What should be the blood pressure in children, its norm is in the table
Each age has its own blood pressure (BP) parameters.
What is the normal blood pressure in children? The table below shows as fully as possible. At a young age, a person has quite low blood pressure compared to the later period. This is noted because in children the walls of blood vessels are much more elastic, their lumen is wide, and the capillary network is large. Systolic pressure refers to the way blood pushes against the walls of the vessel when the heart muscle contracts. Diastolic shows how the blood presses on the vessels when the heart muscle relaxes. Indicators are distinguished by the tone, elasticity and peripheral resistance of blood vessels, and by the functioning of the kidneys, since they are responsible for the regulation of blood pressure. The indicators are influenced by weight, nutrition, genetic predisposition and height.
Indicators in newborns
To determine what pressure a child should have, let's look at the table.
| How many years | Arterial D (mm Hg) | |||
| Systolic | Diastolic | |||
| minimally | maximum | minimally | maximum | |
| up to 2 weeks | 60 | 96 | 40 | 50 |
| 2-4 weeks | 80 | 112 | 40 | 74 |
| 2-12 months | 90 | 112 | 50 | 74 |
| 2-3 years | 100 | 112 | 60 | 74 |
| 3-5 years | 100 | 116 | 60 | 76 |
| 6-9 years | 100 | 122 | 60 | 78 |
| 10-12 years | 110 | 126 | 70 | 82 |
| 13-15 years old | 110 | 136 | 70 | 86 |
In this case, the numbers may differ from the normal blood pressure within a few mm Hg. Art. This does not mean the presence of health problems. Blood pressure can change even within a few hours and several times a day, depending on the temperature and weather. After eating, it increases, when sleep ends, it decreases.
Normal blood pressure in a child should fit into the formula 76/0.5 from systolic D. By the end of the first month of life, systolic pressure approaches 70-90 mm Hg. Art., and diastolic - 45-60 mm Hg. Art.
A newborn is considered an infant in the first 28 days of life. Later, his blood pressure is calculated using the formula 76 + 2m / 0.5 from systolic. In this case, the systolic will be calculated as 76 + 2m, where m is the number of months, and DBP = 0.5 of SBP. On average it is 80-11/40-74 mm Hg. Art.
Blood pressure is measured in infants using a special children's cuff. Before reaching 1 month, the width of the inner chamber of the cuff does not exceed 3 cm, after 1 month - no more than 5 cm. Children's blood pressure is measured three times with an interval of several minutes. The most correct ones are taken to be the minimum indicators. Newborns and infants under 1 year of age are measured in a supine position. In the first days, only SBP is determined by palpation.
Upon reaching one year of age, the average blood pressure is: 80-100/50-60 mm Hg. Art.
Normal blood pressure in children from one to 3 years of age
The blood pressure norm at this age can also be calculated using the formula: 90+2g, where g is the age in years. Practice shows that blood pressure in children from 1 to 3 years old can range from 110/60 to 112/74. It is worth keeping in mind that one-time pressure surges are most often caused by external factors, but deviations from the norm for 2-3 weeks (with regular measurements) indicate some kind of disturbance in the body.
Norms for children over 1 year of age
Using the formula, you can calculate child pressure in children over 1 year old: 90+21/60+1, given that 1 is age, and SBP = 90+21, DBP = 60+1. In children at this age, the increase in parameters occurs more slowly than before. Upon reaching 2 years of age, the normal blood pressure in children is as follows: SBP 90-105, DBP 60-65 mm Hg. Art.
You can determine the norms using centile tables by age. For indicators, weight and height standards are taken. From the 10th to the 90th centile, blood pressure levels are considered normal. A level of 90-95 centiles indicates borderline hypertension, and more than 95 indicates arterial hypertension.
Between the 5th and 10th centiles, borderline hypotension is established, below 5 - arterial hypotension.
Upon reaching 2-3 years of age, the average SBP is 100-112 mm Hg, DBP is 60-74 mm Hg. An increase is observed only when the digital indicator increases steadily for 3 weeks.
Blood pressure and pulse in infancy
The correspondence of indicators to the norm of pressure and pulse in children by age allows us to judge the condition of the baby’s heart and blood vessels. At the same time, in pediatric practice all norms are conditional. The norm is always purely individual, this is especially true for children. As a rule, blood pressure in infancy, that is, from one to twelve months, is 90-112 at 50-74 mmHg. Art. Up to a year, normal blood pressure in children can be calculated using the formula: systolic (upper) = 76 + 2 x T (month of life), diastolic (lower) = half or a third of systolic. Normal physiological fluctuations are thirty units upward.
Indicators for school-age children
At this time, the lower parameters do not change, but the upper ones become higher. Normal blood pressure in children aged 6 to 9 years is 100-122/60-78 mmHg. Art. Since children at the beginning of school life may have heavy loads, physical activity becomes less, and the load on the nervous system increases, deviations from the norm are considered acceptable. But if they are observed in combination with fatigue and constant headaches, you should consult a doctor.
When determining what blood pressure is considered normal, life stages must be taken into account. The next moment of growing up is puberty. At this time, changes in blood pressure are observed. In girls, such phenomena occur more often, since they experience maturation earlier than boys. The average parameters during this period are considered to be 110-70 and 126-82 mmHg. Art. It is possible to increase the top number to 120.
Hormonal changes during growing up bring their own adjustments. Study loads and other phenomena that cause juvenile hypertension or hypotension increase. The normal level is 110-70/136-86 mm Hg. Art. If there are changes, they are accompanied by loss of consciousness - fainting, pulse fluctuations, headaches. In case of these phenomena, it is better to consult a doctor.
Height and weight chart for girls from 1 to 10 years old
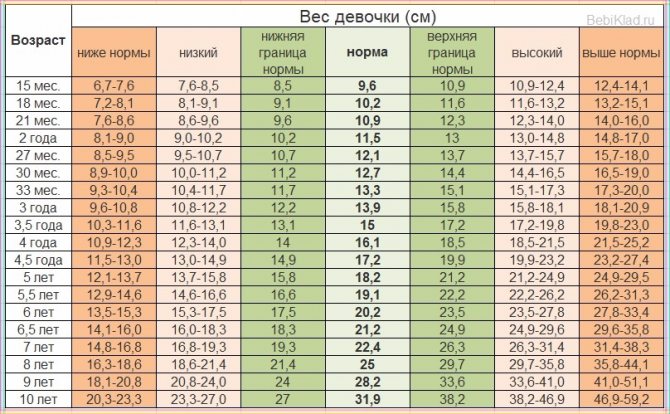
The growth of children begins to slow down as soon as the kids turn one, so for children from one to three years old, the norms are no longer determined monthly, but every three months. For children from 3 to 7 years old - once every six months, and for children aged from seven to ten years - the norms change once a year.
By one year and three months, a girl should normally grow to 77.5 cm and weigh 9,600 grams. The lower limits of the norm: 74.83 (height in centimeters) and 8,500 (weight in grams), the upper limits: 80.3 // 10,900.
The next reference point is defined for the age of one year and six months. Norm: 80.65//10.200. Lower limit: 77.7//9.100. Upper: 83.5//11.600.
At one year and nine months, the norms for girls are 83.65//10.900. Lower limit of normal: 80.6//9.600. Upper limit: 86.7//12.300.
By the age of two, girls normally grow to 86.4 cm and weigh 11,500 grams. The lower limit of the norm: 83.2//10.200. Upper limit: 89.6//13.000.
Average height and weight for babies aged 2 years 3 months: 88.3/12.100. Lower limit: 84.8//10.700. Upper limit: 91.7//13.700.
Girls at 2.5 years old should grow to 90.7 cm and weigh 12,700 grams. The lower limit of the norm: 86.9//11.200. Upper frames: 94.3 // weight 14.400.
At 2.9 years, the average values are: 92.9 // 13.300. Lower limits: 89.3//11.700, upper limits: 96.6//weight 15.100.
Three-year-olds should be 95 cm tall and weigh 13,900 grams. Data below 91.3//12.200 are assessed as low, and figures above 98.8//15.800 are assessed as high.
At 3.5 years old, the standards for a girl are: 99//15,000. The lower line is 95//13.100, and the upper line is 103.1//17.200.
Average height and weight for a four-year-old girl: 102.6//16.100. The lower limits of the norm: 98.4//14.000, and the upper limits of height and weight: 107.1//18.500.
At 4.5 years old, the standards for a girl are: 106.2//17.200. Lower limits: 101.6//14.900, and upper limits: 110.7//19.900.
Average height and weight for a five-year-old girl: 109.4//18.200. The lower limits of the norm: 104.7 // 15.800, and the upper ones: 114.2 // 21.200.
At 5.5 years old, girls should grow to 112.2 cm and weigh 19,000 grams. Parameters less than 107.2 // 16.600 are considered low, and indicators more than 117.1 // 22.200 are considered high.
Standards for six-year-olds: 115.1//20.200. Lower limits: 110//17.500. Upper – 120.2//23.500.
By the age of 6.5 years, girls grow to 118 cm and weigh 21,200 grams. The lower limits at 6.5 years are 112.7 // 18.300, and the upper limits are 123.3 // weight 24.900.
Average height and weight for seven-year-old girls: 120.8 and 23,000. Lower limits: 115.3//21.300, upper limits: 126.3//26.300.
In children over seven years of age, anthropometric indicators are monitored once a year. The standards for eight-year-old girls are 126.6//25,000. The lower limit for eight-year-olds will be 120.8 and 21.400. The upper limit is 132.4//30,000.
If deviations from the norm are observed
Low blood pressure, especially if it drops rapidly, disrupts the metabolic process in the body, reduces renal activity, and creates a risk for liver function. Headaches may occur, fatigue increases, even to the point of fainting when rising from a lying position. If such phenomena occur, you should undergo examination or increase physical activity. You should not resort to medications or other means of increasing tonometer readings on your own; this can lead to a worsening of the condition.
In cases with high blood pressure, it is also worth monitoring the condition of the body, because high levels are even more dangerous. Such phenomena are observed due to a reaction to stress or excess load.
Hypertension can be primary or secondary. The following factors are characteristic of the primary one:
- changes in hormonal levels during puberty;
- moments of stressful situations;
- sleep disturbances during stress at school;
- highly active sports activities;
- in case of conflicts and disputes at school or at home;
- diseases of the cardiac system, abnormalities of the kidneys, diseases of the endocrine system.
For secondary hypertension there are:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- entry of toxins into the body;
- brain diseases.
Low blood pressure and hypotension have several causes:
- ARVI with complications in the bronchi;
- trauma during childbirth;
- allergy;
- lack of vitamins;
- anemia;
- diabetes;
- defect in the development of the heart, myocarditis.
When it is necessary to reduce blood pressure in children, a cloth is soaked in apple cider vinegar and applied to the heels.
When you read the table, you can easily calculate the normal blood pressure in children. It is necessary to pay attention to measurement time, deviations due to weight and height. Changes accompanied by serious health problems should be checked by a specialist. In the case of age-related deviations from the norm, it is important to maintain a normal general condition, adhering to the general rules for organizing sleep, rest and exercise.
Causes and symptoms of low blood pressure in children
During puberty, adolescents often complain of deteriorating health. One of the reasons for this condition is considered to be low blood pressure. However, a decrease in tonometer readings can also be considered as a variant of the norm if the child is active, feels well and has no health complaints. The physiological norm here is associated with the structural features of the nervous system, when its parasympathetic department is more active.

The age of 12–13 years is a period in children when active maturation of all internal organs and systems occurs, hormonal levels change, and the puberty phase begins
You can suspect incipient health problems based on a number of negative signs:
- weakness, complaints of fatigue and lack of the child’s usual activity;
- dizziness and loss of appetite;
- regular pain in the head;
- sudden attacks of nausea, pale skin, increased sweating;
- tendency to faint.
Low blood pressure in children aged 12 years is observed for a number of reasons. This may be a consequence of somatic and infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy, poisoning, alcohol abuse or smoking. Also, low tonometer levels can signal a large amount of liquor fluid inside the skull, the presence of chronic foci of infection in the body and hormonal imbalance.
The psycho-emotional sphere of the child also plays an important role in lowering blood pressure.
If he is stressed, often gets offended and cries, and has problems communicating with peers, the teenager clearly has symptoms of low blood pressure. Also, a similar problem is often identified in children growing up in unfavorable social conditions, in single-parent families, where the child is forced to work a lot and have little rest.
What is diastolic pressure
After a period of contraction of the heart muscle, the aortic valve closes securely, and its walls begin to gradually displace the resulting volume of blood. It slowly spreads through the capillaries, losing pressure. By the end of this stage, diastole, its indicator decreases to the minimum numbers that are considered to be diastolic pressure.
There is another interesting indicator that sometimes helps doctors determine the cause of the disease - the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure. It is usually 40-60 mm Hg and is called pulse pressure.
What blood pressure should a child have?
Blood pressure increases quite significantly in the first year of a child’s life. Until the age of five, boys and girls have the same blood pressure. From five to nine years old it is slightly higher in boys.
Having reached values of 110 – 120 / 60 – 70 mm Hg. Art., blood pressure is then maintained at this level for a long time. With old age, the level of maximum pressure increases more in women than in men. Pulse pressure increases. After 80 years, blood pressure in men stabilizes, and in women it even decreases slightly.
Systolic (upper) blood pressure (SD) in children under 1 year of age can be calculated using the formula:
- 76 + 2n (n – number of months)
In children over one year of age, upper blood pressure is calculated using the formula:
(The upper limit of normal systolic blood pressure in children over one year of age is 105 + 2n, the lower limit of normal is 75 + 2n)
Diastolic (lower) blood pressure (BP) in children is:
- Under the age of one year – from 2/3 to 1/2 of the maximum DM,
- Over the age of one year – 60 + n (n – number of years).
(The upper limit of normal diastolic blood pressure in children over one year of age is 75 + n, the lower limit of normal is 45 + n).
| Age | Blood pressure (mmHg) | |||
| Systolic | Diastolic | |||
| min | max | min | max | |
| up to 2 weeks | 60 | 96 | 40 | 50 |
| 2-4 weeks | 80 | 112 | 40 | 74 |
| 2-12 months | 90 | 112 | 50 | 74 |
| 2-3 years | 100 | 112 | 60 | 74 |
| 3-5 years | 100 | 116 | 60 | 76 |
| 6-9 years | 100 | 122 | 60 | 78 |
| 10-12 years | 110 | 126 | 70 | 82 |
| 13-15 years old | 110 | 136 | 70 | 86 |
Blood pressure in early childhood
Normal blood pressure and pulse in a child aged one year are 110-112 mm Hg. Art. by 60-74 mm. Such indicators will last up to three years, that is, the entire early age of the child. For babies older than one year, the normal pressure can be calculated using the formula: 90 + 2 x T (year of life) = upper, 60 + T (year of life) = lower. Normal fluctuations are up to thirty units upward.
At two or three years old, the baby is constantly moving, expending a significant amount of energy. The heart muscle begins to contract with renewed vigor, the blood moves faster to fully supply all tissues and organs with the necessary substances. Even at such an early age, blood pressure will depend on heredity, the state of the circulatory system and physical activity.
In preschoolers, the body continues to develop, so slight fluctuations in indicators are possible. The normal blood pressure and pulse rate for 4-year-old children is 100-110 per 65-75 mm, 106-115 heart beats per minute. Blood pressure is also within the normal range from 86 to 126 beats. Many preschoolers attend kindergarten and are prone to infectious diseases that affect vascular tone. Severe stress, which predictably leads to vasospasm, is distance from home.
Norms of blood pressure in children
There are blood pressure indicators that are considered normal for a certain age. In newborn babies up to about three weeks of age, upper and lower pressures are normally relatively low.
- The permissible norm for upper pressure in a newborn baby is in the range from sixty to ninety-six millimeters of mercury, and the lower forty to fifty mm Hg. Art.
- Normal blood pressure in a child aged 12 months is from 90-112 to 50-74.
- For a 2-3 year old child, the upper blood pressure is 100-112, the lower 60-74.
- For a five-year-old child, an upper (systolic) pressure of 100-114 mmHg is considered normal. Art. and lower (diastolic) - 60-74 mm Hg. Art.
- For children six to seven years old, upper pressure should be in the range of 100-116 mm Hg. Art., and the lower in the range of 60-76 mm Hg. Art.
- For children eight to nine years old, the normal range of upper (systolic) blood pressure is 100-122 mm Hg. Art. and lower (diastolic) - 60-78.
- At ten years of age, normal blood pressure is, for the upper values, 110-124 mm Hg. Art., and for the lower ones - 70-82.
- For twelve years, these figures are for upper pressure 110-128 mm Hg. Art., and for the lower one - 70-84.
- At thirteen to fourteen years of age, upper pressure should be in the range of 110-136 mm Hg. Art., and the lower one is 70-86.
Normal blood pressure in newborns
Doctors record the lowest pressure values in newborns, that is, in the first four weeks of a child’s life. Children's pulse and blood pressure begin to be measured already in the maternity hospital. Modern medicine accepts as the norm the values recorded in 90-94% of young patients. Immediately after birth, the pressure will be approximately 60-80 at 40-50 mmHg. Art. Normal pulse is about 140 beats. Subsequently, the pulse will decrease slightly (up to 130 heart beats per minute). which will last for up to one year.
Thus, in the neonatal period (the first two weeks of life) systolic pressure is 60-96 mm Hg. st, diastolic - 40-50 mm. The indicators will grow as quickly as possible over the next two weeks. On average, blood pressure can increase by 2 units per day. In the future, the growth rate will slow down. During the newborn period (from two to four weeks), the pressure will increase slightly and will be 80-112 per 40-74 mmHg. Everything that is within these boundaries is normal physiological fluctuations.
What heart rate should a child have?
The normal pulse rate in children is primarily determined by the age of the child: the older he is, the lower the heart rate. In addition to age, the pulse rate depends on the general health of the child or adolescent, the fitness of the body, body temperature and the environment, the conditions in which the count is made, as well as many other factors. This is explained by the fact that by changing the frequency of contractions, the heart helps the child’s body adapt to changes in the internal or external environment.
You can count the pulse in 15 seconds and then multiply the result by 4. But it is best to count the pulse in a minute, especially if a child or teenager has an arrhythmia. The table shows normal heart rate values for children of different ages.