Author's rating
Author of the article
Green Elena Stanislavovna
Otolaryngologist of the second category
Articles written
665
about the author
Laryngitis in a one-year-old child is a fairly common occurrence. This is an inflammation of the larynx caused by viruses, pathogenic fungi, bacteria, even dust. The trachea and bronchial tree are involved in the process. The vulnerability of a child's body to pathogenic pathogens is associated with an insufficient level of development of immune defense. Intrauterine immunity (antibodies received from the mother) is exhausted by the age of three months. The greatest risk is the threat of narrowing of the airways, leading to respiratory failure and obstruction.
The first signs and how laryngitis manifests itself in children
Children aged six months to three years are most often susceptible to laryngitis. The unformed state of the child’s immunity is important in pathogenesis. Laryngitis occurs in the presence of provoking factors:
- diathesis;
- significant hypothermia;
- passive smoking;
- impaired breathing through the nose;
- tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- severe stress on the vocal cords (nodular laryngitis);
- vitamin deficiencies;
- eating food and liquids in a cold state.
There are cases of allergic laryngitis. It can be caused by animal hair, pollen, medications and food components. This type of laryngitis in a child is most often fraught with an attack of stenosis. Children's laryngitis is divided into simple acute, subglottic laryngitis (false croup), chronic (rare).
Laryngitis in a child initially manifests itself as a lack of appetite, increased sweating, and behavioral reactions in the form of tearfulness, drowsiness, and moodiness. A “barking” cough can develop into a silent, hoarse voice. The postauricular lymph nodes are enlarged, the temperature is elevated, and the throat is red. The addition of rhinitis contributes to difficulty in nasal breathing, and the oropharynx is sore.
The process is complicated by a dry cough and hoarseness. By night, the situation may be aggravated by difficulty breathing as a result of edema, air is drawn in with a specific whistle. As the disease progresses, the cough becomes “barking”, temperature readings can reach 40.
How to treat laryngitis in a one-year-old child depends on the factors that caused it. Most often these are herpes viruses, measles, parainfluenza, and adenovirus infection. In case of untimely treatment, bacterial accumulation of streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococcus, and hemophilus influenzae occurs.
Lack of nasal breathing.
How to speed up recovery
Inhalations with mineral water have proven themselves to be quite good. To fill the nebulizer container, take alkaline mineral water with released gas. Inhalations with mineral water have no contraindications, so they can be performed even on young children .
In some cases, with severe swelling, hormonal drugs - Prednisolone and Dexamethasone - may be prescribed for inhalation. They must be diluted with saline solution, and only then used for inhalation.
To reduce swelling and inflammation, you can inhale saline vapor. If this drug is not in the house, then salted water is poured into the container.
With laryngitis, the membranes of the pharynx and vocal cords swell greatly. The disease is accompanied by fever, barking cough and hoarseness. If the disease is not treated properly, serious complications can occur. Treatment of the disease usually takes about two weeks, but the recovery period also takes more than a week. To make recovery from illness smoother, the doctor can prescribe immunomodulators and vitamin complexes to the patient.
How to properly treat laryngitis in a one-year-old child
The structural features of the nasopharynx in a one-year-old child allow pathogenic microorganisms to enter the larynx almost unhindered. In an adult, the size of the nasopharynx is significantly larger. Laryngitis for a baby is a serious problem, while for an adult it is characterized by unpleasant sensations.
At the first symptoms, treatment for laryngitis in a one-year-old child should be prescribed by a doctor. Accordingly, treatment is rather symptomatic. Drink plenty of warm milk, water with soda dissolved in it to moisturize the inflamed ligaments. Cool humidified air. Bed rest. Limitation of voice loads.
Laryngitis in a one-year-old baby is more difficult to treat than in an older child. This is due to the peculiarities of perception of a small patient.
How to properly treat laryngitis in a one-year-old child.
Causes of persistent laryngitis
The most common cause of chronic laryngitis is an untreated acute inflammatory process in the throat, which occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infections and bacterial infections.
In addition, doctors identify other more negative factors that interfere with treatment:
- constant voice loads;
- chronic bronchitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- inhalation of vapor chemicals;
- decreased immunity;
- diabetes;
- predisposition to throat diseases and inflammation of the vocal cords;
- disease of various organs.
Among the main factors that prevent a quick recovery from laryngitis is hypothermia. It is difficult to say how many days therapy will take in this case.

Smoking and drinking alcohol.
Effective drug treatment
Antiviral suppositories: “Viferon”, “Laferobion”, “Alfarekin”. With correctly prescribed treatment, on the third or fourth day, a small amount of sputum begins to be released, for example, taking the cough suppressant “Bromhexine”. Remedies for bronchospasm - "Eufillin".
It is unacceptable to use aerosol sprays on a one-year-old child, which can provoke laryngospasm. To relieve edema, antihistamine drugs with cetirizine and desloratadine are used. Nazivin drops can be used in the nose for rhinitis.
Among antipyretics, preparations with ibuprofen and paracetamol are acceptable, but preparations of acetylsalicylic acid are contraindicated due to the threat of life-threatening Reye's syndrome. Bacterial laryngitis requires the use of antibiotics, mainly the penicillin group.
Treatment with folk remedies
Laryngitis is a serious disease, so you need to use traditional medicine recipes strictly with the permission of your doctor, adhering to his recommendations. In this case, the main treatment is medication. Traditional medicine – additional.
Attention! Treatment of allergic laryngitis with folk remedies is unacceptable, since medicinal herbs and flowers can only aggravate the situation.
Traditional medicine suggests treating the disease by gargling with chamomile and sage flowers. One tablespoon is poured into half a liter of hot water and simmered over low heat for about 2 minutes. Close the container and let the broth brew for 60 minutes. Rinse or take 1 tablespoon orally 3 times a day.

Treatment with folk remedies for laryngitis.
Chronic stage
Chronic laryngitis in a child develops according to the principle of catarrhal inflammation, atrophy or hypertrophy of tissues. Age category: children over ten to twelve years old. Characterized by symptoms such as:
- low-grade fever;
- slight cough;
- rough voice;
- sore throat;
- vocal cords get tired quickly.
These signs in a child increase significantly with exacerbation of laryngitis. There is a high probability of a night attack of false croup occurring in a child under five years of age. A choking child with blue lips makes wheezing sounds, his skin is covered with sweat. Tachycardia is observed - accelerated heartbeat.
An emergency call is required. The doctor will decide on the treatment.
Mechanism of development and symptoms
The primary affected area, from which the virus subsequently spreads to other organs of the respiratory system, is the larynx. This manifests itself in disruption of the mucous membrane, narrowing of the respiratory opening. It is known that the role of the larynx in the respiratory system is to conduct gases through the airways (in particular, the trachea). Dysfunction of this organ prevents the child from breathing and speaking normally.
In children, the disease develops due to the structural features of the laryngotorhinological organs. Such features include: narrowing of the trachea and lumen of the larynx, poor muscle development, looseness of the mucous membrane. The cold season provokes the disease even more. The immune system is weakened, and combined with the peculiarities of the infant’s respiratory system, the infection easily penetrates the respiratory tract.
The course of the disease is acute or chronic. Moreover, the second type occurs when laryngitis appears too often in children. Thus, frequent laryngitis becomes the cause of chronic pathology.
Tolerance depends on the severity, etiology and individuality of the organism. The duration of the disease also varies - from one week to three.
Important! The chronic form threatens disruption of the respiratory system, decreased performance of the child, and rapid fatigue.
Here are a few signs by which you can determine that a child has acute laryngitis:
- hoarse voice, wheezing, the child speaks in a whisper or does not speak at all;
- dry cough, which is more disturbing in the morning and at night - the child wakes up from suffocation;
- discomfort in the larynx - “tears in the throat”;
- pain when swallowing food due to swelling of the larynx;
- when inhaling, a whistle is heard (the lumen of the larynx is reduced, there is a lack of closure of the vocal cords);
- fever with an increase in temperature to a maximum of 39 degrees;
- with allergic laryngitis, the temperature does not rise, swelling appears;
Babies may refuse to breastfeed and become restless and anxious. In chronic laryngitis, a dry cough is observed, accompanied by a change in voice and dysphonia.
Sometimes you can observe bluish skin around the mouth, blood spots on the mucous membrane and rhinitis.
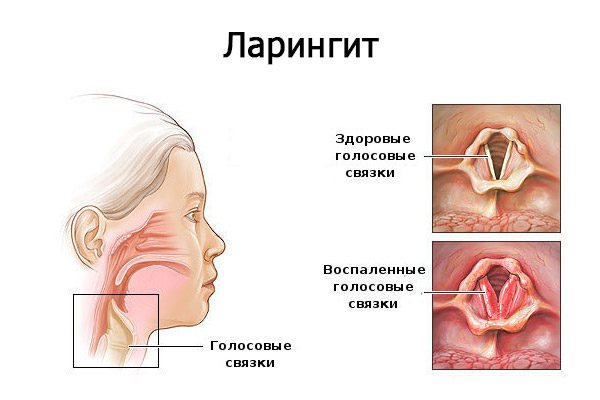
The mechanism of development and symptoms of laryngitis.
Treatment of false croup
In the treatment of false croup, it is important to remember the causes of its occurrence. As a result of inflammation, the lumen of the airways narrows, swelling of the mucous membranes, hypersecretion (mucosal secretions). Also, fear due to difficulty breathing and neurosis on this basis cause spasm of the larynx. This is especially important for children with a narrow larynx, prone to obesity and allergic reactions. So, let’s treat it at home competently:
- Calm the child, eliminate any irritants;
- The room temperature should be maintained at about 18 degrees, humidity maintained at least 40;
- Voice rest (to lure the child with quiet games).
In a hospital setting, the child receives anti-inflammatory therapy and antibiotics. If necessary, resuscitation measures are taken. If there is a threat to life, surgical intervention is permissible.
Treatment of false croup.
Treatment tips
The most important thing is that the patient needs to provide complete rest to the throat. You can't talk at all. If necessary, it is better to speak as quietly as possible, but not in a whisper, since in a whisper the voice becomes more hoarse and becomes muffled.
When treating laryngitis, it is forbidden to eat hot, cold, spicy, sour, alcohol, soda, or smoke. You should avoid exposure to cold air and going outside on a damp, foggy day.
One of the good tips is to drink plenty of fluids, hydrate and ventilate the room. The house where the patient lives should not be damp.
Diagnosis and first aid for false croup
According to the famous doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky, croup is caused by the parainfluenza virus. The most risky period is the winter as a result of heating devices drying out indoor air. When it occurs later, it is especially difficult. You can determine the diagnosis yourself based on three noticeable signs and immediately consult a doctor:
- difficulty breathing when inhaling;
- change in voice (hoarse, disappears altogether);
- barking cough.
Against the background of the symptoms described above, the acute onset of the disease, sore throat, and high temperature are taken into account. The child turns pale and has a laryngitis-like dry cough. There can be no talk of any self-medication. Before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to provide first aid:
- sits you on your lap, unbuttoning your clothes on your chest;
- calm the child;
- provide access to cool fresh air (open the windows, hang wet sheets and towels around the room);
- drink plenty of soda water and milk;
- for hyperthermia above 38 degrees, use antipyretics;
- if the temperature is not high, it is possible to apply a mustard plaster to the calf muscles;
- relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa with vasoconstrictor drops.
If the room is hot, take the child, dressed, out to the balcony in winter, and into the bathroom in summer, turning on cool water to increase the humidity level. In no case should you give expectorants or use hot steam inhalations! Such actions will worsen suffocation and guarantee subsequent hospitalization. Let's say an ultrasonic humidifier.

How to help a child with false croup.
Disease prevention
Prevention of laryngitis, like almost all other respiratory diseases, is to increase immunity. This will help you avoid getting sick. And if it does happen, then thanks to the body’s protective forces it will occur in a mild form.
On a note! The surest way to avoid illness is to naturally increase immunity and avoid contact with people sick with the flu and other infections.
How to prevent the disease: there are the following main ways to prevent laryngitis :
- Hardening : rubbing, dousing with cool water, visiting the pool;
- Regular physical education classes . Physical activity in the fresh air is especially beneficial;
- Proper balanced diet , rich in vitamins and microelements;
- During periods of epidemics of respiratory viral infections, it is necessary to minimize stay in crowded places . Before each forced visit to places of accumulation, you can lubricate your nostrils with oxolinic ointment;
- It is also necessary to minimize the child's stay near sick children .
Antiviral drugs (anaferon, interferon and others) are not a reliable means of preventing respiratory viral infections. Their use will not give any effect - neither positive nor negative.
Nebulizer and steam inhalations
Treatment at home involves the use of inhalations. It is convenient to carry out dosed administration directly into the lesion using a device - a nebulizer. Solutions of Lazolvan, Ambrohexal, physiological sodium chloride solution, Borjomi, drugs for bronchospasm (Berodual, Ventolin), glucocorticosteroids for stenosis (Pulmircort) are used for their intended purpose.
In cases where a nebulizer is not available, steam inhalations over boiled potatoes and chamomile infusion are possible. With false croup, hot inhalations are unacceptable!

Nebulizer and steam inhalations.
Complications of the disease
The main complication of laryngitis in a child is false croup. The soft, short, narrow vestibule of the larynx, its funnel-shaped shape, as well as excessive excitability of the muscles of the glottis, the prevalence of the tone of the sympathetic nerves contribute to it.
Asphyxia is typical when timely assistance is not provided. Hypothermia, convulsions, low heart sounds, complete cessation of breathing up to coma and death.
Laryngotracheitis (cough more often than with laryngitis), pneumonia, bronchitis often occur as complications of laryngitis. They require long-term, sometimes intensive treatment.
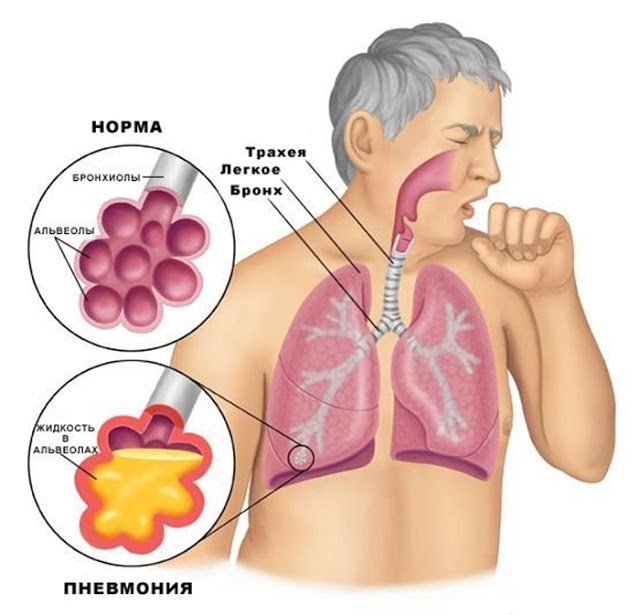
Pneumonia.
Diagnostics
As a rule, a thorough examination of a small patient with an endoscope (laryngoscopy) is sufficient to make a diagnosis. In this case, the redness of the larynx is pronounced . In some cases, pinpoint hemorrhages are found, and sometimes viscous mucus is present.
What is laryngoscopy?
There are two types of laryngoscopy: indirect and direct.
During indirect laryngoscopy, the doctor carefully moves the endoscope to the child's uvula to examine the larynx from above.
Direct laryngoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. The doctor points the endoscope toward the larynx to also see the inner lining of the larynx.
Using laryngoscopy, the doctor can determine whether and how the laryngeal and vocal folds have changed. In addition, acute laryngitis usually differs markedly from chronic laryngitis (see table below).
Table: changes in vocal folds
| Acute laryngitis | Chronic laryngitis |
| Severely reddened, swollen mucous membrane, possible plaque from fibrin (a protein formed during blood clotting). | Pale reddish color, thickened and hardened mucous membrane, dry and uneven surface, formation of plaques in the mucosa. |
If the doctor detects an acute form of inflammation of the larynx, further examination of the child is usually not required.
In some situations, a bacteriological examination is done to identify pathogenic bacteria.