Rules for providing first aid to children
Parents and teachers need to be prepared to provide first aid to children. It is necessary to act calmly so that the baby does not start to panic. Screaming can only make things worse. Actions must be cool and quick.
The child must not only become familiar with the rules of pre-medical care, but also learn how to follow them. Then you will be able to automatically decide how to behave in a given situation. After all, a quick reaction to a child’s injury will help cause less harm to his health.
Causes of suffocation
Among the most dangerous diseases that can cause shortness of breath are:
- acute laryngitis (false croup);
- acute pneumonia;
- allergic reaction;
- laryngeal injury;
- ingestion of a foreign object into the respiratory tract;
- runny nose;
- bronchial asthma.
Acute laryngitis is a disease that is a consequence of a viral infection (cold).
The main symptom of laryngitis is a dry, barking cough. In addition to coughing, the patient’s temperature rises, appetite decreases, hoarseness appears in the voice, and pain occurs when swallowing. The greatest danger is posed by acute stenosing laryngotracheitis, which is known as “false croup”. The danger of this disease lies in the narrowing of the trachea due to swelling of the mucous membrane. In difficult cases, swelling can completely close the lumen of the larynx. If shortness of breath occurs, you should seek help from a doctor. Delay can be fatal.
Acute pneumonia often causes difficulty breathing in a child. With pneumonia, fluid leaks into the lung tissue, making it difficult to oxygenate the blood. When the bronchi are blocked, the child also develops shortness of breath. It is not difficult to treat such a disease; the main thing is to contact a specialist in time who knows what to do.
An allergic reaction is also the reason that a child suffocates. An allergic reaction occurs to various substances that enter the child’s body not only through the respiratory tract, but also through the esophagus and the administration of the drug. An allergic reaction in the form of swelling of the larynx develops within a few minutes after contact with the allergen.
Interesting Providing first aid for a poisonous snake bite
Laryngeal edema is a dangerous condition that can cause death. In case of allergic swelling of the larynx, you need to call an ambulance. In such a situation, it is impossible to refuse hospitalization when, after the administration of a special drug, the child’s swelling subsides. The allergic reaction may develop again after the medication stops working.
Trauma to the larynx can also cause a child to choke. The cause of shortness of breath lies in the blockage of the air path due to partial/complete displacement of the cartilage of the larynx.
To determine the cause of shortness of breath, parents should inform the specialist about the child’s laryngeal injury. After receiving the information, the doctor will conduct a thorough examination, determine and eliminate the cause of shortness of breath. Information received in a timely manner from parents will allow the doctor to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
A foreign object that a child has undetected inhaled often causes the child to become short of breath. Various objects can close the airways (button, bead, seed, coin, pebble). If a foreign object penetrates too deeply into the airway, the child may stop breathing.
If a foreign object leaves the child’s respiratory tract after coughing or sneezing, a complication such as laryngospasm may develop, which manifests itself in a reflex narrowing of the lumen of the larynx.
Bronchial asthma occurs more often in children who were bottle-fed. Bronchial asthma develops in the presence of various types of allergies (dermatitis, rhinitis). This disease often develops in children whose parents smoke. Asthma attacks begin at night during sleep, when cold air and dust enter the respiratory tract.
Bronchial asthma is treated throughout life. You should consult a doctor at the first signs of shortness of breath. Early detection helps to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe an appropriate course of treatment.
Performing artificial respiration
In some cases, the child’s respiratory function may be impaired, and as a result artificial respiration will be required. In this case, you need to act like this:
- Clear the nasal passages and oral cavity of the contents. If there are splints on your teeth, they need to be removed. When assisting a drowned person, remove the water: to do this, place the victim’s head below the level of the body.
- Air needs to be blown: in adolescence (as in adults) from the mouth into the nasal cavity. For a small child (and infants), artificial respiration is performed mouth to mouth or directly into the oral and nasal cavity.
The mouth-to-nose procedure involves blowing air through the victim’s nose:
- Place the child on his back on a hard surface.
- The person providing assistance should stand or kneel next to the patient.
- Using one hand, the baby's head is tilted back by grasping the chin and simultaneously pushing it forward and up to avoid swallowing the tongue.
- Place the other palm on the parietal area of the child.
- With both hands, firmly fix your head in this position.
- Then the assistant inhales air, brings his mouth closer to the nose of the injured baby and lets in the air forcefully. How effective artificial respiration will be is determined by the level of elevation of the child’s chest.
- After blowing in air, release the baby's nose: spontaneous exhalation should follow, thanks to the return of the chest to its original position.
The procedure for performing artificial respiration for children using the mouth-to-mouth method involves the following actions:
- Place the baby on his back.
- The head is fixed as indicated in the previous method.
- The difference between the techniques is that the assistant blows air through the baby's mouth.
- When assisting an infant, the rescuer's mouth may immediately cover the child's mouth and nose.
When performing artificial respiration, air should be inhaled at the following frequency:
- for schoolchildren (and adults) – 20 breaths per 1 minute;
- children of the younger age category - 30 breaths per 1 minute;
- infants – 35 breaths per 1 minute.
How to give help correctly
If a child is choking, emergency care should be provided until medical personnel arrive. Intervention is necessary if the victim's breathing becomes severely difficult and other life-threatening signs are observed. Emergency assistance is provided when:
- the skin takes on a blue tint;
- the child has profuse salivation;
- the baby begins to choke and holds his throat with his hands;
- loss of consciousness occurred.
If your baby has difficulty breathing, he should provide first aid himself.
If a child over 1 year of age (who is conscious) needs help, life saving is carried out using the following technique:
- To remove a foreign object from the respiratory tract, you need to stand behind the person with your arms around his waist.
- A palm clenched into a fist is placed in the area above the navel (intercostal space).
- Clasping your fist with your other palm, you should make 4 presses on the victim’s stomach. The movement is made in the direction from bottom to top. When performing manipulations, you need to spread your elbows to the sides.
- It is advisable to repeat the action until the bone leaves the respiratory tract.
In case of loss of consciousness, another method of assistance is recommended:
- The child is placed on his side, and his head, supported by the chin, is pulled back.
- If there is no breathing, artificial ventilation is performed.
- The person providing assistance should draw air into their chest and then exhale, pressing their mouth over the baby's nose and mouth.
- The manipulation is carried out 5 times, then the victim is checked for breathing.
- If the baby is still not breathing, apply 30 pressures with 2 fingers to the lower part of his chest.
- After this, you need to take 2 more breaths and press on the chest area again.
If there is no breathing, artificial ventilation is performed until the emergency team arrives.
Heart massage technique
If a child is found unconscious as a result of an accident, if pulsation or heartbeat cannot be heard, you must immediately begin cardiac massage.
For infants, heart massage is performed as follows:
- using your index and middle fingers, press sharply and forcefully on the area of the middle of the baby’s chest;
- Press at a frequency of 120 times per minute.
For preschoolers, indirect cardiac massage is performed as follows:
- Using the pads of the palm of one hand, press into the middle of the sternum;
- You need to press 90 times in 1 minute.
A closed heart massage is performed for a schoolchild (and an adult) as follows:
- with two palms (one on top of the other), strong and sharp pressure is applied to the area of the lower third of the victim’s chest;
- You need to make 60 clicks in 1 minute.
If a simultaneous disturbance in the functioning of the heart and respiratory functions is detected, a combination of indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration is required. Both manipulations must be carried out together (if there is an assistant) or in turn, in the case when assistance is provided by one person.
What to do if a small child chokes on food?
If a small child chokes on food and at the same time he is actively coughing, spitting up or vomiting, then nothing more needs to be done, except to provide access to fresh air into the room, since vomiting and coughing are nothing more than a protective reflex of the body to the ingress of food or fluids into the respiratory tract.
If your baby is vomiting after choking or coughing, you should never shake him or knock him on the back - this can drive the foreign body or liquid even deeper and worsen the condition. Allow the child to clear his throat and regain his breathing. If the baby vomits or burps, you need to turn his head to the side or hold him in a “column” so that the baby does not choke on the vomit.
Emergency assistance should be provided if food that has entered the respiratory tract has completely blocked it and the child cannot breathe. Urgently call an ambulance if the baby begins to choke, saliva flows from his mouth, the baby can neither cry nor cough, and even more so if the baby begins to lose consciousness, and his skin has acquired a bluish tint.
While one adult calls the ambulance, another should immediately begin providing first aid to a choking child. To do this, the baby needs to be turned face down and placed on the adult’s hand so that the baby’s buttocks are higher than his head, and his face lies on the adult’s palm. With the heel of the other palm, you need to forcefully push the child laid in this way between the shoulder blades 5 times. Then turn the baby onto his back so that his head is below the buttocks and with two fingers press 5 times on the sternum (where the ribs end). If it doesn’t help, push again with your palm 5 times between the shoulder blades and then press on the sternum.
Every mother should learn to do these actions. It would be better if you not only read what to do if a child chokes on food, but also watch educational videos on this topic online and try to perform these actions on a doll. Then you definitely won’t be confused in an emergency situation, the subconscious will give out information.
Heimlich maneuver
If the baby chokes, which leads to suffocation, you should resort to the Heimlich maneuver. To do this you need:
- Place the injured baby on the floor face up.
- Kneel down near his feet.
- Press sharply with the middle and index fingers of both hands on the area of the peritoneum between the navel and ribs up towards the diaphragm.
- Make sure that the sternum remains unconstrained so that nothing puts pressure on it.
- Repeat the manipulation until the airways are cleared.
The main requirement after this procedure is a mandatory inspection by a specialist, even if the foreign object is successfully removed.
Probable causes and mechanism of occurrence
Nature has provided all sorts of protective mechanisms, so for natural reasons only a small amount of mucus may appear at night, aimed at eliminating the exogenous agent in the respiratory tract. A dry, unproductive cough acts as a reaction to an external negative stimulus.
The reasons that can lead to a night cough with sputum in a child can be divided into several broad groups, and none of them will be caused by natural causes. Dry air or excessively warm air may cause an involuntary cough reflex, but it will not work so hard that it will immediately lead to the appearance of copious phlegm.
Following recommendations for improving the air in the nursery allows you to optimize the quality of sleep and eliminate provoking factors of exogenous (external) origin. If a child chokes on snot in his sleep and coughs, the logical explanation is that mucus drains from the nose to the back of the throat and acts as phlegm. And the reason for this is nothing more than a runny nose, resulting from irritation of the nasal mucosa by provoking factors. In much the same way, a thick secretion gets into the throat and the baby begins to choke on it in his sleep. The ingestion of a product produced by the mucous membrane to remove harmful disease products from the body is the main reason for the occurrence of a wet cough.
What pathogenic agent forces the immune system to fight through the production of a specific secretion needs to be clarified. When a child coughs from snot during sleep, there is a desire to help - put drops in the nose, rinse the mucous membrane, use an inhaler or suck out the mucus with a syringe.
A child's wet cough at night also requires similar immediate help. Because a night cough, which normally should not appear, can only be caused by a strong or persistent provocateur:
Diseases of the lungs and bronchi
Wet and viscous, in which it is impossible to cough - a characteristic symptom of croupous pneumonia, false croup, any inflammatory process in the lungs and bronchi. A large accumulation of modified bronchial mucus, which has lost its natural transparent consistency, leads to irritation of the walls of the bronchi, the desire to constantly cough, but due to the strong viscosity of the substrate, expectoration does not occur. Hence the constant desire to cough, which is provoked at night due to a negative process in the lungs or bronchi. Often this is the initial symptom of bronchial obstruction, an invariable sign of bronchial asthma.
Diseases of the nose and nasopharynx
Snot that gets onto the back wall during sleep, because the child is in a horizontal position, makes you want to cough up and remove mucus from the throat, which the baby begins to choke on in his sleep. The mechanism works in approximately the same way for sinusitis, acute respiratory infections, and inflamed ears, for which mucus in the nose is a characteristic and indispensable symptom that forces you to cough at night.
Viral infection
With a virus, coughing is triggered by the production of waste products of the virus and one’s own blood cells, which fight them. Acute respiratory infections and viruses are not always accompanied by fever, but in the initial stages of development, the cough cannot be alleviated, and it is quite difficult to calm the attack.

Bacterial and parasitic infections
Diseases such as whooping cough, worms, and bacteria cause vomiting when coughing, copious sputum production that does not stop at night, due to the constant presence of the aggressor in the body. Intoxication, from which the child vomits, because the vomiting and cough centers are almost nearby.
Allergy
Exposure to allergens on a child’s body is not always accompanied by sputum production and coughing, but can cause an allergic runny nose. During an attack from contact with a permanent allergen, the child has a desire to constantly cough or cough in his sleep.
Other reasons
Cough can occur due to reflux esophagitis syndrome, intestinal diseases, and pathology of the cardiovascular system. These ailments can make normal sleep impossible, and no homeopathy can help.
The causes of a strong wet cough at night in a child almost always lie in internal causes, and if the pathogenic diseases are not stopped and treated in a timely manner, things can end badly.
It is recommended to consult a doctor and begin treatment immediately as soon as the child begins to cough with sputum. Without qualified help, there is a risk that the child will choke in his sleep.
First aid for children with bleeding
The first aid algorithm is determined by the type of bleeding: capillary, venous or arterial.
Most often, a child can notice the flow of blood from the capillaries due to wounds, abrasions, and small cuts. To stop the blood oozing from such a vessel:
- pinch the wound;
- treat it with an antiseptic;
- cover with a bactericidal plaster or apply a bandage.
If your child has a nosebleed:
- tilt his head forward;
- insert a cotton swab into the nostrils;
- apply something cold to the bridge of your nose;
- if there is no effect after 15-20 minutes, call an ambulance.
During blood loss, dark red blood flows smoothly from the vein, without pulsation. With such an injury, emergency care involves performing the following actions:
- apply a pressure bandage (be sure to leave a piece of paper with a note indicating the time when the dressing was made);
- call an ambulance.
When bleeding from an artery, a pulsating discharge of bright scarlet blood is observed. In such a situation, emergency assistance consists of the following actions:
- stopping blood loss from the artery should be carried out within a maximum of 2 minutes;
- pinch the wound with your fingers; if blood flows from the axillary area, use a fist; if the femoral artery is damaged, press on the thigh area just above the injury;
- in an exceptional situation, a tourniquet is applied for a maximum of 60 minutes, with the obligatory indication of the time of its application.
First aid for laryngeal stenosis in children
Call an ambulance.
The ambulance dispatcher, in addition to accepting a call for stenosis in a child, will tell you what to do to help the baby before the ambulance arrives.
Calm the child.
If the adults around the baby do not panic and fuss, the child will feel calmer and it will be easier for him to breathe. Of course, there are plenty of reasons to panic (the child is choking at night, what to do?! But it is important to remember that your behavior can frighten the child and aggravate his condition. Therefore, we calm ourselves down and calm the child.
Provide access to fresh cool air.
In winter, a dressed child can be taken out to breathe on the balcony; in summer, he can be seated in front of an open refrigerator or freezer.
Humidify the air your child breathes.
You can do inhalation with saline or Borjomi using a nebulizer.
Rules for applying a tourniquet
A tourniquet is applied over the wound to stop the flow of blood to this area.
It is prohibited to apply a tourniquet in the area of the forearm and lower leg, as there is a danger of pressing the nerve against the bone tissue, which can cause injury and paralysis of the arm or leg.
It is better to apply a tourniquet in the area of the lower third of the shoulder or the upper third of the thigh near the inguinal fold (do not forget that the tourniquet must be applied over the wound).
Basic Rules:
- Such a device should be applied over thin fabric or clothing.
- Application should be fast and removal should be slow.
- When a tourniquet is applied correctly, blood immediately stops flowing, and pulsation on the injured arm or leg below this device cannot be felt.
The duration of the tourniquet's stay on the body is half an hour in the cold season, and in the summer - a maximum of an hour, and the temperature, rather than the calendar, serves as a guide (in summer - above zero, and in winter - below zero).
If you use a tourniquet longer, the tissue may become numb and die due to insufficient blood circulation. A purulent complication and anaerobic infection may also develop. In winter, prolonged use of the device can lead to frostbite, as blood flow stops in the injured arm or leg.
After the allowed time has passed, re-clamp the damaged vessel, loosen the tourniquet, and after 2-3 minutes apply it again, but slightly higher than the previous place.
The time of application of the tourniquet must be noted. To do this, you can put a note under it indicating the time, or write this data with a marker on a visible area of the victim’s body.
First aid for children with a fracture
A child can get a fracture when falling, jumping, or hitting an object. A fracture is characterized by severe pain, changes in the shape of the limb, mobility becomes limited, and abnormal mobility in the area of injury is occasionally observed. With a serious fracture, bone fragments may be displaced, the integrity of the skin may be compromised, and traumatic shock may also develop.
Providing emergency assistance in such a situation involves performing the following actions:
- a fixing bandage is applied;
- if the fracture is open, a sterile bandage is necessary;
- if the need arises, a tourniquet is used to stop blood loss and a splint is applied.
A board, stick or rods may be suitable for applying a splint; they need to be wrapped with cotton wool, cloth or clothing. The splint is applied very carefully so as not to further injure the child or cause severe pain.
If there is no material that can be used as a splint, the injured arm can be taped to the body and the leg to the other leg. In any situation, at least two joints are fixed (above and below the fracture).
The injured child should be transported to a medical facility as quickly as possible. Give him painkiller before sending him to the hospital.
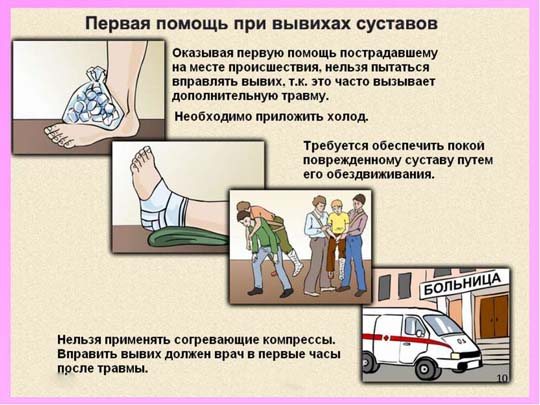
First aid for children with sprains
The reason for the appearance of a dislocation also lies in the baby falling or a strong blow to the area of the joint tissue. As a result, the bones in the joint are displaced, the joint capsule is torn or stretched, and blood vessels and nerves are injured. In case of a dislocation, a child may complain of pain in the damaged joint tissue, its deformation, limited mobility and forced posture of the arm or leg.
As first aid for this condition, the child should be ensured immobility of the injured limb:
- the hand is suspended using a “kerchief”;
- if a leg is injured, lay the baby down and place pillows, a blanket or clothes around the injured limb;
- You should not try to reduce the dislocation yourself.
The child should be immediately taken to the emergency room. When transporting the victim, do not under any circumstances change the position of the limb acquired after the injury.
First aid for children with burns
In some cases, the child may get burned. Emergency assistance in such a situation is determined by its degree. Each stage of a burn is characterized by certain signs:
- at stage 1: the skin turns red, becomes swollen, and pain appears;
- at stage 2: the skin becomes red and swollen, pain and blisters appear;
- at stage 3: the skin is red and swollen, pain develops, blisters develop, blood begins to flow;
- at stage 4: tissues become charred.
Since in everyday life we usually have to deal with stage 1 and 2 burns, let’s learn how to act when they occur.
If a child receives a stage 1 burn, you need to do the following:
- Place the affected area in water at a temperature of 15-20o for 15-20 minutes. This will help prevent the burn from penetrating deep into the tissue.
- Then treat the affected area with a healing preparation. Never use oil.
If your baby has received a stage 2 burn, do not open the resulting blisters under any circumstances; leave the burnt items of clothing in place. In such a situation, apply a moistened cloth or something cold to the affected area (but on top of the cloth). Be sure to call a doctor.
If your eyes are burned, lower your face into a bowl of water and blink in it, then close your eyes and cover them with a damp cloth.
If you receive a chemical burn, you should proceed as follows:
- a burn with alkaline substances is treated with preparations such as 1-2% boric, citric, acetic acid;
- To treat skin burned with acids, use soapy water or with the addition of soda, or clean water in large volumes. A sterile bandage is applied on top.
First aid for children: what everyone needs to know
The type and philosophy of nutrition undoubtedly has a strong influence on our health. But there are situations when we are all in equal conditions and our health, and even life, depends on the actions of people nearby, on the timely assistance provided or not provided. Children find themselves in the zone of increased danger in emergency situations, and, of course, adults are in the zone of increased responsibility. Therefore, it is very important for every person, especially a parent, to have at least minimal first aid skills.
In this article, with the support of specialists from the Maria Mama charity organization, which conducts free master classes with certified Rossoyuzspas rescuers in Moscow, we have collected tips that help quickly and correctly provide first aid to children.
First aid for loss of consciousness
First, it is necessary to determine the signs of life in a person:
- Reaction to sound (call by name, clap your hands near your ears);
— Presence of a pulse (check the pulse in the neck with four fingers, duration is at least 10 seconds. The pulse is felt on both sides of the neck);
- Presence of breathing (you need to lean towards the child’s lips or use a mirror).
If you do not detect a reaction to at least one of the above signs of life, you must proceed to cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and do it continuously until the ambulance arrives.
How? Here are the instructions:
— Unfasten the buttons of clothing, the waist belt; - Use your thumb to move your hand up to the chest along the abdominal cavity, feel the xiphoid process; — Move 2 fingers away from the xiphoid process and do an indirect heart massage in this place; — For an adult, indirect cardiac massage is performed with two hands, placing one on top of the other, for a teenager and a child - with one hand, for a small child (up to 1.5-2 years) - with two fingers; — CPR cycle: 30 chest compressions – 2 breaths into the mouth; - When performing artificial respiration, you need to tilt your head back, raise your chin, open your mouth, pinch your nose and inhale into the victim’s mouth; — When assisting children, the inhalation should not be full; for infants, it should be very small, approximately equal to the volume of a child’s inhalation; — After 5-6 cycles of CPR (1 cycle = 30 compressions: 2 breaths), it is necessary to check the pulse, breathing, and the reaction of the pupils to light. If there is no pulse or breathing, resuscitation should continue until the ambulance arrives; - As soon as a pulse or breathing appears, CPR must be stopped and the victim must be brought into a stable position (raise the arm up, bend the leg at the knee and turn over to the side).
Important: if there are people around you, ask them to call an ambulance before resuscitation begins. If you are providing first aid alone, you should not waste time calling an ambulance; you must begin CPR. An ambulance can be called after 5-6 cycles of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, this takes about 2 minutes, after which it is necessary to continue actions.
First aid for a foreign body entering the respiratory tract (asphyxia)
Partial asphyxia:
breathing is difficult, but there is, the child begins to cough heavily. In this case, he needs to be allowed to cough on his own; a cough is more effective than any assistance measures.
Complete asphyxia
characterized by noisy attempts to breathe or, conversely, silence, inability to breathe, red and then bluish complexion, loss of consciousness.
Procedure to follow if a foreign body enters the upper respiratory tract:
— Place the victim on his knee upside down, make progressive claps along the spine (the direction of the blow is towards the head); - If the method described above does not help, it is necessary, while in an upright position, to grab the victim from behind with both hands (one clenched into a fist) and sharply press on the area between the navel and the xiphoid process. This method can only be used on adults and older children, since it is more traumatic; — If the result is not achieved and the foreign body is not removed after two methods, they must be alternated; — When providing first aid to an infant, it must be placed on the hand of an adult (the face lies on the adult’s palm, fingers between the child’s mouth, supporting the neck and head) and apply 5 blows between the shoulder blades towards the head. Then turn it over and check the baby's mouth. Next – 5 presses on the middle of the sternum (the head should be lower than the legs). Repeat 3 cycles and call an ambulance if it doesn’t help. Continue actions until the ambulance arrives.
Do not: slap the back in a vertical position and try to reach the foreign body with your fingers - this will lead to the foreign body passing deeper into the respiratory tract and aggravating the situation.
First aid for drowning in water
There are two types of drowning:
True drowning is characterized by bluish skin and profuse foam from the mouth and nose. In this type of drowning, a person swallows a large amount of water.
Procedure for providing assistance:
— Lean the victim over the knee; - By pressing on the root of the tongue, induce a gag reflex. Continue until all the water comes out; — If the reflex is not evoked, begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation; — Even if the victim was able to be brought to consciousness, it is always necessary to call an ambulance, since drowning has a high risk of complications in the form of pulmonary edema, cerebral edema, and cardiac arrest.
Dry (pale) drowning
occurs in ice or chlorinated water (ice hole, pool, bath). It is characterized by pallor, the presence of a small amount of “dry” foam, which will not leave marks if wiped off. In this type of drowning, a person does not swallow a large amount of water, and breathing stops due to a spasm of the respiratory tract.
Procedure for providing assistance:
immediately begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation.

First aid for electric shock
- Free the victim from the action of the current - push him away from the electrical object with a wooden object, you can use a thick blanket or something that does not conduct current; — Check for the presence of pulse and breathing, if they are absent, proceed with cardiopulmonary resuscitation; — If there is a pulse and breathing, call an ambulance in any case, since there is a high probability of cardiac arrest; — If a person faints after an electric shock, bend your knees and press on the painful points (the junction of the nasal septum and upper lip, behind the ears, under the collarbone).
First aid for burns
The procedure for dealing with a burn depends on its degree.
1st degree: redness of the skin surface, swelling, pain. Grade 2: redness of the skin surface, swelling, pain, blisters. Grade 3: redness of the skin surface, swelling, pain, blisters, bleeding. 4th degree: charring.
Since in everyday life we most often encounter the first two types of burns, we will consider the procedure for providing assistance for them.
For a first-degree burn, place the damaged area of skin under cold water (15-20 degrees, not ice) for 15-20 minutes. Thus, we cool the surface of the skin and prevent the burn from penetrating deep into the tissue. After this, you can anoint the burn with a healing agent. Do not apply oil!
If you have a second degree burn, it is important to remember not to burst the blisters that appear on the skin. Also, do not remove burnt clothing. It is necessary to apply a damp cloth or cold through the cloth to the burn site and seek medical attention.
If your eyes are burned, you need to lower your face into a container of water and blink in the water, then apply a damp cloth to your closed eyes.
Procedure for chemical burns:
In case of an alkali burn, it is necessary to treat the skin surface with a 1-2% solution of boric, citric, and acetic acid.
In case of an acid burn, treat the skin with soapy water, water and soda, or simply plenty of clean water. Apply a sterile bandage.
First aid for frostbite
- Go into the warmth; - Undress the child and begin GRADUAL warming. If your limbs are frostbitten, then immerse them in water at room temperature, warm them for 40 minutes, gradually increasing the water temperature to 36 degrees; - Give plenty of warm, sweet drinks - to warm up from the inside. — Later apply wound healing ointment; — If blisters or thickening of the skin appear, or if the sensitivity of the skin is not restored, seek medical help.
You cannot: rub the skin (with your hands, cloth, snow, alcohol), warm the skin with anything hot, drink alcohol.
First aid for heatstroke
Heat or sunstroke is characterized by dizziness, nausea, and pallor. The victim must be taken into the shade, moistened bandages applied to the forehead, neck, groin, and limbs and changed periodically. You can place a cushion under your feet to ensure blood flow.
First aid for poisoning
- Give the victim a lot of water and induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue, repeat the action until water comes out.
Important! You cannot induce vomiting in case of poisoning with chemicals (acid, alkali), you just need to drink water.

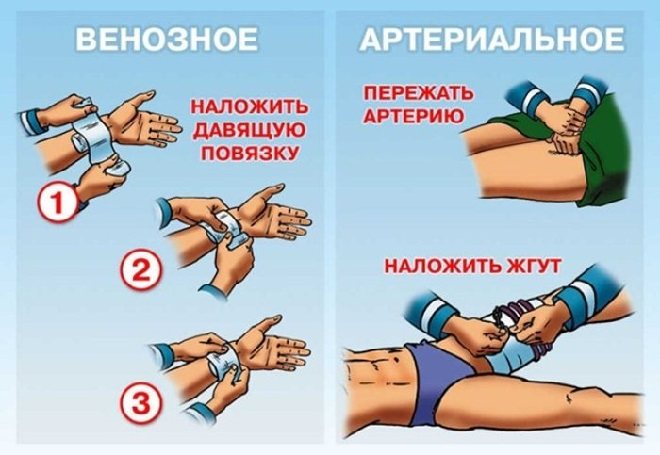
First aid for bleeding
The procedure for assisting with bleeding depends on its type: capillary, venous or arterial.
Capillary bleeding
– the most common bleeding from wounds, abrasions, and minor cuts.
In case of capillary bleeding, it is necessary to clamp the wound, disinfect it and apply a bandage. If you are bleeding from the nose, tilt your head forward, hold the wound with a cotton swab, and apply cold to the bridge of your nose. If the bleeding does not stop within 15-20 minutes, call an ambulance.
Venous bleeding
characterized by dark red blood, a smooth flow, without a fountain.
Procedure for providing assistance:
apply direct pressure to the wound, apply several bandages and bandage the wound, call an ambulance.
Arterial bleeding
observed when an artery is damaged (cervical, femoral, axillary, brachial) and is characterized by a gushing flow.
Procedure for providing assistance:
— It is necessary to stop arterial bleeding within 2 minutes. - Press the wound with your finger, for axillary bleeding - with your fist, for femoral bleeding - press your fist on the thigh above the wound. - As a last resort, apply a tourniquet for 1 hour, writing down the time of application of the tourniquet.
First aid for fractures
— In case of a closed fracture, it is necessary to immobilize the limb in the position in which it was, bandage it or apply a splint; — In case of an open fracture, stop the bleeding, immobilize the limb; — Seek medical help.

First aid skills are something that is better to know but never use than to not know and be helpless in an emergency. Of course, such information is remembered better in practical classes; it is especially important to understand in practice, for example, the technique of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Therefore, if you are interested in this topic, we advise you to choose first aid courses and attend them.
For example, the organization “Maria Mama” with the support of the “Russian Union of Rescuers” monthly organizes a FREE practical seminar “First Aid School for Children”, about which you can read in more detail here.
Maria Shvetsova
First aid for children who faint
The cause of fainting can be severe pain, fright, or fear of expected painful sensations. A similar condition in a child is characterized by the following signs:
- pale skin;
- the appearance of cold sweat;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- dilated pupils.
After some time, the baby comes to his senses.
Providing emergency assistance to a child who faints involves performing the following actions:
- Place it on a horizontal surface and slightly raise your legs, create conditions for air access.
- Loosen clothing items.
- Bring a cotton swab dipped in ammonia to his nose.
- When the baby comes to his senses, give him a valerian tincture (5-10 drops, dilute in a small amount of cool water) and place him on the bed.
In the future, you need to visit a pediatrician for advice.
First aid if a child is choking
If a child gets a foreign object in the throat, the following actions are required:
- Place the victim on your lap with the head hanging down. Clap progressively along the spinal column towards the head.
- If the described method is not effective, you should resort to the Heimlich maneuver.
- If you do not get the desired result after using both methods, try performing them alternately.
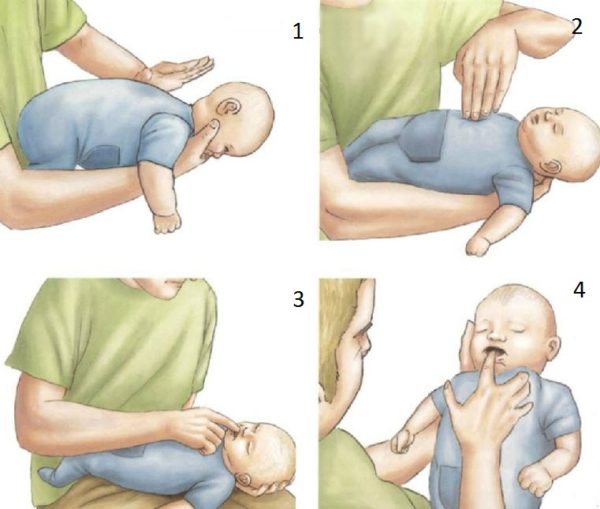
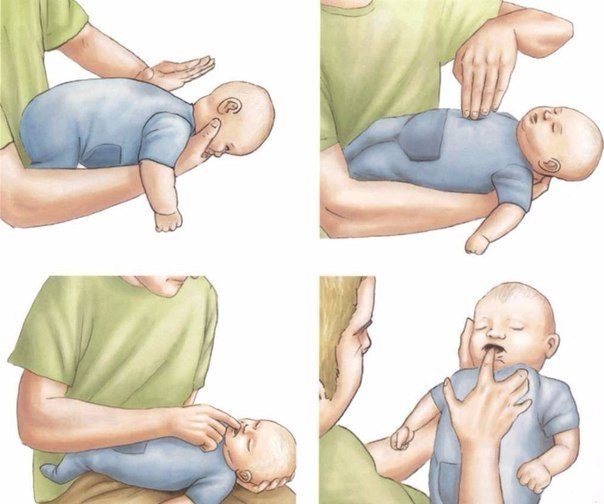
If you need to provide emergency assistance to a baby, proceed as follows:
- Place the baby on the adult's hand so that the face lies on the palm, the position of the fingers is between the baby's mouth, the neck and head are supported.
- Make 5 claps in the interscapular area towards the head.
- Then turn the baby over and check his mouth.
- Press 5 times on the center of the chest. At this time, you need to lower your head below the level of your feet.
- The cycle is repeated three times. If there is no effect, call an ambulance.
- You need to repeat the manipulations until the doctor arrives.
You should not slap the back when the child is standing, or try to pull out a foreign object with your fingers - this may cause the foreign body to penetrate further into the larynx, which will worsen the situation.
Ways to make breathing easier for a newborn
When a newborn has difficulty breathing, you should do the following:
- The newborn is placed on his tummy, with his head turned to the side. In this position, saliva and tongue move forward, providing enough space for air to pass through.
- The room for a newborn to sleep should be clean from dust and fluff.
- Keep nasal irritants away from the newborn. Irritants include tobacco smoke, sawdust, perfume, hairspray, and paint fumes.
- To make mucous secretions more easily detached from the walls of the nose, you can use a saline spray or drops.
Interesting What to do if a child swallows glass, a coin or a button?
First aid for children in case of drowning and heatstroke
The cause of drowning can be not only complete immersion under water, but also liquid that has penetrated only into the mouth and nose (when swimming in a bathtub, a small body of water, etc.).
In such a situation, proceed as follows:
- Free your torso from clothing.
- As quickly as possible, clean the mouth and larynx of foreign objects, remove any liquid that has entered the respiratory system. This is done by opening the mouth using the index finger wrapped in cloth. All foreign objects are removed as much as possible, the tongue is pulled out and held with a loop of bandage. Then the child lies on the adult’s lap, face down, with his head and legs hanging, and pats on the back are performed.
- If the water has been removed and respiratory functions have not resumed, artificial respiration is required; if a heartbeat cannot be heard, a closed cardiac massage is required.
- When the respiratory function is restored and the baby wakes up, warm him up, give him strong coffee or tea, and transport him to the hospital.
With heat or sunstroke, the child becomes pale, nauseated and dizzy. In such a situation, take the baby into the shade, place a damp cloth on the forehead, neck, groin, arms and legs, and change it regularly. You can elevate your legs using a bolster to stimulate blood circulation.
Child choked - first aid.

Our children are very active and restless, they strive to do several things at the same time. What to do if a piece of cookie or small object gets into the baby’s respiratory tract instead of the esophagus? Almost automatically, you pat him on the back. But breathing does not normalize. It's time to take more radical measures.
Look after the child
If the baby is 2-3 years old, he can try to explain to his mother or whoever is nearby at that moment what happened. But how can we understand infants in this case? First of all, unusual behavior should alert you. If the child is choking or gasping for air, and is breathing with hissing or whistling, if a strong cough suddenly begins, the child sucks in the tummy and supraclavicular fossae, while goggles his eyes, urgent measures must be taken.
If the baby coughs, do not interfere - the stuck piece may fly out on its own. If the little one cries or screams, this, paradoxically, is also a plus in such a situation, because it means that the airways are not completely blocked, and you have time to act. You must immediately, without hesitating for a second, instruct someone to call an ambulance. In this case, the dispatcher must immediately be notified of what happened and given not only the necessary information about the baby (age, condition of the baby, the alleged cause of the trouble), but also explain in detail how to get to the house, inform not only the floor and apartment number, but also code on the entrance door to the entrance.
If a choking child tries to gasp for air and begins to turn blue and loses consciousness, the situation is truly critical, and you have no more than three minutes at your disposal. Therefore, if there is no one at home except you and the baby, there is no time to waste time calling an ambulance.
Take action!
No matter how scared mom is, she must remember that panic can only do harm. Therefore, it is better to pull yourself together and at least look calm outwardly, so as not to scare the baby even more.
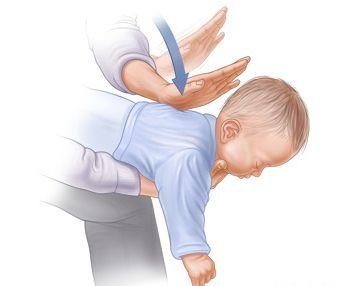
“The first thing to do is try to clear the airways. Try turning the baby upside down and shaking it a little: the piece may fall out on its own. You can take the baby by the legs and shake him upside down.
- If this does not help, you need to visually examine the pharynx and try to examine the entrance to it with your finger. If you find the culprit, try to remove it with two fingers or tweezers.
- Take the baby in your arms and, supporting the head and neck with one hand, place him face down on the forearm of your left hand so that the head is lower than the level of the body (hold the chin with two fingers). The next step is “knocking the cork out of the bottle”: slap the baby on the back between the shoulder blades 4-5 times.
- If the object that caused the trouble does not fall out, place the child on his back on a flat surface, move his head to the side and press your fingers several times on the lower part of the sternum and upper abdomen towards the spine and up. But remember: this manipulation must be done extremely carefully, because internal organs can be damaged in children under one year old.
Unfortunately, sometimes all the above steps are unsuccessful. In this case, it’s the turn of artificial respiration (you must allow at least a small amount of air to get into the children’s lungs!). The technique is simple: tilt the baby’s head back so that the chin protrudes upward, use the “mouth to mouth” method and inhale forcefully several times. If your chest rises at the same time, it means that your actions have achieved their goal, and some of the air is already entering the lungs. Continue to do the same until the ambulance arrives.
You can see how to perform artificial respiration here.
You can see how to properly help a child in this video. At minute 14, Dr. Komarovsky will clearly demonstrate how to behave in such situations.
First aid for children with hypothermia
If your child is hypothermic, you should do the following:
- Take your baby to a warm room.
- Undress and begin to gradually warm up. If your hands or feet are frostbitten, place them in a container of room water and warm them for 40 minutes by gradually increasing the water temperature to 36o.
- Give him something warm and sweet to warm him up inside.
- Over time, treat damaged skin with a wound-healing ointment.
- If blisters or lumps appear on the skin, or if there is no sensitivity in the frostbite area, consult a doctor.
It is forbidden to rub the skin with your hands, alcohol, cloth or snow, use something hot to warm the skin, or give alcohol.
First aid for shortness of breath
If a child begins to choke, it is important not to get confused and to begin providing first aid correctly. At the same time, you should call a team of specialists, who will provide pre-medical care before their arrival. First aid for shortness of breath consists of following these rules:
- Concentrate, don't panic.
- The main thing to do when an attack begins is to call an ambulance.
- Provide the child with moist air. To do this, you can turn on the hot water in the bathroom to create steam. Invite your child to breathe in this moist air.
- Calm the child down (sing him a song, turn on a cartoon, read a book).
- If you have vasoconstrictor drops in your home medicine cabinet (Gasolin, Tizin, Sheaf, Vibrations), you should drop them into each nostril.
- If you have an inhaler, the child should breathe in mineral water. For alkaline inhalations, Borjomi, Essentuki 4, 17 is suitable. For inhalations, you can use a 0.9% Sodium Chloride solution.
- If the child is too excited, he is allowed to be given a sedative (valerian).
- The effect on the vessels of the extremities also helps to distract the child and reduce fear. It is prohibited to do it at elevated temperatures. There are several options for influencing blood vessels:
- lowering the upper limbs alternately into hot/cold water;
- the lower limbs are placed in a container with warm water;
- applying mustard plasters to your feet.
Interesting Pulled stomach: basic principles of treatment
If a child’s temperature rises due to shortness of breath, he should be given an antipyretic drug and provided with plenty of fluids (milk with mineral water, water, mineral water).
First aid for children in case of poisoning
Any child tries to put everything he likes into his mouth. Therefore, you should not keep chemicals, medications and other toxic substances in the baby’s access area. Even excessive consumption of simple vitamins can cause poisoning.
If the baby still manages to eat something prohibited, immediately call an ambulance and begin providing emergency assistance:
- Use a damp cloth to remove the harmful substance from the child’s mouth and give plenty of clean water to drink.
- Do not feed him milk under any circumstances, as this will speed up the penetration of poisons into the bloodstream.
- Grind activated carbon at the rate of 1 piece per 10 kg of body weight, give it to the child to drink.
If the baby loses consciousness, turn him on his side to prevent vomit from entering the nasopharynx. You should not provoke vomiting yourself. Wait for the specialists to arrive.
Poisoning
Of course, you protect your child from low-quality products and feed him exclusively freshly prepared food. But no one is immune from trouble, and a child who finds himself unattended even for a minute can try something that is absolutely not intended for him: eat spoiled food, sip from a glass of alcohol, sip cleaning fluids from bottles, or eat pills.
- If you notice that the baby has eaten or drunk something harmful to him, call an ambulance, and then take action yourself. First aid for a child will consist of immediately inducing vomiting in the baby. Make him drink salt water (3 tsp per glass) and press on the root of the tongue.
- Before the EMS team arrives, give your baby a “solution” of activated carbon: 1 tbsp. Mix the crushed tablets in 1 glass of water and feed the baby with a spoon.
- Be sure to report your actions to the arriving doctors and tell them what poisoned the baby.
But we don’t always notice right away that the baby has eaten something “forbidden.” Unfortunately, it often happens that we already see signs of increasing intoxication, and at the same time we must act clearly and harmoniously, trying to provide first aid to the baby and discover what exactly he was poisoned with.
Signs of poisoning
- Weakness and pallor;
- vomit;
- with severe intoxication, convulsions appear and the baby loses consciousness.
The situation with poisoning of an infant is complicated by the fact that a small child, especially one who feels unwell, often cannot explain and show what he drank and ate. If there are no empty bottles, pill blisters or detergent containers in sight, sniff the baby. If he smells of gasoline, turpentine, bleach or vinegar, you should not induce vomiting, since these substances can cause severe chemical burns when they pass through the esophagus again. In such cases, it is better to call an ambulance and consult with the dispatcher.
While waiting for the ambulance team, place the baby on his side and constantly monitor his pulse and breathing so that if they stop, you can begin resuscitation measures. If, after calling an ambulance, you find out what exactly poisoned your baby, do not be afraid to call again and ask the dispatcher how you can help your child before the doctors arrive.
First psychological aid for children
If a child has suffered stress, he needs psychological help. In such a situation, experts recommend acting as follows:
- You need to let your child know that his feelings are close to you and that other children also face this.
- Try to create conditions so that the baby feels protected (hug him, talk to him and play with him).
- Take a look at positive pictures of you together, happy and smiling. This will help ease unpleasant memories.
- Try to reduce the conversation about what happened from conveying details to feelings.
- Try to make plans with your child, defining specific goals and deadlines for completion.
- Tell your child that feelings of helplessness, fear, and anger are quite natural.
- Work on increasing his self-esteem (try to praise him more often for good deeds).
- Encourage him to play in the sand and water. The main thing is that the baby expresses his own anxieties in images.
- Don't let your baby become a dictator. You should not comply with all his whims out of sympathy.
First aid for children with electric shock
A child's curiosity often ends in disaster. Sockets and electrical wires are dangerous, so you should try to prevent electric shock to your baby. Use plugs for sockets, and try to place the wires behind furniture or in a specially designed box. Sometimes it happens that a baby bites the wires or sucks on them, this causes a strong electric shock.
In the event of such an incident, first unplug the device. If this is not possible, pull the baby away from the wires. To do this, you need to pull him by his clothes or use a stick.
When performing first aid, proceed as follows:
- if the baby faints, artificial respiration and closed heart massage are required;
- when he comes to his senses, lay him on his side and call an ambulance;
- if burns are detected on the body, wash them with water for 15 minutes and apply a sterile bandage;
- You can give your child a painkiller.
Choking
Now many parents practice early swimming in the home bathroom or in the pool under the guidance of instructors. This, of course, useful undertaking for the development of the baby can turn into a tragedy. Despite the action of self-preservation instincts, a baby left unattended even for a couple of seconds is capable of choking.
- First of all, the baby needs to be pulled out of the water. If he is conscious and actively coughing, hold him in your arms, tilting him slightly, but so that his stomach is lower than his head.
- If the baby has lost consciousness, you should lay the baby down, turning his head to one side and raising his upper body, and call an ambulance. At the same time, you must assess the child’s condition: feel the pulse and make sure that he is breathing. If they are absent, proceed with resuscitation measures.
First aid for children with bites
In the summer, a child may be bitten by a mosquito or other insect. The baby begins to scratch the affected area, resulting in an infected wound. As a preventive measure, to prevent germs from entering the wound, the damaged area must be treated immediately.
For this purpose, you can use a cold compress to relieve pain. If itching occurs, it is necessary to take antihistamines: Suprastin or Loratadine. You can use an antiallergenic external agent to treat the wound, for example, Fenistil.
Sometimes, while playing or quarreling with someone, a child may bite an enemy. In such a situation, if the bite does not provoke bleeding, simply wash the damaged skin with laundry soap. To make the wound heal faster, lubricate it with Rescuer ointment.
If the bite was severe and blood appeared, treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide or Chlorhexidine, and also visit a pediatrician.