Pneumonia in children - symptoms:
- Headache
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Fever
- Dizziness
- Abdominal pain
- Vomit
- Chills
- Sweating
- Drowsiness
- Cough
- Chest pain
- Labored breathing
- Hard breath
- Rapid breathing
- Flatulence
- Refusal to eat
- Coughing up blood
- Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle
- Moodiness
- Sputum in the form of rust
What is pneumonia in children
Pneumonia in children is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the respiratory sections of a child’s lungs. The pathology can have a different etiology, but is always severe, and children under 3 years of age suffer from pneumonia three times more often than older children (from 3 to 16 years).
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Predisposing factors for newborns are perinatal pathologies, congenital heart and lung defects, immunodeficiency states and hypovitaminosis, as well as rickets - in such cases congenital pneumonia develops.
Predisposing factors for older children may include:
- passive smoking;
- the presence of foci of chronic infection and other pathological conditions in the body.
At the same time, you need to understand that for the onset of the disease a necessary condition is the presence of such a predisposing factor as hypothermia of the child.
Causes of pneumonia in children
There are a lot of bacteria and viruses that can cause the development of this disease in a weakened child’s body. In particular, pneumococci are the most common pathogens, but there are other bacteria that can cause this disease, and these are:
- chlamydia;
- staphylococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- streptococci;
- Proteus;
- E. coli, etc.

Etiology of pneumonia in newborns.
The pathogen enters the body through the respiratory tract, enters the lung tissue and infects the alveoli. Depending on the type of pathogen, there are several forms of pneumonia in newborns:
- bacterial and fungal;
- mycoplasma and viral;
- rickettsial;
- a disease resulting from helminth infestation.
In addition, pneumonia in children can be allergic in nature and be associated with the fact that the baby’s body is not yet fully formed and cannot adequately respond to certain irritants. Pneumonia in newborns can also be caused by exposure to a variety of chemical or physical irritants.

Separately, it is necessary to say about pneumonia in newborns and older children caused by viruses. They are also divided into several groups, depending on the type of virus, and are:
- influenza;
- parainfluenza;
- adenoviral;
- respiratory syncytial.
As mentioned above, for the development of pneumonia in a child, predisposing factors must be present. The following states can be added to those listed earlier:
- prematurity;
- hypovitaminosis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- birth injuries.
And all children are given vaccinations at birth, which are designed to protect the child from various pathologies. And such a vaccination can cause a decrease in the protective reaction of the baby’s body, as a result of which pneumonia can develop.
Prevention of pneumonia in children
Prevention of pneumonia includes the following components:
- The use of vitamin complexes and restoratives to improve the condition of the immune system.
- Walks in the open air.
- Ventilation of the room.
- Isolating the child from sick people.
- Breathing exercises.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Vaccination. Vaccinations are indicated for children who often suffer from bronchopulmonary pathologies.
It is very important to choose the right places for games and walks. It is imperative to protect children from exposure to cigarette smoke, which negatively affects the condition of the lungs and the entire body.
Pneumonia is a dangerous disease that often develops in childhood. Pneumonia can have serious health consequences. To avoid this, you need to consult a doctor at the first manifestations of the disease.
Classification of the disease
In modern medical practice, pneumonia in newborns is classified not only by etiological signs, but also by causal ones. Taking into account the cause of pneumonia in a child, pneumonia is divided into primary and secondary. Primary occurs when an infection enters the baby’s body, and secondary occurs as a consequence of other foci of infection existing in the child’s body.
In addition, the disease can be classified according to the nature of its course. It could be:
- acute pneumonia in children;
- subacute form of the disease;
- protracted.
According to the degree of damage to the lung tissue, several types are distinguished - the disease can affect one lung or two at once (one or two-sided pneumonia) and most often it is the right one that is affected - right-sided pneumonia develops.

Symptoms of pneumonia in children
Depending on the type of disease, signs of pneumonia in children can be very diverse. Nevertheless, there are some symptoms characteristic of each type of pneumonia, these are symptoms of general intoxication:
- heat;
- drowsiness and weakness;
- refusal to eat;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- unreasonable sweating;
- rapid, heavy breathing;
- headache (moody in young children due to pain symptoms).
To distinguish the signs of pneumonia in a child, you need to know how this or that type of pneumonia manifests itself:
- focal pneumonia in children. A disease that affects only a small area of the lung. It is the mildest form of the disease and can sometimes occur hidden, without any particular symptoms or with unexpressed symptoms. The source of infection can be located in any part of the lung - often in young children, hilar pneumonia occurs, which is characterized by damage to the root of one or two lungs, and is characterized by severe intoxication and severe symptoms;
- segmental pneumonia in children. We talk about this disease when individual segments of the lung are affected. The disease begins abruptly and is characterized by an increase in temperature to high numbers and a rapid increase in symptoms of intoxication. A newborn's cough with pneumonia is absent or mild, while the baby feels pain in the chest or abdomen and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis of this disease is carried out on the basis of radiography methods - the x-ray shows individual affected lobes merging into a single segment;
- lobar pneumonia in children. A disease in which the process involves not only a lobe of the lung, but also part of the pleura. As with segmental, the onset of the disease is acute. The temperature rises, the child complains of dizziness and nausea, and chills are observed. Newborn babies often cry, breathe heavily and their temperature also rises, which can reach critical values. Cough with this type of pneumonia in newborns is rare, and in the first 3 days it may even be completely absent, then it becomes dry, and after a few days rust-like sputum appears. Often the course of the disease is associated with the appearance of abdominal syndrome (especially in young children), which is manifested by flatulence and vomiting. Only an experienced doctor can diagnose the disease - based on X-ray data, anamnesis and physical examination of a small patient. A blood test taken from a child with lobar pneumonia will show a shift in the leukocyte count to the left, an acceleration of the ESR;
- interstitial pneumonia in children. This type of disease is less common than others - it often occurs in premature babies, as well as in newborns with immunodeficiency conditions. In addition to the symptoms described above (hyperthermia, excessive sweating, etc.), interstitial pneumonia of newborns is characterized by changes in the gastrointestinal tract, a drop in blood pressure and disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. This type of pneumonia is characterized by a debilitating cough with scanty sputum, and you can also visually observe swelling of the chest.
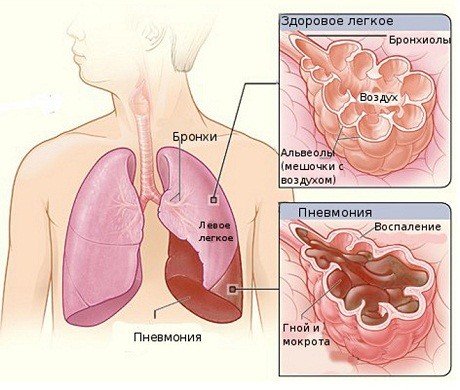
Focal pneumonia in children
Diagnostics
As mentioned above, one or another type of pneumonia is diagnosed in infants and older children on the basis of bacteriological tests, radiography and local examination. In particular, they check the temperature reaction, the presence of signs of respiratory failure (shortness of breath, cyanosis of the mucous membranes and skin).
Patients are prescribed a blood test, which notes leukocytosis, increased ESR and neutrophilia. X-rays confirm the damage to a certain lobe, segment or the entire lung.
It should be noted that the most severe prognosis for the course of the disease is in newborns, since their body is weak and cannot cope with the infection on its own. Moreover, such children often experience destruction of lung tissue, which can lead to death. Therefore, the earlier pneumonia is detected in a small child and the sooner its treatment is started, the better the prognosis.
Possible complications
If treated promptly, pneumonia usually has a favorable prognosis and does not lead to complications. However, sometimes unpleasant consequences arise. These include the following:
- sepsis;
- pleurisy;
- respiratory failure;
- pulmonary abscess;
- problems with the heart.
Sometimes negative consequences include diarrhea and skin rashes. Similar manifestations are observed after the use of certain medications.
Treatment of pneumonia in children
Newborns suspected of having this disease are subject to immediate hospitalization. The hospital also provides treatment for pneumonia in children with moderate and severe forms of the pathology. Children aged 3 years and older in the presence of the initial stage of the disease with mild symptoms can be treated at home, with the necessary medical supervision several times a week. It should be remembered that the consequences of pneumonia can be the most severe - often, if not treated in a timely manner, children experience damage to internal organs and the central nervous system.
Treatment of the disease should be comprehensive and include:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- normalization of diet and drinking regime.
The main place in the treatment of pneumonia is given to antibiotics. Within a day after the start of treatment, the condition improves, provided that the drug is selected correctly, taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to it. The treatment process takes from 6 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the little patient’s condition.
If the disease is caused by viruses, antiviral drugs are prescribed. Immunostimulants and mucolytics are also indicated. Antipyretic drugs are prescribed if the child’s temperature rises above 38.5.
Depending on the symptoms, other medications may also be prescribed to maintain and protect other organs and systems. For example, antihistamines, corticosteroids, cardiac glycosides. Breathing exercises are mandatory, helping the child’s lungs restore their functions (for children over 3 years old) and massage, which is suitable for children of any age. Sometimes it is necessary to take medications that reduce bronchospasm - in this case, the child is prescribed aminophylline.
The prognosis for treating the disease is favorable, provided that treatment is started in the early stages of the disease. The child is discharged from the hospital after completing the course of antibiotics, but at home he still needs symptomatic treatment to eliminate residual effects.
In addition, prevention of pneumonia in children plays an important role in preventing relapses of the disease. Doctors recommend using traditional medicine in the post-clinical period to eliminate the consequences of the disease and increase immunity. In particular, inhalations with fir oil, consumption of radish with honey, cabbage juice with honey as an expectorant, a mixture of butter with propolis as an immune-strengthening agent, etc., help well.
Antibacterial treatment
The mainstay of treatment for pneumonia is antibiotics. To cope with the disease, parents must strictly follow all the pediatrician’s instructions regarding the use of these products.
Such medications must be taken strictly according to the clock. If the medication needs to be taken twice a day, the break between doses is 12 hours. If the product is taken 3 times a day, the interval is 8 hours.
Typically, drugs from the penicillin or cephalosporin categories are used to treat pneumonia. They are discharged for 7 days.