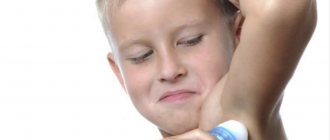
In adults and children, there are situations when the area between the nose and lips begins to turn pale or blue. Paleness of the nasolabial triangle is often accompanied by redness of the rest of the face and occurs as a result of physical or emotional stress, heat, or various diseases.
What does pallor or cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle indicate?
- Doctors say that such a picture may indicate heart pathology. We are not talking about prolapse, and, most likely, about more serious heart diseases.
- This bell also signals vascular dysfunction. If the nasolabial triangle turns pale, then we are talking about a violation of vascular contraction, and blueness indicates stagnation of venous blood.
- The nasolabial triangle can also turn blue during pneumonia.
What should you do the moment you notice that your child’s nasolabial triangle has turned blue or pale?
- Visit a neurologist and cardiologist with your child. It is better to consult with these two specialists.
- Give your body moderate cardio exercise, such as cycling.
- Taking a contrast shower will help strengthen blood vessels. It is necessary to start with a minimum temperature difference and in no case rush to increase it. You don't need temperature shock.
- Vitamin C. If necessary, your doctor will prescribe an industrial medicinal product, and you, in turn, should increase the amount of currants, strawberries, cabbage and other vitamin-rich vegetables, fruits and berries in your diet.
Some diseases of infants are not very easy to determine by external indicators. It is on this basis that during the examination the pediatrician asks young mothers many questions about sleep, behavior and external transformations of the baby. Short-term or long-term blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle can be the first indicators of a deviation in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The real concern for their parents should be the child's extra limbs. Blueness of the nasolabial triangle in children with bright and thin skin can be called a false alarm. Similar effects may appear in the first days of life, also around the eyes.
Heart disease is much more often determined by just such symptoms. a light blue tint to the skin appears due to the mixing of two types of blood - arterial and venous. This process is caused by a simultaneous decrease in oxygen in the blood. Before the nasolabial triangle turns blue, the child may suddenly become worried. From time to time his movements resemble a strong tremor.
If such a situation happens to your baby, then immediately consult a doctor. It is better to bring it to a specialist at home. During the inspection, you need to accurately describe all the details you noticed. In addition to disruption of the heart, similar symptoms may indicate the presence of diseases of the nervous system or abnormal structure of the heart partitions. In some cases, timely intervention is prescribed.
Child examination
When a light blue tint to the skin of the nasolabial triangle appears in a child, he is prescribed a special set of examinations. First, the baby needs to be demonstrated to a pediatrician, surgeon and neurologist. Be prepared for the fact that you will additionally need to undergo an ultrasound examination. Only after all these steps have been completed will the baby be diagnosed. Under no circumstances should any suspicious observations be kept silent. Be sure to tell your children’s doctor about all your concerns.
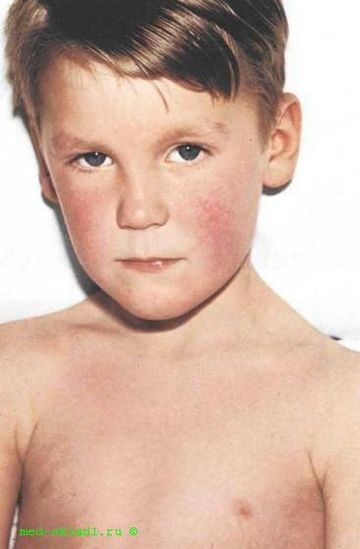
Main reasons
Below we will describe in detail the main causes of physiological and pathological blueness of the nasolabial area in children of different ages.
Physiological blueness
From the moment of birth and in the first 2-3 weeks, a newborn baby may experience blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, which occurs against the background of incompetence of the respiratory system. This condition is especially pronounced during the screaming and crying of a child, when there is a drop in oxygen saturation of the body. In the process of growing up, this phenomenon goes away on its own.
If the blueness of the nasolabial triangle does not disappear on its own after 2-3 weeks from the birth of the child, then this is a good reason to seek medical advice. It should be borne in mind that such a condition can threaten not only the health, but also the life of the child, therefore postponing a medical examination is unacceptable.
Long and complicated labor can also cause blueness of the nasolabial triangle in a newborn. The reason for this may be short-term hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the child’s body during passage through the birth canal.
Another reason for the physiological blueness of the nasolabial triangle in children may be the increased transparency of the skin in this area, especially in newborns. Through thin skin, vascular (venous) plexuses can be seen, giving a blue tint.
Pathological blue discoloration
One of the probable causes of this condition may be a disease of the child’s respiratory system. Examples include acute bronchitis and pneumonia (pneumonia). Additional symptoms of these diseases may include pallor of the child’s skin, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing, as well as coughing attacks. The more pronounced such symptoms are, the more intense the blueness of the baby’s nasolabial triangle. The appearance of this symptom in a child aged 3 years can be observed both in case of untimely diagnosis of cardiac pathology and in cases of respiratory diseases.
A foreign body in the respiratory tract can also cause this condition.
Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, accompanied by difficulty in inhaling, may indicate the presence of a foreign body in the respiratory tract. In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance. Learn how to provide first aid if your child has an obstructed airway.
Particular attention should also be paid to the child’s body temperature, since hypothermia can cause cyanosis (blue discoloration) in this area.
More serious causes of this symptom include congenital defects of the heart and large vessels (pulmonary artery), as well as heart failure. Accurate diagnosis of such conditions is only possible with the use of special medical equipment and with the participation of qualified medical specialists.
Many medical specialists have noted that blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle in a child, associated with malformations of the cardiovascular system, is accompanied by the appearance of blue in the area of the orbital sockets, which is not observed in pulmonary pathology.
The reason for urgent consultation with a doctor is the presence of blue discoloration for 3 weeks from the moment of birth, and at moments when the child is completely at rest.
Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle in a healthy child
Often, blueness of the nasolabial triangle appears in completely healthy children. The main reason for this result is possible hypothermia. In this situation, pay attention to the air temperature in the room and the clothes the child is wearing. The baby's lips may turn blue, for example, if you gave him a bath and did not pay attention to the fact that the temperature in the child's bathroom and bedroom is very different.
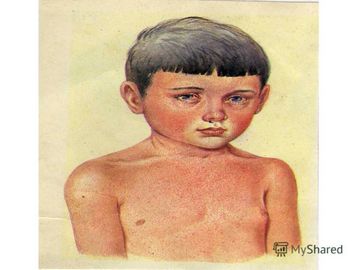
Much more often, blueness of the nasolabial triangle is observed in capricious and restless children. Due to constant emotional stress and crying, blood transformations occur. The amount of oxygen in it decreases significantly. The result of the process is a light blue tint to the skin near the nose and above the upper lip.
Open your mouth, open your eyes and take off your clothes. And we will tell you why you don’t need to be afraid of the dentist and have a condescending attitude towards the ophthalmologist, memorizing the third line from the bottom in the table for checking visual acuity (N K I B M S H Y B, by the way). People who in one way or another deal with your body (and even the same hairdressers), like real investigators, are able to see in your eyes, hair, mouth, etc. more than just hair and teeth - they see the first signs of the most various diseases, from hypertension to brain cancer. Don’t be lazy to ask them if everything is okay with what they are inspecting (cutting, crumpling). And if you’re not okay, go straight to a specialized doctor for an examination. We begin medical examination.
Investigator: dentist
Even if you brush your teeth and use dental floss, papillomavirus, transmitted through oral sex, can live in your mouth. So open your mouth wider and your dentist will look for any strange patterns in the back of your throat, the inside of your cheeks and gums, and under your tongue. And, if you are not sure of the attentiveness of your dentist, ask a specialist to check for such subtle signs of disease as:
Causes of blueness around the mouth
The phenomenon in which, due to certain factors, blueness of the skin occurs is called cyanosis. It should be noted that this name refers to a whole group of disorders in which such a symptom appears. In particular, these include blue discoloration around the mouth of a child, which is one of the most common types of the disease.
The main reason for the change in skin color is the content of a large amount of hemoglobin in the blood, which has already given oxygen to cells and tissues. When exposed to this substance, the blood becomes much darker, which is why it can be visible through the skin. This is most noticeable in places where the skin is thin, which includes the facial area.
Possible reasons:
- Prolonged crying. Many children, especially in infancy, cry when exposed to even the most minor irritating factors. Because of this, blood flow to the lips and chin increases, and oxygen consumption is significantly accelerated due to increased lung activity. Typically, after the baby calms down, the skin around the mouth returns to its normal color.
- Effect of low temperature. Blue skin can be caused by sudden changes in temperature, for example, when walking in cold weather or while swimming. Hypothermia provokes an increase in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, which may cause the corresponding color to appear. It is important to note that the child may experience tremors and a decrease in body temperature.
- Respiratory diseases. Blueness around the mouth is a sign of a large number of respiratory diseases. This symptom can occur with pneumonia, pleurisy, pulmonary edema, and various types of infection. In addition, cyanosis can be caused by foreign objects entering the respiratory tract, which interferes with the normal breathing process.
- Poisoning. Blue discoloration of the skin often accompanies intoxication, but it is important to note that in this case, as a rule, not only the area around the mouth turns blue, but also the skin in other parts of the body. In childhood, the most likely cause of poisoning is the use of various drugs, or accidental ingestion of alcohol-containing products, medications or household chemicals that are harmful to the child.
- Congenital defects. The cause of cyanosis in a child may lie in genetic abnormalities that arose in the body during the gestation period. The most common provoking factor is considered to be a heart or lung defect, due to which an insufficient amount of oxygen enters the body. Due to lack of blood, the skin gradually acquires a blue tint, and returns to normal color only after special breathing exercises or hardware procedures.
Thus, blue discoloration around a child’s mouth is most often the cause of cyanosis, a disease associated with insufficient oxygen flow into the tissues.
Sluggish, sunken tongue
If you sleep alone and have no one to kick you at night, you may not even realize how unbearably you snore. And this is important to know, since snoring may be one of the signs that you are susceptible to obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (breathing stops for a period of 10 seconds to 2-3 minutes). This threatens you with a stroke, heart attack, deterioration in potency, and even sudden death in your sleep. Because your head is tilted back in the dental chair, the doctor can see if your tongue is retracted and if your soft palate is likely to cause your airway to collapse while you're unconscious. If the doctor doesn’t like something, be sure to visit a somnologist after you’re done with your teeth.
Apnea in newborns
Apnea, or holding your breath during sleep, in young children is a rare but quite serious phenomenon that can occur for various reasons. Basically, apnea occurs in infants who were born prematurely and prematurely, since the breathing control centers in their brain have not yet been formed. The younger the baby is born, the more common it is to hold your breath, but fortunately, this problem goes away with age.
Other reasons for holding your breath may be hereditary diseases, injuries during childbirth, brain hematomas, inflammation of the throat, etc. Holding your breath can recur and can be quite a serious problem.
Sleep apnea often occurs during sleep, and parents or doctors may not always notice it. The main symptoms of breath holding (apnea) in infants:
The severity of holding your breath is determined by its duration. The longer the child does not breathe, the more serious the situation. Severe apnea is considered to be the absence of breathing for 10-15 seconds or longer.
With central apnea, the child simply stops breathing without making any effort. With obstructive apnea, the child tries to take a breath, but cannot due to blockage of the airways: larynx, throat or bronchi. Both types of apnea are equally dangerous in terms of consequences, but the first type is much more difficult to notice.
Often before breathing stops due to blockage, the child wheezes, whistling and other extraneous sounds are heard. With central apnea this is not the case, and all symptoms are reduced to cessation of breathing and blue skin color.
If your baby was born premature, you need to take into account his tendency to stop breathing. Until he reaches the level of development of his peers, you need to be ready to help him.
• Take the child in your arms, shake him, run your finger several times along the back from bottom to top. Wherein
Source
Weak jaw
Scientists say that the density of the mineral components of your lower jaw can be used to judge the condition of the bone structure of your spine and hip bones. If you go to the same dentist a couple of times a year, he may compare old pictures and his memories with new ones and find that you are losing bone mass. And before you develop osteoporosis, remember: According to a report from the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, about one in five men reach the extreme stage. If the disease is detected early, it can be stopped and even improved bone health through strength training and a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
Bad teeth
In 2011, scientists at Columbia University conducted a study: they took blood from a group of people who had something in common: gum problems and the absence of four or more teeth each. 73% of subjects had either diabetes or a predisposition to it. High blood sugar is a great catalyst for the growth of bacteria in the mouth. If your dentist is not happy with the way your gums look, go to your GP for a referral for a blood test for glycated hemoglobin.
Investigator: ophthalmologist
You came to get a prescription for new glasses, and the ophthalmologist happened to look right inside you. How? The eyes are the only place in the entire body where blood vessels can be examined without surgery.
Poor peripheral vision
It's not just your agility on the football field that is at risk. If you feel that you have to turn your head more and more often to contemplate the world around you, ask your ophthalmologist to conduct a test to determine the zone of clear vision. Deterioration in peripheral vision may indicate tumors in your brain. An ophthalmologist may also suspect a brain tumor if a fundus examination reveals swelling of the optic disc. Tumors increase intracranial pressure, the brain compresses the optic nerve, causing the same swelling.
Investigator: massage therapist
Here, as in the case of other specialists from this material, consistency is important: if you go to the same massage therapist year after year, he will be able to discern unpleasant changes on your skin.
Suspicious spots
The massage therapist sees your skin better than you (for example, your back) or your woman (because he works in full light). He may be the first to notice you have melanoma, a suspiciously swollen mole, or a scattering of warts. A massage therapist, of course, cannot replace a dermatologist - but many of us get a massage more often than a specialized skin specialist.
Investigator: hairdresser
Hair reacts to any change in the functioning of internal organs. Let's see what you need to be wary of if the hairdresser said that your hair is:
Fat
The dermatologist blames it all on poor diet (and in particular, sweets, coffee, alcohol, fatty foods, fried foods), frequent washing of hair with hot water and hormonal disorders that increase the functioning of the sebaceous glands. “I always advise people with this type of hair to go on a diet as soon as possible,”
- Cherkashina insists. And that's the best case scenario. If everything was normal since childhood, and then at some point you noticed that your hair is like icicles, this may be a signal from the liver or endocrine system. Mind you, mind you.
Parts of the child's body turn blue
A child's skin color may vary. Normally, the skin is pale pink in color. With various diseases and conditions, children may experience changes in skin color. The skin may appear blue (cyanotic), yellow (icteric), red, marbled, or white. Changes in skin color can be a manifestation of the norm, but in most cases such changes appear as a result of diseases.
The appearance of blueness is associated with a decrease in blood oxygen saturation or oversaturation of the blood with carbon dioxide. Cyanotic staining can be observed both in individual parts of the body (acrocyanosis, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle) and in the entire body of the child.
The appearance of a bluish coloration of the skin of a newborn baby may be associated with imperfections in the muscular layer of the heart and its nervous innervation. Such conditions are called cardiovascular maladaptation . These conditions are transient, appear only in the early neonatal period and do not require drug or surgical treatment. One of these conditions, characterized by the appearance of a cyanotic coloration of the skin, is neonatal pulmonary hypertension. This condition is due to the fact that the blood vessels of a newborn baby are capable of sharply spasming in response to a decrease in oxygen in the bloodstream. This reactivity of blood vessels can persist up to 7 days of a child’s life. The appearance of a bluish color is observed when the child screams and is restless. There is no need for treatment; this condition goes away on its own.
The appearance of bluish coloration of the skin can also be physiological. The appearance of cyanosis is normally observed in a newborn baby due to changes in ambient temperature . A bluish discoloration of the skin is observed only in the area of the hands and feet. However, this condition can also be pathological, especially in older children with hypothermia. If the child is hypothermic, it is necessary to place him in a warm room and warm the child, but only gradually.
In addition to chronic hypoxia of the body, acute hypoxia can be observed. This condition develops when a foreign body enters the child’s airways . In this case, the child experiences difficulty breathing (the child cannot take a breath), and cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle appears. In this case, the child must be given first aid and contact an emergency medical team.
But the most common reason why children's limbs or nasolabial triangle turn blue is the presence of congenital heart defects . Heart defects are of the white type, when the appearance of cyanosis is not observed, and the blue type, when the appearance of a bluish color is observed. Defects that cause cyanosis: transposition of the great vessels, common truncus arteriosus, atrioventricular communication, tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary stenosis, patent ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defect.
1. Transposition of the great vessels . This defect is characterized by an incorrect arrangement of the vessels leaving the heart: the aorta comes from the right ventricle, and the pulmonary artery comes from the left. Because of this, the blood, which nourishes all organs and systems, is not saturated with oxygen, since it does not enter the lungs. Violations are detected in children right in the maternity hospital. The severity of the condition varies and depends on the presence of communications between these two vessels. If there is a message and it is large enough, mixing of the two blood streams occurs, and the blood, to some extent, is still enriched with oxygen. With this condition, general cyanosis of the child’s skin is observed (that is, the entire child turns blue). Children lag behind in physical development and gain weight poorly. Providing medical care to a child while still in the maternity hospital is the key to the child’s survival. Early surgical intervention is very important to eliminate anomalies in the location of blood vessels.
2. Common arterial trunk . This defect is characterized by the departure of a common vessel from the right and left ventricles simultaneously. In this case, the blood in the bloodstream is mixed (arterial and venous at the same time). This means that there is a decrease in blood oxygen saturation and oxygen starvation of tissues and organs. Children are born completely normal, with normal weight and development. However, in the first weeks of life, a general bluish coloration of the skin appears, children stop gaining weight, and shortness of breath appears. To eliminate the defect, surgery is performed. The operation is usually performed at 3-5 months, however, in extremely severe conditions, surgery can be performed in the neonatal period up to 3 months.
3. Atrioventricular communication . In this case, communication between the two circles of blood circulation (small and large) occurs at the level of the cavities of the heart. Blood from the left side of the heart flows to the right. In this case, the right parts of the heart and pulmonary circulation are overloaded. Because of this, blood stagnates in the lungs and their swelling occurs. Children are born physically full, however, from the first months of life they begin to lag behind their peers in their development, fatigue when feeding, shortness of breath, and blue extremities when crying and feeding are observed. Since pulmonary edema occurs, children experience wheezing in the lungs, moist, medium- and large-bubbly. The liver and spleen increase in size. Swelling appears. For children with pronounced changes in the heart, surgical treatment is indicated in the first months of life. In case of minor violations, surgery to eliminate the defect is performed after a year.
4. Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common heart defect, characterized by the appearance of cyanosis. This congenital heart defect is characterized by the presence of 4 heart defects: pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, dextraposition (improper location) of the aorta, hypertrophy (increase in size) of the right ventricle. Due to a ventricular septal defect, blood mixing occurs and mixed blood, which is poorly saturated with oxygen, enters the aorta. Depending on the severity of the heart defect, both total cyanotic coloration of the child’s skin and so-called acyanotic forms, when no bluish discoloration of the skin is observed, can be observed. The appearance of cyanosis is an unfavorable sign; with total cyanosis, the death of a child at an early age is possible. This defect is characterized by the appearance of clinical signs at 2-3 months of a child’s life. Children become restless, cyanosis of the extremities appears, loss of consciousness and convulsions are possible. Crying, feeding, and defecation can cause deterioration in the condition of children. For minor circulatory disorders, children are treated with conservative medications. If the condition worsens, surgical treatment is performed. For health reasons, surgical intervention is performed in the early neonatal period.
5. Pulmonary artery stenosis . With this defect, a narrowing of the lumen of the pulmonary artery occurs, which carries blood from the heart to the lungs. This makes it difficult to deliver blood to the lungs, where it is saturated with oxygen. The appearance of cyanotic color is observed only in very severe conditions, when there is complete closure of the lumen of the pulmonary artery. Surgical treatment is indicated only if the condition worsens or there is complete atresia (closure) of the pulmonary artery. Surgical treatment is carried out at the age of 3-4 years.
6. Patent ductus arteriosus . This duct normally functions in children in the first 2-3 days after birth, after which it closes and completely closes in the first 2-8 weeks of the child’s life. This duct connects the pulmonary artery and the aorta. If it remains open, then blood is discharged from the aorta into the pulmonary artery, and an overload of the pulmonary circulation is observed. The appearance of clinical signs of this congenital heart defect is characterized by rather late manifestations - by 2-3 years of a child’s life. With a large defect, the appearance of clinical signs can be observed in the first months of life. Since more blood enters the pulmonary circulation, all organs and systems suffer. When the child screams, is restless, or feeds, a bluish coloration of the child’s limbs (arms, legs) appears. Children get tired quickly, the child cannot suckle for a long time, and often interrupts to rest. Children gain weight poorly and lag behind in physical development. Treatment of this malformation is carried out both with medication and surgery. However, surgical treatment is indicated only if drug therapy is ineffective. Children tolerate surgery very well. Mortality after surgery is almost zero.
7. Atrial septal defect . With this defect, there is no septum separating the two atria into the right and left. Because of this, blood mixing occurs in them, and mixed (arterial-venous) blood enters the systemic circulation. Children tolerate this defect quite well, and often it is detected only after a year of the child’s life. Up to a year, a cyanotic coloration of a child’s skin may appear only when crying or restless. This coloring is slight and disappears quickly. After a year, the persistence of persistent pallor of the child’s skin and retardation in physical development are noticeable. Treatment for this defect is only surgical.
In addition to bluish discoloration of the skin, children may also experience other skin colors.
With excessive use of ventilation, especially with a 100% oxygen mixture, children may experience a dark red coloration of the skin . A similar condition can also occur when a child overheats.
Harlequin's symptom . This condition is characterized by the appearance of redness of the skin of the child’s body on only one side when the child is positioned on his side. This condition is associated with the immaturity of the child’s nervous system and is most often observed in children born with asphyxia. When a child is overheated, the color takes on a brighter red color, and when a child is overcooled, it becomes bluish. Treatment of this condition is carried out by a neurologist.
Marbling of the skin . This condition is also associated with imperfections in the child’s nervous system and is manifested by the appearance of a lacy red coloration of the child’s skin. Most often it appears when the child is hypothermic. This condition does not require treatment.
The appearance of yellowing of the skin often indicates an increase in bilirubin in the blood and liver pathology.
The appearance of changes in skin color should always alert parents, especially if a similar condition appears in a small child. Changes in skin color can hide very serious diseases, some of which can be fatal, so it is very important to consult a doctor in time for advice.
Pediatrician Litashov M.V.
Thin and brittle
“Dry, lifeless hair can indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract, in which the absorption of vitamins and minerals is impaired”
, says Denis Lebedev, a gastroenterology specialist at the Semeynaya clinic, warning that with hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) the same thing can happen.
Investigator: fitness trainer
A good coach does not leave your side - he will be the first to see how you react to the load and will be able to distinguish a normal reaction from a pathological one.
Chest pain
For some reason, people are negligent about the fact that they have “something stabbing” in their side or chest, considering this a natural reaction of the body to stress, the fitness trainer complains. “One client of mine suffered from chest pain during every session. I advised him to do a cardiogram, to which he told me that he had osteochondrosis. It seems like that's what the doctors told him. Then he disappeared somewhere, and after a while, when he came to us again, I accidentally saw a scar on his chest. It was a scar from coronary artery bypass surgery. As it turned out, he was diagnosed with coronary heart disease,”
- Mikhailov shares.
Cyanosis in newborns: the problem is in the details
Medically speaking, the severity of cyanosis in newborns directly depends on the concentration of oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. If oxyhemoglobin drops to a level of 85%, symptoms of cyanosis appear.
Total and regional cyanosis
There is a distinction between total and regional cyanosis - it is easy to guess that we are talking about the localization of visual manifestations of the problem. The following localization can be distinguished:
- Perioral cyanosis in newborns - the area around the lips is affected;
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- Acrocyanosis: distal areas are affected: the tip of the nose, tongue, hands, feet, lips, earlobes.
The problem may result from pneumonia in a child (or other lung diseases), heart disease in newborns, impaired blood flow, etc. If the child is healthy, the cause of cyanosis may be that the child was at high altitudes, for example - in particular, this is why doctors do not recommend flying for fragile patients.
Central (arterial or warm) cyanosis
Central cyanosis is a condition characterized by the inability to warm the baby’s extremities due to low hemoglobin levels in the blood. There are hemoglobin and methemoglobin cyanosis of newborns.
Peripheral (venous or cold) cyanosis in newborns
Visually identifying peripheral cyanosis is not as easy as central cyanosis. As the baby warms up, its skin takes on a normal pink tint. but when you press on it, after a while a bluish tint appears. Such symptoms indicate a decrease in minute blood volume.
Methemoglobinemia
If a baby receives a large amount of medications in the first days or months of life, he may develop methemoglobinia - in this case, cyanosis gives the skin a brownish tint. The blood becomes dark, almost chocolate in appearance.
“Gray” cyanosis in newborns
There is another form of cyanosis in newborns - the so-called “gray” syndrome. It develops as a result of the use of chloramphenicol, which provokes sulfhemoglobinemia.