Features of the structure of the spleen in children
In newborn babies, the spleen should be 40 mm wide and 38 mm long
The spleen is an organ located in the abdominal cavity, consisting of lymphoid tissue and taking part in many important processes in the body. Yes, she:
- actively participates in hematopoiesis processes, creating lymphocytes - cells that destroy pathogenic microflora;
- processes old red blood cells and transports them to the liver for subsequent bile production;
- accumulates platelets;
- participates in regulating brain activity.
The process of formation of the spleen begins five to six weeks after fertilization of the egg and ends by the fifth month of pregnancy.
Attention! Negative effects on the fetus during the formation of the spleen can lead to malformations of the organ - its complete absence or the appearance of several spleens, kinks, pinching.
The spleen of a newborn is round in shape and weighs about 9 grams. However, by the age of one year she triples her weight.
Where is the spleen located?
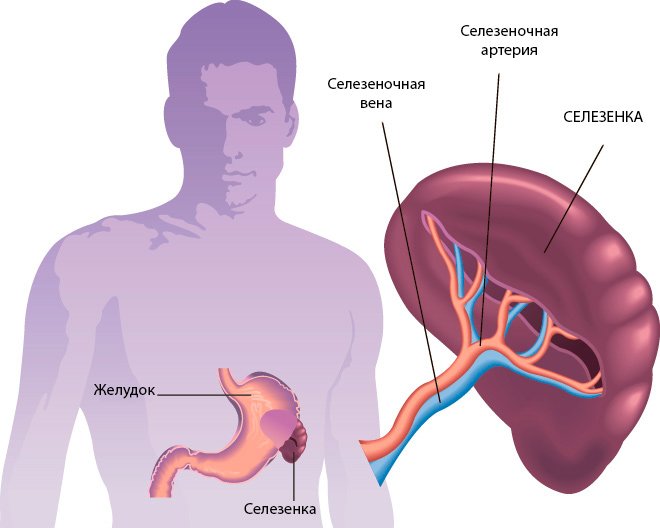
The spleen is an unpaired, oval organ. Length - about 16 cm, width - up to 6 cm, thickness - 1.5 - 2 cm. A healthy organ weighs 150 - 200 grams. The spleen occupies a place below the diaphragm, in the upper left part of the abdominal cavity, which is commonly called the left hypochondrium. In front of it is the stomach, the spleen is in contact with the pancreas, kidney and large intestine.
The spleen is not a vital organ, but it is not superfluous in the body. All organs, including the spleen, are entrusted with performing their functions. A small oval organ that stores blood. It collects blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients until needed. Then it begins to be released into the general blood stream. For example, when a person runs, there is an attack of pain, aching and stabbing in the left hypochondrium.
It hurts when running not only for those who have just started exercising, but also for those who have exposed themselves to physical activity. This problem is not terrible, the release of blood when running is easy to prevent. Restoring the disturbed blood balance is the main function of the organ, but not the only one.
Purpose of the spleen:
- Providing a protective function. Acting as a cleansing filter, the spleen allows everything necessary for active life to pass through and blocks pathogenic substances. Viruses and bacteria do not pass into the blood. By removing an organ, a person’s immunity decreases many times, and before it reacts, hundreds of viruses and bacteria penetrate the body.
- Control of living cell activity. The organ is not able to process the remains, so when it detects old red blood cells, it removes them. Waste is sent to the liver. The most amazing thing is that it is able to separate only part of the cell, separating the red body and iron.
- Carrying out important immune processes in the body. The synthesis of immunoglobulin, without which the immune system cannot be an active defender, is impossible without the spleen.
- During metabolic processes, the spleen is responsible for the production of iron.
- During pregnancy, the formation of leukocytes and red blood cells is the main function of the organ. After the baby is born, the bone marrow takes over this responsibility.
Normal indicators
Children may experience a physiological enlargement of the spleen on the 2nd – 3rd day of life, which depends on the blood filling of the organ
In adults, it is impossible to determine the location and size of the spleen by palpation, since it is located behind the ribs and is covered by them. But in newborns and infants, the organ can be palpated during external examination due to the weak rigidity of the bones and abdominal muscles, as well as the absence of fat deposits in the abdominal cavity.
The size of the spleen in a child depends both on his age and on physiological parameters - height and weight. At birth, the mass of this organ is only 9 grams, during the first year of life it grows to 25-28 g, and from one to 6 years of age, the children's spleen doubles in size - up to 50 g. In 16-year-old adolescents, it is on average equal to organ of an adult and weighs 160 grams. The parameters of the spleen should approximately correspond to the indicators in the table below:
As can be seen from the table, there are no strict restrictions on the normal indicators, and it is different at different ages. In some pathologies in children and adolescents, there is a persistent increase in the size of the spleen, reaching 15 percent or more of normal. A similar sign, called splenomegaly (the term comes from the Latin name of the organ - splen) indicates that certain pathological processes are occurring in the child’s body.
Splenomegaly can be either primary, indicating a disease of the spleen itself, or secondary – one of the symptoms of any pathology not directly related to it. Correcting the situation does not consist in reducing the size of the organ to normal, but in eliminating the root cause of such symptoms. There can be many such reasons - from relatively harmless to very serious. In the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), which includes all pathologies officially recognized today by medicine and having specific symptoms, splenomegaly, not classified in other headings, is assigned code R16.1.
Dimensions of the spleen according to ultrasound in children and adults
It is advisable that the spleen be scanned in three linear dimensions, which is considered more accurate than two linear dimensions. Demand that the ultrasound specialist include digital data in the scanning protocol, and not just a description - “enlarged” or “not enlarged”, this will allow you to observe changes in the size of this organ over time.
During ultrasound examination, the size of the spleen in children directly depends not only on age, but also on its height.
The size of the spleen and the diameter of the splenic vein according to ultrasound, depending on the child’s height
| Height, cm | Length (mm) | Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Splenic vein (mm) |
| 60-69 | 54,60 ± 6,77 | 26,20 ± 3,56 | 24,33 ±3,79 | 3,27 ± 0,64 |
| 70-79 | 62,07 ± 5,79 | 28,36 ±3,86 | 25,00 ± 3,46 | 3,02 ± 0,39 |
| 80-89 | 67,06 ± 4,97 | 31,18 ±3,50 | 27,63 ± 4,00 | 3,06 ± 0,42 |
| 90-99 | 70,85 ±7,10 | 34,21 ±3,80 | 33,00 ± 4,45 | 3,47 ± 0,52 |
| 100-109 | 73,14 ±7,20 | 36,25 ± 3,67 | 32,78 ± 3,76 | 3,96 ± 0,76 |
| 110-119 | 76,90 ±6,12 | 37,66 ± 3,85 | 35,09 ±5,19 | 4,22 ± 0,60 |
| 120-129 | 83,97 ± 7,44 | 40,58 ± 3,92 | 35,67 ± 5,03 | 4,62 ± 0,75 |
| 130-139 | 88,86 ± 9,30 | 41,86 ±5,81 | 38,80 ± 6,02 | 4,92 ± 0,53 |
| 140-149 | 92,20 ±9,21 | 44,98 ± 5.49 | 40,34 ± 4,99 | 5,40 ± 0,68 |
| 150-159 | 98,11 ±9,58 | 46,50 ±5,17 | 42,46 ± 5,49 | 5,46 ± 0,82 |
| 160-169 | 102,44 ±8,62 | 48,96 ± 5,59 | 45,52 ± 5,35 | 5,76 ±0,91 |
| more than 170 | 108,45 ±9,25 | 51,60 ±6,81 | 46,03 ± 5,29 | 6,10 ±0,68 |
Causes of splenomegaly in children
Acute infections (sepsis, typhoid fever) can cause childhood splenomegaly
The spleen is a vulnerable organ that responds to almost all pathological processes that occur in the body. Moreover, specific diseases affecting this lymphoid gland itself are extremely rare in childhood. These include:
- Splenic infarction - as a result of blockage (thrombosis) of the splenic artery supplying the organ with blood, normal tissue nutrition is disrupted and their complete or partial death (necrosis) develops.
- Malignant or benign tumors.
- The appearance of abscesses (ulcers) on the surface of the spleen.
- Development of an acute inflammatory process in organ tissue.
As a rule, splenomegaly in children is a kind of friendly reaction of the body to diseases of other organs and general pathologies. Enlargement of the spleen is caused by the increased load on the immune system that occurs in these cases, of which this organ is an important part. It can be triggered by:
- Acute infections of bacterial etiology, both common and rare and severe, such as sepsis or typhoid fever.
- Acute inflammatory processes in the abdominal region, regardless of etiology, including pathology of the “pancreas”: studies show that with splenomegaly in a child, the pancreas is often enlarged.
- Sluggish chronic infectious diseases - tuberculosis, malaria, HIV infection.
- Diseases that cause disturbances in metabolic processes (metabolism).
- Hematological disorders – hemoglobinopathy, anemia.
- Severe cardiovascular pathologies – congenital heart defects.
- Cysts and tumor neoplasms of various etiologies, developing in the tissues of the spleen itself, as well as oncopathologies of the blood (Hodgkin lymphoma, leukemia).
- Injury to the organ due to abdominal bruises.
- Liver pathologies – hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis.
The reason for the development of splenomegaly can be fungal infections - histoplasmosis, blastomycosis; helminthiasis – ascariasis, echinococcosis, trichinosis; autoimmune pathologies in which the body destroys its own cells, mistaking them for foreign ones - lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis. Splenomegaly is also one of the symptoms of severe forms of rickets, which are rare these days.
Also, childhood splenomegaly can be provoked by the herpes virus. Another possible reason for such symptoms in children is helminthic infestations.
An enlarged spleen in newborns and infants is usually associated with bilirubin jaundice and anemia, which can be caused, among other things, by incompatibility of the Rh factor of the blood of the mother and child. Another factor contributing to infantile splenomegaly is prematurity. In adolescence, moderate splenomegaly is evidence of autoimmune processes in the body.
Splenomegaly in infants: why is the spleen enlarged and what to do about it?
Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen) is common among young children. This condition is caused by various reasons.
If therapy is not carried out, the pathology will progress and cause severe complications. It is important for parents to know what to do if the spleen of a baby is enlarged.
The spleen is an abdominal organ that consists of lymphoid tissue.
It takes part in the processes of hematopoiesis (responsible for the production of lymphocytes, accumulation of platelets), regulates the functioning of the immune system. In newborn children, this organ has a maximum length of 45 cm. As the spleen grows, it increases in volume.
Its parameters are determined by ultrasound. The table below shows the normal values of spleen size for children depending on height.
| Height in centimeters | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm | Diameter of the splenic vein, mm |
| 60-69 | 54,6 | 26,2 | 24,3 | 3,0 |
| 70-79 | 62,1 | 28,4 | 25,0 | 3,1 |
| 80-89 | 67,1 | 31,2 | 27,6 | 3,3 |
| 90-99 | 70,9 | 34,2 | 32,0 | 3,5 |
| 100-109 | 73,1 | 36,3 | 32,8 | 4,0 |
| 110-119 | 76,9 | 37,7 | 35,1 | 4,2 |
| 120-129 | 84,0 | 40,6 | 35,7 | 4,6 |
| 130-139 | 88,9 | 41,9 | 38,8 | 4,9 |
| 140-149 | 92,9 | 45,0 | 40,3 | 5,4 |
| 150-159 | 98,1 | 46,5 | 42,5 | 5,5 |
| 160-169 | 102,4 | 49,0 | 45,5 | 5,8 |
| More than 170 | 108,5 | 51,6 | 46,0 | 6,1 |
Minor deviations from the data given in the table are allowed.
It is important to differentiate splenomegaly from malignant and benign formations, cystosis, and abscess.
Possible reasons for the increase
There are many reasons why a baby's spleen may be enlarged. Enlargement of this organ is medically called splenomegaly. In order to understand the cause of this condition, it is necessary to examine the child.
The most common causes of an enlarged spleen are:
- infectious diseases . They lead to disturbances in the functioning of the spleen and its enlargement. As a rule, this applies to severe infectious diseases (for example, diphtheria, rubella, measles, toxoplasmosis, mononucleosis, tuberculosis). Some of these pathologies can be protected by vaccination;
- mycoses . Fungal infections cause histoplasmosis, blastomycosis. Such conditions lead to lung damage, fever, yellowing and blanching of the epidermis, and foamy, loose stools. Not only the spleen, but also the liver increases in size;
- metabolic hereditary disorders . These include hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, essential hyperlipidemia, glycogenosis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system . May be caused by leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, osteoporosis, chronic hemolysis. An enlarged spleen is associated with inhibition of metabolic processes;
- focal lesions . These are cysts, benign tumors, suppurations. In infants, the spleen may become enlarged when infected with worms (schistosomiasis, echinococcosis).
To identify the cause of an enlarged spleen, ultrasound diagnostics, scintigraphy, MSCT of the abdominal cavity, and plain radiography are performed. Laboratory tests are also performed (general and biochemical blood tests, study of urine and feces).
Symptoms and signs of splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is more a symptom than a disease. The spleen increases in size due to certain pathological processes occurring in the body. Splenomegaly is characterized by signs of the disease that provoked its appearance. The pathology may have an inflammatory or non-inflammatory form.
In the inflammatory form of the pathology, the child will have the following signs of a painful condition:
If the spleen is enlarged due to the baby having a non-inflammatory disease, then the following symptoms will be present:
- weakness;
- increased body temperature to the level of low-grade fever (sometimes it remains within normal limits);
- pale skin;
- apathy;
- weakness;
- increased sweating at night;
- lack of appetite.
If the organ is greatly enlarged, the process of defecation may be disrupted (difficult bowel movements or complete absence of stool passage). Flatulence, heartburn, and bloating are also typical for this condition.
It should be borne in mind that the baby may not experience any discomfort with an enlarged spleen. Severe symptoms are characteristic of disease progression.
Why is this dangerous for an infant?
Splenomegaly is a rather dangerous condition for infants. Uncontrolled and rapid increase in width and length of the spleen leads to compression of nearby organs and disruption of their functioning.
When examining babies with splenomegaly, thrombocytosis, a lack of hemoglobin and leukocytes are detected. Such children suffer from frequent infectious viral and colds due to reduced immunity.
If an enlarged spleen is associated with a cancerous tumor, then ignoring this condition can lead to death. If the cause is helminthic infestation, then this can lead to severe intoxication and the spread of helminths throughout the body. Splenomegaly complicates any disease that causes it.
In severe cases, splenic rupture is possible with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, even minor deviations in the size of this organ cannot be ignored. The sooner treatment is started, the faster the recovery and the lower the risk of complications.
There are medical and surgical types of treatment for splenomegaly. The choice of treatment method is made depending on what caused the increase in the size of the spleen.
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the disease and prevent complications. For bacterial causes of splenomegaly, the child is prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs. For inflammation, hormonal medications are recommended.
In cases of anemia, iron supplements and vitamin complexes are indicated. If the enlargement of the organ is due to the activity of worms, then doctors prescribe anthelmintic medications. If the pathology is viral in nature, then antiviral drugs are selected.
If a tumor is present, antitumor medications are prescribed. Many drugs are prohibited for young children. This complicates the selection of therapy.
If the cause of the enlarged spleen is caused by a malignant neoplasm, then surgery is performed to remove the tumor.
If the organ reaches a critical size and is on the verge of rupture, then doctors resort to a radical method - removing the entire spleen. Without prior treatment, a similar operation is performed for lymphogranulomatosis.
After surgery, the child’s immunity drops significantly, so the risk of infectious and viral damage increases. To prevent the development of diseases, quarantine and taking vitamins and minerals are recommended.
Some parents prefer traditional medicine. The essence of using unconventional methods is to prepare various decoctions, drinks from plants and food.
For example, when the spleen is enlarged, healers recommend the following recipes:
- honey with ginger . These products can be added to drinks or food. They help strengthen the immune system and improve the functioning of the spleen. Honey and ginger are especially useful when there is a high concentration of platelets in the blood;
- propolis decoction . The plant is a natural antibiotic and contains bioactive components. Allows you to get rid of various pathogens;
- St. John's wort decoction . This plant has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the spleen. It eliminates spasms and has a pronounced antimicrobial effect;
- infusion based on hop cones . This product has anti-inflammatory properties. Therefore, healers recommend it when the spleen is enlarged due to an inflammatory process.
St. John's wort decoction
There are many other traditional methods of treating splenomegaly. But most pediatricians do not recommend using alternative therapy methods, especially for infants.
Herbs, honey and other ingredients can cause a strong intolerance reaction. In addition, plant-based decoctions will be ineffective in the presence of helminthic infestation, neoplasms, and infectious pathology.
Therapeutic measures for splenomegaly
Treatment of the spleen includes various techniques and depends on the nature and stage of development of the disease. In critical situations (rupture, bleeding, complete loss of organ functions, necrosis, malignant tumors of the splenic tissue), surgical intervention is performed to partially or radically remove the spleen. However, this happens extremely rarely with children.
Drug therapy
The choice of medications for an enlarged spleen in children depends on the nature of the disease, its causes and stage of development.
In bacterial infections, antibiotics play a leading role. If we are talking about a pathology of a viral nature, antibiotics are powerless - antiviral drugs are needed.
Liver damage requires the use of hepatoprotectors.
Autoimmune diseases are treated with immunomodulators and vitamins.
If the examination shows that splenomegaly is caused by oncopathology of the splenic tissue, a course of specific antitumor drugs, both oral and injectable, as well as radiation or chemotherapy, may be prescribed. In case of low effectiveness of these techniques, partial or complete splenectomy is performed.
Diet
For splenomegaly in children, fresh fruits are recommended
The diet of a sick child should include the following foods:
- meat: poultry, beef, fish, preferably sea. Frying as a cooking method should be replaced by boiling or baking;
- liver - beef, chicken;
- porridges and soups from cereals with water or with milk diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 1. Buckwheat, which contains a lot of iron, is the healthiest;
- boiled and baked potatoes;
- chicken eggs;
- fresh vegetables and fruits: red beets, white cabbage, cranberries, citrus fruits (in the absence of allergies), sour apples (Antonovka and similar in taste).
Foods such as cheese, butter and whole milk, and ice cream should be limited. It is better to completely exclude sausages, canned food of all types, pasta and confectionery. You should also not eat chips, fast food, or carbonated drinks.
Physiotherapy
Motor activity with splenomegaly is forcedly limited, since the sick child feels constant weakness and quickly gets tired. But it is necessary to do breathing exercises: this helps to normalize the tone of the spleen and reduce its size.
The complex includes the following exercises:
- Lying on the floor or flat surface on your back, take a deep breath. Exhale in portions, saying “cha-cha-cha.” Repeat 15-20 times.
- As you inhale, pull your stomach in as much as possible, and as you exhale, push it out. Take 10-12 breaths.
- While standing, take a deep breath through your nose with your lips tightly closed. Exhale through your mouth, blowing air through pursed lips. Repeat 15 times.
These simple exercises should only be performed on an empty stomach. It is recommended to do them in the morning and evening, gradually increasing the number of repetitions to 40 times.
Folk remedies
The spleen is a small internal organ and not everyone knows where it is. But in physical education classes, many of us often complained of pain in the left side that appeared during or immediately after running. This is the spleen, and it reacts this way to a sharp increase in blood volume.
Despite the fact that the absence of a spleen generally does not affect general well-being and a person without a spleen can live peacefully, its removal is not a disaster for the body. But the spleen is still a very important organ for many reasons - it fights diseases of the blood and bone marrow, participates in the formation of humoral immunity (when the body’s defense system produces special antibodies that fight infections) and cellular immunity (cellular immunity is responsible for resisting bacterial and viral infections). It is also involved in the metabolism of iron, lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Spleen hurts
Why does the spleen hurt and what to do? - only a specialist can answer this question. Disturbances in the functioning of this organ can lead to serious health problems, so it is important for patients to promptly seek medical help after the first manifestations of the disease.
What functions does it perform?
The spleen is one of the most mysterious organs of the human body. It is located behind the stomach, in the left hypochondrium, and has the shape of an elongated hemisphere. For a long time it was believed that the spleen performs digestive functions, but modern scientists have proven its relationship to the immune system.
Functions of the spleen:
- formation of red blood cells and lymphocytes
- cleansing the blood of harmful microorganisms
- formation of immunity
- normalization of metabolic processes in the body
In an adult, the length of the spleen is about 8-14 cm and the width is 4-6 cm. Its weight does not exceed 400 g. The organ is covered with a capsule. The place where blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as nerve fibers, enter it is called the hilum.
Fixation of the spleen is carried out due to intra-abdominal pressure, which is provided by special ligaments covering the organ on all sides (with the exception of the hilum of the spleen, as well as the place of contact with the tail of the pancreas).
Symptoms
Severe pain behind the stomach, in the area of the left hypochondrium, indicates a pathology of the spleen. Discomfort may extend to the shoulder blade area. Similar manifestations occur due to various cracks and wounds, ruptures of the spleen. If the problem is accompanied by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, the patient may experience an attack of shock. In this case, symptoms are observed:
- nausea and vomiting
- tremor
- paleness of the skin
- thirst
- lowering blood pressure
- anemia
- difficulty breathing
A protruding lump in the left side may indicate an enlarged spleen. At the same time, a person’s skin turns pale, especially on the face. When moving or straining, the pain in the left hypochondrium intensifies, and discomfort occurs in the navel. These manifestations are accompanied by excessive fatigue, decreased immunity, and damage to the lymph nodes.
Symptoms of an enlarged spleen:
- decrease in hemoglobin
- decreased immunity
- ulcers on the upper and lower extremities, as well as in the mouth
- increased heart rate
- frequent bleeding
- increase in temperature indicators
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach
If you experience such symptoms, you should seek medical help.
Causes
The peculiarity of the spleen is that it does not have pain receptors, so it cannot hurt.
Discomfort occurs due to stretching of the splenic capsule against the background of various pathologies, open or closed injuries. Pain in the spleen is often a consequence of damage to other organs and systems.
As a rule, the cause of this problem is injury, infectious diseases, tumors, abscesses, and tuberculosis.
Also, disturbances in the functioning of the spleen occur against the background of:
- congenital defects (absence of the spleen, its non-standard size or shape)
- twisting of the splenic pedicle (volvulus)
- irreversible degenerative processes in elderly people
- splenomegaly (pathological enlargement of the spleen due to infectious diseases, increased temperature or lymph nodes, jaundice, anemia, etc.)
It is impossible to identify the cause of pain in the spleen without qualified medical care. Timely consultation with a doctor increases the patient’s chances of recovery.
Infectious diseases
Infectious diseases of individual organs and systems caused by pathogenic biological agents (viruses, fungi, bacteria, etc.) cause dysfunction of the spleen.
As a rule, discomfort or pain in the spleen area occurs as a complication of the following diseases:
- sepsis
- typhoid fever
- measles
- meningitis
- scarlet fever
- anthrax
- sepsis
- syphilis
- malaria
- hepatitis
- mononucleosis
- lymphocytosis, etc.
These diseases can provoke the occurrence of an arterial thrombus, which, in turn, causes a severe pathology - splenic infarction. Another consequence of infectious diseases is spleen abscess. Enlargement of the organ occurs due to damage by toxins, poisons, and pathogens.
Closed and open injuries
According to the generally accepted classification, splenic injuries can be open or closed. The first type is wounds (gunshot or stab wounds), with damage to nearby organs and systems. According to statistics, open wounds of the spleen are much less common than closed ones.
As a result of such injuries, the functionality and integrity of the stomach, liver, lungs, gall bladder, etc. are impaired. Closed (or subcutaneous) injuries to the spleen occur as a result of injuries, bruises, single or multiple ruptures. With such injuries, the integrity of the capsule and parenchyma is destroyed (separately or together).
The most severe complications of closed-type spleen injuries are rupture of the capsule, hemorrhage into the peritoneal cavity, and complete separation of the organ.
Infectious diseases
Swelling of the spleen is one of the common signs of infectious diseases. The organ increases in size within 350-550 g, its structure and color change.
If the patient has an infectious disease, the spleen becomes very fragile. Minimal trauma or bruise can cause rupture of this organ.
A person feels mild discomfort or acute pain in the left hypochondrium due to enlargement and stretching of the spleen capsule.
Splenic infarction
Vascular spasms, blood clots or embolism can provoke a serious disease - splenic infarction. The pathology is characterized by the death of organ tissue (necrosis). In advanced cases, the following clinical picture can be observed:
- discomfort, heaviness, pain in the left hypochondrium
- temperature increase
- stool disorders
- general intoxication
To make a diagnosis, studies using ultrasound, MRI, and CT are required. In the final stages of the disease, death of large areas or all of the splenic tissue can be observed. The pathology is common between men and women, whose average age is about 65 years.
Typically, splenic infarction occurs from spasm or blockage of the splenic artery. Such conditions lead to:
- hematological pathologies
- deterioration of blood properties
- heart or vascular diseases
- benign or malignant formations
- open and closed injuries
- infections and parasites
A splenic infarction develops due to a disruption of the blood supply to the tissues of the organ and blockage of the arteries. This affects the immune system, endocrine and metabolic processes in the body.
Abscess
A splenic abscess is an abscess (suppuration) of a certain area of the organ. This is a cavity filled with pus, which is often a consequence of another disease: an infectious process, hematoma, or splenic infarction. The formation can be large, single, or collected from multiple small ulcers, capable of connecting with each other as the disease progresses.
Symptoms of splenic abscess:
- pain in the left hypochondrium area
- pain may radiate to the left side of the body and intensify with breathing, tension, or increased load
- weakness
- dizziness
- temperature increase
- digestive disorders: nausea, vomiting
The cause of an abscess can be trauma, infection, parasites, or splenic infarction. As a rule, the patient is indicated for urgent surgical treatment in combination with drug therapy.
Patients suffering from immune system disorders: HIV infection, lymphocytic leukemia, anemia, leukemia are predisposed to abscesses.
A spleen abscess can cause the development of complications: fistulas, intestinal bleeding, purulent contents entering the abdominal cavity, sepsis.
Tuberculosis
In most cases, splenic tuberculosis is a complication of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients. As an independent disease, this pathology is much less common. The causative agents of the disease are pathogenic bacteria that spread throughout the body through the blood or lymph.
Tuberculosis of the spleen is characterized by the appearance of small single or multiple nodules on the tissues of the organ. A provoking factor in the development of the disease can be reduced immunity, polluted air, or the presence of a patient diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis. As a rule, the disease progresses slowly, without pronounced symptoms.
Over time, the pathology becomes chronic.
Symptoms of chronic tuberculosis of the spleen:
- temperature rise to 37-37.5 degrees
- pain in left side
- loss of appetite
- weakness, low performance
- pain in the left side of the body
- enlarged spleen
- changes in blood composition, decrease in blood clotting
- anemia
- liver tuberculosis
Splenic tuberculosis in acute form is manifested by a sharp increase in temperature, a decrease in platelets and leukocytes in the blood. The person becomes weak and sick.
Oncology
Malignant tumors of the spleen are rare. As a rule, this problem is a consequence of other oncological processes in the body.
Malignant formations in the spleen area:
- sarcoma
- lymphosarcoma
- reticulosarcoma
- fibrosarcoma
- angiosarcoma
At the initial stages of the disease, an enlargement of the spleen and its bulging may be observed. The patient's general condition remains unchanged, as do the blood composition indicators.
Discomfort on the left in the hypochondrium area, extending to the scapula area, can occur in the later stages of cancer. Such a symptom indicates the neglect of the disease, and possible death within several years.
Women may develop cysts in the spleen. The reasons for their appearance are one or a combination of several unfavorable factors:
- frequent changes in hormonal levels;
- bad ecology;
- poor nutrition;
- other diseases;
- injuries;
- bad heredity, etc.
Symptoms of cysts in the spleen include stool disturbances and pain in the left hypochondrium. A woman may feel heaviness in the stomach and nausea immediately after eating. Manifestations of allergies may occur; upon palpation, the doctor diagnoses an enlarged spleen.
What to do
Spleen diseases are rarely diagnosed at an early stage. A person begins to suspect a problem after the organ increases significantly in size, causing severe discomfort or severe pain. If you have alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor without waiting for the condition to worsen.
After this, you will need to undergo an examination and pass all tests prescribed by a specialist. If you have severe acute pain in the spleen, you need to call an ambulance. After this, the patient needs to take a lying position.
In this case, it is recommended to monitor the patient’s breathing - it should be deep and calm.
It is forbidden to apply hot or warm compresses to the sore spot, as such actions can harm the patient’s condition.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have pain in the spleen, you should consult your family doctor or general practitioner. In the future, the patient will need the help of highly specialized doctors - a gastroenterologist or surgeon. Treatment of spleen diseases is carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
In advanced cases, surgical removal of the organ is recommended. This procedure will not affect the patient’s performance in the future.
Drug therapy for pain in the spleen is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, relieving pain, and stabilizing the functions of the organ.
As prescribed by a doctor, the following can be used:
- allergy remedies
- anti-inflammatory and/or painkillers
- antibiotics
- vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system
- antitumor or antituberculosis drugs, etc.
Treatment of spleen diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Traditional medicine can be used as supportive medications (after consultation with a specialist).
Diagnostics
The very first and most important methods for diagnosing spleen diseases are a visual examination of the patient, palpation of the sore spot, and taking an anamnesis. Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the following may be prescribed:
- X-ray - allows you to see an increase in the size of the spleen, gall bladder, stomach, adrenal gland, kidney. Before the procedure, oxygen is injected into the patient’s abdominal cavity to improve the information content of the study.
- Examination of an organ sample obtained by puncture. The method is used extremely rarely due to its complexity.
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
The difficulty of diagnosing diseases of the spleen arises due to the close location of this organ to the gallbladder.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle will help to avoid problems with the spleen: a balanced diet, regular exercise. The body must receive a sufficient amount of nutrients, especially copper, in the form of vitamin complexes.
Other recommendations:
- avoid bruises and wounds in the abdominal area
- drink enough water to cleanse the body, in particular the spleen
- give up alcohol, especially low-quality alcohol
- Conduct regular preventive examinations and laboratory blood tests
- wear loose clothing that does not cause discomfort while moving
The diet of patients suffering from spleen diseases must contain a sufficient amount of nuts, beef liver, and fish. It is recommended to eat carrots and beets as vegetables.
Timely treatment of any diseases, including infectious ones, will avoid the development of complications in the form of disruption of the spleen.
It is also necessary to examine injuries and bruises of the torso, in particular those resulting from fights and falls.
: Why does the spleen hurt?
Source: https://GuruSpa.ru/pochemu-bolit-selezenka/
Pathological enlargement of the spleen
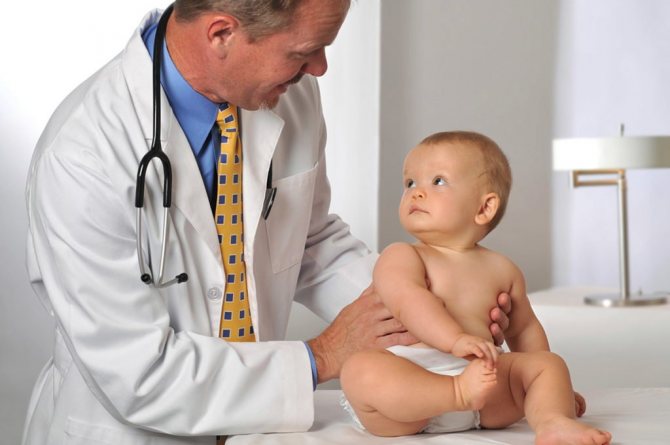
In a normal state, the spleen is completely obscured by the ribs of the left side; the doctor will not be able to feel it with his hands, but with enlargement (splenomegaly) it significantly extends beyond its specific location
Enlargement of the spleen, not associated with age-related changes, is called splenomegaly. The disease requires careful attention due to the fact that it may be a consequence of:
- pathologies of the organ itself - heart attack, abscesses in the cavity, inflammation, paralysis of the muscular system;
- infections of bacterial origin;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- liver diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- syphilis;
- metabolic disorders;
- cardiovascular system defects;
- oncological diseases;
- benign neoplasms;
- spleen cysts;
- measles;
- rubella;
- chicken pox;
- mononucleosis;
- herpes;
- parasitic lesions of the intestines and liver.
Symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, the enlargement of the spleen is asymptomatic. However, occasionally the pathology may be accompanied by:
- prolonged diarrhea;
- nausea and bouts of vomiting;
- pain in the hypochondrium;
- increased body temperature;
- paleness of the skin;
- fatigue;
- apathy;
- increased sweating at night.
Diagnostics
Splenomegaly is best diagnosed by ultrasound
Diagnosis of splenomegaly in children is carried out comprehensively and includes:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs, giving an idea of the size of the organ, its structure, the presence or absence of tumors, cysts or abscesses.
- General and detailed blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Stool analysis.
In some cases, computed tomography (CT) is used.
Attention! Palpation of the spleen with splenomegaly in children is uninformative - in adolescents the organ is almost not palpable, and in children a slight increase in size is considered normal.
The primary examination of children is carried out by a general practitioner.
Danger
An enlarged spleen in itself, as a rule, is not dangerous - the main danger is the primary disease that led to the development of the pathology. However, in some cases, splenomegaly can lead to certain consequences.
Thus, a significant enlargement of the spleen can result in compression of neighboring organs, including the stomach, which, in turn, leads to disruption of digestive and metabolic processes.
In addition, improper functioning of the organ can lead to problems with the blood - from the usual decrease in hemoglobin levels to more serious diagnoses. The most dangerous pathology is hyperslenism - massive destruction of blood cells in the spleen, accompanied by thrombocytopenia (with the death of platelets) or anemia (with the disappearance of red blood cells and proteins that transport oxygen).
If stagnation of venous blood, cysts and neoplasms prone to growth are observed in the spleen, then the main danger is rupture of the organ and subsequent bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
Enlarged spleen in a baby: reasons, what to do?
While the embryo develops in utero, the spleen is responsible for the hematopoietic function, synthesizing platelets.
But as the fetus grows, its function changes - at the time of birth, platelet production moves to the bone marrow.
However, if for some reason the bone marrow stops reducing blood cells, the organ will start working again. In addition, the spleen is responsible for the number of monocytes and lymphocytes in the blood.
However, the main functions of the organ are completely different.
Purpose
The spleen has three functions in the human life system:
- immune (basic);
- purifying (filters blood);
- participation in protein metabolism (formation of immunoglobulins).
Location
The spleen is a bean-shaped organ located in the left hypochondrium. In an adult, its parameters are:
- length – up to 12 centimeters;
- width – up to eight centimeters;
- thickness - up to five centimeters.
Permissible deviations and norm
Normally, an increase in organ volume corresponds to changes in the child’s development.
- By twelve months, the baby’s spleen is: up to 65 millimeters in length and up to 25 in width;
- by two years: length – up to 72 millimeters, width up to 34;
- by six, can reach 71 millimeters, up to 41 in width;
- in adolescence it grows to a volume of 120 by 48;
- upon reaching adulthood it increases a little more: 121 by 51 millimeters.
If there is a suspicion that the size does not correspond to age, an ultrasound scan is prescribed - ultrasound, which will confirm or refute the assumption.
Infectious diseases
One of the main prerequisites for disruption of the spleen, and this is usually an increase in its size, serious infectious lesions:
- measles;
- toxoplasmosis;
- tuberculosis;
- mononucleosis;
- rubella;
- diphtheria.
Pathologies of the circulatory system
The spleen will increase in infants and in case of disturbances in the circulatory system:
- with chronic hemolysis;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- leukemia;
- osteopetrosis.
Organ growth cannot be ruled out in pathologies associated with inhibition of metabolic processes. For example, osteomyelitis or a manifestation of hereditary Gaucher disease.
Metabolic disorders
Having a hereditary metabolic disorder, the baby also runs the risk of experiencing abnormal enlargement of its organ. Several diagnoses are considered:
- glycogenosis (failures in glycogen metabolism);
- Wilson's disease (copper metabolism disorder due to genetic pathology of the nervous system and liver);
- essential hyperlipidemia (disorder of the fat metabolism mechanism);
- hemochromatosis (improper iron metabolism due to liver failure);
Focal lesions
In addition to diseases and painful conditions, structural disorders of tissues can be the cause of ill health. In infants - benign tumors, cysts, suppurations, in adults - local heart attacks and cancerous formations. Children are also characterized by abnormal enlargement of the organ due to helminthiasis (worms) caused by:
- The tapeworm Echinococcus is a dangerous parasite that causes serious damage to internal organs. Once in the spleen, they form cysts, causing atrophy of the parenchyma.
- blood flukes living in the venous circulatory system. Their eggs penetrate through the bloodstream into the tissue of the spleen, affecting it from the inside.
Schistosomiasis (schistosomiasis), along with echinococcosis, are common parasitic infestations.
Mycoses
The next reason for a change in the size of the spleen in a child is a fungal infection. Against this background, blastomycosis or histoplasmosis develops, with symptoms:
Symptoms of splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is more a symptom than a disease - a condition of an enlarged spleen that develops against the background of various pathologies.
Inflammatory forms
Splenomegaly itself is externally asymptomatic, but has signs of the disease that caused its development. For example, with the inflammatory nature of the enlargement of the spleen (bacterial or viral infections, worms, benign tumors), it manifests itself in the form of:
Non-inflammatory
Non-inflammatory form of splenomegaly, characteristic of:
- Hepatolienal damage (destruction of liver cells)
- Hemolytic anemia (breakdown of red blood cells)
- Thrombocytopenia (platelet transformation, increase in the number of megakaryocytes)
- Polycythemia (increased concentration of red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes)
- Mechanical factors (for example, impaired outflow of the splenic veins due to thrombosis).
In these cases, the symptoms are less pronounced, splenomegaly passes without temperature changes with mild aching pain.
Diagnostic methods
It is necessary to examine the child, even if there are no deviations from the norm. This is necessary in order to adequately assess his condition starting from the age of one month. Diagnostic procedures will be required:
- External examination, palpation, tapping;
- Biochemical study - assessment of liver functionality.
- Immunological – detection of infections or damage by parasites.
- Echography, scanning, computer diagnostics - determination of splenomegaly.
- Laparoscopy.
- Biopsy (rarely performed in young children due to the high likelihood of bleeding)
- MRI, computed tomography, ultrasound, x-ray - if there are difficulties with diagnosis.
Palpation of the spleen, unlike other organs, is a technically difficult element of diagnosis. The organ cannot be palpated in normal condition, and excess zeal can damage it. Therefore, only a specialist can palpate.
Identification of other diseases against which the development of splenomegaly can be expected is diagnosed by laboratory tests:
What to do?
When an enlarged organ is detected in a child, he is registered and his further condition is monitored.
Surgery, which was once widely used, is now rarely used. Only when the size of the enlarged spleen is too large (it has been proven that its removal makes the baby vulnerable to infections).
Treatment is carried out in three areas:
- Treatment of the disease causing splenomegaly.
- Elimination of painful manifestations (pain, fever, vomiting or diarrhea).
- Complete restoration of the organ’s performance indicators.
For example, bacterial or viral infections are treated with antibiotics or antiviral drugs, and tumors and blood diseases are treated with antitumor drugs. Vitamin therapy helps with anemia and vitamin deficiency. Radiation therapy can also be used, as can drainage if pus has accumulated. Folk remedies for cleansing the blood and bile ducts.
However, if conservative treatment fails, when the child is at risk of splenic rupture or internal bleeding begins, splenectomy is prescribed.
If an organ excision operation is performed, parents should be aware that the baby will be susceptible to infections for up to 3 years.
Preventive measures
The main preventive measure for splenomegaly in an infant is the nutrition of its mother during pregnancy. The diet is agreed with the doctor and consists of healthy products, taking into account balance. The expectant mother should give up bad habits.
Otherwise, the recommendations depend on the causative disease, and since there are many of them, they are limited to general strengthening ones.
Possible consequences of splenomegaly
For a growing baby, an enlarged spleen increases the risk of:
- hemoglobin deficiency (anemia and anemia develop);
- lack of leukocytes (leukopenia);
- decreased platelet levels (thrombocytopenia).
Splenomegaly leads to complications of any of the diseases that caused its increase. But the most dangerous thing is a decrease in the density of the organ and an increase in the risk of rupture.
:
Mucous stool in infants
Ulcers in infants
Umbilical hernia in a baby
Colic in infants
Blood in baby's stool
Source: https://grudnichki.com/zdorove/414-selezenka-grudnichka
Indications for spleen ultrasound in children
At the slightest suspicion of disturbances in the activity of the spleen in children, you should consult a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment. The specialist will ask in detail about the child’s illnesses and recent injuries. During the initial examination, palpation determines whether there are changes in the size of the internal organ. The patient lies on a horizontal surface, relaxing the abdominal muscles. When the spleen is enlarged, the edge of the organ is palpated.
Based on the results of palpation, an ultrasound is prescribed; it will allow you to visually assess the situation and prescribe the correct treatment. Before the ultrasound, the child should not eat or drink for 3 hours.
Indications for referral for ultrasound:
- Previous injuries in the abdominal area - the study will help to see ruptures, cystic formations, tissue necrosis and hematomas.
- Organ pathologies: absence of the spleen from birth, extra lobe, several organs, “wandering spleen.”
- If malignancy is suspected, to determine the location of the tumor and identify metastases.
- Neoplastic diseases.
- Enlarged spleen – splenomegaly. In addition to ultrasound, blood and urine tests are performed to provide a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
Decoding echogram data
If there are changes, decoding of the echogram data is required. To avoid errors and inaccuracies, decoding must be carried out by a qualified specialist. The presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity in the subphrenic space is evidence that the spleen has ruptured. Blurred contours of the organ being examined are also interpreted as a rupture of the spleen tissue.
If during the decoding process it is discovered that the organ is enlarged and appears lighter, but has a uniform structure, this tells the doctor about a possible inflammatory process called splenitis. If the decoding is based on the presence of dark zones in the parenchyma of the organ, then perhaps the doctor will describe the situation as “the inflammatory process ended with necrosis of the parenchyma tissue.”

Only a specialist can interpret the echogram data.
Depletion of organ tissue or the presence of compacted areas when interpreting an echogram can be interpreted as a heart attack. An uneven contour and the presence of an anechoic structure may be a sign of a hematoma. An abscess on ultrasound examination appears as a hypoechoic structure. The cyst is visible as a formation with uneven contours.
The size of the organ depends on age, gender (women have a smaller spleen) and the constitution of the human body, so the parameters vary by several millimeters - the normal limits are not strict.
Spleen sizes according to ultrasound for adults:
- thickness - 4-5 cm;
- width - 6-8 cm;
- length - 11-13 cm;
- diameter of the splenic vein - 5-8 mm;
- diameter of the splenic artery - 1-2 mm;
- medium echogenicity;
- maximum oblique cut area - from 15.5 cm to 23.5 cm;
- crescent shape;
- weight ranges from 150 g to 250 g.
The normal size of the spleen indicates its proper development and functioning. Enlargement of the organ - splenomegaly, detected by palpation and confirmed by ultrasound, may indicate the following health problems:
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- development of malignant cells;
- infectious pathologies (toxoplasmosis, scarlet fever, malaria, endocarditis, mononucleosis);
- inflammatory process in the body (rheumatoid arthritis);
- autoimmune pathologies;
- injuries;
- storage diseases (amyloidosis, Gaucher disease);
- hematopoietic pathologies: myeloid leukemia, chronic hemolytic anemia.
- hematoma, heart attack, cyst, abscess.
Let's take a closer look at the last point - formations and altered areas in the structure of the spleen that affect its size.
Abscess - during ultrasound diagnostics it is visible as a focus with reduced echogenicity; may consist of gas bubbles - then areas with high echogenicity will be visible. Visually defined as a round or oval formation, with uneven boundaries and a mixed structure. An abscess in the spleen (single or multiple) can develop as a result of the following influences:
- parasitosis (hydatid infection);
- injury;
- sepsis;
- infectious diseases.
The cyst is determined by the ultrasound machine as an anechoic area with a clear and rounded contour. Cystosis occurs for the following reasons:
- abdominal trauma;
- parasitic diseases (alveococcosis, echinococcosis);
- after the operation;
- congenital.
Not all formations are dangerous, but cysts caused by parasitic infestation pose a threat to human life and require immediate surgical intervention.
An infarct on ultrasound appears as a hypoechoic triangular and well-defined area. Hemorrhage into tissue occurs as a result of embolism, vascular thrombosis that occurs due to infection, blood pathologies or cardiovascular system.
Ultrasound examination will determine a hematoma as an area of mixed or anechoic structure with uneven boundaries. In the event of a hematoma rupture into the peritoneum, ultrasound allows you to see the presence of fluid there. A splenic rupture occurs as a result of a blow or fall or accident. An ultrasound will show unclear boundaries of the organ and fluid in the abdominal cavity. This diagnosis rarely allows you to save the spleen - in 99% of cases it is removed.
The location is also determined using an ultrasound machine and is important for making a correct diagnosis. The spleen has the shape of a crescent, the outer side of which is convex and the inner side is concave. The organ is located in the peritoneum - between the diaphragm and the stomach, approximately in the region of 9-11 ribs.
Treatment

Medicines for each little patient are selected individually
When an enlarged spleen is detected in a newborn baby, doctors take a wait-and-see approach. This is explained by the fact that the size of the organ in infants is directly related to the intensity of blood circulation - the stronger the filling with blood, the larger its size. In all other cases, splenomegaly requires medical attention.
Therapy in this case is prescribed after a complete examination of the children and is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
If the cause of splenomegaly is infectious processes of bacterial origin, treatment with antibacterial drugs is prescribed.
Pathologies that develop against the background of neoplasms are treated with antitumor drugs or surgery.
For autoimmune causes of the disease, immunosuppressants are recommended - drugs that suppress the immune system.
Regardless of the reasons that led to an enlarged spleen in children, treatment is always supplemented by taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is recommended when conservative therapy for the underlying disease has not given the required results, as a result of which the organ has greatly increased in size. In this case, we are usually talking about deletion.
The exception is cases of lymphogranulomatosis - malignant degeneration of lymphoid tissue or a strong increase in the size of the organ, leading to thinning of its tissues - in such situations the spleen is removed immediately, without prior treatment.
The operation to remove the spleen is called splenectomy. When treating children, it is performed laparoscopically, which is the most gentle, practically bloodless and favorable from the point of view of subsequent rehabilitation. Other removal methods require direct access to the organ through an incision in the peritoneum.
After surgery, the child’s immunity is greatly reduced, and he becomes susceptible to various infections, both viral and bacterial in origin. Bacteria pose a particular danger in this case, and therefore operated children are vaccinated against pneumococcus, meningococcus and Haemophilus influenzae.
A decrease in immunity is, as a rule, temporary - in the vast majority of cases, the body compensates for the absence of an organ within one and a half to two years from the date of surgery. The child begins to get sick much less, his life becomes full, not requiring any restrictions.
Prevention

Smoking in adolescence increases the risk of spleen pathologies
There is no specific prevention of splenomegaly, however, measures can be taken to protect children from an enlarged spleen.
The child should be vaccinated from birth. This must be done in a timely manner and in full. Refusal of vaccinations increases the risk of developing diseases that a child’s body simply cannot cope with without damaging the spleen.
When planning trips to exotic countries, you should find out what specific diseases exist at your destination and get vaccinated in advance. This is explained by the fact that vaccines, for example, against malaria are not included in the national vaccination calendar (you can vaccinate your child in any private clinic at your own expense).
When a child engages in active sports, he should be warned against excessive stress, which could lead to traumatic rupture of the spleen.
Teenagers should stop drinking alcohol and smoking, which increase the load on the organ.
And, of course, if you suspect a viral, infectious or autoimmune disease, you must immediately show the child to a pediatrician.
Preparation for ultrasound of the spleen
It is necessary to prepare for an ultrasound of the spleen in the same way as for a similar examination of the abdominal cavity. Before the examination, do not take food or water for 8 hours. Children, if conditions permit, should refrain from eating and drinking water for 3 hours before the test. It is advisable to stop taking foods that promote gas formation (sweets, legumes, cabbage, wheat bread, baked goods, milk, etc.) 2-3 days before the ultrasound.
Preparation for an ultrasound involves taking enterosorbents, such as lactofiltrum, activated carbon, smecta for several days before the ultrasound. These drugs are taken one tablet two to three times a day. Taking enterosorbents is necessary in order to completely avoid gas formation, which can greatly complicate this study.
The ultrasound of the spleen itself lasts five to ten minutes. During the ultrasound, the patient does not feel any discomfort, and there are no contraindications to ultrasound examination. First, the ultrasound doctor scans the organ in a position where the patient is lying on his back, and then lying on his right side.
Features of the study
There are some recommendations for performing an ultrasound of the spleen, adherence to which will make the work of the ultrasound doctor easier.
This procedure does not require special preparation.
It is better to perform the procedure on an empty stomach, eat 6-9 hours before the procedure, 2 days before the ultrasound of the spleen, foods that cause gas formation are excluded: legumes, vegetables, sweet fruits, flour products, especially yeast, carbonated drinks.
If the patient has concomitant diseases that lead to excessive gas formation, then in this case, before an ultrasound scan of the spleen, it is recommended to take activated carbon or another sorbent an additional day, the required dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
Exception: people with diabetes are allowed a light snack.
Ultrasound of the spleen is normal in adults. Indicators (decoding):
- length – 11-12 cm, normal up to 13 cm;
- width – 6-8 cm;
- thickness – 4-5 cm;
These normal sizes of the spleen in adults according to ultrasound depend on the gender and constitution of the person.
- diameter of the splenic artery – 1-2 mm;
- diameter of the splenic vein – 5-8 mm;
- the area of the maximum oblique cut of the organ is 15.5-23.5 cm;
- echogenicity – average;
- shape - crescent;
It is mandatory to describe its location in relation to other organs: stomach, left kidney, tail of the pancreas.
Like most diagnostic techniques, ultrasound requires little attention at the stage of preparation for manipulation. Ultrasound examination is a procedure that does not require penetration into the human body - that is, it is carried out percutaneously with a special sensor. To ensure the reliability of the results obtained, it is necessary to begin preparation 3 days before the scheduled diagnosis.
Preparation for ultrasound of the spleen:
- Exclude from the diet foods that increase gas formation - cabbage, legumes, confectionery, baked goods, milk, fresh vegetables - bloating makes it difficult to determine the exact location of the organ.
- For patients with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, manipulations are carried out in the morning before meals.
- The last meal is recommended at least 9 hours before the ultrasound.
- 10-12 hours before diagnosis, it is recommended to take sorbents - activated carbon, Enterosgel, white carbon.
There are situations when such an amount of time is not allocated to prepare for the procedure. If a rupture is suspected as a result of injury (patient after a fall, beating, accident), an ultrasound is performed as soon as possible without preparatory measures.
Why is an enlarged spleen dangerous in a child?
An enlarged spleen is not an independent disease, but a consequence of a number of diseases that are not diagnosed by ultrasound and require consultation not only with a pediatrician, but also with a number of other specialists.
The main thing is to monitor the size of the spleen in children; they should not be too high, otherwise there may be irreversible consequences. If the organ is significantly larger in size than it should be, then the slightest blow to the abdominal area can rupture the spleen, which will cause large blood loss, life-threatening.
Any deviation from the norm in the development of internal organs in a child alarms and frightens parents. Quite often, mothers and fathers hear from the doctor that the child has an enlarged spleen. After reading this article, you will learn what this may mean, what to do if a child has an enlarged spleen.
Diagnostic measures
Since enlargement of the liver and spleen is not an independent disease, but a manifestation of some illness in the child, it is worth finding out why hepatosplenomegaly developed. At the appointment, the doctor will first of all conduct an external examination, including palpation and percussion, assessment of the abdominal circumference, and detection of a pronounced venous network in the abdomen. He will talk with parents and ask questions.
Most often, a child with an enlarged liver:
- yellowness of the skin is observed,
- I feel pain in my stomach,
- signs of intoxication appear.
Several doctors deal with the problems of hepatomegaly. You will have to visit:
- pediatrician,
- gastroenterologist
- and infectious disease specialist.
Diagnostic tests include, first of all, ultrasound and a general blood test. Additional tests include:
- immunological examination;
- identification of parasites;
- tumor markers;
- radiography, endoscopy, etc.
Peculiarities
The spleen is located in the abdominal cavity. It consists entirely of lymphoid tissue and takes part in immune and other important processes. Although this organ is not vital (a person can live without it), the importance of the spleen for the body is difficult to overestimate. It is involved in hematopoiesis, being a direct participant in the creation of lymphocytes.
These cells are capable of destroying bacteria and viruses that enter the body, and without them there is no question of normal functioning of the immune system. The spleen processes old red blood cells (red blood cells) and then sends them to the liver, thereby contributing to the production of bile, which is needed for digestion.
This organ stores platelets. About a third of all platelets come from the spleen. Indirectly, the organ also participates in the hormonal regulation of bone marrow activity.
Age
The spleen begins to appear in the fetus at the earliest stage of pregnancy - 5-6 weeks after fertilization. This process ends by the fifth month of pregnancy. If at this most important stage the fetus is affected by negative factors (bad habits of the mother, genetic “failures”, toxins, an acute infection that the expectant mother fell ill with), then malformations of this organ are possible. Defects, as a rule, are of three types - the complete absence of an organ or the presence of two or more spleens in one body, as well as kinks and pinching.
In a newborn, the lymphoid organ has a round shape and weighs only about 9 g. By the age of one year, the weight of this organ almost triples and is about 25-28 g. At 7 years old, the child’s spleen weighs more than 50 g, and at 16 years old - more than 160 g.
The presence of a healthy, normally functioning spleen is very important for childhood, because children are more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections. Without the participation of the spleen, resisting diseases will be much more difficult.
Normal sizes
The size of the spleen increases as the child grows. To assess the condition of this organ, a table of acceptable sizes is used. It is not entirely correct to start from the age of the child. Same-year-olds can have different heights and weights. This means that the size of the spleen will vary.
It is much better to use a table compiled by pediatricians and approved by the Ministry of Health, which is based on the possible sizes for a particular child’s height. As you can see, the normal size range varies quite widely. An error of five to six mm is quite normal fluctuations.
The normal dimensions should not differ too much from those presented in the table. Any increase in the area of the spleen (by 15% of normal or more) in an infant, preschooler or schoolchild should necessarily become the basis for a medical diagnosis.
Symptoms
It is impossible to quickly guess that a child has an enlarged spleen. Usually the process of splenomegaly itself does not cause any clinical symptoms. The child may be tormented by manifestations of other diseases that were primary in relation to the enlarged spleen. Typically, parents learn about splenomegaly only during an examination:
- The inflammatory process in the spleen is characterized by such manifestations as frequent and fairly prolonged diarrhea, slight nausea and occasional vomiting, pain under the ribs, and increased body temperature.
- Non-inflammatory processes in the spleen rarely cause pain on palpation. The temperature also usually remains normal. The skin in pathologies associated with an enlarged spleen may be pale, the child may become more tired and apathetic. Increased sweating may occur at night.
However, all these signs are indirect, ambiguous, and in this case it is not possible to make one or another diagnosis only based on the totality of symptoms.
The child may not feel anything bad, but the spleen may be enlarged. This also happens quite often.
Causes
If a child has an enlarged spleen, doctors talk about a phenomenon called splenomegaly. Independent primary diseases of the spleen are very rare. Typically, this organ increases in size due to certain diseases; this is only one of the symptoms of the underlying disease.
The list of possible causes of splenomegaly is very extensive:
- infections of bacterial origin, including severe ones - sepsis or typhoid fever;
- hematopoietic diseases;
- liver pathologies (cirrhosis, cystic fibrosis and others);
- severe chronic diseases - tuberculosis, syphilis;
- metabolic diseases;
- cardiovascular system defects;
- cancer diagnoses;
- benign tumors and formations, as well as cysts of the spleen itself.
The spleen itself, with various pathologies in the child’s body, can undergo different conditions, almost all of them are accompanied by an increase in the size of the lymphoid organ:
- splenic infarction;
- abscesses (ulcers) in the organ cavity;
- organ inflammation;
- paralysis of the muscular apparatus of the spleen.
There are diseases that are the undisputed leaders among the possible causes of splenomegaly in children. These are acute viral diseases: measles, rubella, chickenpox, mononucleosis, herpes infection, and so on. In second place are hereditary metabolic problems.
Parasitic damage to the liver and intestines (by some types of helminths) often occurs. In this case, the spleen immediately “reacts” to the problem with a painful increase.
Finding the cause of splenomegaly is very important; without this, proper treatment is impossible. After all, therapy is not based on shrinking the spleen, but on eliminating the disease that causes its growth. After this, the spleen will shrink on its own.
Diagnostics
It is not possible to obtain much information using the method of palpation of the spleen. In adolescents, this organ is practically not palpable, and in young children, a slight excess in size is sometimes even normal.
The main diagnostic method, which allows us to judge not only the size of the spleen, but also its structure, the presence of possible abscesses, cysts and tumors, is ultrasound diagnostics. The doctor will send you for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs first.
However, the diagnostician’s measurements using an ultrasound scanner alone are not the basis for making a decision. The child will also have to undergo tests:
- general blood analysis;
- detailed blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis.
To get a complete picture, sometimes it is necessary to undergo a computed tomography scan and visit a hematologist.