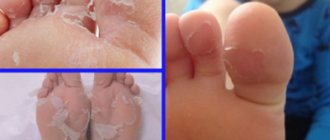
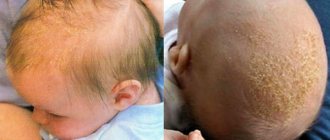
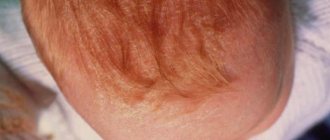
Scrofula is familiar to everyone from the well-known proverb - when they are plagued by failures, they say: “Then diarrhea, then scrofula.” However, few parents imagine the symptoms of scrofula in children and know how to deal with it. Although many babies after birth have yellowish crusts, peeling and weeping on their heads, which are scrofula. Such symptoms are often attributed to diathesis.
At first glance, it seems that the disease is not serious and will go away on its own, but this is not at all the case. Scrofula needs to be treated, and the sooner the better.
Scrofula is most common in infants
What is scrofula, and for what reasons does it occur?
Scrofula is a skin disease caused by the tubercle bacillus. It most often affects children under 10 years of age. Very rare in adults.
Scrofula's symptoms are similar to allergies and diathesis, so it is important to carry out a differential diagnosis. The danger of scrofula is that the pathogen is associated with Koch's bacillus, which causes tuberculosis. Some experts believe that the advanced stage of the disease can develop into this dangerous disease. However, scrofula is not contagious, and sick children are not isolated. They can safely play with their peers and attend kindergarten.
Why does this disease occur? Experts have conflicting opinions on this matter. Some believe that scrofula is associated with disorders of the circulatory system, others - with metabolic disorders.
Sometimes this is only a symptom of another disease, so it is important not to start treatment on your own, but to consult a doctor.
Possible causes of scrofula:
- unhealthy lifestyle of the mother during pregnancy;
- intrauterine infection in combination with poor baby hygiene;
- late pregnancy;
- lack of vitamin D;
- excessive sweating;
- decreased immunity;
- violation of sanitary standards, lack of bathing;
- eating large amounts of sweets;
- feeding infants with non-adapted formulas;
- malnutrition, deficiency of vitamins, minerals and microelements;
- illness of syphilis or tuberculosis in close relatives.
The skin behind the child’s ear is peeling – Pediator
Various factors can cause the skin behind a child's ears to crack.
If parents pay attention to such a symptom in a timely manner and seek help from a specialist, then there will be no special problems with treatment. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe therapy with appropriate medications.
Self-medication for pathologies with such a symptom is not recommended, as this can negatively affect the child.
Causes of cracks behind the ears
The cause of cracks behind the ears in a child may be too hard water.
Often parents are faced with the problem of cracks behind their child’s ears. The main factors that provoke their appearance include:
- Sudden changes in ambient temperature and insufficient humidity.
- Swimming in hard water.
- Genetic predisposition to allergic reactions.
- A diet that includes frequent consumption of a variety of sweets and rich foods. If a woman during pregnancy or breastfeeding is addicted to allergenic foods, this can negatively affect the baby.
- Weakened immune system of the child's body.
- Functional disruptions of the digestive system and metabolism.
- Mechanical damage in the area behind the ear, accompanied by the penetration of a fungal infection.
- Hygiene products and synthetic detergents, the composition of which can cause an allergic reaction (shampoo, soap, gel, powder).
- A baby's delicate skin and excess weight can cause diaper rash behind the ears due to constant rubbing.
Such negative factors can affect the occurrence of the following diseases characterized by the presence of this symptom:
- exudative diathesis;
- scrofula;
- eczema;
- dermatitis;
- otomycosis.
If the crack gets wet
When a child begins to get wet behind the ear, this is a clear symptom of the presence of a pathological process in the body of a dermatological nature.
Weeping diathesis
This disease is often diagnosed in infants and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- scaly crusts of yellow-gray color;
- rash;
- redness of the skin behind the ears, followed after a few days by the appearance of blisters filled with liquid;
- constant itching and burning;
- pain in the area of the burst blister.
Weeping diathesis occurs in a child due to an allergic reaction to food or mother’s breast milk. In this case, parents urgently need to identify the allergen and eliminate it from the child’s life.
Important: Unconsciously scratching the wet area behind the ear can cause infection in this area.
Allergy
Due to contact of the child's parotid area with an irritant contained in a hygienic detergent, the temples of glasses or the metal of earrings, an allergic reaction on the skin may occur.
Not least important in the occurrence of this pathology is the genetic factor. Children of parents with allergies are often more predisposed to allergies of various forms.
Children are diagnosed with a chronic pathology such as gneiss.
In this case, the skin behind the ear is susceptible to the following symptoms:
- dryness;
- burning and itching;
- redness due to inflammation;
- the lobe and area behind the ears are peeling;
- if spots become wet behind the ear, this indicates an acute course of the disease. Swelling and crusts appear;
- cracks.
As in the previous case, it is necessary to remove all objects in contact with the affected area and consult a dermatologist about medications to eliminate the symptoms that appear.
Scrofula
This non-infectious disease manifests itself in children under 10 years of age and is considered the initial stage of atopic dermatitis. Basically, the affected area is considered to be the area behind the ears, but if the process is advanced, scrofula can also appear on other areas of the skin (forehead, cheeks). The main symptoms are:
- the formation of whitish-gray spots behind the ears, gradually spreading to a large area of the head;
- unbearable itching;
- peeling;
- rash and the appearance of lichen;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the spots are covered with golden-colored crusts. When they peel off, a wet, reddened skin remains, so the child’s earlobe may become wet.
The main reasons for the manifestation of such a disease in a child are considered to be an abundance of sweets, insufficient walking time, the presence of cancer, syphilis or tuberculosis in parents, a lack of vitamins and a weakened immune system.
The sooner parents see a doctor, the easier it will be to get rid of this pathology.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the treating specialist will conduct an examination and clarify with the parents the possibility of a hereditary factor. To understand the cause of cracks behind the child’s ear and make the correct diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe certain examinations:
- a general blood test to determine the presence of inflammation;
- bacterial culture of ear secretions. It is taken if otitis is suspected in order to clarify the type of pathogenic microorganism and the necessary antibiotic to combat it;
- allergen detection tests;
- a smear from the skin behind the ear to identify the fungal parasite and, if necessary, its sensitivity to drugs;
- immunogram.
Based on the research results, the doctor selects the necessary medications for therapy.
How to treat
After determining the cause of the crack behind the child’s ears, the following types of medications are prescribed:
- antihistamines in the form of tablets (Suprastin, Loratodin) or drops (Tavegil, Parlazin) to relieve itching;
- ointments with a drying effect (zinc ointment) will help get rid of weeping lesions;
- after water procedures, it is recommended to treat the area behind the ears with Bepanten or creams with depanthenol for a healing effect;
- Corticosteroid ointments can be used to treat severe cases. From 6 months, children are recommended to apply Celestoderm B;
- if an infectious infection occurs, then antibiotics are added to therapy. At the same time, it is important for the child to combine such treatment with taking medications to restore intestinal microflora (Linex, Bifiform);
- immunomodulators and vitamins;
- Weeping cracks should be treated with Levomekol;
- crusts are removed by preliminary softening with prednisolone ointment;
- fungal infection is treated with appropriate medications.
Physiotherapy through the use of ultraviolet rays has a wound-healing and anti-inflammatory effect.
As folk remedies for scrofula, you can use lotions made from string and chamomile, and for weeping diathesis, a bath with oak bark is an excellent remedy.
It is important during treatment to carefully select food products and maintain ear hygiene.
Symptoms of skin disease
- the appearance of red diaper rash behind the ears and under the hair, after some time they become yellow, but the hair does not fall out or break (we recommend reading: reasons why hair falls out in a 6-year-old child);
- as the disease develops, the area of the lesion increases, it spreads to the neck, face, arms and legs;
- the skin becomes cracked, becomes wet and peels (we recommend reading: what to do if the skin on the head of a 5-year-old child is peeling?);
- severe itching;
- peeling of the earlobes;
- bloating, digestive system disorders;
- inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes (we recommend reading: what causes inflammation of the lymph nodes in a child’s neck?);
- joint pain, swelling;
- redness of the eyes.
Causes of crusts and peeling
The main provoking factors that can lead to the formation of scales and cracks behind the ears in a child include:
- Neglect of hygiene rules.
- Staphylococcus. If hygiene standards are observed, but the problem does not disappear, the help of a pediatrician will be required. The bacterium is detected using a special analysis - microflora culture. Staphylococcus is an opportunistic microorganism that is present in most people. If the body's protective functions work normally, and hygiene procedures are carried out regularly, correctly and in a timely manner, the bacterium does not cause harm. In the opposite situation, its active reproduction and spread occurs.
Important! If, in addition to crusts and peeling, the baby has a fever, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Redness and pus formation are often observed around the crusts. With such symptoms, it is forbidden to take a bath or apply heat to the source of inflammation. Treatment is carried out using antibacterial agents, the areas behind the ears are treated with antiseptic ointments.
- Allergic reaction. Often a newborn's ears become flaky due to certain types of allergies. Most often, a negative reaction is associated with the consumption of certain products. The most common allergens are:
- Chocolate, honey;
- Citrus;
- Other fruits (grapes, persimmons, bananas);
- Nuts;
- Melon, tomatoes, eggplants, carrots, beets;
- Milk and dairy products;
- Cocoa, coffee, tea;
- Eggs;
- Meat;
- Seafood;
- Mushrooms.
If the baby is on IV, it is better to switch to another milk formula, and also exclude complementary foods from the diet. If negative symptoms persist, other allergens may be the cause of the appearance of crusts:
- Various baby care products (ointments, powders, shampoos);
- Washing powder and other household chemicals;
- Dust;
- Animal wool;
- Plant pollen;
- Poplar fluff;
- Mom's new cosmetics;
- Toys.
Features of treatment for children of different ages
As a rule, therapy for this disease does not depend on the patient’s age. If you suspect scrofula or diathesis, the skin is dry, cracking, or wet wounds appear behind the ears, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible (see also: dry skin on the legs and arms of a child). He will refer you for consultation to a pediatric dermatologist and allergist.
Experts will determine the cause of the sores and cracks. A special diet will be developed.
The next stage is the prescription of medications to relieve itching and remove crusts. If left untreated, a secondary infection may develop due to constant trauma to the skin when scratching; the wound behind the ears rots and enlarges. With timely treatment, scrofula can be cured in a short time.
It is important to strengthen the child's immunity. The defenses of a healthy baby’s body are able to cope with scrofula on their own.
Drug therapy
- Ointments. For the treatment of scrofula, Sudocrem, Tsindol, zinc ointment, Topicrem, Drapolene are used. They dry the wet crusts well, which then come off easily. Typically, these products are applied 2-4 times a day to clean skin, without washing off for several hours.
- To moisturize the skin with cracks and dryness, Bepanten is used.
- Cauterization with Fukortsin. This is a crimson-colored drug that effectively disinfects and cauterizes disease-affected skin. The child may complain of a burning sensation in the areas treated with Fukortsin. It is used if there is no improvement after 3-4 days of treatment with ointments.
- Enterosgel and other sorbents are used to remove toxins and cleanse the body. They also remove allergens.
Hygiene procedures
When scrofula does not cause symptoms other than crusts on the scalp and does not progress, it may not be treated. In this case, they get by by simply combing out the scab, that is, the crusts. Before this, the skin is generously lubricated with nourishing baby cream or Vaseline oil, and they are combed out with a regular comb. When removing crusts from a child under one year old, you need to be careful not to damage the fontanel.
When drug therapy is carried out, before using ointments it is important to thoroughly clean the skin and carry out other hygiene procedures. It is useful to take antiseptic baths with herbal decoctions.
Special diet
Strong allergens must be excluded from the diet of a child or nursing mother: candy, chocolate, citrus fruits, nuts, milk, etc. For scrofula, a food diary is kept, where parents write down everything that their child ate. This will allow you to track which products the reaction occurs to. You are allowed to eat low-fat broths and meat, hypoallergenic vegetables and fruits, and water-based porridge. Subsequently, other foods are gradually and carefully introduced.
Newborns and bottle-fed infants must be given only adapted formulas. It is unacceptable to feed your child goat or cow milk, as it causes very severe allergies.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers an extensive list of recipes against scrofula. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.
Due to its effectiveness, baths with chamomile decoction are in great demand in the treatment of scrofula.
For scrofula in a child, baths with:
- chamomile decoction;
- oak bark;
- walnut leaves;
- decoction of currant leaves;
- tea tree essential oil.
An infusion of string is used internally and externally. It dries the skin perfectly and has an antiseptic effect.
What to do if a child’s earlobes crack?
My nephew's ears are wet and cracks have appeared near his earlobe.
He is one and a half years old. It happens that the cracks are even bloody. We treat it with baby cream, but it does not heal the wounds. Cracks appeared in winter, but were not observed in summer. Could this be a manifestation of diathesis or something serious? What could it be? This could be a food allergy, often starting when you were pregnant. It’s better to go to a good dermatologist and do not self-medicate, so that later this problem does not develop into a more complex form, even eczema. While this is a mild form, it may signal more serious problems.
Our pediatrician told us that peeling often occurs behind the ears in children. They lie around a lot, rubbing these places. We, too, when I was little, often peeled off. And even now it happens sometimes (although you’re already a year and a half old, it should have passed). We applied bepanthen. Give it a try. Or zinc ointment - it dries it out. In general, both of these remedies are harmless and are most often found in the medicine cabinet of young mothers. If it doesn’t help, then a pediatrician or a dermatologist.
I don’t want to scare you, but peeling behind the ears with the formation of weeping, non-healing wounds can be signs of a very unpleasant disease called scrofula. It’s just that, a long time ago, I was lying with my son in an infectious disease ward, and there in the next box there was a girl sick with scrofula. I remembered how her mother said that the first signs of this disease in the child began with weeping wounds behind the ears. I think that consulting a doctor in your case will not be superfluous.
The first step is to consult a doctor. But don’t shy away from traditional methods either. From time immemorial, scrofulous children were bathed in a decoction of the string. Or in a decoction of the second layer of linden bark - linden sapwood. Another simple and affordable remedy is to sprinkle dried ginger powder on the wounds, which is sold as a seasoning. Great for adults and children.
If they crack like crazy, then yes, see a doctor. Well, most often, the skin on the ears dries out if the child eats a lot of sweets ("cakes" can also form behind the ears). Therefore, you need to stop giving your child a lot of sweets, and think about his health. Apply baby cream, then everything will go away quickly.
Olyushkin, both my children had this problem at one time, and if with the first we spent a long time running to the doctors, then with the second we quickly solved the problem (experience is a great thing!): diet (do not burden the gastrointestinal tract), drink plenty of clean water, after When bathing, rinse the irritated areas with a solution of soda and salt (half a teaspoon of both per glass of warm boiled water), do not wipe, but blot and immediately smear with zinc ointment (it costs a penny at the pharmacy) and you can also apply a rich baby cream directly on top of the zinc ointment . Give it a try, I hope it helps your nephew as effectively as it did my kids!
Your advice is correct, they help in most cases, but it’s still better to see a pediatrician first so that he can make an accurate diagnosis. This is further aggravated by the fact that the appearance of various rashes on a child’s skin can lead to traumatization due to the special sensitivity of the skin, as well as the body’s reaction to various irritants. In this case, cracks can appear behind the ears not only in small children, but also in adult children.
This phenomenon is far from rare and occurs quite often in pediatrics. Moreover, there can be many reasons, so you need a doctor to establish them. He will conduct a visual examination and refer you for additional diagnostics, if necessary, to establish an accurate diagnosis and the necessary treatment.
Cracks can be caused by an allergic reaction, atopic dermatitis or exudative diathesis, eczema, or fungal infection. It must be said that they do not arise out of nowhere - they are provoked by a number of factors.
One of them is the aggressive influence of the environment. Temperature changes, dry air, hard water. In this case, the task of parents is to minimize the negative impact of such factors on the child’s body.
The air temperature in the room should not exceed 20 degrees, and the humidity should be below 70%. In addition, it is necessary to constantly ventilate and do wet cleaning. The child should not overheat or become hypothermic both at home and outside. In addition, after bathing, it is better to always treat the child’s skin with special creams, paying attention to the area behind the ears.
You should not discount allergies, which manifest themselves as various rashes on the skin. Moreover, if one of the parents has such a problem, then it can be inherited by the child.
Disease prevention
To prevent scrofula it is necessary:
- observe the rules of hygiene - bathe and wipe all folds of a newborn baby on time;
- keep the home and children's room clean, do wet cleaning;
- spend more time outdoors, sunbathe according to the season;
- get enough sleep; children must have a quiet hour during the day;
- eat properly and balanced, take vitamin complexes (VitaMishki, Pikovit);
- up to 3 years of age, completely limit the consumption of sweets - sweets, chocolate, marshmallows, etc.;
- maintain immunity (harden yourself, play sports, walk in the fresh air).
The most important preventive measure to prevent the development of the disease is to monitor the child’s hygiene
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Experienced and respected pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky believes that the appearance of any skin rash occurs in three ways:
- due to non-compliance with the diet;
- through infection from a sick person through touch;
- by airborne droplets.
In order to avoid the development of the disease, you need to follow simple rules:
- maintain hygiene;
- do not introduce complementary foods very early;
- do not give children exotic fruits and products, so as not to cause allergies;
- do not overfeed the baby;
- do not bathe your child in water that has been chlorinated;
- wash children's clothes with special hypoallergenic products;
- bathe the baby using soap and detergent no more than 2 times a week;
- Avoid contact of the baby with strong household allergens: pets, sprayers, aggressive household chemicals.
Pediatrician of the 2nd category, allergist-immunologist, graduated from the Belarusian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development. Read more »