Why does an abscess occur?
There can be many reasons for the formation of a lump (fistula, swelling), but the most common of them is undetected or ignored caries. Not all children maintain oral hygiene and eat properly, and not all parents carefully control this, which causes caries to appear on one or several teeth at once.
If caries is not treated, it will develop into pulpitis, extending beyond the tooth area and affecting the upper part of the root. As a rule, a lump appears just near the tooth whose root is inflamed. Typically, a lump can be noticed near a tooth with caries or with a filling that was placed long ago or poorly; Another common reason for its appearance is an injury received from a strong blow or an accidental fall, which can trigger the onset of the inflammatory process.
Stages of development of an abscess:
- As a result of caries, the infection penetrates into the pulp, affecting the root tip.
- Pus begins to form near the top of the root.
- Purulent formations fall under the mucous membrane of the gums.
- A cyst appears, looking like a small lump from the outside.
The most important symptom of an abscess is a soft and painful swelling, even with slight pressure.
Sometimes, due to an excess of pus, the lump may burst under pressure, and then a fistula appears - a small hole in the gum, which is connected with the source of inflammation located in the upper region of the root. A feature of the fistula is the constant release of purulent formations.
If inflammation decreases for some reason, the fistula may close on its own. However, when the child’s immunity decreases and the inflammatory process begins again, accompanied by pus formation, the appearance of a fistula will not be long in coming.
How to treat an abscess on the gum?
If an abscess or fistula appears, then you should not expect that the situation will resolve on its own: you need to make an appointment with a dentist. Treatment of an abscess on a baby tooth and a molar one will be different.
The appearance of an abscess on a baby tooth indicates periodontal inflammation. Such teeth must be removed, since the inflammatory process in the upper part of the root, accompanied by the formation of pus, may well spoil the molar, which will soon erupt in place of the milk tooth. This happens because the roots of temporary teeth are located next to the rudiments of molars. Bad bacteria and infection can also enter the lymph nodes under the jaw, causing them to become inflamed. The occurrence of a fistula means that pus will constantly seep into the mouth, which can cause the development of tonsillitis, since the tonsils will become infected. Various colds in a child are a direct consequence of an abscess on a tooth. Also, do not forget that toxins formed in the area of inflammation will definitely enter the bloodstream: this can result in allergic reactions, asthma and other serious general somatic diseases.
If we are talking about an abscess on a molar, then ordinary treatment is required for adults (provided that the tooth is not fundamentally damaged and can still be saved from removal).
Having discovered an abscess in a child, you should not try to cure it on your own. You can easily find a lot of advice on the Internet on how to relieve inflammation, but no amount of rinsing or even taking powerful antibiotics can eliminate the inflammatory focus located at the root of the tooth. Moreover, it is useless to hope that the tooth ache will stop. A bursting lump (this often happens) indicates only a short respite, during which, meanwhile, bacteria will still continue to enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This situation can turn into a serious problem if the child has diseases of the respiratory system, heart and other internal organs.
Often, dentists suggest leaving teeth near which the inflammatory process is occurring, persuading the parents of a young patient to carry out the silvering procedure. The arguments for refusing removal can be very compelling: possible problems with diction and pain during the removal operation. However, such dentists neglect the information contained in every textbook on dentistry, which clearly states that a baby tooth with a purulent focus must be removed. Silvering will only complicate the situation, and an unresolved inflammatory process can lead to asthma, tonsillitis and even diabetes: in comparison with these diseases, temporary problems with diction will seem like sheer nonsense.
But the formation of an abscess can be prevented, and this is not difficult to do - just teach the child to maintain oral hygiene. At an early age, a child cannot be adequately responsible for his actions, including those related to the care of the oral cavity, teeth and gums, so responsibility for the procedure lies entirely with his parents, who must control how and when the child brushes his gums and teeth . It is the parents who should buy the most effective baby toothpaste that guarantees maximum protection against caries.
A lump on an area of the gum where there is no tooth yet: what to do in this case?
A couple of weeks before the tooth erupts, a cyst may appear on the gum, looking like a lump filled with a clear or bluish liquid. Such bumps are by no means common: dentists do not consider such formations to be a pathology requiring treatment. In addition, such formations on the gums in no way indicate an inflammatory process.
According to statistics, a small percentage of children are affected by the appearance of such a cyst. The child may not even suspect that he has a lump in his mouth, because if he touches it, there is no pain. However, a dental examination is still necessary, because the inflammatory process may still begin, in which case intervention will be required. The presence of inflammation is indicated by such signs as increased body temperature, pain when touching the lump, and swelling of the mucous membrane.
Most parents do not like the fact that their child has a lump in his mouth: in this case, you can ask the dentist to make an incision under anesthesia, as a result of which the fluid inside the cyst will come out. As a rule, when part of the cyst is removed, the crown of the tooth about to erupt is visible.
Reasons for the formation of cones
The appearance of a swelling or bump in the oral cavity in children can be caused by two fundamentally different conditions:
- Inflammation of tissue in the area of the roots of milk or permanent teeth with the formation of an abscess.
- The formation of a cyst-like structure on the gum in the area where a temporary or molar tooth is about to emerge.
Since cysts and ulcers have different origins, it is worth considering their symptoms and treatment separately.
Purulent lump
The main reasons for the development of pustules on the gums:
- The most important factor that leads to the formation of a purulent lump or gumboil is periodontitis, which develops as a result of untreated caries. In this case, the size of the carious defect does not matter, and even the smallest lesion can cause a strong inflammatory reaction.
- Also, the cause of the formation of an abscess over a tooth can be an injury received from a fall or blow.
- Sometimes flux is a consequence of tissue damage from sharp objects (for example, if a child has the habit of chewing a pencil or toothpick).
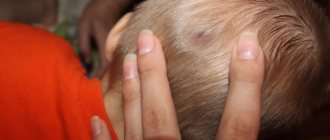
In the photo: an abscess on the upper gum of a child
Manifestations
The symptoms of this pathology are quite specific. At the initial stages of development of the purulent process, the child complains of pain and a feeling of fullness in the tooth area. At this time, a red swelling appears on the gum in the projection of the tooth root, which gradually increases in size, and pus accumulates in its center. This lump is soft to the touch and hurts when you press on it. As inflammation progresses, the formation becomes whitish and a white abscess forms.
At the same time, the general condition of the baby may suffer. Children become restless, refuse to eat, and their temperature rises.
If full treatment is not carried out at this stage, then as pus accumulates, the pressure inside the abscess increases and spontaneous opening of the white lump occurs. In this case, a fistula is formed, which connects the surface of the gums with the pathological focus. After the lump bursts, the child experiences relief of symptoms: pain decreases.
As the inflammatory process subsides, the fistulas can close on their own, but this does not mean that recovery has occurred, since the pathological focus itself remains unsanitized. With a decrease in the protective properties of the body, the disease can be activated with the reappearance of an abscess and fistulas.
Treatment
If a purulent lump is detected in the child’s mouth, it is necessary to contact the dentist as early as possible.
If the cause of the formation of an abscess or fistula is a baby tooth, then treatment will be reduced to its urgent removal. It is impossible to leave such a tooth, since the preservation of even a slight focus of inflammation can lead to the death of the permanent tooth germ.
If flux has formed over a molar, then all therapeutic measures will be aimed at preserving it. In this case, the dentist will open the lump, clean the cavity from purulent masses and treat it with an antiseptic. Removing a permanent tooth is a last resort and is carried out only when there is significant destruction.
Complications
Despite the fact that purulent bumps are rarely large, their complications can be extremely serious and dangerous.
- The death of the rudiments of permanent teeth leads to edentia. Such a condition in childhood can cause improper development of the maxillofacial apparatus and bite pathology, which will require serious orthodontic treatment in the future.
- Chronic purulent lesions and fistulas in the oral cavity are a source of infection, which can spread and cause inflammation in other organs: tonsils or adenoids.
- The constant inflammatory process changes the activity of the immune system, which becomes more sensitive to the effects of various allergens. In this case, the child may develop hypersensitivity reactions even to those substances to which allergies were not previously observed.
- If the abscess does not open outward, then the pus can spread deep into the tissues with the formation of phlegmon - a severe complication that is life-threatening.
Memo to parents
If you find a purulent lump in your child, then you need to remember several important nuances:
- It is strictly forbidden to try to open an abscess on your own. This can lead to pus entering the bloodstream and the development of sepsis - blood poisoning.
- You cannot carry out any warming procedures: apply compresses or rinse your mouth with hot liquid. This will only worsen the inflammation.
- Cold can be applied externally to the cheek in the area of the lump; this will somewhat alleviate the symptoms and slow down the development of the abscess.
- At the first symptoms of gumboil, you should contact your pediatric dentist for professional treatment.
Let's recognize the reason that formed a purulent sac on the gum
It is extremely important to establish why this pathology occurred, since therapeutic measures will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. The most common causes of a purulent sac are:
Periodontitis
This is an inflammatory process with the formation of purulent exudate in the area of the apexes of the roots of the teeth. The disease may not manifest itself for a long time. All symptoms usually begin to increase only with exacerbation. Complaints first appear about unpleasant sensations, then about the inability to eat food, since chewing causes sharp pain.
Gradually, purulent exudate begins to accumulate at the tips of the roots. With a large volume, it thins the bone tissue of the alveolar process and a fistulous tract is formed and the fluid begins to come out. The mucous membrane retains it and in this case a purulent ball forms on the gum.
Periodontitis itself is formed due to the lack of treatment of caries and pulpitis. In addition, the cause of its occurrence may be poor-quality dental treatment of root canals.
Periodontitis
This disease is characterized by damage to the periodontal mucosa, destruction of the bone tissue of the alveoli and the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth. The course is accompanied by severe pain, swelling and periodic bleeding of the gums.
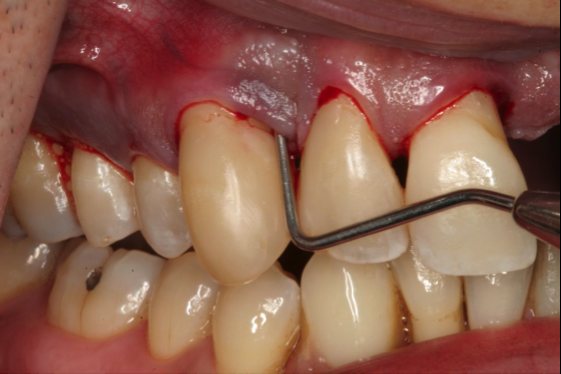
The photo shows the initial stage of development of periodontitis (mild periodontitis)
During the examination, deep formations between the teeth and periodontal tissues are determined. These are the so-called periodontal pockets. Purulent discharge appears with a long course of the disease. Its discharge is observed both independently and when pressing on the edge of the gum. The video in this article will tell you in more detail about diseases such as periodontitis and periodontitis.
Subsequently, abscess formation occurs and local pathological foci with purulent contents form. This formation is very similar to the one that forms during periodontitis.
Causing injury
It can be either accidental or caused by bad habits.
Injury to soft periodontal tissues often occurs for the following reasons:
- improper and careless use of toothpicks and floss;
- using an overly hard toothbrush;
- installation of orthopedic structures that are manufactured incorrectly or require some correction;
- the presence of extensive destruction of tooth crowns, which injure and infect soft tissues;
- periodontal injury from excessively hard food;
- habit of picking teeth with a needle or match.
Manifestation of pathology: symptoms make it possible to accurately make a diagnosis. If a purulent sac has formed on the gum, this is usually not limited to only local manifestations.
Symptoms of the neoplasm are accompanied by the following manifestations:
- the appearance of soft tissue swelling in the area of the causative tooth;
- loosening of 1 or several teeth that are located nearby;
- increased pain response, especially when pressing on the tooth;
- the appearance of bleeding that increases when brushing teeth;
- the presence of purulent periodontal discharge;
- disturbances in the general condition of the body, especially increased body temperature;
- hyperemia of the gums and general swelling in the affected area;
- the presence of a swollen mucous membrane on the gum, filled with purulent contents.
Pain syndrome, as a rule, is not limited to just one affected area. If it lasts for a long time, the pain can radiate to neighboring areas, including the temple and eye.
After the purulent bubble on the gum has completely formed, the body temperature rises sharply. Slight chills, headache, and aches in the joints appear. The use of painkillers gives a temporary effect.
After the pathological process invades the surrounding tissues, these drugs practically stop working. At this time, a specific formation in the form of a lump is clearly visible on the periodontium.
Usually this pathology is characterized as gumboil. The neoplasm requires immediate medical intervention to prevent the development of more severe consequences.
Teething cyst
Bumps on the gums that appear during the eruption of milk or permanent teeth (usually at 5-6 years old or much less often at 7-8 years old) have a major difference from abscesses - they are not inflammatory in nature and are only a reaction of soft tissues to the advancement of the dental crown .
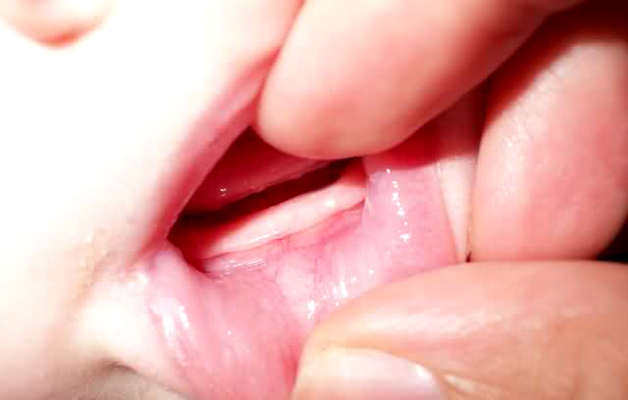
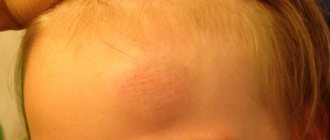
In the photo: teething cyst in children
Signs of an eruption cyst
Such formations form quite rarely and can appear both on the upper gum and in the area of the lower teeth. Non-inflammatory bumps do not cause any discomfort to the child and are detected only during examination of the oral cavity. Only sometimes infants may experience excessive salivation.
2-3 weeks before the tooth appears, a transparent or blue lump forms on the mucous membrane of the gum, which has a soft consistency and does not hurt when pressed. If the developing cyst affects a small blood vessel, then hemorrhage into its cavity is possible. She turns black. At the moment of eruption of the dental crown, such a lump is imperceptibly opened or gradually dissolves without a trace. The general condition of the children does not change in any way.
Treatment
This type of dental cyst does not require treatment. Sometimes, if such a lump appears in the area of the front teeth and causes cosmetic discomfort to the child, then it is possible to open it in the sterile conditions of a dental office.
An abscess on the gum of a child -
Reasons for the appearance of an abscess on the gum -
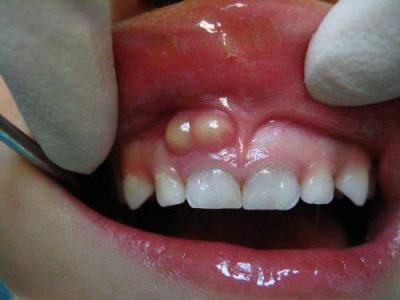
The main reason for the appearance of such a lump (swelling, flux in a child, and a low temperature. Anyone who has had a fistula, take a look) is untreated caries of one of the teeth in time. As a rule, a lump appears precisely in the projection of the tooth whose roots are inflamed. In most cases, the causative tooth will have a carious defect or an old filling. Another reason may be a tooth injury resulting from a fall or blow (in this case, inflammation may also develop at the root of the tooth).
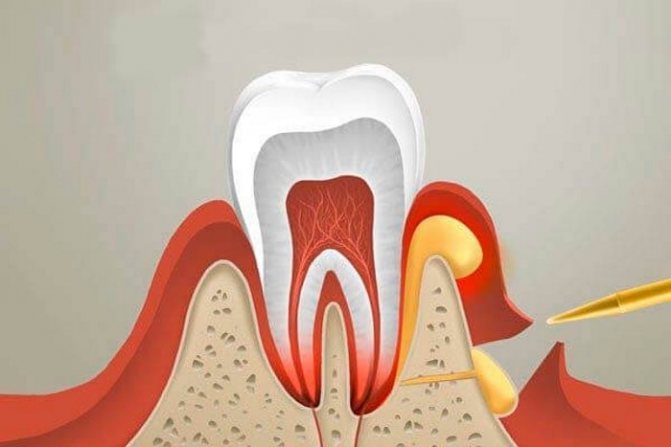
The development of an abscess occurs as follows - from a carious defect, the infection gradually penetrates into the pulp of the tooth, and then (through root canals) into the bone tissue around the apex of the root of this tooth. As a result, purulent inflammation develops at the apex of the tooth root. The resulting pus seeks a way out and gradually finds its way out under the mucous membrane of the gums. This is how a cyst forms on the child’s gum, which looks like a lump filled with pus.
→ In Fig. 4A you can see the following clinical picture - in the projection of the root of a baby tooth on the gum there is a clearly defined swelling, soft when pressed. This swelling is usually painful when pressed. This is nothing more than an abscess (abscess), i.e. under the mucous membrane in the center of such a lump there is pus.
→ Figure 4B shows an x-ray of the causative tooth that caused inflammation in this case. The area on the x-ray, limited by the white circle, is a zone of purulent inflammation in the area of the roots of a baby tooth (it has a darker color, which indicates inflammatory destruction of the bone in this area). https://24stoma.ru/wp-content/uploads/2012 /09/gn4.jpg
The lump can burst with the formation of a fistula - if the amount of pus in the inflammation site constantly increases, then the pressure inside such a lump increases - as a result of which it can burst. The pus then comes out, and a fistula forms at the site of the burst cone (Fig. 5). A fistula is usually called a hole in the gum, which through the fistula canal is connected to the source of inflammation at the apex of the root of the “sick” tooth. Purulent discharge will gradually be released from the fistula.
https://24stoma.ru/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/gn5.jpgIf the inflammation temporarily subsides, the fistula may close. However, with the next decrease in the child’s immunity, the inflammation may become active again, then there will again be active pus formation at the source of inflammation, and thus, first an abscess on the child’s gum (swelling) will again appear, and then a fistula will form.
Abscess on the gum of a child: treatment
Thus, if a lump or fistula appears on a child’s gum, you should immediately go to the dentist. The tactics for baby and permanent teeth are completely different:
- If the causative tooth is a milk tooth , a fistula and swelling on the gum indicate a diagnosis of periodontitis of one of the milk teeth. Milk teeth diagnosed with periodontitis are always removed (no options). If this is not done, then prolonged purulent inflammation in the area of the apex of the root of a baby tooth will most likely lead to the death of the permanent tooth germ. In Fig. 6 you are presented with a panoramic radiograph, which shows how close the roots of baby teeth are to the rudiments of permanent teeth.
In addition, the infection from the source of inflammation enters the lymph nodes (usually submandibular), causing their inflammation. In addition, if there is a fistula on the gum, then through it pus will constantly enter the oral cavity, which will lead to the colonization of the tonsils with infection and the development of chronic tonsillitis. In general, constant colds are guaranteed in this case.
In addition, from the source of inflammation at the apex of the root, infection and toxins will be absorbed into the blood, and since they have a very strong allergenic load, the risk of developing allergies, bronchial asthma and other severe general somatic diseases increases many times.
- If the causative tooth is permanent , permanent teeth in children diagnosed with periodontitis are subject to the usual treatment as in adults, of course, if the tooth is not very damaged and can be saved.
Symptoms of abscess formation in a child?
The primary symptoms of abscess formation in a child may go unnoticed. Usually parents find out about the problem when the baby begins to be capricious and refuses to eat.
In addition, bleeding gums appear, bad breath, and parents can visually notice that the cheek behind the abscess is swollen. The process of cone development occurs according to the following scenario:
- the gums become inflamed - redness and slight swelling are visually noticeable;
- a ball gradually forms in which pus accumulates, and the child’s temperature may rise;
- when pressed, unbearable pain occurs, the formation is soft;
- If treatment is not started at this stage, the purulent sac will burst, and in its place there will be a fistula.
Abscess at the site of a missing tooth
Abscess on the gum of a child
When a child's gum tissue festers, it worries parents. However, panic is inappropriate here. What to do? You need to figure out why the lump appeared. An abscess on a child’s gum, regardless of age, can appear in infancy, during school, or in kindergarten. The ball can pop out when the toddler still has milk units or already has indigenous chewing organs. Inflammation can be associated with diseases of the oral cavity and other organs and systems. In such a situation, parents should respond immediately to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Possible complications
As is already known, a purulent formation on a baby’s gum is an accumulation of infection. With reduced protective functions of the body or untimely treatment, negative consequences may occur:
- development of malocclusion and pathology of the formation of the jaw apparatus;
- death of molar rudiments;
- permanent complications that lead to premature tooth loss;
- penetration of infection into nearby tissues and organs: orbit, veins or mediastinum.
Among other things, it is possible that pathologies of periodontal tissue (periodontitis) may be associated. The long process of abscess formation can weaken the child’s immunity, which can lead to the development of allergies. If pus enters the venous system, thrombophlebitis will occur, which can spread to the base of the skull and sinuses.
Even in advanced cases, infection of the skeletal system with the formation of osteomyelitis and septicemia, as well as blood poisoning, cannot be ruled out. Penetration of infection into the tonsils provokes the appearance of tonsillitis. That is why, as soon as an abscess is discovered on a child’s gum, do not delay treatment.
Reasons for education
The most common reason why suppuration occurs is infection. The development of the pathological situation is influenced by a number of unfavorable factors.
- Untreated caries of a temporary crown leads to pulpitis.
- Poor quality filling installation.
- The penetration of pathogenic microbes into the area where the tooth cannot erupt.
- Lack of therapy for pulpitis of the root masticatory organ.
- Infection of the gum tissue after injury with a sharp object, as the crumbs are pulled into the mouth.
A pus-filled lump pops out when the infection enters the root canal. Toxins quickly penetrate the mucosa, causing inflammation with exudate. When it gets under the gingival membrane, a painful sac appears. Also, the inflammatory process starts due to periodontitis. This disease often develops with multiple carious lesions. If left untreated, the bacteria first attack the pulp and then settle in the bone tissue. Periodontitis of milk units often leads to the death of the indigenous chewing organs, as it affects their rudiments.
Reasons for appearance
The reasons for its formation are different. It can appear due to improper dental treatment. For example, after tooth extraction, if infection gets into the wound.
Pathogenic bacteria enter the upper part of the tooth. The bubble may become inflated due to caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. Caries destroys the tooth from the inside. With periodontitis, the infection comes from the teeth or maxillary sinuses. With untreated caries, complications are possible.
Read also: Stomatitis in a small child
A purulent bubble is dangerous. Its contents can reach the pulp, and then the infection can penetrate the tissue around the tooth. As long as there is outflow in the channel, a bubble does not form. If the outflow is closed and microorganisms have accumulated there, then a growth forms on the gum in the form of a bubble.
HIV, tuberculosis or chronic hepatitis can contribute to the appearance of blisters. It happens that blisters on the gums appear due to burns from hot food. To establish exactly why such a formation appeared, a laboratory study of scraping from the surface of the bubble and its liquid is necessary.
In 50% of cases, the appearance of such formations is associated with herpes. It can occur in patients of any age group. A characteristic sign of herpes is a sharp increase in temperature. Blisters appear on the inside of the cheeks or on the gums. They are filled with cloudy or clear liquid. Pain is felt when eating or touching. Later, the bubbles open, forming red wounds.
Viral pemphigus occurs after tonsillitis, flu, tonsillitis. The rash on the gums is abundant, it can spread to other parts of the patient’s body. Due to intoxication, the temperature rises. A bubble on the gum sometimes forms when injured by sharp objects and hard foods. If the bubble remains on the gum for several weeks, this indicates a chronic manifestation of the disease.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of a purulent lesion is quite specific. The sooner the first symptom is noticed, the easier it is to cure gum inflammation in a child and prevent serious complications.
In such a situation, children refuse to eat and become capricious. Their temperature rises. If the child is not treated, the ball will burst and a fistula will form. It may close on its own, but the fireplace will remain unsanitized, causing the problem to recur.
Treatment
It is imperative to treat an abscess on a child’s gum. Treatment depends on many circumstances, in particular on which tooth the tissue is affected. For periodontitis of temporary chewing organs, therapy is very difficult, so extraction is more often used. When tissue near the root unit is affected, the purulent sac requires opening. True, in this case the unit is not removed, but treated by using filling materials after eliminating the infection of the bone tissue. The doctor decides which method of therapy is most suitable. Before making a decision, the doctor carefully analyzes the situation. Parents can also carry out procedures at home, which will speed up the healing process. Learn more about different methods of therapy.
In dentistry
A lump with pus on a child’s gum can lead to complications if the little one is not shown to a pediatric dentist in a timely manner. The pathology of the mammary units passes to the rudiments of the indigenous masticatory organs. Also, pathogenic microbes enter the tonsils, which provokes their inflammation. Lymph nodes may suffer from the development of lymphadenitis. In severe situations, exudate enters the bloodstream, causing suppuration in other parts of the body. It is dangerous when the infection spreads into the deep layers of the jaw, causing phlegmon.
To avoid such troubles, parents should immediately contact the children's clinic. Treatment tactics will be determined depending on the stage of the pathology and the type of unit. It is better if treatment is started at an early stage. If this was not possible, show your baby to the doctor after the swelling breaks through so that the doctor can eliminate the source of infection. It is important to carry out hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity in a timely manner. If you keep your mouth clean, the risk of disease will be minimal. Treatment tactics:
- Manipulations in the area of primary teeth are carried out after the administration of anesthetic drugs. The formation is opened, the cavity is cleaned. Then the temporary unit that caused the defeat is torn out. Often, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics and mouth rinses.
- The cones above the molar masticatory organs are also cut after local anesthesia. If the abscess is large, drainage is used. When the pulp becomes infected, the canals are opened and cleaned. After this, fillings are installed.
At home
If pus appears on a child’s gum, you should not self-medicate. Medical procedures, on the advice of a doctor, can be supplemented with folk remedies. Often used:
- Strawberry leaves, calendula, in the decoction of which a cotton swab is moistened. The ball is applied to the sore spot several times a day.
- St. John's wort infusion with the addition of natural honey can be used to rinse your mouth every two hours.
- Chamomile, oak bark, and sage are also used for rinsing the mouth.
With the help of these remedies, unpleasant sensations are relieved. But these prescriptions do not replace a trip to the doctor. There are situations when it is not possible to see a doctor right away. Parents should know:
- The baby can only be fed warm, soft food.
- To relieve pain, apply a cold compress to your cheek for a short time.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is beneficial.
The affected area should not be heated, pressed on it, or rinsed with hot infusion, so as not to cause intense formation of exudate.
Cutting an abscess
If the abscess bothers the parents, they get rid of it. In such a situation, the dentist, under anesthesia, cuts the cyst and clears the cavity of accumulated fluid. Sometimes during the operation, the doctor also removes part of the wall of the cone, after which the top of the erupting fang becomes visible.
Remember that an abscess on a baby’s gum is a very painful formation. In order to prevent surgical intervention, it is necessary to accustom the child to oral hygiene from an early age, and also periodically visit the dental office with him.
News MirTesen
Prevention
An abscess on a child’s gum must be treated. To prevent its formation, preventive measures should be taken.
- Parents need to clean their little one's mouth morning and evening. After three years, he will carry out this procedure independently.
- The child must be taught to rinse his mouth after eating.
- You should limit sweets, baked goods, and candies in your diet.
- The child should be regularly shown to the dentist, and caries, gingivitis, pulpitis and other diseases should be treated promptly.
If you protect the gum tissue from injury, balance the children's diet, carry out fissure sealing and fluoridation as indicated, the risks of dental diseases will be minimized, and the child's health will improve.
+7 St. Petersburg, Maly Prospekt V.O., building 4
You can ask any questions you may have and find out the available time for making an appointment with the administrators of the ARTES clinic! Call and come for an appointment!
How to help a child with such an illness?
If a child has an abscess on his gum, not everyone knows what to do in such a situation. The first thing you should do if you notice a lump on your gum is to see a doctor. But before seeking medical help, you should not squeeze, puncture or burn abscesses on your child’s gums. They should not be touched at all, so as not to cause additional infection.
READ ALSO: Why do acne appear on the face of women after 30-35 years and how to deal with them - on
There is no need to apply bags of heated salt or a heating pad to the swelling on your baby’s gums. Hot compresses and rinses are also not recommended, since heat will only accelerate the spread of bacteria. A child with such a problem should not be given any medications, especially antibacterial ones.