If a child breathes intermittently during sleep, this may mean that he or she has sleep apnea - a temporary cessation of breathing that lasts more than 20 seconds. This is more common in premature babies and occurs during REM sleep (when the baby sleeps more soundly).
Sleeping baby
Important! Short pauses in breathing, lasting 5-10 seconds, are very often observed in newborns and are mostly not a pathology.
Reasons for holding your breath
Apnea occurs in 1 in 100 newborns. Infants born at term have the lowest incidence of apnea (about 0.1%), decreasing in accordance with the degree of fetal maturation. Breath holding occurs in 5-7% of children born after 34-35 weeks of pregnancy, and in almost all newborns after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
The most common cause of breath-holding in a child's sleep is the incomplete development of the mechanisms that regulate the respiratory rhythm, associated with the immaturity of the premature baby.
Other causes of apnea in infants:
- infections;
- perinatal hypoxia;
- congenital metabolic pathologies;
- unsuitable ambient temperature;
- maternal use of opioid medications or medications containing high doses of magnesium in the period preceding childbirth;
- the use of medications to treat infants that reduce the function of the respiratory center in the brain;
- intracranial bleeding;
- necrotizing enterocolitis;
- heart diseases;
- low blood glucose.
Premature baby
related to the obstructive nature of the disease come to the fore
- anatomical abnormalities - Robin's syndrome, cleft lip, etc.;
- allergic reactions;
- heavy weight;
- enlarged tonsils and growth of adenoids;
- spasms of the laryngeal muscles;
- delayed formation of cartilage tissue, resulting in excessive softness of the palate.
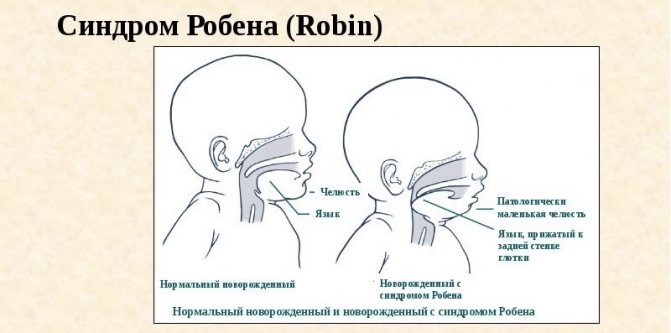
Robin's syndrome in infants
How do babies breathe?
If a newborn breathes frequently during sleep, and no symptoms of pathology appear, this is the absolute norm. This happens due to the physiological immaturity of the upper and lower respiratory tract. The baby’s body must be fully saturated with oxygen, but the baby cannot take a deep breath. Frequent breathing is a compensatory function that newborns use. Due to the fact that the air supply has not yet been fully adjusted, small children may breathe unevenly.
The breathing rate is also different from that of an adult. Most often, babies take two or three short breaths, and then one long one. This process is normal for children from birth to one year; over time, the rhythm of inhalation and exhalation will become more even.
The absence of signs such as wheezing, an open mouth, muscle tension and moaning during sleep is a sign of a completely normal baby.
A newborn can breathe quite frequently when calm. It is difficult for parents to determine whether such a condition is within the normal range or beyond it. To confirm or refute irregularities in the child’s breathing rate, it must be measured. This is done using a phonendoscope. Its membrane is preheated with your hands and applied to the baby’s chest. If you don’t have a special device, you can simply put your hand on the baby’s chest and monitor the number of times it rises for one minute.
In pediatrics, there are regulated respiratory rate indicators for children of different ages:
- from birth to two weeks of age - the norm is 40-60 breaths per 1 minute;
- at the age of two weeks to three months, the norm is 40-45 breaths;
- from four to six months – 35-40 breaths;
- from seven months to one year – 30-36 breaths.
If the indicators are within the normal range, the child has no signs of infectious or inflammatory diseases, he is steadily gaining weight, you don’t have to worry about his breathing. Over time, all organs and systems begin to function correctly, breathing becomes uniform and less frequent.
Not only the frequency of inhalation and exhalation can become an indicator of the baby’s health, but also the type of breathing itself. It determines how well the lungs and upper respiratory tract will be ventilated, what the quality of gas exchange in the tissues will be, and how quickly the brain cells will be saturated with oxygen.
To find out your child's breathing type, just look at which parts of his body are movable during inhalations and exhalations.
In total, it is customary to distinguish three main types:
- The first is the chest, we can talk about it if, when inhaling air, the baby’s chest actively works, it rises and falls rhythmically. This type results in insufficient ventilation of the lower part of the lungs.
- If movement of the abdominal wall and diaphragm is observed, then the child has abdominal breathing. When it occurs, the upper respiratory organs experience a lack of oxygen.
- If both the diaphragm and the chest work simultaneously, this indicates mixed breathing. This type is the most useful and allows you to completely saturate the body with oxygen.
A baby's rapid breathing during sleep can be a sign of many serious pathologies, so it is important that parents know how to correctly recognize them. If you notice that your baby has deviations from the norm, you should closely monitor him. The problem may indicate the following pathologies:
- Cold. This is the most common disease among children and is accompanied by a cough and runny nose. In this case, you must definitely call a pediatrician who will prescribe effective treatment.
- Entry of a foreign body. If you hear wheezing, groaning or whistling when breathing, it is likely that there is a foreign body in the airways. In such cases, the mucous membrane swells and the respiratory passages narrow. To solve the problem, an examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary.
- Cardiac pathology. Swelling of the face, blue lips and skin around the eyes, along with rapid breathing, may indicate problems with the cardiovascular system. Calling an ambulance will be the best solution in such a situation.
- Infectious diseases of the bronchi. Rapid breathing, increased irritability, lack of appetite and increased body temperature are signs of bronchial pathologies. Call your local pediatrician immediately to prevent serious consequences.
- Rhinitis. If your baby breathes very quickly and opens his mouth at the same time, he may have rhinitis. Babies do not yet know how to blow their noses on their own, so parents must clean their nasal passages of mucus using special devices.
- Enlarged adenoids. Inflammation of the tonsils is also common in children, since their immune system is not fully formed. This disorder can be recognized by the baby’s open mouth, his jaw hangs down, his facial features become distorted, and night snoring appears. In such a situation, you cannot delay a visit to an otolaryngologist.
- Sleep apnea. The most dangerous disease that leads to the death of babies in their sleep. If your baby's breathing stops for 10 seconds or more and then starts again but becomes too fast and irregular, contact your doctor immediately to help prevent death and other problems.
The breathing of newborn babies can become more frequent for completely harmless reasons.
If you do not see any changes in the child’s condition, then there is no reason to panic. Sometimes a disruption in the rhythm of breathing can occur due to the baby choking on something. Also, mothers can often hear bubbling in the baby’s throat, this happens if he does not have time to swallow saliva. This condition resolves over time and should not cause undue concern. Temporary cessation of breathing also often occurs in newborns. If it does not exceed 10 seconds, then the baby’s condition is normal. The disorder goes away on its own when the baby reaches six months of age.
Also, the breathing rate can be affected by the environment; try installing a humidifier in the nursery and maintaining the humidity at 60-70%, and the air temperature at 18-21 ° C, this will significantly reduce the load on the child’s respiratory system and contribute to the normal saturation of the body with oxygen.
Types of breath holding
Why does a child have heavy breathing - what to do?
There are three mechanisms for respiratory arrest in a newborn:
- central – associated with dysfunction of the respiratory center in the brain;
- obstructive – caused by obstruction of the airways while maintaining the proper functioning of the respiratory center;
- mixed - when airway obstruction precedes a malfunction of the respiratory center in the brain.
Important! Most cases of apnea in infants are central, less often mixed.
Diagnostics
If the breathing process is complicated by symptoms such as confusion, increased chest movements, unusual sounds, it is necessary to pay attention to this and clarify the reasons. Sometimes such manifestations can be caused by nightmares or a common cold, but sometimes heavy breathing indicates a much more serious problem and requires immediate treatment. In most cases, heavy and noisy breathing occurs with false or viral croup in children. We will look at the symptoms and treatment below.

Possible consequences
If a child holds his breath for 20 seconds or more during sleep, this is an alarming symptom that causes oxygen starvation. In this case, nerve cells can die, which leads to serious consequences, these are:
- developmental delay;
- epilepsy;
- neurological disorders;
- attention deficit hyperactive disorder;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
Why does a newborn baby spit up in his sleep?
Lack of oxygen can also cause high blood pressure.
Important! It is assumed that prolonged apnea in a child can lead to sudden death.
Sudden infant death occurs on average in one child in 1,000, and its causes are not entirely clear. According to experts, sleep apnea is one of the possible factors.
Croup in children: symptoms and treatment
Croup is characterized by a triad of symptoms:
- barking paroxysmal cough;
- stridor (noisy breathing), especially with crying and excitement;
- hoarseness of voice.
In addition, the appearance of secondary signs of the disease is noted - severe anxiety, rapid breathing and heartbeat, nausea, hyperthermia.
As respiratory failure increases, all signs worsen, the child’s skin becomes gray or bluish in color, salivation increases, wheezing can be heard even at rest, anxiety is replaced by lethargy.
Children with this diagnosis require hospitalization. The first thing doctors should do is restore the airway. To do this, it is important to reduce laryngeal spasm and swelling, as well as free the lumen from accumulated mucus.

Drug therapy is prescribed:
In difficult cases, tracheal intubation or tracheotomy with artificial ventilation is required.
If a child has difficulty breathing, now we know what to do.
Human life directly depends on blood circulation through the vessels. And in order to prevent various problems, you need to know everything about the breathing habits of your child.

Symptoms of holding your breath
Why does a newborn baby spit up mucus?
A child breathes much faster than an adult. It is normal if he takes 60 breaths per minute. The sounds a baby makes when breathing are very diverse. This is due to the fact that he breathes only through his nose. The baby may sob and grunt in his sleep, which is not a cause for concern.
The infant's breathing rhythm changes during sleep. It can speed up, slow down, and sometimes stop for a few seconds. According to doctors, this is a normal condition, which they describe as periodic breathing. It is likely to occur in an infant under 6 months of age.
Unlike apnea in adults, which is manifested by snoring, a child holds his breath during sleep almost silently, and it is difficult to notice. Parents should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- irritability and tearfulness, the baby may wake up, scream and cry during sleep;
- weakness and apathy;
- lack of appetite;
- mild cough;
- after inhalation, the chest freezes;
- the baby tries to breathe through his mouth when he sleeps;

Baby trying to breathe through his mouth
- sweating;
- strange position while sleeping.
The severity of symptoms is indicated by:
- blue discoloration of lips and facial skin;
- absence of visual signs of expansion and collapse of the chest;
- a sharp slowdown in heart rate.
If a newborn can hold his breath for a few seconds, but this happens infrequently, and no other symptoms are observed, then this phenomenon is considered normal, since the baby is just learning to breathe.
Important! If you hold your breath for more than 15 seconds and there are additional alarming symptoms, you should immediately show your baby to a specialist. The doctor will determine why the baby is holding his breath and prescribe treatment if necessary.
Newborn breathing during sleep
» Newborn » Newborn breathing during sleep
The mother of a newborn child is constantly overcome by fears. One of them is “why does a newborn breathe often in his sleep? Is this normal? Don't panic. To understand, you need to understand what the physiological characteristics of babies are.
Frequent breathing of a child during sleep: normal or abnormal?
When a newborn appears in the house, parents and relatives closely and closely observe its behavior, sometimes trying to find symptoms of dangerous diseases. They have a lot of questions, in particular, is rapid breathing normal for a baby. Most often, it is the mother who notices that the child is breathing rapidly during sleep.
An adult never monitors how often he breathes: for us, breathing is such a natural process that we do not pay attention to it. Things are different for children, because their breathing rate is radically different from ours.
The breathing of a newborn baby begins to gradually adapt to the environment. Difficulty breathing and disruption of its rhythm can cause colds, improper speech development, and lead to serious health problems.
Norms of respiratory rate in newborns and children
During sleep, the baby breathes unevenly and frequently. Inhales abruptly - it seems that in one breath he cannot satisfy his need for oxygen; Due to the large number of breaths, snoring is observed and the nasal mucosa dries out.
Sometimes many short breaths, varying in duration, follow each other in a row, and then a long one (10-15 seconds). Sometimes it seems to parents that the child has stopped breathing altogether, but the rhythm resumes again.
If a baby breathes frequently during sleep, then this is considered normal and can be observed during the first month of life, but in weakened and premature babies, breathing can remain frequent and intermittent for a very long time.
If you want to know how many breaths your baby takes during sleep, carefully monitor his chest and count the number of movements. It is considered normal for a newborn to take from 40 to 60 breaths per minute, so it seems that the child is breathing very quickly in his sleep.
The neonatal period lasts up to 28 days. Then gradually the breathing rate begins to decrease: a two-month-old baby takes from 35 to 48 breaths per minute, from 6 months to a year - from 30 to 40 breaths, from 2 years to 4 - 20-30 breaths, from 8 to 12 years – 23-31 breaths, after 12 years – only 18-20 breaths.
The main causes of rapid breathing
Rapid breathing (tachypnea) of a newborn is due to the imperfection of the respiratory system, because it continues to develop. Over the next two to three months, the lungs open, and as a result, the number of inhalations and exhalations begins to decrease.
Tachypnea of the newborn is a normal phenomenon for both infants born at term and premature babies.
Rapid breathing is also observed with increased physical activity. In all other cases, it indicates deviations in the child’s health.
Diseases that cause rapid breathing
- Apnea.
First, the child begins to wheeze, then he holds his breath for a long time. It returns to normal on its own, but sometimes the baby’s legs, arms, and lips begin to acquire a bluish tint, and he loses consciousness, which indicates oxygen starvation. If you notice such a condition in a child in a dream, you must quickly call an ambulance, because oxygen starvation is very dangerous for a newborn: it can lead to serious health problems and developmental disorders. - Diseases of the respiratory system.
These include colds, which are characterized by a runny nose, fever, cough, hoarse voice, and general weakness. In this case, due to swelling of the nasal mucosa, the child sniffles in his sleep and his breathing frequency is disrupted. - Bronchial asthma. Rapid breathing during sleep appears before an attack.
- Allergy.
It is not considered a direct disease of the respiratory organs, but can manifest itself through them. An increase in the number of breaths appears when the mucous membrane swells, the baby begins to sigh frequently, which indicates a lack of oxygen. - Chronical bronchitis.
The main signs of the disease are a cough that lasts up to two months (wet in the morning, with the discharge of purulent sputum), and heavy breathing. - Pneumonia. Difficulty breathing, slight fever and cough are observed. Older children may complain that they have trouble breathing.
- Tuberculosis.
Main symptoms: loss of appetite, weakness, slight increase in temperature, constant coughing, noisy breathing in the child. - Cardiovascular diseases. Tachypnea sometimes indicates heart disease, with the child breathing frequently during sleep, experiencing weight loss and shortness of breath even after minor physical exertion.
- Nervous tension. With severe stress and hysteria, the breathing process is disrupted. It becomes noisy, the child sighs heavily, his appetite increases or, conversely, his appetite disappears, headaches begin to bother him, irritability, tearfulness appear, and sleep is disturbed.
Make it a rule that if you suspect a dangerous disease in an infant or discover an illness, immediately contact your local pediatrician.
How to help your child breathe properly
Correct and uniform breathing promotes stable gas exchange in the lungs and has a calming effect. Many adults in a stressful situation use this breathing technique: inhale deeply and exhale slowly.
In this case, active oxygen saturation occurs and the person gradually calms down. This technique also applies to children. If your child is having a tantrum, ask him to take a deep breath and exhale slowly.
The baby will be distracted, and as a result his breathing will normalize.
Rapid and shallow breathing of an infant at night indicates a lack of oxygen. The child sniffles in his sleep, it seems that he does not have enough air.
The first month of a baby’s life is very difficult, because the lungs are actively developing, and therefore the breathing rate is constantly changing.
This is completely normal: the newborn is trying to take in more oxygen to saturate the blood in order to prevent oxygen deficiency in the body.
The respiratory rate is influenced not only by physiological processes, but also by external factors.
When dressing your child in pajamas, pay attention to whether it is comfortable enough for the baby, whether it restricts his movements, whether the collar is free, and what material it is made of. Choose only natural fabrics.
It is advisable for the child to sleep in it once during the day, and you watch him. After making sure that everything is fine, you can put it on at night.
It is necessary to monitor the temperature and humidity in the room. Snorting while sleeping at night indicates dry air in the room.
When the air is dry, the child begins to sniffle, and viruses accumulate in the nose. The result is a runny nose, difficulty breathing, lack of oxygen and poor sleep at night.
In the cold season, you need to ventilate the room twice a day, and in warm weather, leave the window open around the clock for good air circulation. Pay special attention to your baby's crib: the mattress should be hard; a pillow is not needed at all in the first year of life.
In the first month of life, a newborn should sleep only on his side. If he turns over on his stomach, he must be returned to his original position, since he cannot yet consciously turn his head during sleep so as not to suffocate.
The child rests his nose on the mattress, begins to snore, and the frequency and rhythm of breathing are disrupted due to lack of oxygen.
Does your child breathe frequently in his sleep? No need to panic ahead of time! It is worth observing his behavior and state of health, and if any doubts arise, it is better to consult a pediatrician for advice.
DobryjSon.ru
The baby breathes frequently in his sleep. Normal or pathological?
A newborn is always the object of increased attention from parents. Every change in a baby's behavior becomes alarming, and the way he breathes is no exception. Frequent and intermittent breathing is a case that 90% of parents are familiar with. But in order to “survive” this without stress, mothers and fathers must understand the causes of this phenomenon.
First, you need to determine the baby’s breathing rate - this is the initial diagnosis to determine the healthy state of the newborn. Independent monitoring of the “number of inhalations and exhalations” per minute allows you to draw preliminary conclusions about the baby’s condition, since if the baby breathes frequently while sleeping, this may be evidence of the development of pathologies.
Determination of respiratory rate in newborns
During sleep, a baby's breathing is usually rapid and uneven. The newborn begins to inhale abruptly, it seems that one full breath cannot saturate the body with oxygen. It must be remembered that uneven breathing is the norm for all newborns. It begins to normalize a month after birth, and by a year it becomes completely stable.
Counting the number of inhalations and exhalations can be done in several ways. You can use the medical method using a phonendoscope, remembering to heat its metal membrane, or simply place your palm on the baby’s chest. In modern pediatrics, there is a certain register that regulates breathing standards for newborns:
- 0-12 months - 50-60 breaths per minute;
- 1-2 years - 30 breaths per minute;
- 3-5 years - 25 breaths per minute.
If these norms overlap, this indicates violations, which means you need to consult a pediatric doctor.
Causes of increased breathing
- If a baby breathes heavily during sleep, with wheezing or whistling, this is a reason to consult a doctor as soon as possible, as the cause may be an infection in the baby’s body. Also, bronchitis and pneumonia have a similar manifestation;
- if the newborn sleeps with his mouth open, then the cause may be an increase in body temperature - one of the methods of thermoregulation. If this is accompanied by severe swelling, then this may be a sign of cardiac pathology, and immediate medical attention is required;
- a newborn baby experiences reflex activity during sleep, which leads to a change in breathing rates - such phenomena do not require medical supervision and go away on their own.
Source: https://www.babysovet.ru/novorozhdennyj/dyhanie_novorozhdennogo_vo_vremya_sna.html
How to help your child
In most children, apnea goes away as the nervous system matures. The respiratory center in the brain fully matures at about 1 month of age in full-term infants. If the baby was born premature, then these dates are shifted by 2-3 months.
If the pulse suddenly slows down and the skin turns blue, as well as if the movements of the chest stop and the arms and legs sag, the baby needs urgent help.
Parent actions:
- Quickly lift the child from the crib, turn him so that his face is facing down, and lightly pat the baby on the back. If this does not help, you need to start artificial respiration.
- Place the baby on his back on a flat, hard surface and see if the tongue is retracted. If there is vomit in the mouth, clean it with gentle movements using a finger wrapped in a clean napkin.
- Placing your hand under your neck, lightly press on your forehead so that your head tilts back a little and the airways are cleared.
- Take a deep breath, cover the baby’s nose and mouth with your mouth at the same time and exhale, watching the movement of his chest. After lifting it, stop exhaling.
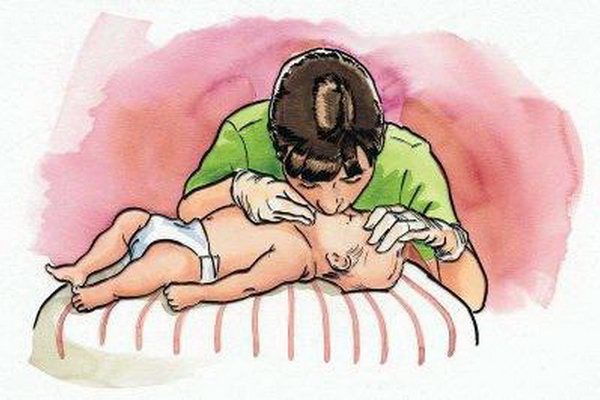

Carrying out artificial respiration for an infant
Important! The volume of a baby's chest is much smaller than that of an adult, so under no circumstances should you exhale all the air.
- Free the baby's nose and mouth to take a new breath. His chest will collapse and a natural exhalation will occur.
- The frequency of manipulation is 30 times per minute.
- If it is noticed that the baby is breathing on his own (by the expansion and collapse of the chest), artificial respiration should be stopped. When he breathes weakly and intermittently, the manipulations must be continued, trying to ensure that the artificial breath coincides with the natural breath of the baby.
- In the absence of a pulse, which can be better felt in the neck, it is necessary to combine artificial respiration with chest compressions. To do this, you need to take 2-3 breaths, then place 2 fingers of one hand just below the nipple line and apply 5 pressures. The order of alternation in the future is 5 pressures per 1 breath. The total number of manipulations for indirect cardiac massage should be 100 per minute.
Simultaneously with the start of resuscitation procedures, it is necessary to call an ambulance and continue them, if necessary, until doctors arrive.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to give the baby a breast or a bottle of water, as well as any medications.
Respiratory system of newborns
- small wide nose;
- underdeveloped nasal sinuses;
- short lower nasal passage;
- insignificant thickness of the nasal mucosa.
The respiratory system of an infant also differs in many ways from similar organs of an adult. In the first year of life, the epiglottis in a child is located above the root of the tongue, and the laryngeal parts of the pharynx have special pear-shaped pockets through which milk bypasses it when swallowing without interfering with breathing. Thanks to this, a baby can suck milk, swallow it and breathe at the same time, while adults are deprived of this opportunity.
The larynx and trachea of a newborn are characterized by a funnel-shaped shape. It has a narrow passage, and the cartilage is soft and pliable, easily displaced. The right bronchus in children under one year of age has a straight direction and is a continuation of the trachea, and the left one departs from it at an angle. Lung tissue is not elastic enough, poorly developed, rich in blood vessels, but poor in alveoli - bubbles that absorb oxygen from the air. However, their number begins to increase rapidly almost immediately after birth.
The formation of the alveolar layer in the lungs ends already at the age of eight. By this time, the respiratory system fully develops and becomes the same as in adults.
Preventive actions
Preventive measures to prevent breath holding in infants mainly come down to the correct arrangement of the child’s sleeping place and position:
- Make sure that your newborn does not lie on his tummy when sleeping. The best position is on the side or back;
- You should approach the choice of mattress responsibly. It must have sufficient rigidity. The use of down feather beds, pillows and blankets is not allowed. The presence of large soft toys in the baby’s bed is also prohibited;
- It is better to use a light blanket as a blanket, without lifting it above the baby’s shoulder line;
- It is necessary to control the air temperature in the room where the child sleeps. Its ideal value is 18-20ºС. Maximum – 24ºС. At higher temperatures, the brain requires more oxygen and becomes more sensitive to hypoxia;
- Smoking is contraindicated in the baby's room;
- It is better to place the crib of babies who are prone to holding their breath in the same room with their parents to make it easier to monitor the child.
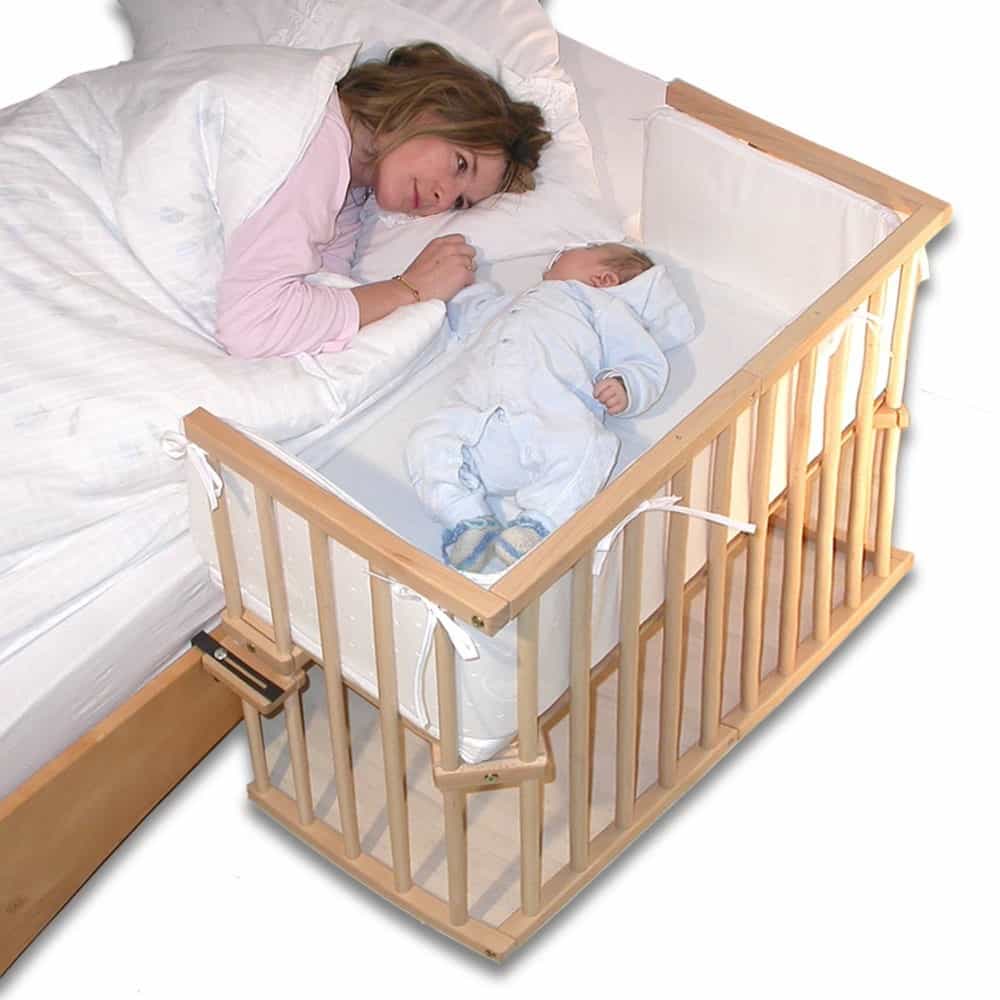

Baby sleeping in parents' room
Children who experience sleep apnea at an early age do not require any specialized treatment later on. The risk of complications is also low with careful monitoring of the baby and timely referral to specialists.
Frequent breathing of a child during sleep: normal or abnormal?
When a newborn appears in the house, parents closely monitor its behavior, sometimes trying to find symptoms of dangerous diseases. They have a lot of questions, one of which is whether rapid breathing is normal for a baby. Usually it is the mother who begins to worry that the baby is breathing too quickly.
An adult in a calm state inhales deeply and measuredly. In newborns, the upper and lower respiratory tracts are not fully formed, so they are simply not able to take a full deep breath, like adults. But since the developing organism needs a large amount of oxygen, it compensates for its lack by increasing the frequency of inhalations.
The breathing rhythm of a baby is also different from that of an adult. A child up to one year old breathes unevenly, taking two or three short breaths, and then one long one. Over time, breathing movements become more rhythmic.
If a baby breathes frequently during his sleep, this is considered normal during the first month of life. In weakened, premature babies, breathing may remain frequent and intermittent for a very long time.
INTERESTING FACTS!
- The left lung of an adult and a child is slightly smaller in size compared to the right: this frees up space for the heart.
- A baby's lungs are different in color from those of adults. Immediately after birth, they have a soft pink tint, which becomes increasingly darker over time. This occurs due to dust entering with the air.
- Scientists believe that breathing is not the only function of the lungs. Their other purpose is additional protection of the heart from mechanical damage.
Norms of respiratory rate in children up to 2 months
To find out how many breaths your baby takes during sleep, you need to carefully monitor his chest and count the number of its movements. The norm is when a newborn takes from 40 to 60 breaths per minute. For an adult, such breathing may seem too frequent. Then gradually the frequency of respiratory movements (RR) begins to decrease: a two-month-old baby takes from 35 to 45 breaths per minute, from 6 months to a year - from 30 to 40, from 2 to 4 years - 25-30, from 8 to 12 years - 20 –22, after 12 years – only 18–20 breaths. The standards can be seen in the table.
| Age | NPV per minute |
| Newborns (up to 28 days) | 40–60 |
| 2 weeks–3 months | 40–45 |
| 4–6 months | 35–40 |
| 7–12 months | 30–35 |
| 2–3 years | 25–30 |
| 5–6 years | 25 |
| 10–12 years | 20–22 |
| 14–15 years old | 18–20 |
What to do in case of an attack of apnea in children?
If signs of apnea in newborns are accompanied by pallor and/or cyanosis, decreased muscle tone (“limp”), and lack of movement, then it is necessary to shake, stir the child, and blow on his face to excite the respiratory center. In most cases, these actions help restore breathing. If they are ineffective, immediately begin resuscitation measures: open the baby’s mouth, tightly clasp his nose and mouth with your lips and blow air into his respiratory tract, while simultaneously performing chest compressions.
What should you do if a child’s apnea is caused by food particles or particles of regurgitation (vomit) getting into the “wrong throat,” especially in cases where milk “flows like a river”?
At this moment, an instant reflex closure of the glottis occurs, preventing the entry of foreign particles (milk, vomit) into the respiratory tract. Despite the fact that this reaction is defensive in nature, parents' panic can be boundless. Of course, watching your baby stop breathing and turn blue is very scary. But this condition lasts a few seconds and goes away on its own as soon as the cause that caused the respiratory arrest is eliminated. What to do in such cases?

Grab your baby firmly by the legs and turn him upside down. Milk will flow out of the throat, and eliminating the cause will lead to the opening of the larynx and restoration of breathing. Such a short respiratory pause does not harm the child, but, on the contrary, protects him from the development of aspiration pneumonia.
Sometimes the cessation of breathing lasts longer, the child turns blue, and the heartbeat becomes rare. Perhaps a few drops of milk entered the larynx and caused a prolonged cessation of breathing. What to do if a child has apnea in this case? Turn it upside down and tap on the back. Sit on a chair, place your baby with his stomach on your left thigh, head down, and tap on the back. With the index finger of your left hand, press on the root of your tongue or tickle the back of your throat to trigger a cough reflex. Coughing will help clear the airways and breathing will be restored. If vomiting occurs along with a cough, it’s also not scary. There will be a more complete release of the larynx and pharynx from foreign objects.
During an attack of apnea in children in a critical situation, it is important not to panic, but to be able to carry out resuscitation measures for a baby with respiratory arrest: closed cardiac massage and mouth-to-mouth breathing.