. It is not painful and soft to the touch.
- An allergic reaction most often occurs to hair and face cosmetics in children.
- Acne – under the age of 12 is considered a very rare cause of large bumps on the forehead.
- A tumor is the rarest cause, accompanied by changes in size and color, and is hard to the touch.
- Recurrence of a previous injury - in this case, the lump will fester if it is not treated.
- Atheroma is a tumor that forms due to obstruction of the sebaceous glands and the penetration of bacteria. It occurs with accumulation of pus.
- A sebaceous cyst is a neoplasm that occurs due to improper child care.
- Hormonal changes - salt deposition or fluid accumulation appears due to pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- Metabolic disorders - the lump becomes a consequence of the accumulation of elements that have not been eliminated.
Tumors on the forehead can be benign or malignant. If the lump does not go away within 2-3 days, it is better to consult a doctor.
Facial swelling in children is a cause for concern
Swelling of the bridge of the nose and the area between the eyebrows is not a harmless phenomenon.
This may be a manifestation of a hematoma after a blow, the spread of inflammation deep into the nasal sinuses during rhinitis, or a reaction to an allergen. Parents should take this symptom seriously, especially if the child is small and cannot explain what is happening to him. The danger of swelling in the area between the eyebrows is the risk of breathing problems. Also, inflammation can spread from the frontal sinuses to the brain due to its close location. In addition, the inflammatory process can spread to the eyes with the appearance of severe symptoms and dangerous complications.
Pain and burning, breathing problems cause stress in the baby, which negatively affects the nervous system. A hysterical state aggravates the course of the disease. Breastfed babies have difficulty sucking and breathing at the same time when they are swollen, so they may become malnourished and not gain weight. A weakened child gets sick longer and has a harder time recovering.
Swelling of the bridge of the nose is usually a manifestation of an inflammatory process, which can have many causes:
- Inflammation of the nasal mucosa (infectious, vasomotor, allergic rhinitis). In the acute phase, swelling is noted, in the chronic phase, tissue growth occurs due to pathological cell division (proliferation).
- Sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses). Its types are sinusitis (inflamed maxillary sinuses), frontal sinusitis (frontal sinuses are affected), their combination with inflammation of the ethmoid bone (frontoethmoiditis, maxillary ethmoiditis).
- Foreign body inside the nose. The area around it becomes inflamed, the body reacts with an accumulation of white blood cells (pus).
- Injury to the bridge of the nose. When struck, a hematoma (consequence of internal bleeding) and swelling with blue (sometimes black) under the eyes occur.
- Congenital or traumatic curvature of the nasal septum or anatomical narrowness of the canals. The breathing process is difficult, the mucous membrane easily becomes inflamed and swollen.
Damage to soft tissue and blood vessels can occur due to impact or fracture of the bones of the nose and upper jaw. Bone fragments further destroy them, preventing rapid healing and reducing swelling. A comminuted fracture may require surgery. After this, the bones are fixed for several days by packing the nose. Sometimes, when the jaw bones are fractured, the lips are fixed with staples and the patient is given only liquid food.
For any injury to the nose, it is advisable to take an x-ray to check the condition of the bones. A fracture that does not heal properly will cause breathing problems and recurring swelling in the future. If the nose is injured, cold should be applied to the damaged area to prevent swelling.

When a small child explores the world around him, he “tastes” things - he tries to put them in his mouth or nose. These can be small parts of toys, peas and even tablets. In nature, insects, poplar fluff or dandelion seeds can get into the nasal passages. When swimming, microorganisms living in the water can crawl in.
The presence of an object in the nose impairs the ventilation of the sinuses, leading to an inflammatory process (even suppuration) and swelling. If the object is not removed for a long time, polypous tissue growths, dysfunction of the lacrimal process, suppuration and swelling of the conjunctival sacs are possible. The presence of a foreign object can be indirectly determined by the release of exudate from the affected nostril.
Conjunctivitis of viral or bacterial origin often occurs in children during seasonal epidemics. Children attending nurseries and kindergartens are especially susceptible to them. They occur in combination with rhinitis and sinusitis, cough, and fever. Inflammation of the conjunctiva and nasal mucosa can cause swelling of the eyelids and nasal area. The baby's condition is aggravated by a painful and uncomfortable eye condition.
Swelling of the forehead often has the same etiology as swelling of the upper part of the nose. It occurs as a result of the penetration of inflammation into the frontal sinuses or as a reaction to injury to both zones. Swelling of the forehead without swelling of the bridge of the nose can be a manifestation of contact dermatitis, an insect bite, sunburn, or a pinpoint injury.
As a rule, contact dermatitis occurs when the surface of the skin comes into contact with an allergenic substance. If your forehead is swollen, it may be a reaction to creams, ointments, liquid repellents, or fabric headgear. The symptom is accompanied by itching and redness of the skin. It can be eliminated with the help of external antihistamines containing corticosteroids.
A bite of an insect
Bites from large insects that inject venom into the wound cause particularly extensive swelling. These could be wasps, bees, gadflies. Multiple bites from mosquitoes and other mosquitoes, especially midges, can cause swelling of the entire face. Midges bite off part of the flesh and inject hemolytic poison into the wound with their saliva, which causes an allergy in many people in the form of simulidotoxicosis.
With renal failure, fluid retention in the body and changes in blood composition occur (decreased protein levels, increased concentration of Na ions, toxins). This leads to swelling of the upper torso, eyelids, and area around the eyes. With swelling of the upper eyelids, the swelling extends to the brow ridges.
Renal edema can be distinguished by its mobility (when pressure is applied, it moves), pale color and normal body temperature. Indirect signs: small amount of urine excreted, deviations in its composition, lower back pain.
Associated symptoms requiring medical attention

If the pain does not go away after a few hours, your child may have a concussion.
If a lump on the forehead appears after a child falls, but persists for a long time and is complicated by additional symptoms, you should not self-medicate. Danger signs include:
- after the injury, the child lost consciousness or became pale;
- the pain does not go away within 20 minutes and intensifies;
- prolonged headaches, sensations in the eyes and disorientation occur;
- pupils dilate or their size becomes different;
- bleeding from the nose or ears appears;
- vomiting, weakness or nausea;
- the child became drowsy;
- the lump throbs or hurts when walking;
- lips turn blue;
- difficult to turn your head in different directions;
- constant, long crying of a small child;
- severely damaged skin;
- the eyes began to squint in different directions;
- convulsions appeared.
Even one of these symptoms can pose a serious risk to a child's health. But only a pediatrician or traumatologist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Even if symptoms do not appear immediately, you should not leave your child alone for several hours after the injury. It is important to monitor his condition for at least 2-3 days.
Possible consequences of a bump on the forehead
Leaving dangerous symptoms unaddressed can lead to problems in the future. The most common complication of a blow is a concussion. The head contains many vessels and nerves, so severe trauma can lead to their rupture or compression. This requires a medical diagnosis. Severe damage to the skull or brain is also fraught with long-term damage to the central nervous system and individual organ structures.
Diagnostics
Swelling on the forehead between the eyebrows on the bridge of the nose requires a comprehensive diagnosis, after which we can draw a conclusion about the reasons that caused such a symptom. First of all, this is a visual examination by a doctor, then additional laboratory research methods. The following tests and procedures are usually prescribed:
- general urinalysis and urine analysis according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky to identify abnormalities in kidney function;
- biochemical blood test (urea, creatinine, immunoglobulins, etc.);
- allergy tests;
- swab from the nasal mucosa;
- rhinoscopy;
- X-ray or tomography of the nose and sinuses;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys if their pathology is suspected.
First aid after a fall
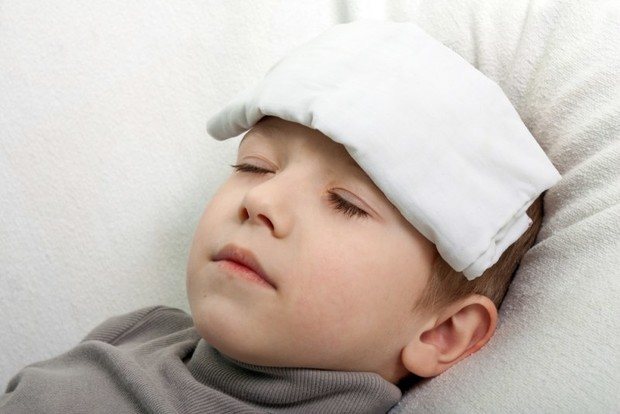
For the first 2 - 3 hours, it is necessary to apply cold compresses to the hematoma to reduce blood circulation
If the parents notice that the baby has fallen, or he himself has complained, he needs help. There is no need to scold, this can worsen the child’s condition.
First aid measures after an impact include:
- Using a cold compress. You can use frozen food, a metal spoon, or a cold towel.
- Providing peace. It is important to put your baby down and let him rest before looking for additional symptoms.
- Treatment of open wounds. If the skin is damaged, it must be lubricated with an antiseptic composition.
If the open wound is deep, it is better to consult a doctor. Stitching may be required. Do not wash open wounds with cold water or wash your child.
Treatment methods
Treatment tactics are determined by the cause. If the lump is caused by internal processes, treatment will require long-term use of medications - for metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalances, benign formations and cysts. Also, for tumors and wen, the patient will be prescribed surgery and subsequent physical therapy.
Ointments and gels for bumps from impact

Lyoton prevents hematoma from enlarging
If a child has a lump on his forehead after a blow or fall, the fastest-acting and easiest to use are pharmaceutical creams.
- Lyoton. A product with heparin, which improves blood clotting and has anti-inflammatory properties. Helps against severe swelling and bruising.
- Wobenzym. Ointment with anti-inflammatory enzymes that accelerates healing.
- Heparoid. Another drug with heparin for bruises, scars and swelling of damaged areas.
- Ibalgin. An NSAID cream that effectively relieves pain and swelling. Helps against vascular injuries.
- Arnica ointment. Helps with swelling and bruising, contains natural ingredients.
- Comfrey ointment. A product based on a herbal mixture is indicated for children who do not suffer from allergies.
- Aescin. An effective gel for swelling and inflammation, aimed at improving blood circulation.
- Repaired. Cream for bruises and pain, can be used to treat children.
There are special remedies for bruises, bumps and bruises, for example, Bruise-off cream.
Before using any medication, you should read the instructions. If there are no contraindications or dangerous side effects, you can use it. When treating a child under 3 years of age, it is better to consult a pediatrician.
Traditional recipes for pain and bumps

Grated raw potatoes are applied to the bump the next day
Many alternative therapies are suitable for eliminating bumps caused by various reasons. Natural products and herbs have powerful anti-inflammatory, analgesic and healing effects.
Popular and fast-acting recipes:
- Lotions from thyme leaves. Used as part of first aid, helps against tumors and heals wounds. Apply fresh leaves to the sore spot or steam dry leaves.
- Potato compress. Apply raw potatoes wrapped in cheesecloth, grated on a fine grater.
- Parsley. Grind the fresh product and apply it to the forehead. You can make ice from chopped herbs in advance.
- Plantain. Prepare a puree from fresh herbs and apply it to the pine cone. It has powerful absorbent properties.
- Banana peel. Apply with the inner side to the injured area.
- Onions and salt. Prepare a compress from some chopped onion and the same amount of salt. Wrap in a light cloth to prevent the juice from leaking into your eyes.
- Cabbage. Finely chop and apply to the sore spot. You can take a whole sheet and lightly rub it.
- Bay leaf. Brew 3-4 leaves in a glass of water. Freeze water in molds.
- Sagebrush. The plant contains flavonoids and substances that accelerate healing. Grind the fresh plant and squeeze out the juice. Lubricate the area of the bump with it.
- Nettle. Contains substances that help fight hematomas. Prepare a decoction of fresh or dried herbs, then soak gauze in it and apply it to the diseased area.

Badyaga cream resolves hematomas and bumps
You can use other means that are at hand in almost every home. One of these products is pharmaceutical badyaga. A substance with silicon oxide quickly dissolves bumps and stimulates blood flow. Apply the compress for 20 minutes, diluting it with some water.
You can use potato starch and laundry soap. The first product contains substances that relieve pain and inflammation, envelop and heal. Use 2 tbsp. l. and 2-3 tbsp. l. water. The mixture is applied directly to the forehead. The soap contains a unique combination of animal fats, alkali, salt, soda, and acids. Together they act as a powerful antiseptic with anti-inflammatory properties. Grated soap is mixed with yolk and applied to the bump on the forehead for 10-20 minutes.