Source of the disease
Where can a newborn get an intestinal infection? First of all, the culprits of the event may be the mother or medical personnel who are not too scrupulous in observing the rules of hygiene. In the second - diapers, medical devices or instruments, pacifiers, etc.
The causative agents of the disease are considered to be microbes that can pass from a sick person to a healthy person through the mouth, that is, orally. All you have to do is touch a newborn’s lips with dirty hands, give him an unsterilized bottle, or miss the moment when the baby pulls soiled diapers into his mouth, and the result will be obvious. More precisely, on the intestines.
Another source of the disease is viruses that are transmitted through dirt and contaminated water. A striking example is rotavirus, which children can most often catch during the transitional periods of the year. It is at this time, thanks to the damp weather, that the infection rages everywhere.
Causes of infection in infants
Common pathogens of intestinal infections are:
- rotavirus (provokes the development of pathology most often);
- salmonellosis;
- enterovirus infection;
- dysentery.
The main route of infection is oral (through the mouth). This means that all things and food that are not washed and not heat-treated end up dirty in the child’s mouth. Bacteria and viruses then spread throughout the gastrointestinal tract, affecting the intestines.
The following causes of intestinal infection are identified:
- Human carriers. This category includes anyone who has an infection or virus and can pass it on to the baby.
- Household items, toys. Very often, unwashed toys that a child puts in his mouth can cause infection.
- Food. Any products that are not heat-treated or cleaned of contaminants can cause an intestinal infection if they enter the baby’s mouth. The most dangerous of this group are chicken eggs with fecal particles on the shell. Chicken droppings may contain salmonella, and when it enters a child’s intestines, they actively multiply, causing salmonellosis. This is a dangerous and serious disease that is treated in the infectious diseases department of the hospital. Therefore, if a mother buys chicken eggs, it is necessary to carefully inspect them for the presence of chicken droppings on them.
- The water is of poor quality. All of the above phenomena can be easily prevented by keeping the house clean and carefully handling the food that the child eats.
Can animals cause intestinal infections?
Yes, any animals that are in a house where there are children under 5 years old are a threat to the baby’s health. Why? The fact is that pets (dogs, cats, turtles, hamsters) carry many pathogenic microorganisms. For example, cats are carriers of helminthic infestations and toxoplasma. Turtles are carriers of salmonellosis, so washing a turtle in the kitchen sink is prohibited.
If you already had pets in the house before your baby arrived, don't panic! There is no need to throw your pets outside. Just take better care of them, clean the room, ventilate it and try to prevent the child from coming into contact with them.
If you decide to buy an animal, and you have a baby under 5 years old, wait until the child’s immunity is stronger and various types of bacteria and viruses are not as scary for him as for a baby.
Signs and symptoms
What should a young mother be wary of in the behavior and condition of her newborn?
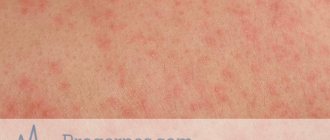
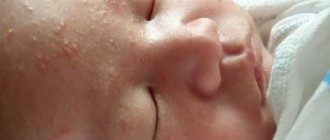
- The most obvious symptom is a sharp rise in temperature. It is impossible to miss or not notice it. Even if you don’t touch the child’s forehead or use a thermometer, an increase in body temperature can be easily noticed by a change in skin color.
- When infected with an intestinal infection, the child may begin to vomit violently. The baby may completely refuse to eat or give everything back immediately after eating.
- The normal color and thickness of an infant's stool is yellow and mushy. In the first days, the baby may pass greenish stools with small, grain-like inclusions. These are substances that were with the child in the womb. After three days, the stool takes on the normal color of a child's surprise. If suddenly the discharge turns green again, and even with mucus, acquires an unnatural smell and the consistency of water, this is a reason to sound the alarm.
- The fact that abdominal pain torments a newborn can be easily understood by his behavior. The baby shows discomfort from intestinal colic by bending his knees under his stomach, constantly jerking his legs, screaming loudly and pitifully. It is impossible to confuse these cries with the cry of a hungry child. When a child just wants to eat, his cry is demanding and categorical. If a child is in pain, he will become hysterical loudly and sadly, clearly asking for help.
Main symptoms
The very first symptom of rotavirus in an infant is vomiting, after which diarrhea usually begins and the temperature rises. The stool is very liquid without any blood, and quite a lot of it is released. The most severe period of diarrhea lasts 4-8 days, but its residual manifestations can persist even after improvement in health, up to several weeks.
Rotavirus diarrhea, especially when combined with vomiting, can quickly cause dehydration. Therefore, it is very important to feed your baby breast milk as often as possible and be sure to give him water. Among the main signs of rotavirus in infants, the following symptoms should be highlighted:
- dry tongue and lips;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- sunken eyes;
- deepened fontanelle;
- rapid breathing and heart rate;
- decrease in the amount of urine.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately call a doctor at home. This can be very dangerous, as it provokes the development of dangerous complications.

Symptoms of rotavirus in infants largely depend on the severity of the disease. In mild cases, the child experiences severe weakness and loss of appetite. Then the temperature rises to 37-37.5 degrees and lasts for 1-2 days. After a few hours, vomiting appears, and this does not depend on whether the stomach is empty or full. Loose stools are observed almost immediately 2-3 times a day. After two days, the symptoms weaken, and by about 4-5 days complete recovery occurs.
The average form of the disease is characterized by an increase in temperature to 37.5-38 degrees. Vomiting precedes the appearance of loose stools and can be repeated many times within two days. Painful cramps appear in the abdomen, often in the navel area. There may also be watery stools up to 7-15 times a day. Moreover, diarrhea can last 1-3 days, subject to proper treatment. When the child begins to recover, vomiting initially goes away, and then the temperature returns to normal.
Symptoms of rotavirus in infants, which occur in a severe form, are characterized by the fact that the disease has an acute onset. The peak severity of the condition occurs on days 3-4. As a result of severe and prolonged vomiting and diarrhea, dehydration occurs. The level of acidity in the stomach increases. The baby is constantly tormented by thirst, and dry mucous membranes and skin appear.
How to treat?
Infants are those patients who are completely unprotected from the dangerous influences of the surrounding world.
It will take at least a year until the baby gains the strength to give a worthy response to diseases. Therefore, whether it’s scary or not, whether you like it or not, the first thing a mother should do is call an ambulance. Newborns are still so weak that their health should not be risked under any circumstances. Intestinal infection is dangerous because with constant vomiting and diarrhea, the body loses water in huge quantities without the ability to restore it. Dehydration in such young children can be fatal.
Emergency doctors will immediately suggest hospitalization. In the hospital, the newborn will undergo tests to quickly identify the causative agent of the disease.
While the results are being prepared, the baby will most likely be placed on a glucose drip to restore fluids and lower the temperature. They can also give you an antiemetic and antipyretic drug. The first results can be obtained already on the second day after collecting stool. Some bacteria are sown only on the third day, others only on the fifth day.
Treatment of intestinal infections can only occur with the use of antiviral drugs, bacteriophages or antibiotics. The method of treatment must be prescribed by a doctor . The decision will depend on the results of the research and the patient’s condition upon admission to the infectious diseases department.
While waiting for a diagnosis, a mother can help her child get better faster. To do this, you need to constantly give your child something to drink. Most often in hospitals they use rehydron - a powder that is diluted in water. It restores fluid and salts well in the body. The taste of rehydron is not very pleasant, so children drink it with great reluctance. To force the baby to express at least a little, you need to pour the solution into the baby’s cheek using a syringe at short intervals.
Dangers of intestinal infection
Intestinal infection is a dangerous disease not only in infants, but also in older children. In order to understand what exactly the danger is, it is necessary to understand the peculiarities of the digestive process of an infant. When a baby is born, the microflora in the intestines is sterile and there are no microorganisms in it. In the first stages of life, a newborn receives breast milk or an adapted formula.
As a result, the gastrointestinal tract is gradually populated by microorganisms. But in addition to beneficial bacteria, the following can enter the children's intestines:
- pathogenic microorganisms;
- viruses;
- toxins.
They disrupt the normal functioning of the intestines, causing intoxication of the body.
How does the disease progress?
Infants experience almost any inflammation very acutely. With high fever, vomiting and other troubles. Intestinal infection is no exception. If medical care was provided in a timely manner, the child’s severe or moderately severe condition will pass within the first day of taking the medication. The vomiting will stop, the temperature will drop to a less dangerous 38.5. Abdominal pain and stool normalize during the first days of treatment.
Most likely, already on the second day of observation in the hospital, the mother will notice that the baby is happier, eats with a greater appetite and does not suffer so much from colic.
Treatment
Treatment of rotavirus in children should be strictly under the supervision of a specialist. When a child develops diarrhea with vomiting against a background of high fever, call an ambulance and start feeding the baby. Your competent actions will reduce the severity of dehydration and help your baby recover faster.
The arriving team will examine the child and decide whether he needs hospitalization. If cholera or other infections are suspected, as well as in severe cases of dehydration, you will be admitted to a hospital, where they will take stool for analysis and give your baby much-needed fluid intravenously.
If your competent actions help keep the level of moisture in the baby’s body at a safe level, the ambulance will schedule your treatment and transfer your address to the “asset” of the local pediatrician. Your doctor should see you the next day and adjust your rotavirus treatment if necessary.
Rotavirus, in fact, goes away on its own 5-7 days after the first episode of diarrhea, but the symptoms and consequences accompanying the infection require adequate therapy. It is especially important to organize proper treatment for children under one year of age, for whom dehydration can cause enormous harm.
- First of all, you need to fight dehydration. Give your baby a drink, gradually increasing the volume of liquid and the intervals between doses. If the baby has had episodes of excessive vomiting, give him saline solutions often and little by little. In the first 24 hours, you may have to stay up all night and feed your baby with a spoon every 5-10 minutes, but his life directly depends on this process.
- On the third day, as a rule, babies under one year old are given probiotics to repopulate the microflora washed out during diarrhea.
- Since the intestinal sections are very affected by infection, it is important to follow a certain diet during the period of illness and carefully introduce the same complementary foods into the diet of children under one year old.
Features of the treatment of intestinal infections in young children
Many mothers mistakenly believe that any gastrointestinal disease should be treated exclusively with antibiotics. This is a misconception that can literally kill the baby’s immunity, so self-medication is not the best option. When it comes to infants, self-medication is inappropriate and even dangerous, so therapy can only be prescribed by a gastroenterologist or pediatrician. However, this does not mean that you need to waste time waiting for a doctor’s visit: parents themselves can provide first aid to their baby, stopping the most dangerous signs of the disease.

Fight dehydration in your baby. Chamomile infusion and fennel tea have an excellent effect on the functioning of the stomach. But if fennel can be given even to a newborn, then chamomile can only be used by children who have reached the age of one month.
It is possible to reduce body temperature in case of poisoning and infectious gastric diseases only if it has exceeded 38°C. For children, special liquid suspensions (Nurofen, Ibufen) or syrups (Paracetamol for children) are used. Before use, carefully read the instructions, because each age category has its own dosage.
Antibiotics for childhood intestinal infections are prescribed by the attending physician in cases where:
- there are blood impurities in the stool or vomit;
- there is a severe form of cholera;
- persistent diarrhea due to giardiasis.
Often, sorbents are used to relieve the symptoms of this disease: activated or white carbon, Smecta, Regidron (in older children). They absorb toxins and promote their safe and complete elimination from the baby’s body naturally (in most cases during bowel movements). Therefore, watch your baby’s stool - this is very important!
If, due to some circumstances, you cannot or do not want to give your baby pharmaceutical rehydration products, then you can prepare such a solution yourself, and it will be absolutely safe:
Stir the mixture well: there should be no lumps or residues of salt and sugar. The baby should be given medicine in such a way that its temperature fully corresponds to the patient’s body temperature. This is necessary for rapid absorption of fluid into the blood. Only in this case will the treatment give results and the little patient’s condition will stabilize.
Prevention of disease development in infants
In order to prevent the occurrence of intestinal infection in newborns, it is recommended to follow a number of rules:
- Be sure to wash your hands after walking.
- Visits to the child by acquaintances and friends of the parents should be kept to a minimum. Parents should prohibit kissing their child.
- All objects, toys and anything that can get into a child's mouth must be clean.
- Before feeding, the breast should also be washed and treated with a weak soda solution.
- Underwear must be clean.
- If one of the family members is sick, contact with the baby must be excluded or minimized.
- When artificial feeding, only baby purified water should be used.
Thanks to such simple prevention methods, it will be possible to maintain the baby’s health and prevent the development of intestinal infections. If this happens, you should not self-medicate and rely on “it will go away on its own.” If any alarming signs of an intestinal infection appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.

Every year, experts identify billions of cases of rotavirus infection in infants. At home, it is difficult to distinguish it from ordinary poisoning, so it is better to immediately consult a doctor when the first signs of the disease appear.
Symptoms and treatment are inextricably linked. Therefore, the more accurately you describe the child’s condition to the doctor, the more correct the therapy will be. We will tell you in this article what to do if you suspect rotavirus in your baby.
Prevention and vaccination against disease
Vaccination is the only method of preventing rotavirus infection . The vaccine is only effective between 6 and 32 weeks of age. Today there are two vaccine options:
- monovalent. It's called "Rotarix";
- pentavalent. It has the name "RotaTek".
In Russia, the second option is used, since it is based on a human strain. Vaccination does not pose any danger and has no adverse reactions. Given orally as drops.
In 2009, WHO recommended that rotavirus vaccination be part of national vaccination schedules . 69 countries around the world made this decision, and in 2014 Russia was included in this number.
Contraindications to vaccination:
- allergy to the components of the vaccine,
- if the child has recently been ill, then you should wait 2-3 weeks with the vaccination,
- history of intestinal diseases.
What to do: diagnosis and treatment
To accurately determine the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct blood, urine and stool tests in a special laboratory. Pharmacies also sell special rapid tests that help determine rotavirus at home.
So, you should immediately consult a doctor if your child:
- is capricious and cries constantly. Draws in the legs - this indicates pain in the abdomen;
- looks lethargic, refuses to take the breast (a bottle with formula), or eat usual or favorite foods;
- complains of nausea or vomits more than twice in an hour;
- diarrhea;
- has a body temperature of 37.2.
If at least two or three signs are present, it is important to suspect the presence of an infection in time and begin to fight the virus in order to prevent it from multiplying in the body.
How to treat
Treatment of rotavirus must be comprehensive . Loss of water and salts in the stool can lead to mild dehydration. You can determine that dehydration in an infant has reached a critical point by the following signs:
- dry tongue
- constant crying for no reason,
- no urination for more than 3 hours,
- no sweat is produced
- convulsions begin, the child loses consciousness.
Replenishing fluid balance . Since the most dangerous thing with this infection is dehydration, the main and primary task will be to replenish the balance of fluid lost in the first days of the disease.
To replenish moisture, experts recommend giving your baby oral rehydration solutions:

To prepare the solution, you need to dissolve one sachet in 1 liter of boiled water. It is necessary to give it to the child throughout the day. He should drink about 500 ml per day.
It is also important to give your baby clean water and breastfeed him . Mother's milk is half water, so it will well replenish lost fluid in the body. Treatment with rehydration drugs is the only method recognized by the World Health Organization (hereinafter referred to as WHO).
We normalize the balance of intestinal microflora . With rotavirus infections, intestinal disorders occur, in which the microflora is washed out, and an imbalance of beneficial bacteria in this environment occurs. To correct the balance of intestinal microflora, doctors prescribe medications that contain the necessary lactobacilli and probiotics.
Adjusting the temperature . The temperature should be reduced only when it reaches 38 degrees and above. In such situations, antipyretic suppositories help well:
- "Nurofen". Used from 3 months;
- "Cefekon". Possible from birth.
The child must be undressed and the diaper removed. It is recommended to wipe with warm water, then cover the baby with a diaper. You should not wrap your child up, as this may increase the temperature. It is forbidden to rub down with vodka or vinegar, as this can cause intoxication of the body.
How to treat at home
If parents manage to recognize the symptoms in time, they can prevent the baby from being hospitalized. The main thing is to start giving your child as much fluid as possible . For a child aged 0 to six months, offer clean, boiled water at room temperature (maybe lukewarm). If your baby has already tried compotes, then cook them from dried fruits, black currants, but without adding sugar.
Do not allow the temperature to rise . If the thermometer shows 37.5 or higher, then:
- do wiping (wet a towel in warm water),
- undress the baby
- temporarily stop wearing diapers (wear them only at night).
It is easier to prevent a temperature jump than to deal with a high temperature later. Call your local doctor and make an appointment. The pediatrician will prescribe competent treatment, which you can carry out at home.
When is hospitalization required?

It is necessary to call an ambulance if:
- convulsions;
- noticeable lethargy. If a child (especially an infant - up to 6 months) has stopped responding to his parents;
- temperature from 39 degrees. It is almost impossible to bring down such a fever on your own; doctors will inject a special lytic mixture;
- severe diarrhea.
If, after the local pediatrician has prescribed treatment, but the symptoms remain (within a week), you should also go to the hospital.
How not to treat
Rotavirus is an intestinal infection that cannot be treated with antibiotics . If diarrhea (diarrhea) is observed, then antibiotics are prescribed if:
- when studying the anamnesis, a diagnosis of “Cholera” was made (suspicion of it),
- There are blood clots in the stool,
- diarrhea does not stop for more than 14 days,
- Worms were found in the stool.
Features of the diet for infants and artificial babies
Inflammation in the intestines inhibits the production of enzymes, such as lactase . This enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of milk sugar. If treatment is started in a timely manner, the body's production of this substance begins to recover, but this takes about 20 days.
After the child feels better, he will have an appetite . You should not stop breastfeeding during illness, but you should reduce the number of feedings. Do not let your baby hang on your breast 24/7; feed as needed and monitor his reaction.
If your baby is bottle-fed, switch to lactose-free formula . If you have managed to introduce complementary foods, then completely eliminate dairy products from your diet.
Diet during and after illness
Intestinal flu causes dehydration of the body, so the child must constantly drink saline solutions.
- As for feeding, it must be said here that rotavirus in infants suppresses the synthesis of enzymes that can break down lactose. This is why some experts believe that breastfeeding should be stopped or reduced during treatment and for 3 weeks after recovery. Instead, lactose-free or soy mixtures are introduced into the diet.
- If the mother is breastfeeding, breastfeeding must be done frequently to prevent the baby from becoming dehydrated. Preventive fasting should also not be done. If the baby refuses to breastfeed, nutrients are administered in the form of a dropper.