Diagnostics: how to determine LVHL
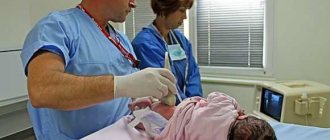
When the doctor tells you that your baby has a heart murmur, there is no reason to panic. The condition does not require emergency resuscitation measures or intensive treatment. The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination. It will help clarify the location and number of additional strands. There are the following types of LVDC:
- according to location in the ventricle - apical, middle, basal;
- in relation to the axis of the heart - diagonal, longitudinal, transverse;
- by number - singular and plural.
If echocardiography has revealed an additional chord in the cavity of the left ventricle in a child of any age, I advise parents to undergo the following examinations:
- A general blood test is not important in terms of diagnosing LVHL, but it will reveal anemia or an existing inflammatory process in the body, which can aggravate the condition of a child with a minor cardiac anomaly.
- Electrocardiography. It is advisable to conduct Holter monitoring, which will exclude arrhythmia with greater diagnostic accuracy.
- ECG tests with physical activity will show how well the child’s heart “copes” with its function.
- Consultations with specialized specialists (orthopedist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist).
I always explain to parents of infants that sometimes the abnormal chord can lengthen and “grow” into the valve, so during subsequent ultrasounds the doctor does not detect LVDC. In such cases, they say that the baby has “outgrown” this pathology.
If echocardiography has revealed an additional chord in the cavity of the left ventricle in a child of any age, I advise parents to undergo the following examinations:
Symptoms
In most cases, the additional chord of the left ventricle does not bear any functional load on the heart and does not interfere with its normal functioning. For many years, this minor anomaly may not be detected, because it is not accompanied by any special symptoms. A pediatrician can listen to a systolic heart murmur in a newborn, which is detected between the third and fourth ribs to the left of the sternum and does not in any way affect the functioning of the heart.
During intensive development, when the rapid growth of the musculoskeletal system significantly outstrips the growth rate of internal organs, the load on the heart increases, and the additional chord may make itself felt for the first time. Your child may experience the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- rapid or unmotivated fatigue;
- psycho-emotional lability;
- cardiopalmus;
- pain in the heart area;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
The same clinical manifestations can be observed with multiple abnormal chords of the left ventricle. Most often, such symptoms appear during adolescence. In the future, they can completely disappear on their own, but sometimes they remain in adulthood.
When symptoms appear, the child is required to undergo ECHO-CG, ECG and 24-hour Holter monitoring. These studies will allow the doctor to determine the presence or absence of hemodynamic disturbances. If the additional chord is “hemodynamically insignificant,” then the anomaly is considered safe, and the child only requires follow-up with a cardiologist. With a “hemodynamically significant” diagnosis, the patient is advised to observe, adhere to certain restrictions and, if necessary, treatment.
When symptoms appear, the child is required to undergo ECHO-CG, ECG and 24-hour Holter monitoring. These studies will allow the doctor to determine the presence or absence of hemodynamic disturbances. If the additional chord is “hemodynamically insignificant,” then the anomaly is considered safe, and the child only requires follow-up with a cardiologist. With a “hemodynamically significant” diagnosis, the patient is advised to observe, adhere to certain restrictions and, if necessary, treatment.
Accessory chord of the left ventricle: clinical picture and symptoms
Almost always, the additional chord does not lead to disruption of blood flow. But sometimes hemodynamics are disrupted and blood regurgitation occurs. In such cases, mitral valve (MV) prolapse may develop - inversion of its valves into the atrium cavity during systole. As a result, MV insufficiency develops when blood is thrown back into the left atrium. There are 4 degrees of uric acid deficiency:
- I. The reverse flow of blood reaches a quarter of the depth of the atrium.
- II. The blood flow reaches half the depth.
- III. Reverse blood flow extends to ¾ of the depth of the left atrium.
- IV. The blood reaches the opposite wall of the atrium.
Children with a hemodynamically significant additional chord may get tired faster and complain of weakness. They do not tolerate physical activity very well. In some cases, chest discomfort and dizziness occur. If such a chord is combined with other anomalies in the development of the heart, then rhythm disturbances may appear.
Newborns rarely suffer from symptoms of this pathology. Most often it manifests itself in primary school or adolescence. If the additional chord does not disrupt the blood flow, then there may be no symptoms at all.
Children with a hemodynamically significant additional chord may get tired faster and complain of weakness. They do not tolerate physical activity very well. In some cases, chest discomfort and dizziness occur. If such a chord is combined with other anomalies in the development of the heart, then rhythm disturbances may appear.
Features of the pathology
Due to the fact that it does not affect hemodynamics, it is almost always detected by chance. Only a small part (this applies to transversely located muscular and mixed chords) can have negative consequences for the work of the heart and all hemodynamics. The peculiarity of the false chord in childhood is its incomplete development. But the situation should be constantly monitored by parents (they should not miss the first warning signs) and the local doctor. In the first year, a false chord of the left ventricle in a child cannot be eliminated without surgery, but its development can be influenced.
Only a hemodynamically significant abnormal chord can “make itself known.” This can be seen from the following signs:
- discomfort in the chest (but the newborn baby will not be able to report pain);
- high fatigue and poor exercise tolerance;
- frequent attacks of heartbeat;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- changes in psycho-emotional behavior (most often the baby becomes whiny and irritable, and the teenager may become withdrawn).
The doctor may suspect the presence of an abnormal chordae due to one more sign - a murmur upon auscultation of the heart.
- Uncorrectable rhythm disturbances associated with an abnormal chord. This is especially true for young people and children.
- Rapidly progressive heart failure due to accessory chordae.
Symptoms
Typically, false chord of the left ventricle is not accompanied by manifestations at any age of the patient with this deviation. This is true for those cases where the pathology is not characterized by connective tissue dysplasia and has one additional thread.
If an ultrasound scan reveals not one additional chord in a child, but several, they are placed transversely, then heart complaints are likely to appear during the rapid development and growth of the child, during pregnancy and the pubertal stage of development. Among such complaints are:
- Pain in the left side of the chest.
- Increased fatigue.
- Constant physical weakness.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- It seems as if there is not enough oxygen.
- Pale skin.
Some patients, due to the presence of an abnormal chord formed in the cavity of the left ventricle, experience arrhythmic symptoms or attacks of tachycardia.

If the diagnosis of MARS is provoked by the pathology of dysplasia, the following symptoms of the disease are possible:
- Thin body structure of a child.
- Abnormally high growth.
- Increased joint mobility.
- Violation of the structure of the ribs.
- Weakening of the spine.
- Frequent cases of joint dislocations.
- Changes in the structures of the organs of the urinary and respiratory systems.
- Other anomalies.
The false chord of the left ventricle does not overload the heart and does not interfere with normal functioning. This minor anomaly may not be detected for many years, since no symptoms appear. During the visit, the pediatrician may hear slight murmurs in the newborn’s heart. However, it does not affect cardiac function.
Clinical manifestations are possible during the development and growth of a child, when the increase in limbs and body is many times faster than the increase in organs inside, which increases the load on the cardiac system. In this case, children may experience the following symptoms:
- Heartache.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Rapid rhythm.
- Unreasonable fatigue.
- Mental instability.
If an extra chord in the heart makes itself felt, the child needs to be examined, have a cardiogram done, and be under the supervision of a cardiologist. Heart tests will help the doctor identify hemodynamic abnormalities.
Most doctors equate this minor cardiac anomaly to normal. The presence of an abnormally attached chord inside the left ventricle is not a terrible verdict. After all, the anomaly does not require surgical treatment, and when there are no hemodynamic disturbances, it does not need to be treated with medication.
Treatment
Drug therapy is prescribed to children with excess chordae only when there are clinical manifestations of the problem, for example, if the child complains of discomfort in the chest. Also, drug treatment is necessarily prescribed when rhythm disturbances are detected. In rare cases, when the false chord includes the conduction pathways of the heart, it is excised or destroyed by cold.
Among the medications that are prescribed for additional chord, there are B vitamins, potassium orotate, Magne B6, Panangin, Magnerot, l-carnitine, Actovegin, ubiquinone, piracetam and others. They normalize metabolic processes in the tissues of the heart, improve the conduction of impulses and nourish the heart muscle.
In addition, a child with an extra chord is advised to provide:
- Balanced diet.
- Daily exercise.
- Frequent walks.
- Hardening.
- Minimum stress.
- Optimal daily routine.
- Timely treatment of diseases.
Such children are not prohibited from outdoor games and moderate physical activity, such as swimming, gymnastics or running.
Komarovsky emphasizes that in most cases such children do not need treatment and there is no need to change their lifestyle. The only thing that a well-known doctor warns parents about is that children who have grown up with an additional chord should not work as divers or jump with a parachute.
Natural
Natural chords have a normal structure; they help the valves contract and the heart perform its usual work. The chordae stretch like a sail and prevent blood from flowing back. If there were no chords, then the valves would not be able to close and open, and the heart muscle would not be able to function fully. The notochord ensures normal blood flow in the myocardium.
Heredity plays a huge role in the appearance of an extra chord, and much more often on the maternal side. It is generally accepted that the following factors during pregnancy lead to the development of this anomaly:
What is an accessory chord in the heart?
The chordae are tendinous threads of equal thickness and size, consisting of muscle and connective tissue and connecting the valve apparatus and the ventricle. When they contract, they pull the valve leaflets towards themselves, which promotes the formation of a gap and the release of blood from the atria. During relaxation, the passage is closed. The additional (false) chord does not perform its intended functions. It has an atypical structure and can connect to the ventricle or valve at only one end.
The abnormal chord has a code according to the ICD (International Classification of Diseases) 10th revision Q20.9. It stands for Congenital Abnormalities of the Heart Chambers. “False chord” is not considered as an independent pathological process. It is divided according to its location in the cardiac cavities as follows:
- Direction: transverse;
- diagonal;
- longitudinal
- right ventricular;
- single;
- basal;
An extra chord in the heart usually does not pose a particular danger, but whether this is so depends on the hemodynamic significance. Transverse tendon threads can disrupt the flow of blood, which will lead to various consequences (stroke, arrhythmia, heart block). Multiple chordae are no less dangerous, as they are perceived as a sign of genetic pathologies.
In most cases, a single left ventricular filament is detected in newborns during an ultrasound examination of the heart. Sometimes it is noticed in the fetus in the womb during routine diagnostics. In adults, its detection is associated with a medical examination or the occurrence of cardiac symptoms.
False tendon filaments in infants are often combined with other minor anomalies of the heart structure:
- excess trabecula;
- open oval window;
- insufficiency of valve apparatus.
Unlike other anomalies, the patent foramen ovale closes with age. Only in rare cases does it remain forever.
A well-known pediatrician, E. O. Komarovsky, commented on the presence of “false chords” in babies. According to the expert, the baby will not experience any discomfort. This anomaly is more an individual feature than a serious defect. Only in exceptional cases, in the presence of many tendon threads, is it possible that hemodynamic disturbances may occur. Treatment will be aimed at stabilizing the heart. Single chords do not require any treatment regimen or restrictions regarding the type of activity, sports or diet.
Treatment
If an additional chord is detected, which is accompanied by symptoms or hemodynamic disturbances, in addition to the recommendations described above and more stringent restrictions on physical activity, drug therapy is recommended.
These children may be prescribed the following medications:
- vitamins B1, B2, PP - prescribed to improve myocardial nutrition, taken for a month, the course of treatment is repeated twice a year;
- Magne B6, Magnerot, Potassium orotate, Panangin - are prescribed to improve the conduction of nerve impulses and prevent arrhythmias, drugs are selected depending on age and taken in courses for a month or more;
- L-carnitine, Cytochrome C, Ubiquinone - prescribed to normalize metabolic processes in the heart muscle;
- Nootropil, Piracetam - are prescribed when symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia appear.
Indications for immediate hospitalization in a cardiology hospital may include the following severe heart rhythm disturbances:
They can develop with multiple or transverse chordae and require detailed examination and subsequent treatment.
In rare cases, muscle fibers of the cardiac conduction system may be included in the structure of the accessory chord of the left ventricle. Such cardiac abnormalities can cause ventricular arrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation. To eliminate them, the following surgical interventions are indicated:
Causes
An additional chord in a child’s heart appears in the womb due to certain factors:
| Cause | Description |
| Hereditary predisposition | The presence of false tendon threads or other heart ailments in one of the parents is the main cause of abnormalities in their baby. |
| Bad habits | A woman who drinks alcohol, drugs and smokes cigarettes during pregnancy significantly increases the likelihood of developmental defects in the unborn child, affecting not only the heart. |
| Poor environmental situation | Polluted air and water contribute to the formation of abnormalities in the baby during intrauterine development. |
Clinical picture
One extra chord in the left ventricle rarely manifests itself. The situation is different if the filament is located transversely in the right ventricle, or if there are quite a lot of them. The patient begins to experience discomfort associated with impaired hemodynamics and heart function in general:
- fast fatiguability;
- irregular heartbeat;
- stabbing chest pain;
- mood swings;
- general weakness;
- dizziness.
Signs are most often detected during adolescence. The child begins a stage of intensive muscle and bone growth, which puts additional stress on the heart. If they are detected, it is necessary to register with a cardiologist so that he can monitor the development of the situation and take timely measures to stabilize the condition.
Diagnostic methods
A cardiologist should be involved in identifying excess chordae and drawing up a treatment regimen. They are detected using instrumental diagnostic methods and by auscultation (listening to noises):
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) allows you to visualize the structure of the heart and examine hemodynamic features.
- Auscultation helps to hear diastolic murmurs arising from the accessory chord.
- Electrocardiography (ECG) displays the electrical activity of the heart and allows you to see possible impulse conduction abnormalities.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe daily ECG monitoring and bicycle ergometry. The first examination helps to obtain accurate data on the work of the heart muscle throughout the day. The second test is carried out to evaluate her response to physical activity.
An identified extra chord in a child’s heart may gradually “disappear.” The baby is actively growing, which leads to a displacement of the anomaly. Instrumental diagnostic methods will confirm its absence. A treatment plan will not be drawn up. In conclusion, the doctor will indicate that the heart is without pathologies.
Course of therapy
In the absence of symptoms of disruptions in blood flow, there is no point in treating the anomaly. A person will have to undergo an ultrasound and ECG annually and, with the results obtained, make an appointment with a cardiologist to monitor the condition of the heart muscle.
If the clinical picture of a hemodynamic disorder is still present, then drug therapy is prescribed:
- Preparations rich in B vitamins (“Neurovitan”, “Superum”) are involved in nervous regulation, increase cellular metabolism and stop the development of atherosclerosis.
- Tablets containing magnesium and potassium (Asparkam, Orocamag) help stabilize blood pressure, vascular tone and neuromuscular transmission.
- Antioxidants (“q-Protect”, “Resveratrol”) prevent the development of atherosclerosis, normalize heart function and stimulate metabolic processes in the myocardium.
- Medicines with nootropic effects (Aniracetam, Semax) are used to improve cognitive abilities and increase tolerance to stress (physical, mental). They are also used to relieve signs of VSD against the background of severe disruptions in hemodynamics.
Antiarrhythmic and other cardiac medications are prescribed by the attending physician depending on the patient’s condition. To complement the therapy regimen, you should follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- create the right diet;
- spends more time outdoors;
- take breaks while working;
- exercise;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- sleep at least 7-8 hours a day.
With the development of various life-threatening conditions, the patient must be hospitalized. They are usually the result of multiple or transverse accessory chordae. In a hospital setting, a detailed examination will be carried out and treatment will be prescribed.
Surgery is required if the accessory tendon thread disrupts the conduction of impulses and leads to severe disruptions in blood flow. Doctors will perform a procedure of cryodestruction (destruction of tissue by exposure to cold) or excision of the chord.
What is the accessory chord of the left ventricle?
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
The human heart consists of several chords that prevent the valve from bending during contraction. Thanks to their presence, the organ can hold blood and push it through the vessels. In some people, in the first weeks of development, an additional chord of the left ventricle is formed. Most often it has a thread-like structure, but in some cases it is based on muscles and tendons. In 90% of cases, this abnormality is found in adolescents aged 13-16 years, but many people with this diagnosis live into old age without problems with the heart. Below we will analyze what it is and how this condition affects well-being.
Reasons for development
An additional chord in the left ventricle most often appears due to a genetic predisposition. It is transmitted in 95% of cases from mother to child. MARS develops in utero, and the catalyst for this process is a failure during the formation of connective tissue in the cavity of the left ventricle. For this reason, women who have been diagnosed with this need to have their children examined for the presence of this anomaly. Also, the reasons for the development of additional chords may be:
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- poor environmental situation in the region;
- physical and nervous overstrain;
- drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.

Varieties of chords
An additional chord in the left ventricle of the heart can be of the following type:
- muscular, fibrous or fibromuscular;
- with longitudinal, transverse, diagonal connecting fibers;
- with single or multiple strands;
- median, basal or apical.
The most dangerous are the transverse chords. They can block blood flow and pose a danger to the human body. In other cases, these MARS are considered harmless and do not cause any burden on the heart.
Symptoms
The additional chord on the heart practically does not manifest itself until a certain age. With a certain structure, it may not appear even at a more mature age. It is believed that the first signs of LVDC can be detected during the active growth of the child, when the skeleton develops faster than the organs. The following symptoms may indicate the presence of MARS:
- fatigue quickly without any heavy load;
- dizziness;
- pain in the heart area;
- sudden change of mood;
- racing heartbeat.
A similar symptom complex is given not only by an additional chord in the cavity, but also by other multiple MARS. Therefore, all diagnostic work should be carried out by a doctor with extensive experience. After the active growth stage is completed, the signs of the accessory chord of the left ventricle disappear, but then appear in an adult. But a diagnosis is not made based on the symptoms listed above. The young patient will have to undergo various types of diagnostics.

If, after examination, a child is diagnosed with several extra chords in the heart, then the doctor should refer the patient for additional diagnostics. As you know, connective tissue in the human body is concentrated not only near the heart, but also in muscles and other organs. Therefore, clinical manifestations on their part may occur. If they can be detected, the child is diagnosed with connective tissue dysplasia. This disease is characterized by changes in the skeleton, muscle tissue, and the structure of some organs.
Is this anomaly dangerous?
One additional chord in the heart is considered a slight deviation from the norm. Surgery is not required for this type of MARS, so parents and child should remain calm. If there are no disturbances in the blood flow, then surgical and drug treatment of the disease will not be needed. As you grow older, it can lead to the development of blood clots and changes in heart rhythm, but it is impossible to predict the appearance of these pathologies.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after an ultrasound of the heart. The patient is first listened to for the presence of systolic murmurs. To make sure that the anomaly is harmless to the child’s body, a classic and stress ECG may be prescribed. The doctor decides which specific diagnostic methods to use after examining the patient.
Treatment
If an additional chord with symptoms of hemodynamics is detected in a child or adult, it is recommended to limit physical activity. Patients are also recommended to take the following medications:
- l-carnitine, ubiquinone to restore metabolic processes in the heart muscle;
- piracetam to remove signs of neurocirculatory dysfunction;
- intravenous B6, B12 and nicotinic acid to improve myocardial condition;
- magnesium and potassium to improve the conduction of nerve impulses and prevent arrhythmia.
The development of atrial fibrillation and tachycardia may serve as indications for prompt hospitalization. But most often these diseases appear when there are several chords or one chord is transverse. Then doctors conduct a detailed analysis of the heart and determine a treatment method for the problem that has arisen. Most often, chords that interfere with blood flow are excised or removed with nitrogen.
If an additional chord is found in a child or adult as a result of a routine examination, but does not cause any discomfort, then medications are not taken. Such patients should normalize their daily routine and avoid overexertion and excessive relaxation. You will have to give up intense physical activity in favor of walking in the fresh air.
If a child is involved in a certain sport, then you should not sharply prohibit him from attending the section. You should discuss the possibility of classes with a doctor so that he can adequately assess the patient’s condition. There is no need to isolate a child from society, prohibit him from going out and playing with friends, because... this approach will make him feel inferior.
Prevention of complications
Considering that the disease is genetic in nature, it is impossible to prevent its occurrence. If an additional chord is detected in an adult or child, you must follow the specialist’s recommendations in this regard. To avoid complications, in older age you should monitor the amount of cholesterol consumed and your own weight. Excess body weight creates additional stress on the blood vessels, causing the heart to work harder.
Physical therapy classes are needed for children with an additional chord. They help strengthen the heart muscle, preventing the development of all kinds of pathologies. Most doctors do not advise people with excess chordae to participate in sports at a competitive level. Long swims, practical training at a flying club, and diving can harm people with this anomaly. But sprinting, yoga and bodyweight exercises will make your heart muscle stronger.
Possibility of complications
It is impossible to predict in advance whether an additional chord will lead to the development of disruptions in the functioning of the heart or not.
The most favorable prognosis is in the presence of an anomaly in the left ventricle.
In most cases, it does not lead to pathological changes and does not require treatment. The use of medications to improve the functioning of the heart muscle significantly reduces the likelihood of complications. The only thing to be wary of is transverse and multiple tendon strands. They have the most unfavorable prognosis.
Accessory chord of the left ventricle: is it dangerous?
There are several chords in the human heart that prevent the valve from bending during contraction of this organ. Thanks to their presence, it retains blood well and ensures adequate hemodynamics. The normal chord is a kind of spring with a muscular structure. Sometimes during intrauterine development, an additional chord appears in one of the ventricles of the heart, which is a thread-like cord of connective tissue. In some cases, this abnormal formation includes muscle or tendon fibers.
In this article we will look at such a minor cardiac anomaly as an accessory chord of the left ventricle. In most cases, it is found in children under 18 years of age, but some people live with this diagnosis for many years and do not feel any changes in the functioning of the heart. Usually, an additional chord is detected by chance: during an examination for another disease or during a preventive examination. It is not detected either by listening to a heart murmur or by an ECG, and an accurate diagnosis can only be made after an ECHO-CG. Having heard a heart murmur, the doctor can only suspect the presence of this minor heart anomaly and recommend an ultrasound examination to refute or confirm the diagnosis.
In our article we will introduce you to the causes of development, types, symptoms, methods of observation, treatment and prevention of accessory chord of the left ventricle. This knowledge will help parents of children with such a heart anomaly choose the right tactics to approach the problem and save them from unnecessary worries.
Military service
In the presence of a single false chord, young people who have reached the age of 18 are still drafted into the army for service. Representatives of the medical commission believe that it will not have any effect on well-being during the next year of life. The conscript does not need to undergo treatment in a hospital setting. He will be able to follow orders and engage in physical training on an equal basis with other military personnel. A contraindication to service in the armed forces is an abnormal heart rhythm and other severe complications caused by the anomaly.
Excess chords in the ventricles of the heart muscle are perceived by specialists as a minor anomaly that does not require treatment and does not limit human life. It is enough to do an ultrasound every year to monitor its development. If signs of disruption in hemodynamics and arrhythmia occur, drug therapy is prescribed. If it does not help to achieve relief of the condition, then surgical intervention will be required.
What to do?

The baby grows, the body changes, and the load on the heart muscle changes. What may cause the following:
- dizziness;
- causeless fatigue;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- signs of arrhythmia;
- psycho-emotional instability.
The health of young patients is monitored by specialists; control ECHO-CG is carried out annually. With an additional chord, almost no one is drafted into the army, and many cases where physical activity is provided are subject to restrictions or prohibitions. Treatment and preventive measures are aimed at:
- maintaining a daily routine;
- balanced diet;
- distributed physical activity (physical therapy, wall bars, light running, race walking, slow dancing);
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- massage;
- stabilization of nervous system functions;
- treatment and prevention of other health disorders.