Can cause the development of many diseases. First of all, the respiratory organs are affected, purulent foci appear on the body, and deviations in the functioning of the nervous system are observed. Children under 4 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets, through household items and bedding. In preschool age, the disease is very severe and can be fatal.
Dosing information: Get the vaccine if you develop one of the predisposing conditions. Dosing information: Receive a single dose of this vaccine if you develop one of your predisposing conditions. Redness, pain, swelling at the injection site, fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle pain.
- Get a second dose after 5 years for some conditions.
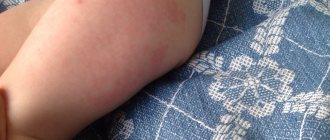
- About 50% of patients experience redness or pain at the injection site.
- The timing of doses should be discussed with your doctor.
Influenza is an unpredictable respiratory virus.
It is capable of causing a large amount of inflammation of the larynx, trachea and bronchi with swelling of the mucous membrane. This can damage and weaken the cells lining your airways so they don't protect you as much. This creates a greater risk of developing pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia.
The infection is dangerous because it can lead to the development of related ailments. These are purulent meningitis, pneumonia, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, otitis media, mastoiditis. To avoid such serious complications, you need to get your child vaccinated in a timely manner. Today, a polysaccharide vaccine is used, which is administered separately or in combination with other drugs.
Flu can lead to further complications, including: Primary infantile viral pneumonia Bacterial superinfectious pneumonia Exacerbation of chronic lung disease. Uncommon complications include: myositis, myopericarditis, pericarditis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, Reye's syndrome, encephalopathy, and transverse myelitis.
Preparing for vaccination against Hib infections
People who have higher priority for receiving the flu vaccine include: Influenza can be spread through saliva, nasal secretions and feces. Sneeze and cough particles can travel up to three feet. An infected person is contagious 24 hours before and up to seven days after symptoms begin. Viruses can also continue to live for several days to several weeks on dry surfaces. A person is most likely exposed through touching a contaminated surface and then touching their nose, eyes, or mouth.
For vaccination, drugs such as Pentaxim, Hiberix, and Infanrix Hexa are used. All of them are of high quality and have an excellent effect on developing immunity in children to infection.
Does a child really need a hemophilus vaccine? What it is? You can find out all the necessary information from the article.
Transmission of influenza can be prevented by thorough and frequent hand washing and coughing into a barrier such as a tissue or elbow. People should be aware of flu season, avoid touching their eyes, nose and mouth, and avoid close contact with someone who is infected, even if that person is on antiviral therapy and should stay home if they are sick. Finally, you can vaccinate!
Risks of hepatitis B virus infection with biological agents
Side effects of flu vaccines. Patients should be screened for viral hepatitis before starting biologic agents. If there is a possibility that a patient may become infected with hepatitis B, the patient should be vaccinated. There is an effective non-live vaccine. It is not easy for a person with rheumatic disease to protect themselves from shingles because only live vaccines are available. There are currently no killed vaccines.
Vaccine "Pentaxim". Composition of the drug
The vaccination is intended to prevent whooping cough, tetanus, diphtheria and other infectious diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B. The vaccine is a white suspension that is administered intramuscularly. The drug contains several toxoids: diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus. The vaccine also contains filamentous hemagglutinin, inactivated polio virus types 1,2,3.
Shingles is a reactivation of the varicella zoster virus and is associated with aging as the immune system loses some strength with age. Taking immunosuppressants increases the risk of shingles. Once a person gets chickenpox and recovers from it, the virus remains in the body forever. At some point in life, it may begin to rearrange itself in the nerve, presenting itself as a striped pattern on the surface of the body. After a shingles infection, some patients develop severe pain in the area where they had the rash.
The medicine is supplied in glass syringes containing one dose of the vaccine in a volume of 0.5 ml. The Pentaxim vaccination will help your child develop immunity to
Indications and contraindications
The reason for vaccination is the prevention of diseases such as diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio and others associated with invasive infection. The vaccination is given to children starting from the age of three months.
Shingles vaccine can help prevent shingles from occurring, and when shingles do occur, it can reduce the likelihood of pain. Additionally, a person should receive antiviral treatment as soon as shingles is diagnosed, which may reduce the risk of postherpetic neuralgia.
As people get older, the value of the vaccine in preventing shingles decreases. It may decrease by up to 20% as the patient ages, but its ability to prevent postherpetic neuralgia remains unchanged. The shingles vaccine prevents about 65% of cases of postherpetic neuralgia. You need to consult your rheumatologist before taking this vaccine because it is a live vaccine.
A contraindication to the vaccine is considered to be progressive encephalopathy with or without it. If after the previous vaccination the baby had a strong allergic reaction, Pentaxim should not be used either. After vaccination, you need to monitor the child’s well-being and measure his body temperature. You should tell your pediatrician about any changes in your baby’s health. Hemophilus influenza vaccine reviews are most often positive. Negative reactions to the drug are quite rare.
Acceptability of herpes vaccine. Screening for a history of chickenpox is not necessary to administer the vaccine to a person aged 50 years or older. Complications of herpes infection. Postherpetic neuralgia, which may persist for weeks or months after the rash, resolves ophthalmic zoster, which is the involvement of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve and the eye. Spread with generalized skin rashes and involvement of the central nervous system, lungs, liver and pancreas. Vaccine against herpes.
Contraindications
Serious consequences after vaccination against hemophilus influenzae are possible if doctors did not promptly identify contraindications for vaccination. These include:
- allergy to tetanus toxoid - it is a component of the administered drug, a protein that is added to the vaccine to enhance effectiveness;
- any acute or chronic diseases;
- convulsions;
- encephalopathy;
- unexpected, excessive reaction of the child’s body to injections that were given previously.
If there is even the slightest suspicion of the presence of such health problems in children who are preparing for vaccination, vaccination against hemophilus influenzae is either postponed until the child recovers, or is canceled altogether. This happens quite rarely. Complications occur even less frequently in children after vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae, but parents should also be informed about them.
Dosage
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly. The dosage of the drug is 0.5 ml. The medicine cannot be administered subcutaneously or intravenously. Before use, the vaccine must be mixed with a solvent and shaken well. The drug "Pentaxim" can be used three times, with an interval of two months. The first vaccination is given when the child reaches three months of age.
- Approved for persons over 50 years of age.
- Administered by injection under the skin.
For those expecting to receive immunosuppressive medications, the zoster vaccine should be given at least 14 days before starting immunosuppressive therapy, although some experts advise waiting a full month after the zoster vaccine to begin immunosuppression.
Tetanus, diphtheria and acellular pertussis
For those who have immunodeficiency and immunosuppressants such as.
Tetanus is a disease caused by bacteria that enter the body through breaks in the skin, and symptoms are characterized by painful muscle spasms, breathing problems and paralysis. If your baby is being treated with other medications, you should definitely inform your pediatrician about this. Pentaxim is not compatible with all medications.
Many experienced pediatricians argue that hemophilus influenza vaccination is necessary for children. If for a number of reasons it is not possible to vaccinate within a certain period of time, this should be done later.
Diphtheria is a disease that causes a thick coating at the back of the nose or throat, making breathing and swallowing difficult. It can also attack the heart and nerves. There is currently a worldwide epidemic of whooping cough. Tetanus, diphtheria and acellular pertussis vaccine.
It is recommended that this vaccine be given once in adulthood. This is not a live viral vaccine. Patients are advised not to take this vaccine if they have had a life-threatening allergic reaction after a dose of any tetanus, diphtheria, or whooping cough vaccine or if they have had a severe allergy to any part of this vaccine.
Side effects
Hyperemia and soreness may develop at the injection site. This reaction is usually observed within two days. Temperatures often rise to high levels. The child becomes drowsy, vomiting and diarrhea are possible. In rare cases, an allergic reaction is observed in the form of rash, itching and Quincke's edema.
Side effects and complications
Browse advises those who have epilepsy, other nervous system problems, or have ever had Guillain-Barré syndrome to consult with their doctors before taking this vaccine.
However, these problems are very unusual. Latent TB means that a person has an infection, but it is not active—the infection is not visible and the infection is not felt by the infected person. Latent infection is especially relevant to doctors because the patient is often unaware that they are infected. If positive, treatment should be given before any rheumatism-related immunosuppressant therapy that may affect immune function.
What if the hemophilus influenza vaccine causes side effects? What it is? There's no need to panic. If symptoms are severe, you should seek medical help. In most cases, unpleasant reactions pass fairly quickly.
Vaccine "Hiberix"
This is a drug for the prevention of diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Available in powder form for the preparation of a solution, which is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. The vaccine contains purified capsular polysaccharide and tetanus toxoid.
Joint replacement
Before undergoing hip, knee or other prosthetic surgery, Dr. Browse emphasized that a patient with chronic dermatitis should see a dermatologist to ensure that any skin conditions are under optimal control.
Any visible breaks or breaks in the skin may predispose the patient to infection. All dental needs, such as cleanings or dental procedures, must be addressed prior to surgery. Any bladder procedures should also be completed before surgery. If these procedures are not followed prior to surgery, the infection may travel through the bloodstream and infect the prosthesis. During surgery, the care team will work to reduce the infection rate as much as possible using prophylactic antibiotics and laminar airflow. Prophylactic administration refers to the action of administering antibiotics before surgery to prevent infection. Laminar airflow is a system that filters and cleans the air in the operating room.
Hemophilus influenzae infection is quite insidious. Pediatricians recommend not to neglect vaccination.
Action
The drug helps develop immunity to diseases caused by Hemophilus influenzae. Antibodies appear in the blood of most babies within a month after the injection.
Complications and side effects from vaccination
After surgery, it is important to visit a dermatologist if you have a chronic dermatitis condition to maintain intact skin and keep chronic dermatitis under control.
Prophylactic antibiotic therapy is recommended before certain dental and urological procedures for 2 years after implantation. In patients with inflammatory arthritis, in those receiving treatment for immunosuppression, in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes, in patients with previous prosthetic joint infection, hemophilia, or who are malnourished, prophylactic antibiotic therapy is recommended prior to certain dental and urological procedures for life. The Hiberix vaccine does not protect against other types of infectious diseases. The drug must be used strictly as directed.
Reaction to vaccination
In most cases, the reaction to the vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae is not even visible. Therefore, it is completely safe to combine with other drugs in DTP. Rare side effects include only two symptoms:
- local reaction on the skin - where the drug was injected: pain, redness and thickening (observed in 10% of vaccinated children), which should not be associated with the fact that you accidentally wet the injection site - you just don’t need to let the baby comb it, don’t It is recommended to smear it with anything or seal it with a band-aid;
- a slight increase in temperature (occurs in only 1% of vaccinated children).
All these side effects of vaccination against hemophilus influenzae do not require medical intervention, since they do not cause much concern and go away on their own within 2-3 days. Truly serious complications after such a vaccination occur only if contraindications are not observed.
Indications and contraindications
Vaccination is prescribed to children aged six weeks to five years to prevent infectious diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae. You should not vaccinate during exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Causes of hemophilus influenzae infection
If any of the above conditions apply to you, you should discuss this with your dentist or urologist.
Brause ended his talk by emphasizing the importance of protecting yourself from infectious diseases through vaccination. Several vaccines may be helpful and effective for people with rheumatic diseases such as lupus. However, before making any decisions, it is important to talk with your rheumatologist to make sure you are taking vaccines safely and appropriately. Vaccination is prohibited in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the vaccine, including the drug. Do not administer the drug for colds. Vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae is not carried out if the child had a serious allergic reaction during the previous vaccination.
Reviews of vaccination against hemophilus influenzae
Analyzing all the reviews about vaccinations, it turned out that there are good and bad reviews. In some cases, people who speak poorly about vaccines against infection, it turned out that they were vaccinated without consulting a doctor, which led to complications. Almost all types of vaccines have contraindications, since in children the body cannot always react to the drug without consequences; most often, children have an allergic reaction to the vaccine. A very useful and informative video with Dr. Komarovsky about vaccinations:
You should not draw hasty bad conclusions about vaccines, even if you read bad reviews somewhere. After all, not all children are the same, one can live their entire life without preventive vaccination, another is allergic to certain drugs. Almost all the mothers in the reviews shout with one voice that their child got sick in kindergarten, the same conclusion is imposed, they need to be vaccinated. Educational video about how, when, and why vaccination is done:
- < Protargol
- Polyp in the cervical canal >
Features of application
The drug is administered three times, with an interval of one month. Before the injection, the vaccine must be thoroughly dissolved and warmed to room temperature. The medication must be administered into the thigh area, subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
Principles and purposes of vaccination
Complications of hemophilia may include. Bleeding that occurs in the deep muscles can cause the limbs to swell. Internal bleeding can also put pressure on your joints, causing severe pain. If left untreated, frequent internal bleeding can cause arthritis or joint destruction. Infection. People with hemophilia are more likely to receive blood transfusions, increasing the risk of infection from contaminated blood products. The risk of infection through blood products has also decreased significantly since the introduction of genetically engineered blood clotting products. Adverse reaction to clotting factor treatment. In some people with hemophilia, the immune system reacts negatively to the clotting factors used to treat bleeding. When this happens, the immune system develops proteins that inactivate clotting factors, making treatment less effective. What tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis or speed up the evaluation of hemophilia? Outcomes of treatment of acute coronary syndrome in patients with congenital hemorrhage: a single center of experience and review of the literature.
- Deep internal bleeding.
- The swelling can put pressure on the nerves and lead to numbness or pain.
- Joint damage.
- Hematology: basic principles and practice. 6th ed.
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 19th ed.
There has been considerable discussion within the hemophilia community about the optimal protocol for administering vaccines to people with bleeding disorders.
The drug "Hiberix" should be stored at a temperature of 2 to 8 degrees Celsius. Frozen medication is unsuitable for use.
Vaccine "Infanrix Hexa"
The drug is used as a prophylaxis for hepatitis B, whooping cough, polio, tetanus, diphtheria, as well as other infections, the causative agent of which is considered to be Haemophilus influenzae. The medicine is available in the form of a white suspension for intramuscular administration. The drug contains diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus toxoid. Pertactin and filamentous hemagglutinin are used as auxiliary components.
The hemophilus inoculation also contains HBC protein. hepatitis B antigen. Thus, vaccination helps protect the child from a terrible disease.
Indications and contraindications
The medication is administered to children to prevent diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio, hepatitis B and other diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae.
Vaccination is contraindicated for children who have hypersensitivity to the components of the vaccine - neomycin and streptomycin. The medicine should not be administered for encephalopathy of unknown etiology or during exacerbation of chronic infections. If there are cold symptoms and fever, vaccination is postponed. Vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae is contraindicated in acute intestinal infections.
Features of vaccination
Today, vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae infection involves administering to young children one of two registered polysaccharide type b vaccines:
- Act-HIB (produced by the French laboratory Sanofi Pasteur);
- Pentaxim is a complex vaccine known to many parents called DTP (prevention against tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough and polio).
The drug against hemophilus influenzae is usually administered to children in several doses:
- at 3 months;
- at 4.5 months;
- in six months;
- revaccination - at 1.5 years.
If the baby has not been vaccinated three times, the vaccination against hemophilus influenzae infection is given only once after a year - this is quite enough to form stable immunity. For children under 2 years of age, the vaccine is administered into the anterolateral thigh area. Older people - in the deltoid muscle area (shoulder). Parents must have this information in order to make the right decision at the moment when they are asked to consent or refuse vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae.
Importance of vaccination
Does a child really need a hemophilus vaccine? What it is? Parents are increasingly asking questions like this. Every pediatrician will say that vaccination plays an important role in the process of forming the baby’s immune system. Vaccinations cannot be neglected. The only thing that is really worth paying attention to is the quality of the vaccine.
For those who are afraid of Haemophilus influenzae, vaccination will provide reliable protection. However, you should purchase medications for the procedure only in those pharmacies that have the appropriate license. Before vaccination, the pediatrician must examine the baby. A weakened immune system is the first contraindication. It is also undesirable to get vaccinated if you had to deal with a serious allergic reaction the previous time.
Haemophilus influenzae infection is a disease caused by the pathogen Haemophilus influenzae. These bacteria are also known as Pfeiffer's bacillus; they are opportunistic, which means that they can be present in a certain amount in every organism. In 90% of healthy people, during examination of the condition of the nasopharynx, the bacteria Haemophilus influenzae type b, Hib can be detected. This means that bacteria can exist in the human body for a long time, without making themselves felt until its protective properties are weakened.
When these bacteria multiply, they can pose a serious danger, especially to children. Over the past few years, vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae has been considered the most reliable prevention of the development of many diseases.
If you are unsure whether to get vaccinated against Haemophilus influenzae, read about the possible complications caused by the proliferation of Pfeiffer's bacillus. Haemophilus influenzae can cause the development of many infectious diseases of the central nervous system, lungs and other vital organs. Purulent meningitis is a consequence of a long course of hemophilus influenzae infection in children under four years of age, which did not respond to treatment. The second place in the frequency of damage to the child's body after meningitis is occupied by purulent pneumonia.
Just a few years ago, cases of infection with the Pfeiffer bacillus in Russia were isolated, but recently they have become significantly more frequent. Vaccination against hemophilus influenzae, according to doctors, is the most reliable method of protecting a child’s body from many dangerous diseases that arise against its background.
Modern vaccines against Haemophilus influenzae are 100% effective. Vaccine preparations are of high quality, so the risk of developing dangerous consequences during immunization of a child’s body is minimized. The safety of the drug makes it possible, in the event of an epidemic of infection, to vaccinate even two-month-old infants.
When is vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae administered in order to create reliable protection? Vaccination is recommended for all children from three months of age to 5 years. Children who are 5 years old no longer need vaccination, since their immune system itself can fight Haemophilus influenzae.
In Russia, vaccination against Pfeiffer's bacillus is not included in the national vaccination calendar, but in countries such as the USA, Great Britain, France, and Finland, it is a mandatory preventive vaccination. Pediatricians and immunologists especially strongly recommend vaccinating children against hemophilus influenzae in the following cases:
- children on artificial nutrition, because they do not receive antibodies against infection through breast milk;
- premature babies;
- children with immunodeficiencies, regardless of their origin;
- frequently ill children;
- children attending preschool institutions.
Children in the first year of life are vaccinated in order to create reliable protection against the most dangerous forms of hemophilus influenzae infection - meningitis and purulent pneumonia. The peak development of these diseases occurs precisely at the age of 6–12 months. Children vaccinated after 12 months of age are protected from other types of infection - acute respiratory infections, pneumonia, acute otitis media, bronchitis.
What is hemophilus influenzae and why should children be vaccinated against it?
Haemophilus influenzae type b (HIB) is caused by bacteria called Haemophilus influenzae. Usually they do not cause problems for the carrier, but a weakened immune system, virus or allergy can radically change the situation. Most often, HIB affects children between 6 months and 4 years of age. It is transmitted by airborne droplets and affects the respiratory system and central nervous system. The FDA reports that according to the Centers for Disease Control MMWR, before 1985 (the introduction of routine vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae in the United States), Haemophilus influenzae was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children under 5 years of age: it developed in 2/3 of those affected (that's more than 65 years of age). %)! Although this is a bacterial infection that can therefore be treated with antibiotics, patients often develop a fulminant form of meningitis when the clock is ticking and antibiotic therapy is started too late. In addition to meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae can cause pneumonia, epiglottitis (inflammation of the epiglottis), septic arthritis, purulent pericarditis, osteomyelitis and bacteremia. Approximately 4% of all cases of the disease result in death, 15-30% result in hearing impairment or severe neurological complications (view information on the FDA website). Thanks to vaccinations, the incidence in the United States has decreased to 30-50 incidents per year. However, in countries where mandatory mass immunization against Haemophilus influenzae type b has not yet been implemented, the situation is much worse. Worldwide, 3,000,000 cases of the disease and about 386,000 deaths are registered annually (data from the article “Epidemiological monitoring and prevention of hemophilus influenzae type B infection in the Russian Federation” by E. Ya. Frolova and V. N. Filatova, Journal of Infectology, Volume 4 #2, 2012) In Russia, the incidence on average exceeds the threshold of 10 per 100,000 children under 5 years of age.
Hib vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae infection HIBERIX
To protect a child from the action of the Pfeiffer bacillus, a Hib vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae infection is used, which does not contain live bacteria. In Russia, the vaccine against hemophilus influenzae infection HIBERIX Act-HIB is used for vaccination. The absence of living microorganisms in the drug cannot cause the development of the disease after administration of the drug. It was developed by the French based on the capsular polysaccharide antigen of Haemophilus influenzae associated with tetanus toxoid. This is done so that full immunity can be formed even in infants.
The drug is produced in disposable syringe doses, immediately ready for use. The needle of such a syringe is treated with a special compound to reduce pain.
The classic vaccination regimen against hemophilus influenzae infection consists of four vaccinations - at three, four and a half, six and 18 months. Vaccination is carried out on the same day as DPT vaccinations. The advantage of immunization according to this scheme is that it is possible to develop strong immunity against the most dangerous diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae - pneumonia and meningitis.
In some cases, the vaccination schedule may be changed. If a child begins to be vaccinated at the age of 6 months, then the vaccine is administered twice with an interval of one month, revaccination is carried out at one and a half years. For children vaccinated at one year of age, one injection is sufficient. Immunologists recommend combining it with the DPT vaccine. If the drug Tetrakok is used, Act-HIB can be combined in one syringe, reducing the number of injections to one and protecting the child from 5 infections at once.
For children with weak immunity, susceptible to frequent colds, as well as premature and low birth weight children, the first vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae infection can be carried out at the age of two months. Multicomponent vaccines are often used abroad - Tetraxim, Pentaxim, Hexavak, which protect the child’s body from hemophilus influenzae infection at the same time.
Venue and method
Vaccination is carried out in municipal medical institutions free of charge for children at risk. Commercial medical clinics offer vaccination services on a contract basis. They have certified vaccines at their disposal. Before immunization, the patient is examined and the necessary laboratory tests are prescribed.
The vaccine package contains a bottle with lyophilisate, a syringe with solvent and instructions for use. According to the description, the drug is a light gray, odorless powder. The syringe is equipped with a thin needle with a dispenser for 1 dose (0.5 ml). Reusing it is not recommended. Immediately before the manipulation, the lyophilized powder is dissolved with the contents of the syringe and the injection is carried out with the same syringe.

The vaccine is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. When carrying out manipulation, it is necessary to avoid damage to the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The injection site for small patients under 2 years of age is the upper outer quadrant of the thigh. For older children, the vaccine should be given in the superficial muscle of the shoulder.
The vaccination schedule against Haemophilus influenzae infection is determined by the age of the child. In accordance with the table of the national vaccination schedule, the first vaccine is given at 3 months, the second at 4.5 months and the third at 6 months. At 18 months, revaccination is carried out. If the child is more than six months old before vaccination, 2 vaccinations are prescribed at a monthly interval. Revaccination is carried out at 18 months.
When the child is over a year old, a single dose of the drug is recommended. When vaccinating adults at risk, one vaccine is sufficient.