Problems with a child’s nose are a fairly common situation that many parents face. Congestion and snot can await your baby almost all year round: in autumn, winter and spring. Green discharge requires special attention, and if it is also accompanied by suppuration from the eyes, then it’s time to sound the alarm. You will not be able to determine the origin of the symptoms yourself; only a competent specialist will help.
Discharge from the nose and eyes that has taken on a greenish tint is a consequence of an inflammatory process of microbial origin. Most often we are talking about bacterial flora, but viruses can also be the causative agent of the disease. The nasal cavity and the conjunctival sac are connected by a system of canals through which tear fluid is drained from the eye. Pathogens also penetrate through them, causing exudative inflammation (accompanied by suppuration). This occurs in the following diseases:
- Acute rhinitis.
- Adenoviral infection.
- Dacryocystitis.
Each condition has its own characteristics, which are taken into account by the pediatrician when carrying out differential diagnosis. And only on the basis of a complete examination can we say why the child has green snot and festering eyes.
Symptoms
To determine the likely cause of changes in the nose and eyes, it is necessary to analyze the clinical symptoms. This means that the doctor interviews parents and older children, finding out complaints, and then conducts an examination. Subjective information is supported by objective signs, and thus the basis for making a preliminary diagnosis is formed.
Any symptom has its own importance, because it speaks of certain disorders - local or general. And all the features of each of them are considered. Even the nature of the snot can tell a lot. To do this, the following points are analyzed:
- Color: transparent, white, yellow-green.
- Consistency: thick or liquid.
- Volume: scanty or abundant.
- Duration: periodic or almost constant.
- Dependence on external factors: time of day, going outside, physical activity.
Discharge from the eyes is also assessed according to a similar principle. It is extremely important to pay attention to all symptoms - both main and additional. If a child has a fever or cough, they should not be left aside. This is the only way to get a more or less complete picture of the pathology at the primary stage.
Each symptom identified in a child is important for making a preliminary diagnosis.
Acute rhinitis
Nasal discharge due to rhinitis is common. They have a different character, depending on the timing of the development of the acute process. The fact is that an infectious runny nose occurs in three stages:
- Irritations.
- Serous discharge.
- Mucopurulent discharge.
At first there is no snot at all - the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is dry, it is irritated. The patient feels a burning sensation, tickling and itching, and sneezing appears. The inflammatory process is accompanied by a rise in temperature, general weakness and malaise. At the second stage, profuse rhinorrhea appears - clear liquid literally flows from the nose. It becomes increasingly congested, and the swelling makes breathing difficult. Subsequently, the serous discharge becomes mucous and, finally, purulent in nature. When the pathogen spreads through the nasolacrimal ducts, conjunctivitis occurs.
Adenovirus infection
It is not difficult for a doctor to recognize an adenovirus infection. This disease has a fairly characteristic set of clinical signs:
- Rhinitis.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Pharyngitis.
- Fever.
- Lymphadenopathy.
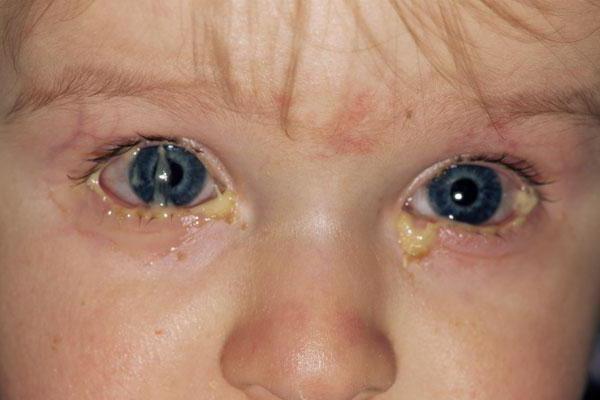
The infection begins acutely, children complain of scratching, sore throat and sore throat, rare cough, nasal congestion and discharge from it (first mucous, and then with a purulent component). The temperature rises, malaise and body aches bother you. At the same time, conjunctivitis appears - in the form of pain in the eyes and a feeling of a foreign body. The eyelids swell and turn red, and a scant yellowish discharge accumulates under them, often sticking the eyelashes together. Enlargement of regional lymph nodes is also characteristic.
On examination, the mucous membrane of the nose, conjunctiva and throat is reddened. Enlarged follicles are often detected on the back wall of the pharynx and the inside of the eyelids. The conjunctiva may become covered with a thin whitish coating. If the process spreads down the respiratory tract, then tracheitis and bronchitis occur. Then the child begins to cough, producing mucous sputum.
Conjunctivitis and rhinitis are typical manifestations of adenovirus infection. In this case, the discharge is often purulent in nature.
Dacryocystitis
If the eyes fester, then a pathology such as dacryocystitis cannot be ruled out. This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac that occurs due to a violation of the outflow from it. This may occur due to swelling of the mucous membrane against the background of acute rhinitis. Therefore, nasal discharge becomes only a preliminary phenomenon. And then quite characteristic symptoms arise:
- Tearing.
- Painful swelling at the inner edge of the eye socket.
- Redness and swelling of the skin at the site of the lesion.
- Discharge of pus from the lacrimal opening when pressing on the eminence.
Acute bacterial inflammation occurs with fairly intense pain and fever. Swelling can spread to the bridge of the nose, eyelids, cheekbones and cheeks. After the infiltration stage, a fluctuation forms in the center of the lesion, and then pus breaks out. You should be especially careful with young children whose eyes fester due to dacryocystitis. After all, in them the process often becomes widespread, transforming into phlegmon of the orbit or giving rise to intracranial complications.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
If pus flows from the eyes and green snot from the nose, the condition indicates a bacterial infection. A change in the color of nasal discharge occurs as a result of the death of pathogenic microbes and leukocytes. The shade of the secreted secretion can be different, from yellow to brown. The brighter the color, the more pathogenic bacteria have entered the body.
Acute rhinitis in children occurs in several stages. Each stage is characterized by certain symptoms:
- At the beginning of the disease, there is no snot. There is dryness in the nasal cavity, burning, tingling. The child sneezes frequently. A rise in temperature and weakness in the body may occur.
- At the second stage of the disease, nasal congestion increases. The mucous membrane swells, copious, clear discharge is observed, breathing through the nose is impaired, and a cough may occur.
- At the third stage of inflammation development, viscous snot of a purulent nature is observed. If the infection penetrates the nasolacrimal duct, conjunctivitis develops.
Conjunctivitis can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. The disease is accompanied by yellow, brown or even greenish suppuration:
- Viral conjunctivitis is more common in newborns. In adult children, it may be the result of decreased immunity or a severe cold. Body temperature rises, tears flow from the eyes. The child is bothered by a feeling of pain in the eyes and photophobia. The eyelids become swollen, red and inflamed. Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis affects both eyes. The child develops green snot and festering eyes. After sleep, the eyelashes stick together and yellowish, dry crusts form.
See also
Is it possible to treat teeth with a runny nose and cold?
Read
Adenoviral disease often begins with pain and discomfort in the throat. At the same time, coughing appears and nasal discharge is bothersome. The snot is initially mucous in nature, and then acquires a yellow-brown or greenish tint. When the infection spreads, the eyes fester.
A baby's eyes may become watery as a result of a disease such as dacryocystitis. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac often occurs against the background of acute rhinitis. Initially, a severe runny nose appears, and only then lacrimation, pain and swelling of the inner corner of the eye occurs, and purulent fluid is released when pressure is applied.
Another reason that a child has green snot is an allergy. Dust, animal hair, plant pollen, chemicals, and food can act as irritants. The eyelids turn red and swell, there is lacrimation, the nose is very stuffy, itching, burning, the snot is initially clear. If the eyes begin to fester, and the color of the mucus in the nose has changed, the condition indicates the addition of a bacterial infection.
Less commonly, the appearance of rhinitis and conjunctivitis is caused by herpes. Small blisters appear around the eyes and nose. When the blisters begin to burst, fluid flows into the eyes, causing purulent discharge.
Additional diagnostics
Additional methods help to understand why a child’s eyes may fester against the background of green nasal discharge. Therefore, the doctor will refer the small patient to laboratory and instrumental procedures:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Analysis of secretions (cytology, culture, PCR).
- Rhinoscopy.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye.
- Probing of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Dacryocystography.
A consultation is required not only with an ENT doctor, but also with an ophthalmologist. And sometimes it is necessary to involve even a maxillofacial surgeon in the examination. Everything suggests that the situation with purulent discharge from the eyes and nose in a child is quite serious and requires increased attention from parents. At the first symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor to find out the exact cause of the disorders and start treatment on time, thereby getting rid of thoughts about possible complications.
The appearance of discharge from the eyes and nose of a baby always frightens parents. Especially if this discharge is of a dense consistency and has a green or yellow color, which indicates the addition and progression of a bacterial infection.
The child has green snot and festering eyes
Problems with a child’s nose are a fairly common situation that many parents face. Congestion and snot can await your baby almost all year round: in autumn, winter and spring. Green discharge requires special attention, and if it is also accompanied by suppuration from the eyes, then it’s time to sound the alarm. You will not be able to determine the origin of the symptoms yourself; only a competent specialist will help.
Causes and mechanisms
Discharge from the nose and eyes that has taken on a greenish tint is a consequence of an inflammatory process of microbial origin. Most often we are talking about bacterial flora, but viruses can also be the causative agent of the disease. The nasal cavity and the conjunctival sac are connected by a system of canals through which tear fluid is drained from the eye. Pathogens also penetrate through them, causing exudative inflammation (accompanied by suppuration). This occurs in the following diseases:
- Acute rhinitis.
- Adenoviral infection.
- Dacryocystitis.
Each condition has its own characteristics, which are taken into account by the pediatrician when carrying out differential diagnosis. And only on the basis of a complete examination can we say why the child has green snot and festering eyes.
Symptoms
To determine the likely cause of changes in the nose and eyes, it is necessary to analyze the clinical symptoms. This means that the doctor interviews parents and older children, finding out complaints, and then conducts an examination. Subjective information is supported by objective signs, and thus the basis for making a preliminary diagnosis is formed.
Any symptom has its own importance, because it speaks of certain disorders - local or general. And all the features of each of them are considered. Even the nature of the snot can tell a lot. To do this, the following points are analyzed:
- Color: transparent, white, yellow-green.
- Consistency: thick or liquid.
- Volume: scanty or abundant.
- Duration: periodic or almost constant.
- Dependence on external factors: time of day, going outside, physical activity.
Discharge from the eyes is also assessed according to a similar principle. It is extremely important to pay attention to all symptoms - both main and additional. If a child has a fever or cough, they should not be left aside. This is the only way to get a more or less complete picture of the pathology at the primary stage.
Each symptom identified in a child is important for making a preliminary diagnosis.
Acute rhinitis
Nasal discharge due to rhinitis is common. They have a different character, depending on the timing of the development of the acute process. The fact is that an infectious runny nose occurs in three stages:
- Irritations.
- Serous discharge.
- Mucopurulent discharge.
At first there is no snot at all - the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is dry, it is irritated. The patient feels a burning sensation, tickling and itching, and sneezing appears. The inflammatory process is accompanied by a rise in temperature, general weakness and malaise. At the second stage, profuse rhinorrhea appears - clear liquid literally flows from the nose. It becomes increasingly congested, and the swelling makes breathing difficult. Subsequently, the serous discharge becomes mucous and, finally, purulent in nature. When the pathogen spreads through the nasolacrimal ducts, conjunctivitis occurs.
Adenovirus infection
It is not difficult for a doctor to recognize an adenovirus infection. This disease has a fairly characteristic set of clinical signs:
- Rhinitis.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Pharyngitis.
- Fever.
- Lymphadenopathy.
The infection begins acutely, children complain of scratching, sore throat and sore throat, rare cough, nasal congestion and discharge from it (first mucous, and then with a purulent component). The temperature rises, malaise and body aches bother you. At the same time, conjunctivitis appears - in the form of pain in the eyes and a feeling of a foreign body. The eyelids swell and turn red, and a scant yellowish discharge accumulates under them, often sticking the eyelashes together. Enlargement of regional lymph nodes is also characteristic.
On examination, the mucous membrane of the nose, conjunctiva and throat is reddened. Enlarged follicles are often detected on the back wall of the pharynx and the inside of the eyelids. The conjunctiva may become covered with a thin whitish coating. If the process spreads down the respiratory tract, then tracheitis and bronchitis occur. Then the child begins to cough, producing mucous sputum.
Conjunctivitis and rhinitis are typical manifestations of adenovirus infection. In this case, the discharge is often purulent in nature.
Dacryocystitis
If the eyes fester, then a pathology such as dacryocystitis cannot be ruled out. This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac that occurs due to a violation of the outflow from it. This may occur due to swelling of the mucous membrane against the background of acute rhinitis. Therefore, nasal discharge becomes only a preliminary phenomenon. And then quite characteristic symptoms arise:
- Tearing.
- Painful swelling at the inner edge of the eye socket.
- Redness and swelling of the skin at the site of the lesion.
- Discharge of pus from the lacrimal opening when pressing on the eminence.
Acute bacterial inflammation occurs with fairly intense pain and fever. Swelling can spread to the bridge of the nose, eyelids, cheekbones and cheeks. After the infiltration stage, a fluctuation forms in the center of the lesion, and then pus breaks out. You should be especially careful with young children whose eyes fester due to dacryocystitis. After all, in them the process often becomes widespread, transforming into phlegmon of the orbit or giving rise to intracranial complications.
Additional diagnostics
Additional methods help to understand why a child’s eyes may fester against the background of green nasal discharge. Therefore, the doctor will refer the small patient to laboratory and instrumental procedures:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Analysis of secretions (cytology, culture, PCR).
- Rhinoscopy.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye.
- Probing of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Dacryocystography.
A consultation is required not only with an ENT doctor, but also with an ophthalmologist. And sometimes it is necessary to involve even a maxillofacial surgeon in the examination. Everything suggests that the situation with purulent discharge from the eyes and nose in a child is quite serious and requires increased attention from parents. At the first symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor to find out the exact cause of the disorders and start treatment on time, thereby getting rid of thoughts about possible complications.
elaxsir.ru
Why is it possible to discharge pus from the eyes when there is a runny nose?
First of all, it is worth noting that this is not pus in the usual sense of the word. The mechanism of occurrence of this condition is completely different. The nasolacrimal duct, which runs through the bone and opens at the inferior turbinate, connects the eye and the nasal cavity. In children, due to their anatomy, it is shorter and somewhat thicker than in adults. This structure greatly facilitates the penetration of infection and mucus from the nasal passages into the eyes.
Pus in the eyes occurs when bacterial agents spread upward from the source of infection. There are also a number of pathogenic microorganisms that can simultaneously infect both the nasal mucosa and eye tissue. Moreover, each disease has manifestations characteristic only of it, which greatly facilitates diagnosis. For example, green snot is a clear sign of a bacterial infection.
But we must not forget about the opposite situation. In inflammatory diseases of the eyeball (conjunctivitis or dacryocystitis), pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the wide nasolacrimal duct. And in this case, the child’s runny nose is secondary.
Description
Green snot in a child occurs to a greater extent during the widespread spread of infectious diseases of a cold nature (autumn, winter, spring). The fact is that at this time children have very weak immunity. Green snot in a baby is explained by the body’s defense system that has not yet formed. When the slightest cold snap occurs, the newborn’s body instantly seizes some kind of infection.

It is not possible to completely avoid a runny nose in a child. The point is to adapt the body and develop the immune system, so you need to be prepared for this!
It is worth noting that green snot in a child leads to discomfort, and for a newborn it carries a huge risk. The fact is that if the nose is stuffy, the baby cannot blow his nose on his own. Because of this, respiratory function is impaired. In addition, increased pressure forms in the head, and because of this, the eyes fester. Cough and fever are often observed.
It is noteworthy that green discharge does not appear immediately. Thus, if such a situation has arisen, then this speaks primarily of the inattention of the parents. That is, either illiterate treatment was carried out, or the initial form of the disease was missed. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the condition of children very carefully.
Green snot is, in fact, an indicator. To understand the seriousness of the situation, it is necessary to talk about possible complications. Often, a common cold can lead to much more serious illnesses. Among them are:
- otitis;
- brain inflammation;
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis.
Probably any adult understands how dangerous the diseases listed above are for children. Treatment should be carried out quickly and in a timely manner. The infection must not be allowed to spread. Well, now let’s talk about how to treat green snot in a child.
What diseases can cause this condition?
Symptoms of eye suppuration are possible not only with colds in a child. Conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis occur with similar manifestations.
Conjunctivitis
Click to enlarge image
This disease occurs with equal frequency among both children and adults. However, the etiology of the disease is somewhat different. For example, viral conjunctivitis is more common in newborn babies, which is explained by the poor development of the immune system and low levels of antibodies. As an independent disease, it can occur against the background of a cold or decreased immunity.
With a bacterial infection, both the right and left eyes are affected with the discharge of greenish pus. After sleep, the eyelids may become glued together, and instead of green pus, parents notice dry yellowish crusts. Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis is a highly contagious disease. Therefore, several sick people appear simultaneously in a kindergarten or school. It is important to closely monitor the eyes of a child who is often in contact with a large number of children. At first, redness may be the only symptom of the disease.
In addition to the eye festering, the child complains of severe itching and pain. Redness of the conjunctiva, photophobia, and profuse lacrimation are noted. Nasal discharge may also appear, but not in the form of green snot, but in the form of mucus. In case of a disease of an allergic nature, the discharge is quite scanty, but the itching and burning are very pronounced.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Loromax
- natural herbal drops with the addition of bioactive components of natural origin, which have a comprehensive effect on eliminating all causes of rhinitis. Thanks to the composition of active substances, the drug instantly relieves swelling of the nasal mucosa, eliminating congestion and nasal discharge. The drug has no side effects.
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac of the eye
Inflammation of the lacrimal sac most often affects newborns and babies up to two months of age. Obstruction of the tear duct leads to disruption of the proper outflow of tear fluid. Parents may feel like their child's eyes are rotting. But this is not true at all! Pus accumulates and is released from the lacrimal sac.
Dacryocystitis is accompanied by redness of the lacrimal caruncle, semilunar fold and the conjunctiva of the eyelids itself. With a long course of the disease, the skin over the lacrimal sac acquires a rich bluish-red tint. Hyperemia and swelling of the tissues can spread to the surrounding soft tissues (the bridge of the nose, the lower eyelid and even the cheek) on the affected side. A runny nose and itchy skin are added. The color of the discharge directly depends on the pathogenic flora. Green snot is characteristic of bacteria, and clear discharge is characteristic of viruses.
In diseases caused by adenovirus infection, herpes virus, measles or chickenpox, in addition to a runny nose and discharge from the eyes, various rashes, fever, redness of the skin and mucous membranes are noted. It is safe to say that a runny nose and discharge of pus from the eyes are only symptoms of the underlying disease and are not enough to make a correct and final diagnosis.
It is not uncommon for another infection to be associated with the underlying disease. Green snot with a simple allergic rhinitis symbolizes streptococcal or staphylococcal flora.
Why does a child have pus coming out of his eyes and a runny nose?
The runny nose will disappear in a matter of days. Try this remedy...
Read more…
The appearance of discharge from the eyes and nose of a baby always frightens parents. Especially if this discharge is of a dense consistency and has a green or yellow color, which indicates the addition and progression of a bacterial infection.
Why is it possible to discharge pus from the eyes when there is a runny nose?
First of all, it is worth noting that this is not pus in the usual sense of the word. The mechanism of occurrence of this condition is completely different.
The nasolacrimal duct, which runs through the bone and opens at the inferior turbinate, connects the eye and the nasal cavity. In children, due to their anatomy, it is shorter and somewhat thicker than in adults.
This structure greatly facilitates the penetration of infection and mucus from the nasal passages into the eyes.
Pus in the eyes occurs when bacterial agents spread upward from the source of infection.
There are also a number of pathogenic microorganisms that can simultaneously infect both the nasal mucosa and eye tissue.
Moreover, each disease has manifestations characteristic only of it, which greatly facilitates diagnosis. For example, green snot is a clear sign of a bacterial infection.
But we must not forget about the opposite situation. In inflammatory diseases of the eyeball (conjunctivitis or dacryocystitis), pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the wide nasolacrimal duct. And in this case, the child’s runny nose is secondary.
What diseases can cause this condition?
Symptoms of eye suppuration are possible not only with colds in a child. Conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis occur with similar manifestations.
Conjunctivitis
Click to enlarge image
This disease occurs with equal frequency among both children and adults. However, the etiology of the disease is somewhat different.
For example, viral conjunctivitis is more common in newborn babies, which is explained by the poor development of the immune system and low levels of antibodies.
As an independent disease, it can occur against the background of a cold or decreased immunity.
With a bacterial infection, both the right and left eyes are affected with the discharge of greenish pus. After sleep, the eyelids may become glued together, and instead of green pus, parents notice dry yellowish crusts.
Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis is a highly contagious disease. Therefore, several sick people appear simultaneously in a kindergarten or school. It is important to closely monitor the eyes of a child who is often in contact with a large number of children.
At first, redness may be the only symptom of the disease.
In addition to the eye festering, the child complains of severe itching and pain. Redness of the conjunctiva, photophobia, and profuse lacrimation are noted. Nasal discharge may also appear, but not in the form of green snot, but in the form of mucus. In case of a disease of an allergic nature, the discharge is quite scanty, but the itching and burning are very pronounced.
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac of the eye
Inflammation of the lacrimal sac most often affects newborns and babies up to two months of age. Obstruction of the tear duct leads to disruption of the proper outflow of tear fluid. Parents may feel like their child's eyes are rotting. But this is not true at all! Pus accumulates and is released from the lacrimal sac.
Dacryocystitis is accompanied by redness of the lacrimal caruncle, semilunar fold and the conjunctiva of the eyelids itself. With a long course of the disease, the skin over the lacrimal sac acquires a rich bluish-red tint.
Hyperemia and swelling of the tissues can spread to the surrounding soft tissues (the bridge of the nose, the lower eyelid and even the cheek) on the affected side. A runny nose and itchy skin are added. The color of the discharge directly depends on the pathogenic flora.
Green snot is characteristic of bacteria, and clear discharge is characteristic of viruses.
In diseases caused by adenovirus infection, herpes virus, measles or chickenpox, in addition to a runny nose and discharge from the eyes, various rashes, fever, redness of the skin and mucous membranes are noted. It is safe to say that a runny nose and discharge of pus from the eyes are only symptoms of the underlying disease and are not enough to make a correct and final diagnosis.
It is not uncommon for another infection to be associated with the underlying disease. Green snot with a simple allergic rhinitis symbolizes streptococcal or staphylococcal flora.
Treatment tactics
Chamomile decoction and green tea can serve as an antiseptic
If a child has a runny nose and discharge of pus from the eyes, the doctor must conduct a full diagnosis and determine the cause of this condition. You need to be especially careful with children, because due to a weak immune system, many pathognomonic symptoms of a particular disease may be mild or completely absent.
All therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. For bacterial conjunctivitis, it is advisable to prescribe antibacterial agents in the form of eye drops. We must not forget about washing. A decoction of chamomile and green tea is used as an antiseptic. Massage of the lacrimal sac prevents congestion and is an excellent prevention of dacryocystitis.
Special mention should be made of the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis. In addition to taking antihistamines, it is necessary to minimize the exposure of the baby to the allergen.
Under no circumstances should you choose medication for your child on your own! Only an experienced pediatrician can prescribe suitable drops, taking into account age characteristics and possible contraindications.
Source: https://nasmorkinfo.ru/dlya-detey/esli-u-rebenka-slezyatsya-glaza-i-nasmork.html
Treatment tactics
Chamomile decoction and green tea can serve as an antiseptic
If a child has a runny nose and discharge of pus from the eyes, the doctor must conduct a full diagnosis and determine the cause of this condition. You need to be especially careful with children, because due to a weak immune system, many pathognomonic symptoms of a particular disease may be mild or completely absent.
All therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. For bacterial conjunctivitis, it is advisable to prescribe antibacterial agents in the form of eye drops. We must not forget about washing. A decoction of chamomile and green tea is used as an antiseptic. Massage of the lacrimal sac prevents congestion and is an excellent prevention of dacryocystitis.
Special mention should be made of the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis. In addition to taking antihistamines, it is necessary to minimize the exposure of the baby to the allergen. Under no circumstances should you choose medication for your child on your own!
Only an experienced pediatrician can prescribe suitable drops, taking into account age characteristics and possible contraindications.
At any age, a child’s eyes can fester: a newborn baby, a preschooler, a schoolchild. This unpleasant phenomenon is not always associated with hygiene. If you notice that your child’s eyes are festering, you should not self-medicate: an ophthalmologist can explain why this is happening, and also tell you what to do to prevent the eyes from festering.
Treatment
In this case, therapy takes an integrated approach. Both medications and home remedies can be used, thanks to which you can overcome the symptoms and eliminate the root of the problem.
Medication
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will be able to create an effective treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
If an infectious process occurs, the following drops are used to treat it:
- Eubital;
- Levomycetin;
- Vitabact;
- Colbiocin.
Some children find ointments better. For this, it is better to use Torbex, Erythromycin or Tetracycline ointment.
To treat adenoviral conjunctivitis, it is worth using florenel or 25% tebrofen ointment. When eye suppuration occurs mainly in the spring, this indicates the onset of an allergy. To treat it, it is necessary to use antihistamine drops:
- Allergodil;
- Spersallerg;
- Lecrolin;
- Allergophthal;
- Diphenhydramine in solution.
To quickly overcome allergies, you need to focus all your efforts on boosting your immunity.
Herpetic conjunctivitis is treated with Acyclovir. For this, both ointment and tablets can be used.
What are the reasons for a child’s eyes to fester?
There are many reasons for pus in the eyes. They depend on the child’s age, previous infectious and/or viral diseases, congenital pathologies, and a tendency to allergic reactions.
In order to properly develop a set of measures to combat festering eyes, it is necessary to determine the cause of this phenomenon. Among the reasons:
- dacryocystitis
is a disease that affects newborn babies and is associated with obstruction of the lacrimal canal; - infections during childbirth
transmitted through the birth canal or unsterile medical instruments; - bacterial infection caused by strains of various “cocci”: pneumococcus, streptococcus, meningococcus;
- viruses that mainly affect the upper respiratory tract: adenovirus;
- foreign body in the eye
, most often an eyelash; - inflammation in the deep membranes of the eye mucosa;
- weak immunity;
- violation of hygiene rules
: rare hand washing; - complications after colds, adenovirus, ;
- microtrauma of the eye;
- barley;
- Conjunctivitis is the most common cause of pus in the eyes of babies.
Doctors: pediatrician, ophthalmologist can determine the cause of pus in a child’s eyes. The final diagnosis is made by an ophthalmologist.
Associated symptoms
In parallel with pus in the eyes, the following symptoms may be observed:
- swelling of the eyelid;
- redness of the eyes;
- itching in the eyes;
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- general irritability, moodiness;
- blisters on the edges of the eyelids;
- runny nose;
- increased body temperature;
- film on the mucous membrane of the eye: do not touch it under any circumstances, this is the prerogative of the doctor;
- poor appetite;
- disturbed sleep;
- yellow dry crusts;
- eyelids glued together after a night's sleep.
After analyzing additional symptoms, the doctor will make a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
What to do if a child’s eyes are purulent
So, if a child’s eyes are festering, then the doctor decides how to treat this condition after collecting an anamnesis and making a diagnosis. The most common diagnoses for which the eyes fester, and sets of treatment measures.
Dacryocystitis in newborns
Dacryocystitis is the most common reason why the eyes of a newborn baby fester. What is the cause of suppuration and how to treat it:
- associated with obstruction of the lacrimal sac, in which infection develops;
- can be successfully treated with a massage, which will be shown to you by an ophthalmologist, and local anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the eyes of an infant are festering, contact an ophthalmologist, he will help establish the correct diagnosis.
Conjunctivitis
It can be accompanied by viral or infectious diseases, and can also be a consequence of untreated sore throat, sinusitis, or adenoiditis. Most often, with viral or infectious conjunctivitis, the child’s eyes are red and purulent. When treating conjunctivitis, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease, as well as:
- remove pus or purulent crusts from the eyes using a solution of furatsilin or chamomile decoction;
- use antimicrobial drops or ointments prescribed by your doctor.
If a child’s eyes fester, there are rashes around the eyes and there is also a runny nose, then this is allergic conjunctivitis. Active flowering of various plants in the spring may support this diagnosis.
Treatment will consist of:
- identifying and eliminating the source of allergies;
- prescribing antihistamines;
- the use of anti-inflammatory drops;
- strengthening the immune system to resist allergens.
Barley
This eye disease cannot be confused with anything. It is characterized by a dense formation with inflammation of the skin of the eyelid. On the 2-3rd day of the disease, the child’s eye swells and begins to fester. Recommended:
- washing the eyes;
- compresses made from strong tea or chamomile decoction (strictly maintain sterility);
- use of antibacterial drops and ointments.
Foreign body
Try to remove anything that gets into your eye. Use tea, chamomile or calendula decoction for this purpose. If you have lens solution or saline solution on hand, use it to rinse them. If you are not sure that you have removed everything that got into the eye, take your child to the hospital. What is important to observe when sanitizing the eyes:
- if a child’s one eye is purulent and watery, both still need to be washed;
- even if the condition of the eye has improved, and the treatment period has not yet ended, it must be completed;
- do not self-medicate, you can trigger the disease, which can lead to loss of vision.
A child has festering eyes and a runny nose - causes, treatment - website about
If during a cold a child’s eyes fester and runny nose, this is because the tear duct is located very close to the nasal passages. And as soon as an infection starts in the nose, it very easily gets into the baby’s eyes.
Causes of purulent discharge
If a child's eyes become infected and a runny nose appears, the mother should visit two doctors - a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist. It is necessary to pay special attention to the eyes and find out the exact reason for the appearance of pus in them. They can be different, for example:
- Most often, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes inflamed and conjunctivitis occurs.
- Newborns often experience obstruction of the lacrimal duct - dacryocystitis. This is a congenital pathology that goes away over time.
- Bacteria of the coccus group, influenza viruses, herpes, measles, chlamydia.
- Allergic reaction to exposure to dust, pollen, pet hair.
- Poorly treated sore throat or sinusitis.
- Infection acquired during childbirth from the mother or through unsterile instruments. This is the cause of symptoms in every second case of purulent eyes in newborns.
- A foreign body entering the eye, such as an eyelash.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Internal inflammation of the mucous membrane, which threatens complete loss of vision.
- Unwashed hands that children constantly rub their eyes with.
- Barley.
- Weakening of the immune system.
A cold is always accompanied by viral or bacterial infections - they are the cause of such symptoms. Such problems can arise at any age and must be dealt with in order to avoid dangerous complications.
The viral or bacterial course of the disease makes the child contagious to others. He needs to be isolated from other children during his illness. If a child goes to kindergarten, he must be left on sick leave until the signs of the disease pass.
Symptoms
In rare cases, parents find out that a child has problems with his eyes when one morning he cannot open them. The eyelids on one or both eyes become stuck together. It happens that without lotions this problem cannot be solved.
But more often, before pus appears in the eyes, other symptoms are observed. If you notice them in time, you can get rid of the disease more easily. It can be:
- redness of the eyeball;
- burning and itching in the eye;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- discharge.
If a child has dacryocystitis, it will be noticeable some time after birth, at the first cold, even the mildest one. But if the child is more than three years old, then we can say with confidence that conjunctivitis occurs, which occurs most often.
You shouldn’t guess where the pus in your child’s eyes came from. The diagnosis must be made by an ophthalmologist. It may well be that the child has some kind of chronic eye disease, and it has worsened with a cold.
Why did the child have green discharge from the nose and pus from the eyes?
If your baby has green snot and his eyes are festering, this indicates that the cause of his illness is an infection. The green color of snot appears when leukocytes and bacteria die. The more of them collect in the nasal cavity, the darker the color will be. It can range from light yellow to dark green.
The baby’s sick body tries to resist the invasion of infection on its own, which is why such discharge is observed.
You cannot ignore such symptoms; you need to go to a doctor, undergo an examination and take treatment. We need to help the little body; it may not be able to cope on its own, and complications will arise.
What are the dangers of purulent discharge from the eyes and what complications may arise?
If a child has snot and his eyes are purulent, but there are no other symptoms, this indicates a mild cold. Perhaps the child took a walk down the street in windy weather and just got a little windy. In this case, eye drops will help, and if you use them in time, everything will go away quickly.
But if a child has green snot and conjunctivitis, this is more serious and indicates an infection. If left unattended or poorly treated, dangerous eye complications can occur. These include:
- Blepharitis is an infectious inflammatory process that occurs under the eyelids. It is very difficult to treat and often becomes chronic.
- Keratitis is an inflammatory process in the cornea. Chronic course leads to the formation of a cataract in the eye and partial loss of vision.
- Entropion - can be congenital or acquired. It is characterized by the edges of the eyelids and eyelashes turned inward. In this position, the eyes become vulnerable to infections and viruses.
- Hypopyon – there is an accumulation of pus in the eye. It is difficult to treat and often requires surgery.
- Dry eye – with advanced infection, the lacrimal gland may be damaged and it ceases to perform its functions. The eyes are not moisturized and become inflamed.
To avoid such complications, you need to be attentive to your eyes. This applies to both children and adults. If your eyes fester in the morning, this is no longer a good sign. If it does not go away for a long time or often recurs, you need to sound the alarm and run to the doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis and runny nose
If a child or adult’s eyes start to turn sour in the morning, it’s easy to fix. To do this, just rinse your eyelids several times with a decoction of chamomile or calendula. A runny nose that occurs can also be treated by rinsing the nose with these decoctions.
But if such measures do not produce results, and the disease progresses, you need to urgently go to the doctor. Only he can determine the exact cause of the disease. To do this, you may have to take microflora tests to find out what pathogen has settled in your eyes.
- medicines in the form of drops and ointments;
- lotions;
- washing.
All these activities are carried out after consultation with a doctor.
Medication measures
Of the medications, the best are drops that can be dripped into both the nose and eyes at the same time. This is convenient and saves money. These drops include Albucid. An ophthalmologist should tell you when and how to use them.
Using medications on your own is dangerous. If you choose the wrong dosage, the disease can be classified as chronic, or you can overdose.
You can also use eye ointments for conjunctivitis, which are placed behind the inflamed eyelid. At the same time, put drops into your nose for a runny nose.
Washings and lotions
You can treat suppuration in the eyes by washing with chamomile, calendula, and tea. You need to rinse your eyes with a cotton swab using movements from the corner to the center. The tampon must be changed after each movement.
If there is so much pus that it has glued the eyelids together, under no circumstances should you force them open. You need to place a cotton swab soaked in some solution on your closed eyelids. For example, furatsilin or potassium permanganate . If you don't have them on hand, you can use regular warm water.
During illness, one must carefully observe hygiene and try not to expose already sore eyes to drafts and dust.
If pus appears in the eyes and a runny nose during a cold, this indicates that an inflammatory process has begun, simultaneously affecting the lacrimal canal and the nasal cavity. The reasons for this may be different, and to understand them, you need a competent specialist.
Source:
Double problem: the child’s eyes are festering and snot is flowing
A runny nose is a sign of various diseases. This symptom does not cause much concern for parents. When suppuration of the mucous membrane of the eyes is added to rhinitis, then mothers begin to worry greatly.
It is important not to panic, but to act calmly and competently. Parents need to understand why their child’s eyes and snot are festering at the same time, and what to do in this case.
Possible reasons
In 85% of cases, this condition is observed with conjunctivitis. This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes. It may be bacterial or viral in nature and be a complication of rhinitis.
It usually occurs in children who do not adhere to hygiene rules and touch their eyes with dirty hands. Discharge of pus from the eyes and rhinitis in an infant may be a sign of infection during childbirth. If the birth canal was inflamed and doctors used inappropriate sterilization instruments, then the likelihood of infection of the baby increases.
In most cases, purulent discharge is associated with the penetration of bacteria into the mucous membrane of the organs of vision. The most common pathogens are pneumococci and streptococci. It is also possible to be affected by the herpes virus, influenza virus, or adenovirus. These pathogens provoke the appearance of signs of conjunctivitis and rhinitis. Sometimes purulent eyes and a runny nose are symptoms of a fungal infection.
Types of conjunctivitis.
Often, such a clinical picture is observed when allergens come into contact with the mucous membrane: plant pollen, animal hair, chemicals and other irritants. Then the child is diagnosed with allergic conjunctivitis.
Also, suppuration of the eyes in combination with rhinitis can occur with dacryocystitis. This pathology is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac due to obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct.
Associated symptoms
In addition to the discharge of yellow and green fluid from the eyes, a child may experience other symptoms of a runny nose. The clinical picture is determined by the type of disease.
The baby may complain of pain, burning, pain in the eyes, and deterioration in the quality of vision. After sleep, the baby's eyelashes are glued together. Nasal congestion and runny nose interfere with sleep and play. The child becomes apathetic and sad.
If the disease is allergic, the baby may experience sneezing, red eyes, and increased tearing.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is accompanied by high body temperature, headache, and weakness. With dacryocystitis, in addition to lacrimation and discharge of pus, the child will have severe redness of the inner corner of the eye.
If conjunctivitis develops as a result of influenza, ARVI or a cold, then the baby may experience a cough, sore throat, and hyperthermia. With any type of illness, weakness, loss of appetite, and fatigue are possible.
What to do at home?
If the cause of purulent eyes and runny nose is allergic conjunctivitis, then it is worth eliminating the influence of the irritating factor.
You may need to take antihistamines. Diseases of bacterial etiology are treated with antibiotics. If the baby has a viral type of conjunctivitis, then antiviral and restorative medications are indicated. Drug therapy should be selected by a doctor.
All parents can do at home on their own is rinse the eyes and nose. To treat the mucous membrane, you can use green tea or a decoction of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, sage). A solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate also helps well. The child’s nose should be washed with special antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions.
It is desirable that the products used are natural based. A solution of sea salt and water works well. You can make it yourself or purchase a ready-made product, Aqualor or Aquamaris.
These drugs moisturize the mucous membrane and make breathing easier. But you shouldn’t carry out salt rinses too often to avoid drying out the mucous membrane.
Nazivin, Nazol Baby, Otrivin are good at removing swelling. It is useful to strengthen your immune system. For this purpose, you can give your baby vitamin and mineral complexes. You also need to reconsider your diet.
It is recommended to maintain an optimal microclimate in the apartment. Too dry or humid air can worsen a sick child's condition.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
The most common cause of pus in the eyes is conjunctivitis, which, in turn, is a complication of acute respiratory infections. This happens because the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and the mucous membranes of the eyes are susceptible to the same viruses and bacteria.
The most important thing in the treatment of conjunctivitis is its diagnosis - you need to correctly determine the cause of conjunctivitis: virus, infection. This is important, since completely different approaches are used to treat all these diseases. The task of making a diagnosis falls entirely on the attending ophthalmologist.
A common cause of purulent eyes in newborn babies is dacryocystitis, in which case Dr. Komarovsky recommends massage. An ophthalmologist at a children's clinic will show and tell you exactly how to perform it.
A child's eyes are festering - video
To determine the cause of pus in the eyes, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. With conjunctivitis, both eyes are most often affected, but inflammation can occur in them alternately and with varying degrees of severity. Watch the video about the causes of pus in the eyes, the different etiologies of conjunctivitis, and the diagnosis of the disease.
At home, if a child’s eye becomes infected, each parent immediately tries to rinse the eye and thereby help the child get rid of this unpleasant phenomenon. However, it is better not to do this, but to seek qualified help from an ophthalmologist.
The doctor knows for sure how to wash a child’s eyes if they are festering. “The eye has become infected” is a very broad concept, so to find out the causes, the affected area, and, most importantly, for effective treatment, contact a specialist. Timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations will help you quickly get rid of pus in the eyes.
Write in the comments why your baby’s eyes fester.
Many parents ask what to do if their child’s eyes fester with a cold. Very often, even with a minor cold, children's eyes begin to become irritated and fester. This occurs due to the fact that the lacrimal canal and nasal ducts are located at a close distance from each other. That is why in children more often than in adults, the infection easily penetrates the eyes.
A suppurating organ of vision in an adult can manifest itself with other symptoms and be a consequence of some serious diseases. If a child’s eyes fester due to a cold, then he should be examined by 2 doctors - a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist. Colds are usually accompanied by the presence of viruses and bacteria, and it is because of them that the eyes fester during a cold.
Why do my child’s eyes fester?
Pus in the eyes of a child is an unpleasant phenomenon that causes great discomfort to the baby. There is a feeling of itching, pain, tearing, and body temperature rises. A number of reasons provoke this condition - from a speck getting into the eye to complications of a bacterial or viral infection.
Table “Causes of pus formation in the eyes of a child”
| Provoking factors | Relationship and characteristics of manifestations |
| Conjunctivitis | Inflammation in the eye is caused by streptococci, chlamydia, and Staphylococcus aureus. Under the influence of pathogenic flora, itching and tearing appear, pus accumulates in the corners of the eyes, which provokes sticking of the eyelids after sleep. In the morning, the baby develops dry yellow crusts at the site of the discharge. The child’s eyes are constantly red, the temperature rises, he is capricious and sleeps poorly, complains of pain |
| Dacryocystitis - blockage or underdevelopment of the tear ducts in newborns | As a result of obstruction of the lacrimal ducts due to the appearance of plugs in them, tears do not pass freely through the nasal cavity - a stagnant process is formed, the eyes become very festered and watery. The disease often occurs in infants up to 3 months of age. |
| Bacteria entering the baby's eyes during childbirth (by passing through the mother's infected genital tract) | The baby's eyelids are swollen, his eyes are red, and there is copious purulent discharge already on the 2nd–3rd day after birth |
| Sinusitis | The sinuses became inflamed and the eyes festered. This happens due to the fact that the maxillary sinuses are close to the lacrimal ducts. Inflamed and swollen, they put pressure on the walls of the canals and provoke obstruction of the fluid in them and, as a result, suppuration, the eyes water, their mucous membranes become inflamed, and pain appears. |
| Inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash | The disease develops as a result of infection entering the eye. The eyelids swell, there is redness, pain when blinking, and increased body temperature. Pus collects from both the outside and inside of the eye |
| Allergy | Negative reaction of the body to an allergen (plants, animals, food, household chemicals, pollen, dust). Signs: itching, swelling of the mucous membrane, runny nose. The child begins to scratch his eyes, introducing an infection into them, as a result, one eye becomes inflamed, the bacteria spread to the second in 2-3 days, yellow pus appears, tearing, redness of the sclera |
| Flu, ARVI, colds | The accumulation of viral and bacterial infections provokes blockage of the tear ducts - pustules collect in the corners of the eyes, while the baby has a fever and snot |
| Gonococcal infection in newborns | Entering the baby’s body during childbirth, the infection causes severe suppuration - green discharge is accompanied by swelling and the formation of ulcers in the mucous membrane |
| Blepharitis – ulcerative, scaly, demodectic, angular, meibomian | The disease affects the eyelids. Inflammation provokes severe suppuration in the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, sticking of the corners of the eyes |
| Contact with the mucous membrane of the eye of a foreign body (speck) | Getting dust or grains of sand into the eyes causes a defensive reaction in the body - the cells try to remove the foreign body: purulent discharge, burning, and painful discomfort appear. |
| Violation of hygiene rules | If a child repeatedly rubs his eyes with unwashed hands, pathogenic organisms begin to develop in the mucous membrane, which leads to suppuration in the eyes, redness of the sclera, and swelling of the eyelids. |
Causes
Why do my child’s eyes fester and his runny nose get worse?
- The cause may be a blockage of the tear duct. There is a certain percentage of children born with problematic tear ducts.
Normally, tears flow from the inner corner of the eye through the duct into the nose. Therefore, during crying, discharge from the eyes occurs and a condition similar to a runny nose occurs. If an obstacle occurs, the tear stagnates in the lacrimal canal, disrupting the evacuation of microbes that enter the palpebral fissure. Stagnation causes purulent inflammation.
With age, this problem in children goes away on its own. Treatment for this phenomenon consists of constantly removing pus from the eye by wiping with a clean cotton pad soaked in warm water and instilling appropriate drops.
Such treatment relieves the symptoms of the disease, but to eliminate the cause, massage of the nasolacrimal sac or treatment of the lacrimal duct is prescribed, which finally solves the problem.
- A runny nose may occur if a child suffers from allergic rhinitis.
If a child has increased sensitivity to various allergens, then he will exhibit all the symptoms of a runny nose and flu. As a result of the resulting active inflammatory process, which is accompanied by profuse lacrimation and swollen nasal mucosa, suppuration of the eye may begin.
The cause will be the same blockage of the tear duct. Treatment of allergic rhinitis consists of eliminating the source that causes the child's allergies and using antiallergic and anti-inflammatory drugs, which the doctor will select.
The flow of tears may be disrupted if the child has a runny nose or a stuffy nose. The same symptoms occur during colds and acute respiratory viral infections.
- During acute viral respiratory diseases, a child may develop viral conjunctivitis.
It is quite difficult. During conjunctivitis, the child’s eyes fester, the temperature may rise to 38 ºС, or even higher, and the nose may be stuffy. The infection causes swelling of the eyelids and redness of the mucous membrane.
The presence of purulent discharge indicates the presence of bacteria. Due to the constant secretion of pus, the eyelids stick together and it is difficult for the child to control the eyes. If the conjunctiva is inflamed, it is better for children not to be in bright light, as they develop photophobia. Severe pain appears and it feels as if sand has gotten into the eye.
What to do and how to treat?
What to do when your eyes fester due to conjunctivitis? The whole point of therapy is to keep the eyes clean and use antibiotics in the form of ointments or eye drops.
They contribute to the fact that the disease occurs in a milder form and less pus is formed. As a result of such treatment, the child tolerates the disease more calmly. He is not bothered by irritation and itching.
There are general rules for parents when children's eyes fester. The main requirement is hygiene. Purulent discharge must be removed. You need to take a cotton pad and, moisten it in boiled water, remove everything that is there.
When pus remains in the palpebral fissure for a very long time, this leads to moceration - bright active inflammation on the surface of the skin around the eyes. This is especially painful for infants who cannot rub their own eyes. They experience pain and severe itching, which makes them very moody.
Most situations in which suppuration occurs in the eyes are not dangerous to vision. As a rule, bacterial conjunctivitis does not cause serious consequences for the festering eye, and usually the disease completely recedes after 3 weeks.
If your baby has a cough, runny nose and festering eyes, it could be a respiratory infection or a cold. Therapy of the disease consists of complex treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and increasing the body's defenses.
If the child receives basic treatment, then there is no need to use eye drops, since as the runny nose subsides and the nose clears, the tear ducts will also clear. Therefore, regular eye rinsing will be sufficient.
When the tear ducts are narrowed, doctors most often solve the problem using conservative treatment methods. However, if suppuration of the eyes and runny nose become chronic, it is necessary to restore the patency of the canal, which is performed surgically.
If a child develops a cough, the nose cannot breathe, and pus comes out of the eyes, complex treatment is prescribed. To combat a runny nose, the baby’s nasal passages are cleaned and drops are placed in the nose. Preliminary cleansing is necessary so that crusts and mucus do not prevent the drug from reaching the mucous membrane and having the desired effect.
How to treat a cold that has caused suppuration in a child’s eyes?
Cough, depending on whether it is wet or dry, is treated with syrups or inhalations.
For inhalation, a nebulizer is usually used, to which appropriate medications are added.
The eyes, if pus accumulates in them, are treated with furatsilin solution during the day. If the discharge of pus is strong, then at night the eyelids are lubricated with antibacterial ointment. To prevent the eyes from festering, eye drops are usually prescribed:
- Levomycetin;
- Albucida;
- Ciprofloxacin.
If a viral infection is accompanied by bronchitis with a severe cough or pneumonia, then treatment will be carried out with antibiotics in the form of intramuscular injections.
If we talk about the use of folk remedies, which many parents love so much, then we would advise washing festering eyes with a decoction of calendula flowers. When treating your eyes with cotton pads, you should adhere to the following rules:
- you cannot use the same cotton pad twice;
- You should use a separate disc for each eye to avoid infection;
- You need to wipe the eye from the outer corner to the inner one.
The mother caring for the child should follow all safety measures to avoid contracting the infection herself. She needs to wash her hands with soap both before and after procedures.
It is advisable to wear a protective mask on your face to prevent viral infection from entering the nasal or oral mucosa. Since the infection is transmitted through airborne droplets, an adult can easily become infected.
Conjunctivitis with a cold
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- constant lacrimation;
- burning and itching of the eyes;
- redness;
- painful sensitivity to light.
The reasons why a child's eyes fester are viruses or bacteria. If inflammation occurs against the background of a cold, then conjunctivitis is viral in nature. Most often it is accompanied by a runny nose, cough, sore throat, fever and other symptoms of ARVI. Typically, pus is caused by an adenovirus, just like a cold. In this case, the main symptoms are severe itching and redness of the conjunctiva. The infection may affect one or both eyes.
Often a bacterial infection is added to a viral infection. Its main symptom is pus that sticks together on the eyelids after sleep and dries on the eyelashes during the day. This complication occurs more often in children and is more severe than in adults. It is important to correctly determine the type of infection, as this affects the choice of therapy. Therefore, it is unacceptable to self-medicate, especially if the child’s eye is festering.