Features of Mantoux
The test is first performed on children aged 12 months. If after the BCG vaccination, which is given to newborn children, their body has developed immunity against Koch's bacillus, then after tuberculin is administered to the baby, immune cells begin to attack it, causing an inflammatory reaction at the site of injection of the substance.
There are situations when doctors prescribe Mantoux once every 6 months, starting from the age of 6 months.
In such cases, indications for its implementation may include:
- the presence of medical indicators or refusal of parents to vaccinate their newborn child with BCG;
- frequent pneumonia or chronic bronchitis;
- diagnosing a child with HIV;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs by the baby.
The Mantoux test is not mandatory and is done only with parental consent. However, you should always remember that for a child this is the only way to promptly identify Koch’s bacillus, because, as an adult, a child cannot undergo a fluorographic examination every year. However, children are more susceptible to tuberculosis due to the immaturity of their immune system.
Mantoux is considered a safe research method. But there are times when a baby develops a complication after the administration of tuberculin or the result turns out to be false. Therefore, before performing the test, the doctor will check the patient for possible contraindications.
These include:
- exacerbation of any infectious or chronic disease;
- skin pathologies;
- epilepsy or other somatic disease;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergy.
Also, the test is not carried out if quarantine is introduced in the children's group that the child attends due to any infectious disease. A temporary medical exemption is given if the baby has received any vaccination within the past 1-2 months.
What to do the day before and on the day of checking for Koch's wand?
Preparing for the upcoming Mantoux does not present any difficulty if you know the basic rules. Let's say your child is not allergic and you are calm about how he will tolerate the injection. But in any case, for preventive purposes, it is recommended to exclude allergenic foods and drinks from food the day before and on the day of the test.
If you have an allergy, it is important to report this and ask for it to be noted on the vaccination form. The medical professional will need to find out from you about all past infectious diseases and existing chronic
All of them can affect the outcome of testing.
A couple of days before the important manipulation and on its day, try not to visit crowded places. This applies not only to shops, but also to playgrounds with a large number of children of different ages and their parents.
On the day of the test, dress your child in clothes made from natural fabrics with loose sleeves.
Do not change your usual diet for 5 days before the injection and 3 days after. Do not introduce new complementary foods, do not give food from your table even in small quantities. After the injection, the little person will become weaker and the likelihood of allergies will be higher. All this can worsen the condition of your son or daughter and affect the outcome. Products with a high calcium content reduce allergic manifestations and will be very useful on the baby’s table. On the day of the tuberculin diagnosis, the baby should be well-rested, well-fed, and calm.
Constipation can be harmful, so try to increase intestinal motility in a small patient and give the baby a weak enema.
Double-check your vaccination records. Diagnostics for Koch's bacillus can be done no earlier than a month after the last vaccination.
If it is possible to take one of your relatives with you, then let him take the baby for a walk outside to minimize contact with other people. A simple acute respiratory infection, which was picked up in a queue, after weakening the immune system with the introduction of tuberculin, can result in serious consequences, such as pneumonia, bronchitis.
On the day of the examination, measure the toddler’s temperature and observe him carefully. Make sure that everything is normal and then feel free to go for testing. There is no need to give any antiallergic drugs.
Mechanism
Before sending a child for testing, the doctor must check his health status.
It is important to pay attention to the following factors:
- It is important that the child is absolutely healthy. If at the moment he has signs of any infectious or other disease, or he has only recently had it, then his immunity may be too weakened, so the decoding of the abbreviation may be incorrect. In this case, he is given a medical outlet in order to allow the body to fully recover.
- In children with reduced immunity who are registered with an immunologist, the result may be distorted. This should be brought to the attention of a doctor.
- If the test is to be done on a child who has previously had allergic reactions to any irritant (food, household, contact, etc.), then before performing Mantoux you should consult with an allergist.
For any of these conditions, it is important to tell your doctor about your current symptoms. If necessary, he will be able to prescribe additional tests to clarify the child’s health status.
There is a relationship between recent BCG vaccination and the Mantoux result. In such cases, the result may be false positive.
It is also important to prepare the child for the procedure. It is important for him to explain the rules of conduct after Mantoux. The injection site should not be scratched or subjected to any other mechanical impact.
How to prepare a child
Tuberculin diagnostics must be planned before preventive vaccinations. You can get vaccinated immediately after assessing the result. If the test is performed after vaccination, you need to make sure that at least 4 weeks pass between the time of vaccination and the time of Mantoux. These measures are mandatory, since the state of immunity after vaccination affects sensitivity to tuberculin.
Before performing the Mantoux test, the child should be examined by a pediatrician to identify possible contraindications:
- acute infectious diseases;
- skin diseases during exacerbation;
- severe allergic reactions.
If one of these conditions is detected, the test is postponed until the period of complete recovery or the onset of stable remission.
Absolute contraindications to the test are severe cardiovascular diseases, epilepsy, and a violent reaction of the body to a previous tuberculin injection. Children prone to allergic reactions are prescribed Suprastin before Mantoux or other antihistamines, which should be started 3-5 days before the test.
The following preparation measures are mandatory for all children:
A week before the procedure, you should avoid visiting places with large crowds of people, so as not to accidentally become infected with an acute viral infection. In children, a TB test may cause weakness, a slight fever, or an allergic reaction.
Accidental infection in this case puts additional stress on a weakened body. It is important that the child is calm and well-fed before the test. On the eve of the diagnosis, you need to provide him with adequate sleep.
How to eat and drink before Mantoux: only drinks and dishes that are well tolerated by the child’s body should be given. You cannot introduce new foods into your child’s diet a week before the procedure, so as not to provoke unwanted reactions from the immune system. Parents of a child with allergies need to closely monitor changes in the condition of his skin. If you have redness or rashes associated with eating, you should take a course of antihistamines before the test. You should consult your doctor about the advisability of diagnostics and medications. If the allergy is associated with flowering plants, the test must be rescheduled for another time. On the day of the test, it is necessary to protect the child from communication with other children. It is advisable that he spend the time waiting for his turn for diagnosis on a walk, and not in the clinic, where there is a high risk of infection.
Overheating or hypothermia must not be allowed: a small patient must be dressed appropriately for the weather, and street clothes must be taken off in the clinic locker room.
Result evaluation
There is an opinion that after performing Mantoux on a child, the test site should not be allowed to come into contact with liquid for 3 days. However, it is not. The drug is administered subcutaneously, so the ingress of any liquid into this area cannot distort the Mantoux results. However, various physical actions (rubbing the injection site with a washcloth or towel) can affect it. Therefore, doctors recommend refraining from water procedures during this period.
You can also hear the opinion that sweets can influence the result. There is no medical evidence of this fact. If you consume allergens such as citrus fruits and chocolate in large quantities, then an allergic reaction of the body is possible, which will affect the sample. However, if such foods are consumed in moderation, the size of the papule will not change.
Within 24 hours after the test, usually no reaction is observed. Later a papule appears. Doctors perform decoding of the Mantoux test on the 3rd day after administering the drug under the skin. To do this, a visual inspection of the injection site is carried out, and the diameter of the papule is measured.
The designation of the Mantoux reaction in the certificate may be as follows:
- Negative means that there is no compaction or the diameter of the redness does not exceed 1 mm. For a child whose BCG vaccination has been at least 5 years old, this result is considered normal and indicates the need for revaccination. This suggests that his body has not remembered the pathogen, so he is unable to effectively protect himself from it.
- Doubtful - the size of the papule ranges from 2 to 4 mm, and there may be no redness. This result occurs primarily in adolescents, adults, and children who require booster vaccination.
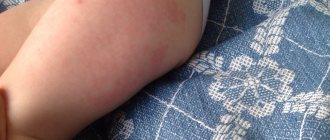
- Positive - the diameter of the seal exceeds 5 mm, but its value does not exceed 17 mm. In this case, several factors are assessed (time since vaccination, the presence of a turn and the size of the scar).
- Hyperergic - the size of the papule is more than 17 mm.
In turn, the hyperegic reaction is divided into:
- general - occurs in hypersensitive patients, manifested by increased body temperature, deterioration of well-being, and so on;
- focal - associated with disturbances during drug administration and manifested by itching or other allergic reactions;
- local - the appearance of an abscess, ulcer or excessive enlargement of a papule at the injection site.
A hyperergic reaction (shown in the photo) is a reason to contact a phthisiatrician, who will prescribe an additional examination to assess the child’s health. This may include a fluorographic examination, bacteriological examination of sputum, computed tomography, and so on.
It is important that there are no pustules or tissue necrosis at the sample site. If no reaction occurs, this means that the patient has not developed immunity against tuberculosis. In this case, you should consult a doctor.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that the result of the Mantoux test with decoding in children may be affected by their age. It is impossible to decipher the size of a papule on the hand of a preschooler or a 12-year-old child in the same way. The norm for them may vary.
There are 2 other possible reactions:
- False positive. It happens that the decoding indicates the penetration of Koch's wand, although in reality it does not exist. This is possible with recent infectious diseases.
- False negative. The test result indicates the absence of the tuberculosis pathogen in the body, while laboratory tests detect it. Typically, this result is possible if no more than 2 months have passed since the infection.
In such cases, doctors recommend taking the test again after a certain period of time.
Proper preparation for Mantoux
Why is Mantu needed and why prepare for it?
The Mantoux reaction, at the current level of development of medicine, is considered the most effective way to diagnose tuberculosis. The result should not be influenced by circumstances unrelated to immunity. Therefore, it is worth properly preparing for this procedure and following certain rules before Mantoux and until the injection site is examined. Caring parents often try to find out how to prepare for manta rays at 1 year old. They ask doctors, friends, and search for information on the Internet. All the necessary information about performing Mantoux for a child is systematized and given here.
Mantoux is carried out for early detection of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on the response to the administration of tuberculin (a drug that contains components of the tuberculosis bacillus).
After penetration of tuberculin, the skin reacts with a local allergy in the presence of antibodies to the causative agent of the disease. Based on the nature of the irritation that appears, the doctor will determine whether the person is healthy, whether he has been infected in the past, whether he is a carrier of the infection, or whether there is a need for revaccination. The information obtained from the sample can be completely trusted. Repeated checks are required in rare cases.
In our country, tuberculosis is considered a common dangerous disease. The treatment itself and the recovery period take a very long time.
The infection can be encountered anywhere, so the importance of vaccination and diagnosis of this disease using tuberculin is not questioned
Sample turn
Sometimes you can come across such a thing as a tuberculin test. What does it mean? This is what is called in medicine an atypical increase in reaction in comparison with the data of previous tests.
The turn is:
- Transition from a negative or questionable sample immediately to a positive one without vaccination against tuberculosis during this period.
- An increase in papule size by 6 mm over 12 months in children vaccinated against tuberculosis.
- Maintaining the Mantoux result within 12 mm for 3 years or more.
- The presence of a hyperergic reaction, regardless of when the child was vaccinated against tuberculosis.
The cause of this condition may be the following factors:
- penetration of Koch's bacillus into the child's body;
- infection of the baby with non-tuberculous species of mycobacteria;
- violation of the test or its implementation if there is a contraindication in the child;
- features of the baby’s immune system after vaccination against tuberculosis.
There is a sign that makes it possible to determine whether a positive reaction to a Mantoux test is due to an infection or whether it is simply a feature of the child’s immune system. If the papule has a pale pink tint, then this fact indicates post-vaccination immunity. In case of infection with tuberculosis, the papule acquires a bright color and has clearly formed boundaries. After some time, this place becomes pigmented.
Contraindications and complications
Mantoux allows you to timely detect infection with Koch bacilli. But in some cases this test is postponed or not performed at all.
Contraindications to tuberculin injection are:
- acute or chronic epidermal pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- epilepsy;
- allergy;
- brain damage;
- rheumatism;
- cold;
- severe neurological diseases of a congenital or acquired nature;
- bronchial asthma.
If you do Mantoux in such cases, the risk of side effects increases.
As a rule, the tuberculin test is well tolerated by children of all age categories. Negative consequences occur extremely rarely and are represented by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- allergic reaction;
- loss of consciousness;
- loss of appetite.
Such manifestations usually subside a few days after the subcutaneous injection. You can give your baby an antipyretic or an antihistamine (depending on the situation). If your health continues to deteriorate, you should seek medical help.
To ensure that the Mantoux test does not cause complications, you should adhere to the following rules:
- On the eve of the procedure, exclude allergenic foods from your diet.
- Diversify the menu with calcium-containing products.
- If your baby has a tendency to allergies, you should give him an antihistamine on the day of the injection.
- If the baby has a high temperature and is not feeling well, refuse to carry out the manipulation.
- Tell your child how to handle the injection site, make sure that he does not wet, scratch or rub the injection area.
The pediatrician tells parents and the child in detail about how to prepare for the Mantoux test and how to behave after it before the manipulation.
What to do after mantu
Doctors, including Dr. Komarovsky, argue that the test cannot provide an absolute guarantee of determining whether a child is infected with tuberculosis. However, its results must be taken into account. If its result is positive, but the child has no signs of the disease, or vice versa - there are symptoms of tuberculosis in a patient with a negative Mantoux result, he needs to contact a phthisiatrician.
It is necessary for other family members to be tested for Koch bacillus infection if:
- The size of the papule increased by 5 mm or more compared to the result of the previous year. In this case, the doctor will study the reasons for the deviation of the sample, which is considered the most informative sign of the presence of the disease.
- The baby has a hyperergic reaction to the administered tuberculin.
- The child had a false positive reaction to the administered substance.
If the sputum analysis does not show the presence of mycobacteria in them, then the baby is considered healthy, and the sample is considered false positive.
When Koch's bacillus is detected, we are talking about infection. Such a child is registered with a tuberculosis dispensary and is monitored. In addition, he will be prescribed chemical prophylaxis, which consists of taking certain medications. It is important to remember that not every person diagnosed with mycobacteria will necessarily develop tuberculosis. According to statistics, the disease develops only in 5-10% of infected people.
Tuberculosis is a dangerous disease, the insidiousness of which lies in the fact that at the initial stage of its development it does not manifest itself in any way. That is why it is so important for every child to have the Mantoux test done every year, which is the most informative way to determine the presence of the tuberculosis pathogen in the body.
Preparation for the procedure
The main condition for conducting a test for tuberculosis is the exclusion of possible contraindications, such as:
- infectious diseases during the course, as well as a month and a half after the illness;
- skin diseases during exacerbation;
- allergies, atopic dermatitis;
- epilepsy;
- manifestation of a violent allergic reaction when the child is given the first test - in this case, alternative diagnostic methods will be used.
In addition, it is unacceptable to do a tuberculin test at the same time as other vaccinations.
If there are other diseases, including chronic diseases, the decision on the possibility of conducting the test is made by the doctor. Thus, hydronephrosis - a kidney disease - will not be a contraindication to Mantoux.
If there are no contraindications, then the question of how to prepare a child for Mantoux will not cause difficulties: it is enough to follow a number of simple recommendations:
- A few days before the procedure, avoid visiting crowded places to avoid accidentally contracting a viral infection. It should be taken into account that the incubation period of the disease can last up to 10 days, and the Mantoux test against the background of the disease can provoke complications, in addition, it itself will most likely turn out to be uninformative. Immediately before the Mantoux test, the baby must be examined by a doctor and given permission to conduct the test.
- The child should be well-fed and calm at the time of the procedure; the baby should be given a good night's sleep. The diet for the week before the test date should be familiar; you should not introduce new foods at this time; it is better to avoid the consumption of foods and drinks that can cause allergies. If you are allergic to pollen from flowering plants, it is better to postpone the test a month before or after the flowering period.
- If a child is allergic, you need to make sure that at the time of the Mantoux reaction he does not have any allergic manifestations: the skin should be clean, without rashes and redness. For preventive purposes, such a patient can be given antihistamines 2-3 days before the tuberculin test (it is not recommended to use first-generation drugs, for example, suprastin; it is better to consult a pediatrician).
- Constipation at the time of the procedure can cause side effects, so parents need to make sure that the child’s intestines are free. Lactose will help improve intestinal function.
- On the day of the Mantoux reaction, it is necessary to minimize the child’s interaction with other children in the clinic. The best option is if the baby spends the waiting time on a walk. This measure is also aimed at preventing possible infection with acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections.
- After administering tuberculin, you need to observe the baby’s reaction for half an hour; during this time it is better not to go far from the clinic: if the child experiences any alarming reaction during this time, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- To avoid the child’s excessive attention to the injection site, it is recommended to choose clothes made from natural fabrics with long, loose sleeves. This will protect the “button” from unwanted friction and moisture.
Rules for caring for Mantoux sample
Even if this diagnostic method is not vaccination or inoculation, damage to the upper skin occurs when the injection is administered.
Due to the occurrence of a wound, there are some actions that are not recommended to be performed in relation to the sample.
Care Tips:
- annual change of the hand on which the diagnosis is carried out;
- the diagnostic procedure should take place in a sitting position and at the same time;
- It is forbidden to comb the wound (to avoid mechanical damage and infection) and use ointments;
- getting wet does not harm the sample, but staying in water for a long time can also lead to infection;
- Do not tape or bandage the injection site;
- treatment of the wound is permitted only after measuring the test result.
Scratching is fraught with the introduction of foreign infection, which will change the test result, making it false positive.
Prevention of tuberculosis
To prevent the spread of tuberculosis infection, it is important to identify sick people as early as possible, isolate them and examine people who were in contact with the patient. For this purpose, the Mantoux test is used, and annual fluorography is performed in the adult population.
To form anti-tuberculosis immunity, the vaccine is administered in the maternity hospital, and then at the age of 7 and 14 years when Mantoux is negative. It can be used at the age of 21 and 28, since its effect lasts only for 7 years. It is rarely used in adults, since vaccination requires a negative Mantoux.
Annual fluorography
If there are signs of infection, even in a latent form, that is, tests show infection, but there are no symptoms, the patient must undergo a preventive course of taking anti-tuberculosis drugs.
General methods aimed at stimulating the body's defenses (nutrition, walks in the fresh air, hardening) are only of secondary importance. It has been established that now people from completely prosperous families also suffer from tuberculosis.
We recommend reading the article about what Mantoux vaccination is. From it you will learn about the composition of the drug, the method of performing the Mantoux test, why it is needed, and whether it is possible to refuse Mantoux. And here is more information about the causes of fever after Mantoux vaccination.
Mantoux in adults is carried out on an individual basis for a disease similar to tuberculosis and risk factors for infection. The most dangerous reaction is a hyperergic reaction, and positive, doubtful and negative reactions often occur in the absence of tuberculosis infection.
How and when is the Mantoux reaction determined in adults, who gives the assessment
The Mantoux reaction in adults is determined 48-72 hours after the injection of a diagnostic solution (2 tuberculosis units in 0.1 ml) into the skin of the forearm, assessment is carried out by changes in the skin. The measurement of the papule itself is carried out by specially trained nurses who have received access to tuberculin diagnostics.
It is very important to take into account that the Mantoux reaction alone never makes it possible to make a correct diagnosis. Therefore, its result in adults is always compared with data obtained during:
- medical examination;
- interviewing the patient about the presence of complaints and possible contacts with patients;
- X-ray examination of the chest;
- blood tests, sputum culture.
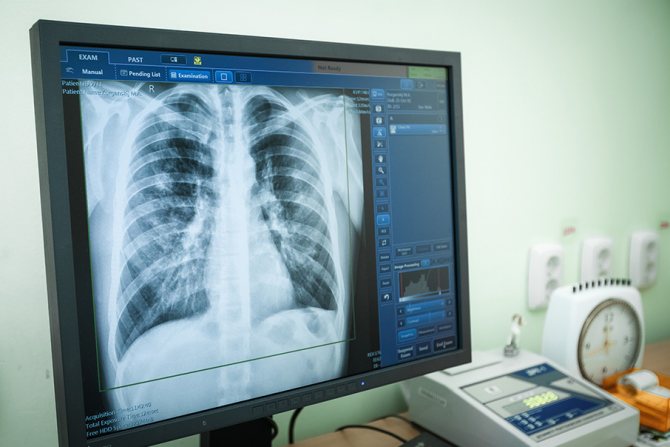
With the result of the measurement, the adult turns to the therapist, he gives a recommendation about the need to consult a phthisiatrician.