- September 10, 2019
- Child's health
- Karina Perevalova
A general (or clinical) blood test is the most frequently prescribed laboratory test, during which it is possible to determine whether any pathological process is occurring in the body of a child or adult. In addition, it can be used to control the course of chronic ailments.
Clinical examination of liquid connective tissue is both a nonspecific and universal test. This is due to the fact that its results can be correctly interpreted only taking into account the patient’s symptoms.
Both infants and older children are faced with the need to regularly submit biological material for research. Below we describe how to correctly take a general blood test for a child, and what nuances need to be taken into account when preparing for the test. In addition, information is provided on how to correctly interpret the study results.
Indications
A clinical blood test is the most common type of laboratory diagnosis, based on the results of which conclusions can be drawn about the general condition of a person. In pediatrics, this test is especially important, because parents cannot always determine what really hurts their children.
Examination of just a few milliliters of liquid connective tissue can confirm or exclude the presence of a pathological process in the child’s body. Repeated analysis allows you to assess the degree of effectiveness of the treatment carried out earlier.
There are many conditions for which a clinical blood test is suspected to be particularly valuable. These include:
- Infectious pathologies of an inflammatory nature. They can have different etiologies (bacterial, viral, fungal) and localization. Most often, a general blood test is performed in children if they have symptoms of respiratory, skin and intestinal diseases, in particular helminthiasis.
- Inflammatory pathologies of non-infectious etiology. These include allergic and autoimmune diseases.
- Anemia.
- Blood loss resulting from injury.
- Impaired coagulation of liquid connective tissue.
- Pathologies of a malignant nature, which can be either congenital or acquired.
In addition, a general blood test is prescribed to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and before admission to educational institutions (kindergartens, schools).

Contraindications
If your child visits a massage therapist, it is necessary to complete the course or reschedule the date of collection of biological material. In addition, it is unacceptable to donate blood immediately after an X-ray examination, ultrasound or any physiotherapeutic procedures.
There are no absolute contraindications to the analysis. However, if a child suffers from certain diseases, in particular blood clotting disorders, low blood pressure, difficulties may arise during the collection of biomaterial. The nurse must be warned about this in advance.
Preparation rules
This stage is very important. Parents should be responsible for preparing for the study. If you do not take into account some nuances before collecting biomaterial, the interpretation of a general blood test in children may subsequently be carried out incorrectly. It is important to understand that liquid connective tissue reacts very sensitively to any changes.
Basic rules of preparation:
- Stop taking medications 14 days in advance. For example, if the child was treated for a completely different reason. If canceling the appointment is impossible, you must inform the doctor about this. The doctor will take this information into account when interpreting the results of the child’s general blood test.
- The day before and on the day of delivery of the biomaterial, it is necessary to avoid physical activity. It is recommended to take your baby for a walk before bedtime, and then put him to bed. For older children, you can read a book the day before, get a massage, or play calm games.
- If the blood sugar concentration is important to the doctor, you should not brush your child’s teeth in the morning. Older children should be prohibited from using chewing gum.
- After waking up, it is recommended to drink a glass of clean water without carbon. Information regarding whether to take a general blood test for a child on an empty stomach or not is presented below.
The psychological aspect plays a very important role. It is extremely important to prepare the child for the blood sampling process itself. If the child is older than 1 year, you can already try to explain to him that everything will go quickly and painlessly.
Blood tests
So as not to be afraid...Almost all children are afraid of medical procedures, especially when it comes to injections. And, of course, there is every reason for these fears, because children, unlike adults, cannot explain to themselves why they should patiently endure painful and unpleasant procedures. Trying to get a child to calm down is unlikely to be a convincing means of combating fears. The baby is simply not able to pull himself together, no matter how much you persuade him. Therefore, even the smallest child needs to be explained, as seriously as possible, what will be done to him and why. It is not so important whether the baby understands your explanations. The main thing is that he has a feeling of the correctness of everything that is happening. |
General recommendations
You should not deceive your child by saying that “it won’t hurt at all” if you have to undergo an injection. It’s better to say that it will hurt, but not for long, you’ll have to be patient a little. If your child is very afraid, be a little afraid with him - shared fear is easier to bear. Try playing doctor by giving “injections” to soft toys, let the child be the doctor, and then the toys themselves will “treat” each other. To reduce pain, you can purchase local anesthetic cream at the pharmacy, do not forget to consult your doctor first. 5-10 minutes before the injection you need to anoint the finger from which blood will be taken and the baby will not feel anything. In this article we will talk about the tests that are most often prescribed for children. Almost all blood tests are done on an empty stomach, i.e. At least 8 hours must have passed since the previous meal. This is important, since food intake can affect the test result, for example, after eating, the blood sugar level, the number of leukocytes, etc. increase. For some tests, which your doctor will warn you about in advance, it is advisable to delay taking blood for analysis for at least 12 hours after eating. However, even small children are usually able to endure this with your help. Some blood characteristics are also subject to daily fluctuations, so the ideal time for tests is morning. After a night's sleep, all blood parameters tend to the daily norm, so the chance of false diagnosis of any abnormality is reduced. In addition, if you delay breakfast, it is easier to donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning. For infants in the first year
of life, the requirements are less strict; they can be fed breast milk as usual, because it is difficult to calm a baby down if he does not have breakfast.
For children over one year old,
1-2 days before the examination, it is advisable to exclude heavy foods from the diet: fatty and fried foods.
Before the analysis, you should also not give your child juices, tea or coffee, especially with sugar - this is also food, so you will have to be patient. You can drink water. In cases where breakfast before the analysis is acceptable, it may consist of unsweetened tea, unsweetened porridge without butter and milk, and an apple. To exclude other factors that could affect the test results: physical stress and fatigue after running, climbing stairs and emotional excitement, before the procedure you should allow the child to calm down and rest for 10-15 minutes in the waiting room. Taking some medications (for example, antibacterial and chemotherapy) can significantly affect test results, even within 10-14 days after stopping the dose. If your child is being treated with such drugs, be sure to notify the doctor ordering the tests. They may need to be moved. Blood should also not be donated soon after an x-ray examination, since exposure to x-rays may distort the analysis data.
Tests for genetic diseases
The first tests in a child’s are taken immediately after birth. Such studies are called neonatal screening, that is, this study is carried out on all newborns. Blood samples are collected during mass screening of newborn children for hereditary diseases in the maternity hospital. Blood for analysis is taken from the baby’s heel and sent to the laboratory with a special form. You must be told what tests are going to be performed. No tests will be performed on the baby without your informed and voluntary consent, but you should not refuse them. The diagnosis will not cause any harm to the newborn, and you will be able to learn about very important features of your baby’s health, which you may have to take into account in further care for him. The list of hereditary diseases that are monitored everywhere includes congenital hypothyroidism (a disorder of the synthesis of thyroid hormones) and phenylketonuria (a general disorder of protein metabolism). These hereditary disorders can have an extremely serious impact on the child’s and pose a risk to his life. However, if detected early, the child can still grow up quite healthy and normal.
General blood analysis
Complete blood count is widely used as one of the most important examination methods for most diseases. The changes occurring in the peripheral blood are nonspecific, i.e. they cannot be used to determine a specific disease. But at the same time, it is these indicators that reflect the changes occurring throughout the body. Thus, using this analysis, it is impossible to determine exactly what the child is sick with, but you can navigate the state of health. Using a general blood test , doctors consistently monitor the child's . Typically, this analysis is taken at the age of 5 days, 1 month, 6 and 12 months, 5 and 10 years. During a general analysis, blood is usually examined for hemoglobin concentration, the number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets, the value of hematocrit and erythrocyte indices (MCV, MCH, MCHC), ESR. Red blood cells
– blood elements containing hemoglobin transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Hemoglobin
is a red substance that carries oxygen.
A decrease in hemoglobin in the blood, called anemia, may indicate various types of bleeding (including internal) or an increased level of destruction of red blood cells. The cause of anemia can also be a lack of iron or vitamins involved in the formation of red blood cells (mainly B12, folic acid), as well as a violation of the formation of blood cells in specific hematological diseases. In the first days of life, newborns have slightly more red blood cells than adults, but during the first year of life the level decreases. Erythrocyte indices
- the ratio of the amount of hemoglobin to the number of red blood cells, the number of red blood cells to the liquid part of the blood, etc.
used to determine the characteristics of the size, shape of red blood cells, etc. Using erythrocyte indices, you can also judge the nature of anemia. Leukocytes
are blood elements responsible for recognizing and neutralizing foreign components, the body’s immune defense against viruses and bacteria, and eliminating dying cells of the body’s own.
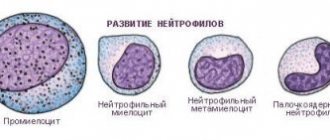
The formation of leukocytes (leukopoiesis) takes place in the bone marrow and lymph nodes. There are 5 types of leukocytes: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils. The percentage of these forms is calculated in a special leukocyte formula test. Each type of leukocyte has its own scope of work in the body. For example, in the presence of a focus of inflammation, the number of neutrophils increases. The number of eosinophils increases significantly during allergic reactions. Platelets
are the elements of blood responsible for blood clotting.
Normal values for platelet levels: 1500-400 thousand/µl. An increase or decrease in the platelet count is a reason for further examination of the blood coagulation system. Normal values of some indicators of a general blood test
| Child's age | Hemoglobin level, g/dl | Red blood cell level, million/µl | Leukocyte level, thousand/µl |
| less than 2 weeks | 13,4 — 19,8 | 3,9 — 5,9 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 2 - 4.3 weeks | 10,7 — 17,1 | 3,3 — 5,3 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 4.3 – 8.6 weeks | 9,4 — 13,0 | 3,5 — 5,1 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 8.6 weeks - 4 months | 10,3 — 14,1 | 3,9 — 5,5 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 4 - 6 months | 11,1 — 14,1 | 4,0 — 5,3 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 6 - 9 months | 11,4 — 14,0 | 4,1 — 5,3 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 9 - 12 months | 11,3 — 14,1 | 3,8 — 4,8 | 6,0 — 17,5 |
| 15 years | 1,0 — 14,0 | 3,7 — 4,9 | 5,5 — 17,0 |
| 5 – 10 years | 11,5 — 14,5 | 3,8 — 4,9 | 5,0 — 13,5 |
ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate
— the test is based on the ability of red blood cells (special substances are added to the blood during this analysis to prevent it from clotting) to settle under the influence of gravity.
A change in ESR can serve as an indirect sign of a current inflammatory or other pathological process. In newborns, ESR is 2 mm/h, in infants 4-8, in older adults 4-10, in adults 5-8 mm/h. If, based on the results of a general analysis, there are suspicions about the presence of any diseases, then to clarify the diagnosis, the child is prescribed special biochemical and hematological tests.
Blood chemistry
Blood for analysis is taken from a vein. For biochemical tests, blood is taken on an empty stomach, 8-12 hours after the last meal; you should not drink sweet tea or coffee before the analysis. Increased plasma protein
blood may indicate the presence of acute inflammatory processes; this indicator also allows you to monitor the course of chronic infectious diseases.
Total protein
is also measured if autoimmune diseases (in which the body produces antibodies to its own cells and tissues) are suspected.
A test for glycated hemoglobin
(compounds of hemoglobin with glucose) and
glucose
is prescribed if diabetes mellitus is suspected, a disease in which the metabolism of carbohydrates in the body is impaired.
Diabetes is more common in children and is associated with impaired functioning of the immune system. It is very important in this disease not to miss its onset. Measuring blood glucose
is the main laboratory test in diagnosing diabetes.
To diagnose various hepatitis, including the so-called “jaundice” - hepatitis A, a bilirubin
.
An increase in the level of this compound in the blood usually indicates acute inflammation of the liver. To assess the normal functioning of kidney function in clinical diagnosis, the determination of urea
in the blood is used.
The formation of urea in a healthy person depends on nutrition: if the diet contains a lot of protein-rich foods (meat, fish, eggs, cheese, cottage cheese), the concentration of urea can increase to the upper limits of the norm, and if plant foods predominate, it can decrease. In children, urea levels are reduced compared to the norm for adults and increase with age. An increase in urea levels may indicate kidney dysfunction. Normal values of some indicators of biochemical blood tests
| Age | Total protein level, g/l | Glucose level, mmol/l | Urea level, mmol/l | Total bilirubin, mol/l |
| less than 1 year | 44 — 73 | 3,33 — 5,55 | 1,8 — 6,4 | — |
| 1 - 2 years | 56 — 75 | 3,4 — 17,1 | ||
| 2 years - 14 years | 60 — 80 |
Creatinine
– a product of protein metabolism.
The daily excretion of creatinine is a relatively constant value, therefore the determination of its content is used to monitor the completeness of urine collection in children. Normal creatinine levels
| Age | Creatinine level, µmol/l |
| less than 1 year | 18 — 35 |
| 1 year - 14 years | 27 — 62 |
An increase in creatinine levels is observed in serious kidney diseases and a number of diseases. A decrease in creatinine levels is determined in muscle diseases - myodystrophy and some other conditions.
Coagulogram
The main purpose of special tests for blood clotting - coagulograms - is the diagnosis of hemophilia, i.e. blood clotting pathologies. However, some other factors also affect blood clotting, for example, some painkillers thin the blood. of activated partial (partial) thromboplastin time are used for the study.
(APTT or APTT) and
prothrombin time
.
The first indicator reflects the activity of platelets, the prothrombin time reflects the clotting time of plasma, both of these indicators demonstrate the readiness of the blood to form blood clots. Normal values for APTT are 24-35 seconds, 78-142% for prothrombin time. Another important factor in blood clotting is fibrinogen
, a protein that makes up the threads that bind the blood clot.
Fibrinogen levels can range from 0.5 to 4 g/l. When the value drops below 0.5 g/l, the blood loses its ability to clot. A coagulogram to a child if it is necessary to undergo any operation, for example, to remove tonsils or if any blood disease is suspected. The fact is that even with a simple operation, insufficient blood clotting can lead to heavy bleeding, while increasing the value of this indicator is no less dangerous, because carries a risk of vascular blockage. Of course, there are many other tests, we only talked about those that are most often prescribed for children. Do not forget that by taking a blood test , you and the doctor will be able to clarify a lot about the baby’s health, prevent many troubles, and cope with the disease.
Features of infant nutrition before biomaterial collection
Many parents are concerned about the question of whether to take a general blood test for their child on an empty stomach or not. Doctors say that at the time the biomaterial is taken, the baby’s stomach should be empty.
As a rule, laboratories are open from early morning until 10-11 o’clock. In fact, this gap is quite enough to plan a visit to a medical facility.
As a rule, immediately after waking up, infants feel hungry. If a child wants to eat, there is no need to deny him this and quickly take him to the laboratory. In this case, the baby will experience enormous stress, and the doctor may receive unreliable test results.
If a child is under 1 year old, it is useless to explain to him why he was not fed before a procedure that was scary for him. Breakfast for infants is required. Porridge, milk, lean meat, vegetables - any dish from his usual diet can be offered to the baby. Then you need to take a three-hour break.
Doctors recommend that parents adhere to the following algorithm:
- Wake up your baby early.
- Feed him. Before a general blood test, the child can eat any food that is familiar to him.
- Go for a walk with your child or play at home.
- After 3 hours, go to the laboratory and submit the biomaterial for research.
Thus, before a general blood test, the child can eat. But after finishing the meal, you must wait 3 hours and only then go to the laboratory.
You can drink clean water in moderate portions. All liquids containing sugar, dyes and preservatives are prohibited. It is unacceptable to drink tea, fruit drinks, compotes and decoctions.
Why do you need to take the test on an empty stomach?
Many people are interested in the question: why is it necessary to take a blood test on an empty stomach? Is it possible or not to drink water?
You can hear and read a lot of advice on this matter. Some claim that they always donate blood after meals and all indicators are normal. The doctor prescribes a test to assess the state of health or if there is already a suspicion of an inflammatory process or infection of the body. It is the result of the blood test that will confirm or rule out the development of the disease.
If the value of the indicators deviates from the norm as a result of non-compliance with recommendations (including blood donation not on an empty stomach), then there is a possibility that the diagnosis will be made incorrectly. Accordingly, the treatment will be incorrect, and perhaps completely unnecessary.
After eating, nutrients are absorbed into the blood and affect its composition, including the concentration of proteins, fats and other compounds, change viscosity, and increase the level of indicators, one of which is leukocytes.
Additional diagnostic methods require a certain amount of time, and while their results are not yet available, the patient will take medications. As a result, it may turn out that the patient has no pathologies, and the test results were distorted due to the fact that the blood was not donated on an empty stomach.
Therefore, no medication was required. And as you know, the use of medications is extremely undesirable without indications, since they can cause harm to the body. In addition, time and money spent on additional examination will be wasted.
There is an exception to the rules when taking a blood test - these are patients with diabetes mellitus or pancreatitis. For this category of patients, long breaks between meals are unacceptable. Patients with diabetes and pancreatitis are allowed to have breakfast before the test.
But there are certain requirements for food. Breakfast should be light. You can eat porridge with water without sugar and butter, a sandwich with cheese, dried bread or some fresh vegetables. You can also drink weak tea without sugar, but it is better to limit yourself to water.
We suggest you read: How to improve blood circulation in the legs ointments to improve blood circulation
A general blood test is a common and informative diagnostic method. Preparing for research does not require complex restrictions. You just need to follow simple recommendations. The main requirement is that blood must be donated on an empty stomach, but drinking clean drinking water is allowed.
The greatest controversy arises when it comes to nutrition before undergoing OAC. Why is a general blood test taken on an empty stomach? To answer this question, you need to understand how food affects the results of the overall analysis.
Doctors recommend taking a general blood test on an empty stomach, that is, on an empty stomach.
In this case, the last meal should be taken the night before. About 10 hours should pass from the last meal to the examination (we assume an interval of 8 to 12 hours).
A clinical blood test must be taken on an empty stomach, because food can change the indicators:
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) can change under the influence of fatty, fried foods and alcohol-containing drinks;
- PTI (prothrombin index), platelet agglutination and sugar levels change after eating any food.
Blood from a fingertip is also donated on an empty stomach, but in some cases it is possible to reduce the interval between the procedure and food intake to 4 hours.
If blood is taken from a vein for a general analysis, then compliance with the rule of donating biomaterial on an empty stomach is mandatory, and the time period is much longer.
In this situation, you can not only eat for 10 hours before the OAC, but immediately before donating biological material, you are prohibited from drinking water and chewing gum. This is due to the fact that all elements that penetrate the gastric mucosa immediately enter the venous blood.
Nutritional features of children over 1 year old
In this case, the child will have to undergo a general blood test on an empty stomach. This rule is unbreakable. It applies to children over 1 year of age and adults. The fact is that the doctor needs to obtain indicators that reflect the actual functioning of the internal organs.
Eating any food before collecting biomaterial will affect the results of the analysis. Due to this, the doctor may interpret them incorrectly. The worst thing is that, due to parental negligence, the doctor may make an incorrect diagnosis and prescribe an inappropriate treatment regimen.
For example, a child had breakfast in the morning and went to the laboratory. About an hour later he donated blood. At this time, food components have already entered the liquid connective tissue and provoked changes in its composition. They affected blood viscosity, the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and the leukocyte formula. After the study is completed, the conclusion form will be sent to the attending physician. The doctor will see certain signs and conclude that an inflammatory process is occurring in the child’s body. Then the doctor will prescribe treatment. Therapy can pose a danger not only to health, but also to life. That is why it is extremely important for parents to know how to properly take a general blood test for a child and follow all established preparation rules.
Should a child over one year old donate blood on an empty stomach or can he be fed?
A general blood test for children over one year old is taken on an empty stomach - this is an unbreakable rule. It applies to both children and adults. The attending physician needs real indicators of how the patient’s body works.
If there is a suspicion of an infectious process, inflammation, or exacerbation of a chronic disease, then this is exactly what the doctor will confirm or refute through analysis. If the patient is getting better, this should be visible in the study results.
Example: a child was fed before the study, food components, when absorbed into the blood, caused a change in its composition, affecting viscosity, leukocyte formula, the ratio of proteins, fats, and more. In the transcript, the doctor sees signs of an inflammatory process that are not actually there. Therapy is prescribed that is unnecessary and dangerous for the patient. This outcome will not please any parent.
It’s good if the doctor finds out the reasons for the false readings. If not, then additional examinations and procedures may be prescribed, which is tiring for the baby and ineffective in general.
An exception is made only for young patients suffering from diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis (we recommend reading: features of diabetes mellitus in children and treatment). Long breaks between meals and donating blood on an empty stomach are contraindicated for them. Before blood tests, such children are recommended to eat a small portion of cereal porridge with water, fresh vegetables or crackers, and cheese.
The conclusion is simple - all other categories of children (over 1 year old) undergo a general blood test strictly on an empty stomach, subject to simple rules. Children are prepared in advance for the procedure and its importance is explained. To make everything go smoothly, the visit to the laboratory is made early in the morning. Then the baby can and should be fed.
Source: vseprorebenka.ru
Taking blood from a finger on an empty stomach for sugar, for example, is an unpleasant but mandatory procedure. In this way, many developments of ailments can be determined. A general analysis will be carried out in the laboratory, and the results will be sent to the therapist. The decoding will tell the doctor what diseases are approaching or progressing. In this regard, a general blood test is a universal health test. You can identify chronic diseases, high sugar levels, draw conclusions about how the body’s healing process is proceeding, and whether additional preventive measures will be required.
Many patients are more interested in another question directly related to the procedure - whether they donate blood from a finger on an empty stomach, on an empty stomach or not. People who take care of their health, take the proper functioning of their organs seriously, and monitor their sugar levels, must know the answer. Also, many are interested in another question - why take blood from a vein if you can take it from a finger. How does clinical analysis differ from one another?
Blood from a finger is taken for a general analysis to diagnose sugar, as well as to determine the norm and level of red blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, monocytes, and leukocytes. The decoding gives an idea of the structure of reticulocytes, ESR, leukocytes, the presence of infectious, inflammatory pathologies, and deviations of indicators from the norm. A biochemical, general analysis for sugar is taken in both adults and children. In this vein, donating blood fluid has its own typical patterns. Before taking blood, it is clear to the laboratory assistant at first glance who will undergo the “scary” procedure.
Adults, as a rule, are not afraid of a general blood test. They behave naturally and at ease, but if the manipulation is a child, especially a small one, this fact immediately catches the eye. The whims of children can be understood. Feeling and seeing living flesh being pierced is an unattractive pleasure. Therefore, the child must first be prepared at home. Without going into details of various psychological techniques, you can simply promise him something, clarify what surprise he expects.
There are laboratories for collecting blood for sugar in virtually any clinic or within a medical architectural group. Before taking a biochemical and general analysis, the child should not be nervous or bothered over trifles. It is important that he behave calmly before donating blood fluid. In an excited child, the normal indicators will be distorted, since an unstable psycho-emotional state increases the level of certain blood elements. However, the main question that remains open is whether it is possible to donate blood on an empty stomach or give the baby a snack before going to the laboratory.
Many doctors say the following in this regard: it is not necessary in every case to starve him in the morning. That is, you only need to donate blood fluid on an empty stomach in a few cases: for sugar, biochemistry, HIV. Something else is also important. It is highly advisable to give him a drink of water before going for a blood draw. That is, essentially, when a referral is issued, it is better to ask the doctor whether the test is being taken on an empty stomach or not.
Adults have a similar picture. A number of rules must be followed before visiting the treatment room. That is, the general analysis is preceded by a little preparation.
- Pay attention to taking medications so that the blood norm is not distorted.
- Tell the doctor about the date of excessive physical and emotional stress.
- Find out how to take tests - before eating or you can eat before the procedure.
- Inform about smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Ask how recent physical procedures (if any) will affect the clinical analysis.
For women there is an additional set of rules. They must notify their GP about their monthly cycle before going to have their blood drawn. Inform about pregnancy and menopause. These and other important nuances will affect the deciphering of the blood norm results.
If the doctor has ordered you to take a clinical test on an empty stomach, you should do so. Don’t eat anything in the morning, but go for a blood draw. As a rule, it is taken between 8.00 and 11.00, but often blood fluid is taken for examination after this time. To properly prepare yourself means to help the doctor create an accurate clinical picture of what is happening in the body. Regardless of the prohibitions, you can drink some water if you are really thirsty. Important:
- Blood sampling is a responsible procedure, so sweet compote should be excluded from the morning menu.
- Before the day of delivery, do not eat smoked, spicy, overly salty or fatty foods.
- Avoid alcohol and excessive physical activity. All this will equally affect the overall analysis.
- Preparation for the procedure involves avoiding many types of medications.
You need to notify your doctor about all this. He has the right to say that the blood draw can be postponed to a later date.
In addition to general recommendations, many health workers are still inclined to say that they must donate blood on an empty stomach. Only in this case, the norm, the required indicators, and the decoding of all important microelements will reflect the real clinical result. The point of view is based on the fact that detection of triglycerides, cholesterol, and lipids can be expected only after a 12-15 hour fast . The same applies when you need to determine the sugar level. Only in this case, analysis in adults correctly shows the real clinical picture. Therefore, donating blood on an empty stomach is a common requirement among doctors.

Another question is how accurate the interpretation of a blood test taken from a finger will be. Not everything is clear here. Blood fluid is taken from a vein to make the diagnosis better and more comprehensive. To recognize the pathology in time, there is no need to “torment” the finger. You need to take blood from a vein.
The laboratories where blood is taken are staffed exclusively by highly qualified health workers who know how to communicate with children.
However, adults also often need to be convinced that a blood test from a vein is a necessary procedure that will show the norm or various abnormalities. Also, the list of responsibilities of doctors involved in blood sampling includes the ability to work with the complex structure of the vein from which a sample of biomaterial will be taken. Today there is no need to worry about this . The procedure is safe and takes minimal time from the patient. Adults and even children tend to tolerate minor stress easily.
A blood test taken from a vein shows a much larger number of parameters. There is no need to remind you that before such a procedure it is also important to comply with a number of conditions, for example, to take it on an empty stomach. Using blood taken from a vein, you can determine:
- some types of infections;
- more accurate diagnosis (normal, deviations from the required indicators);
- determination of the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes, neutrophils, platelets, lymphocytes, eosinophils, color index, ESR;
- excess sugar content;
- the presence of antibodies, the amount of hormones.
The doctor will read all these and other indicators on a form with the results of a blood test taken from a vein. So in many cases, a capillary blood test is not enough.
Source: okrovi.ru
Process of collecting biomaterial
Many mothers and fathers do not know where they get a general blood test from children. Both capillary and venous blood are suitable for the study. These species have different normal values, which must be taken into account when interpreting the results.
Where do they get a general blood test for children? Most often, by default, biomaterial is collected from a finger. But, according to clinical recommendations, if it is impossible to perform this action, the nurse has the right to make a puncture in the vein. It is worth noting that this happens extremely rarely.
Blood sampling for clinical research occurs as follows:
- The nurse wipes the pad of the finger of the non-working hand with cotton wool, generously moistened with an antiseptic. The latter most often is medical alcohol.
- The nurse then very quickly pierces the skin with a lancet or scarifier. Then she puts a little pressure on the pad of her finger so that a few drops of blood come out. This liquid connective tissue is removed with cotton wool soaked in an antiseptic.
- The nurse then collects the escaping blood and transfers it to a tube. Then cotton wool moistened with an antiseptic is applied to the puncture site. It needs to be held on the pad for several minutes. This is necessary in order to stop the bleeding.
The process of collecting biomaterial lasts on average 1 minute. It is necessary to explain to the child that it is not associated with the occurrence of severe painful sensations, but some discomfort may still occur.
Information on how to take a general blood test for a child can be provided by the doctor who ordered the test. He will subsequently be involved in the interpretation of the results.

Normal indicators
During the diagnosis, the laboratory technician takes into account the total volume of blood, counts the number of formed elements, and also evaluates their relationship with plasma and with each other. That is why decoding the result is difficult for people without medical education. Doctors do not recommend considering your own conclusions to be 100% correct and independently prescribing treatment for your child. This can lead to irreparable consequences.
The age of the child must be taken into account. The fact is that as children grow older, the norms for the results of a general blood test in children also change. Information about what indicators are normal for each age is presented in the table below.
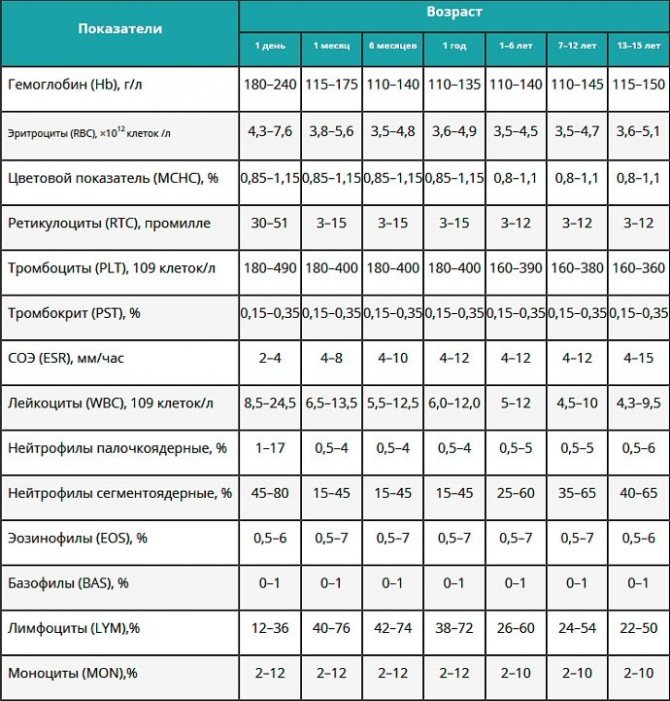
If the child is completely healthy, all of these indicators will be within normal limits. If a pathological process occurs in his body, they will be deviated in one direction or another. It does not happen that only one indicator decreases or increases. That is why a comprehensive assessment of laboratory diagnostic results is important. Only a doctor can do this correctly.

Features of performing blood tests in children
If it is easier for an adult to follow the rules for submitting blood samples for a general analysis, then with children, especially very young ones, things are not so simple. Children are given blood from a fingertip under the main conditions generally accepted for people of all ages - in the morning and on an empty stomach. But for mothers all over the world, the question of whether to take blood on an empty stomach or not, and whether it is possible to make an exception to the rule, still remains open.
Unfortunately, no, because the human circulatory system functions the same, regardless of age.
The question then arises: is it at least possible to drink? If the child is still very young and it is impossible to explain to him the importance of the procedure, and that you need to endure the feeling of hunger for a little while. In such a situation, it will be useful to feed him more often from a bottle with a nipple or with a special drinking nozzle. An important requirement is that drinking water must be free of any flavoring and aromatic additives; it cannot be tea, herbal decoction, or compote. Since everything that is not crystal clear drinking water is food for the body. Drinking in the morning, before you need to take a blood sample from your finger, can and should also thin the blood, so that it is easier for the laboratory assistant to take a sample of the material for research.
Taking into account the arguments presented in this article, it becomes clear that even a non-fasting blood test allowed as an exception is unlikely to be suitable for an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, in the question of whether to donate blood from a finger on an empty stomach or not, the answer is clear - only on an empty stomach. One of the reasons why blood is drawn in the morning is precisely to make it easier to comply with this condition. In the morning, the body is rested and full of energy, emotionally and physically restored, moreover, it has not yet fully awakened and does not feel strong hunger.
What diseases are indicated by deviations from the norm?
It is worth noting that this does not always happen due to a pathological process. Sometimes the reasons are natural. Or parents forgot how to take a general blood test for their child, and, for example, fed him immediately before visiting the laboratory. Both pathological and physiological causes are described below.
One of the most important indicators is hemoglobin. This substance is an iron-containing protein found in red blood cells. When its concentration in the blood decreases, it is customary to talk about anemia. This is a pathological process characterized by a deficiency of oxygen molecules in the body, as a result of which the functioning of all systems is disrupted.
Where to get a general blood test for a child, cost
A clinical study of liquid connective tissue is an analysis for which biological material can be submitted in any laboratory. Moreover, the results will be ready almost immediately.
You may want to contact your primary care physician first. He will issue the directions. In addition, he will tell you how to properly take a general blood test for a child. After this, you need to go to the treatment room and sign up for biomaterial collection. On the appointed day and time you need to come and donate blood for analysis.
In this case, the research will be free. You just need to present your medical insurance policy to the registrar.
You can take a general blood test for your child for a fee. In this case, you must choose any medical institution and come to the treatment room during its opening hours. Moreover, you don't even need a referral. This option is more attractive because it saves a lot of time. Moreover, the cost of the study is on average only 350 rubles.
How is blood taken?
Depending on the blood parameters being studied, it can be collected using two main methods: from a finger or a vein in the elbow. In infants, blood is taken for analysis from the lateral surface of the foot in the heel area.
Blood from a finger
In this case, capillary blood is examined for general clinical indicators (GCA).
This study is basic because it makes it possible to obtain data on the main parameters of blood composition. It shows a picture of its cellular composition (hemoglobin content, leukocytes, platelets, etc.), displays the leukocyte formula, makes it possible to calculate the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, etc. The most common place for collecting capillary blood is the ring finger. This is due to its relatively low physical load and anatomical structure, which avoids injury or infection. If necessary, blood can be taken from other fingers, usually the middle or index fingers.
Taking OAC from the lateral surface of the heel in infants is due to a dense local network of blood vessels and the minimal presence of nerve endings in this place - there is almost no pain for the baby.
Taking blood from a vein
In a number of circumstances, laboratory testing of venous blood is more preferable, for example, when it is necessary to conduct several (more than 5) studies at once.