Patronage of a healthy child
Child patronage is a program created by the state with the aim of monitoring the condition of a newly born child, a woman in labor, as well as assessing the socio-economic living conditions of the family as a whole.
Visits and examinations are carried out by a visiting pediatrician or a nurse from the clinic to which the baby belongs by registration. The observation time will depend on the baby’s well-being and family circumstances.
If the child develops in accordance with the norm, he is completely healthy and grows in a favorable environment, visits to health workers proceed as follows:
- in the first days of returning home from the maternity hospital;
- once a week during the first month of life;
- from a month to six months - twice a month;
- then until the child is one year old - once a month;
- up to three years, scheduled inspection once a quarter.
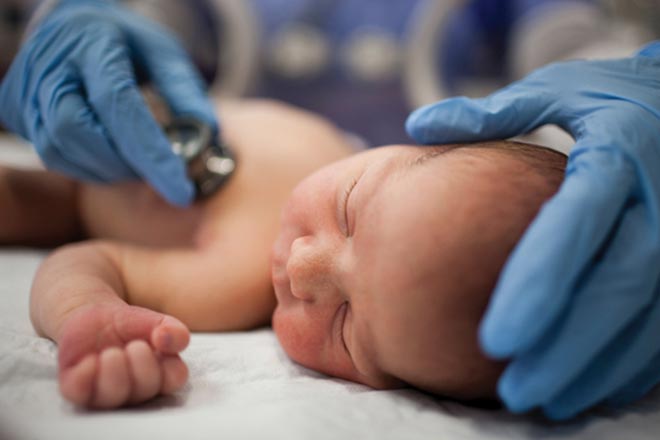
At the first visit, the health worker will ask several questions that will help identify hereditary and chronic pathologies in the baby in the future, as well as information related to the course of pregnancy, childbirth, the condition of the newborn at birth and discharge from the hospital.
Next, the doctor examines the baby:
- Physical development is the presence or absence of defects and microanomalies. There may be minor deviations from the norm that are observed in one of the family members.
- Neurological development - here the baby’s posture, movements and their activity, muscle tone, and the development of reflexes will be taken into account. The shape and size of the head, the size of the large and small fontanel, and the condition of the sutures of the skull bones are taken into account.
- Assessment of the skin - skin tone, the presence of prickly heat, diaper rash. The main focus is on the umbilical wound, the skin around the navel, the level of healing, and the absence of discharge from it;
- Listening to the child’s breathing and heartbeat in order to assess the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, thereby excluding congenital pathologies.
- Feeling the newborn's tummy. Asks about the frequency and nature of stool.
- Checking the symmetry of the gluteal folds and spreading the legs to the sides for early detection of dysplasia and hip joint disease.
Primary patronage of a newborn lasts about 20-30 minutes.
The second patronage of a newborn child occurs on the 10th day of birth. The doctor takes a second look at the baby, examining all organs and systems to determine his well-being. To understand this, the health worker should find out:
- how the baby sleeps;
- behavior of an infant during wakefulness;
- schedule;
- weight gain;
- presence and frequency of regurgitation;
- intestinal colic.
If the above symptoms do not bother the newborn, the doctor makes a conclusion that he is well adapted to external factors.
The third postpartum patronage of a newborn is carried out approximately on the 20th day of the baby’s birth. The purpose of this visit is to monitor the well-being and development of the baby, to assess its neuropsychic development.
After the next appointment, the pediatrician records all the information received in the baby’s medical history and, at the end of the first month, makes a prognosis for the health of his ward and determines developmental risk groups.
This condition is not considered to be a disease and therefore does not require any treatment. As a rule, it appears in infants in the first weeks after birth.
Common borderline conditions:
- jaundice occurs due to the immaturity of liver enzymes and an increase in bilirubin in the blood. It appears on the 3-4th day after the baby is born in the form of a yellow coloration of the skin, which intensifies by the 6th day, and disappears by 8-10 days;
- erythema - manifests itself in the form of redness of the skin on the 2nd day of life. Rarely accompanied by a rash, which goes away by the end of the first week of birth;
- hormonal crisis - symptoms of this condition manifest themselves in engorgement of the mammary glands of the baby or bloody vaginal discharge in girls. This crisis begins on the 2nd–4th day of life and passes by the 15th day.
December 29, 2014 admin No Comments
Patronage of a healthy child
Patronage (French - patronaqe - patronage) is a system of medical care for pregnant women, young children and some categories of patients at home.
The tasks of patronage work include helping the mother in organizing the correct regimen and rational feeding, preventing rickets, anemia, childhood infections, monitoring the physical and neuropsychic development of the child, the state of health and family education, etc.
During the first half of life, a local nurse (paramedic) visits a healthy child 2 times a month, in the second half of the year - monthly, during the second and third years of life - once every 3 months. According to indications, visits may be more frequent.
Patronage of children of different ages has different goals.
a) introduce yourself to the child’s mother and inform her about the purpose of the visit;
b) remove outer clothing, hats, and street shoes;
c) wash your hands;
d) prepare a diary and pen;
e) collect an anamnesis of the child’s life;
g) examine the child;
h) give specific advice to the mother on caring for the child;
i) arrange patronage in accordance with the recommendations: write the date of patronage, medical history, examination of the child and advice on care, regimen, feeding, prevention of rickets.
Scheme for collecting a life history and examining a child
- Last name, first name, patronymic of the child.
- Date of birth, age.
- Home address.
- Information about parents:
mother: age, profession, health status;
father: age, profession, health status
5.1. What pregnancy is this child from?
5.2. How did previous pregnancies end (abortion, miscarriage, birth of a child,
children's health status, age).
- gestosis (in the 1st or 2nd half of pregnancy and how it manifested itself);
— what illnesses did you have during pregnancy?
— did the woman follow a daily routine and eat rationally?
- were there any injuries (physical, mental);
- Have you walked enough in the fresh air?
PATRONAGE.
Patronage is an active visit to the patient at home.
1. The first prenatal pediatric patronage is carried out by a nurse or paramedic of the FAP after the woman is registered with the antenatal clinic and the information is transferred to the children's clinic.
PURPOSE – collecting anamnesis and providing instructions to the expectant mother. Emphasize on:
- Prenatal risk factors;
- Heredity;
- Determine whether pregnancy is desirable;
- Moral and psychological climate in the family.
- Material and living conditions.
Recommendations:
- School visit for young parents at the children's clinic;
- Issues of rational nutrition and healthy lifestyle.
- The second prenatal pediatric patronage is carried out at 31-38 weeks of pregnancy (maternity leave).
Target:
- Checking the implementation of previously received recommendations;
- Reassessment of prenatal risk factors;
- Preparation for the postpartum period (talk about breastfeeding, preparing the mammary glands for feeding, prevention of hypogalactia, preparing a trousseau and a child’s corner, first aid kit).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Order on granting student leave, sample
SCHEME OF PEDIATRIC PATRONAGE.
| CHILD'S AGE | FREQUENCY OF PATRONAGE |
| Newborn | 1 visit in the first 3 days after discharge from the hospital or on the 1st day |
| Newborn (1 week) | 2 times per week |
| Newborn (up to 1 month) | 1 time per week |
| Infant (up to 6 months) | 2 times a month |
| Infant (after 6 months) | 1 time per month |
| Child from 1 year to 2 years | 1 time every 3 months |
| Child from 2 to 3 years old | Once every 6 months |
| Over 3 years old | 1 time per year |
The arrival of a newborn baby home from the maternity hospital is a very important and exciting event. After all, this means that the life of the family changes dramatically and turns 180 degrees. This applies to your daily routine, nutrition, and much more.
December 22, 2014 admin No Comments
— determine the health status of the child and mother, living conditions in the family, the presence of risk factors;

— establish psychological contact with the mother and other relatives of the child;
— teach the mother the skills of care and feeding, inform the mother about the work of the clinic (for primary care of a newborn).
discharge of a newborn from the maternity hospital (we visit a full-term healthy newborn in the first two days, and a premature and “risk group” child on the day of discharge, as well as children with twins and triplets).
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS: do not leave the child unattended.
Inform the mother about the goals and objectives of patronage,
POSSIBLE PROBLEMS: absence of mother and child at home at the time of patronage; negative attitude of the mother towards patronage,
mother's unpreparedness to communicate with and care for her child.

clean gown, mask, umbilical wound treatment kit (for a newborn).
Preparation for the procedure:
- Introduce yourself and congratulate you on the newborn.
- Collect information about the child: health status, appetite, sleep, individual characteristics. Nature of feeding: free or on a schedule. Mother's health status, lactation (adequate, not), nipple shape. Information about the organization of care: temperature in the room, sanitary condition of the room, cleanliness of linen, availability of a first aid kit for child care, organization of walks, the role of the father in care, emotional and psychological climate in the family.
- Wash the hands.
Today you and your baby returned home. All the worries associated with pregnancy and childbirth are left behind. Ahead is a long life together, full of new discoveries and achievements, smiles, laughter and occasional sadness.
What now? Where to start? How to care for your baby? How to bathe, do I need to swaddle? Should I give my baby water and a pacifier? What should I eat myself so that I have enough milk for my baby? There are a lot of questions.
After the birth of her first child, a young new mother does not know how to behave with the baby, so there is help - patronage for newborns, the person who will provide this patronage will teach the mother to be self-confident and raise a healthy and properly developed child.
A young mother who is about to give birth to a child is very worried, because she understands that she will have a lot of responsibilities, that the child will be completely small and fragile, and she has a fear of harming the baby.
Patronage form for children from 0 to one year old withdrawal
5. Instruct the mother and give her recommendations.
Pay special attention to compliance with the age-specific daily regimen, issues of rational nutrition, physical education, educational activities, preparation for vaccinations, prevention of borderline conditions, as well as the elimination of identified deviations.
6. Make an entry on the patronage sheet. The child sleeps most of the day.
Falls asleep quickly, sleep is unstable.
During sleep and wakefulness, periodic chaotic movements are noted.
Medicine. Nursing
Basic Rules:
- Carried out jointly by a pediatrician and a district nurse; Timeliness of implementation; Solemnity; Information content.
This patronage includes:
- examination of the child (including examination of the umbilical wound and BCG site);
instructing the mother on feeding, caring for, and raising the child; sanitary and hygienic conditions for the child in the apartment (sanitary condition and cleaning of the premises, temperature in the room, rules for washing and storing clean and dirty linen, etc.); teaching the mother how to care for a newborn: swaddling, washing, toileting the skin and mucous membranes, etc. organizing walks; the role of the father in raising and caring for the child; information about conditions requiring urgent medical attention (hyperthermia, aspiration, sudden death syndrome)
Methodological recommendations for carrying out patronage of newborns in Moscow
An additional fourth patronage is carried out by a nurse as prescribed by a doctor if there are medical indications (their algorithm will be disclosed below).
It has been established that if deviations in the health of the newborn are detected, the remaining visits to the doctor and nurse are carried out as active visits to the child at home regarding the disease.
To determine the tactics of patronage monitoring of children in the first month of life, the doctor draws up a plan for medical and nursing patronage.
It should be noted that the approved Methodological Recommendations provide for patronage of healthy newborns born on time, aged from 0 to 28 days.
With regard to patronage of full-term newborns in the presence of deviations in the health of the child and newborns born prematurely, it is determined that patronage of babies is carried out according to an individual schedule created by a doctor and agreed upon with the head of the pediatric department.
Patronage of newborns and observation of children up to one year
(from 0 to 1 month of a child’s life): weekly examination of the child by a doctor at home, anthropometry (measurement of weight and height indicators), recommendations for feeding, training parents in massage techniques and proper care.
(from 0 to 12 months of the child’s life): weekly examination of the child by a doctor at home, anthropometry, recommendations for care and feeding, training of parents in massage techniques - for 1 month of life.
From 2 to 12 months, the child is examined by a doctor once a month, anthropometry is performed in the clinic monthly and examined by specialists, laboratory and instrumental studies are performed (complete blood count, urinalysis, determination of blood glucose levels, ultrasound, electrocardiography, audiometry).
(from 0 to 12 months of the child’s life): weekly examination
Templates for local nurse visiting children in the first year of life
Muscle tone: physiological hypertonicity of the flexors, hypotonicity.
Nasal breathing is free, the nose is stuffy, sniffling, mucous discharge from the nose is copious, not copious. The abdomen is soft and painless. Chair: changes _________________________________; No changes: daily, mushy, yellow, without admixtures of blood, greenery, mucus. _____ once a day. Flatulence: yes, no.
Urination is free, painless _____ times a day. Character of sleep_________________________________________________________________ NPR: briefly fixes his gaze on a bright object _______, flinches at a sharp sound ________, first smile ________, tries to hold his head while lying on his stomach ________.
Ac, Az, E, Do - Recommendations: Mode No. 1.
1.Meals: exclusively breastfeeding, upon request. 2. Bathing daily t – 37-380C, rinsing t – 36-370C; with baby soap 1-2 times/week. 3. Toilet the newborn daily; washing
Patronage scheme for children under one year old
dynamics of the health group for 1 year:_________________________________ 7.
Feeding: breastfeeding from _______ to ________ mixed from _____ to ________ artificial from ______ to ________ number of feedings by 1 year: 8. Carrying out massage and gymnastics: - from what age_______________________________________________ - how many complexes have been learned_______________________________________ 9.
Prevention of rickets: - nonspecific________________________________________________ - specific: vit.
D – from what age_________, dose____________, duration____________________, UV irradiation – ____________ sessions, scheme______________________________, 10. Prevention of anemia:__________________________ 11.
Patronage for a newborn
4 The mother and grandmother are primarily involved in caring for the child. 5 The child is provided with linen, toys, and a separate crib.
The sclera is icteric, the skin is slightly icteric.
6 Visible mucous membranes are bright pink. The skin feels dry to the touch. The skin and visible mucous membranes are clean.
There is no pigmentation, petechiae, or rashes. The thickness of the skin fold on the anterior abdominal wall is 1.5 cm.
Skin turgor is within normal limits.
Dermagrophysm – red. There is fluff on the head. The nails are dense, the nail plates completely cover the nail beds.
There is no swelling on the face, lower extremities, or anterior abdominal wall.
7 Oblique system: curvature
Medicine.
Nursing.
Find out problems in mother and child.
Collect anamnesis (genealogical, biological, social). Conduct an analysis of the age-specific daily routine based on a conversation with the mother (number of feedings, number of hours of night and day sleep, how wakefulness is organized). Assess the nature of nutrition (type of feeding, frequency of feedings, complementary foods, appetite, favorite foods).
Conduct an objective examination: Leading lines of scientific development, behavioral parameters (mood and liveliness of reaction to the environment, sleep, appetite, wakefulness, negative habits, individual characteristics); Condition of the skin and subcutaneous fat (color, cleanliness, moisture, skin elasticity, soft tissue turgor, thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer; in newborns, note the condition of the umbilical wound); Condition of the musculoskeletal system (size and condition of the edges of the large fontanelle, number of teeth, order of their eruption, muscle tone, motor skills)
Newborn patronage: caring for mother and child
The initial visit includes three stages:
- Infant examination.
- Inspection of the baby’s living conditions, collection of data about family members.
- Collection of anamnesis of pregnancy and childbirth.
When entering a newborn’s home, the medical staff is friendly.
The pediatrician will congratulate the family on the birth of the baby and meet the mother and father of the child. It turns out how many people live in a given living space and what kind of relationship they have with the baby; Do the family have pets?
During the initial care of a newborn, it is checked in what conditions the child will live: whether he has a sleeping place, a stroller, a bath, a changing table, whether the crib is located away from drafts and direct sunlight.
The temperature and humidity in the room are taken into account, and the mother is given recommendations on how to ventilate the room and carry out wet cleaning. The linen is examined, as well as the conditions for its storage.
Patronage of a newborn at home: timing, goals, scheme. Child patronage form: sample filling
This visit is called the first pediatric visit to the newborn.
- It is noteworthy that in addition to the fact that the initial patronage must be carried out on time, it is assumed to be solemn
- The doctor and nurse should never play the role of strict teachers or supervisors.
A young mother, who is then under physical and psychological stress, should under no circumstances be poked at her mistakes, if any. - The staff of the children's clinic must demonstrate friendliness and willingness to help the woman in any questions regarding the newborn, its health, development and everyday life
The goals of primary care for a newborn are:
- assistance in organizing and establishing feeding of a newborn
- consultations regarding the organization of a newborn’s regimen
- assistance to a woman during the postpartum period, advice on caring for a newborn
Nursing patronage - what is it?
If we translate the word “patronage” literally from French, we get the word “patronage.” If you look at this term from the medical side, then patronage is various activities that are performed by a medical professional, mainly a nurse, and these activities are carried out at home with the mother and newborn.
The tasks of patronage include: treatment, prevention of various diseases, training of a young mother.
Employees of children's clinics are obliged to carry out primary prevention of various diseases, as well as developmental disorders of the baby, in a timely manner.
- medical;
- psychological.
- The first patronage of a newborn child is carried out within 3 days after discharge from the maternity hospital. The young mother is visited by a local children's doctor and a nurse, who will provide patronage;
- consult the mother and tell her all the information about caring for the baby;
- assist with breastfeeding if necessary;
- carry out preventive measures for childhood diseases, for example, anemia, rickets, etc. Also carry out prevention of infectious diseases;
- assess and monitor the baby’s health status;
- conduct consultations regarding examinations by pediatricians and other doctors for the purpose of prevention.
- The first patronage is carried out before birth. The purpose of the visits is to obtain a medical history and educate the expectant mother.
- During prenatal care, the nurse pays attention to perinatal risk factors, whether the child is desired, the moral and psychological climate in the family, and material and living conditions.
- The expectant mother should attend a school for young parents, make sure her diet is correct and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- At 31-38 weeks of pregnancy, the second patronage is carried out. Medical workers check how the recommendations are being followed and prepare the mother for the postpartum period: a conversation is held about breastfeeding babies only for the required period of time, preparing the breast for feeding and preparing a place to care for the child and the necessary medications that should be in the home first aid kit.
- A newborn needs constant care and protection.
- The nurse and doctor who come home to the mother and child assess whether the baby is being fed correctly and whether the situation in the family is normal.
- A medical professional can notice a deterioration in a child’s health in time and take action. Young parents without experience in raising small children may not pay attention, for example, to an increase in body temperature or complications that arise after childbirth.
- Assessment of the baby's health status. Muscle tone is checked, the fontanel is palpated, and the color and condition of the skin are assessed. A visual examination of the child’s body is also carried out and the symmetry in the location of all organs, the functioning of the limbs, the development of the genitals, the correct shape of the head, and more are revealed.
- Assessment of the health and psychological state of the mother. A pediatrician can examine a woman’s breasts for mastopathy and talk about how to place the baby to the breast.
- Assessment of social and economic conditions in the family. Conditions must be favorable, and the child must be provided with everything that a child needs at this age. If the family is dysfunctional, the pediatrician gives a written assessment of the situation and also determines the psychology of the parents’ behavior towards the baby.
- Training mothers in caring for the baby, proper care, and hygiene procedures.
- In the first three days after discharge, a pediatrician and a nurse visit. Once medical workers receive information about the child, they are required to visit him.
- On the first day after discharge, a medical professional comes if the child has health problems or was injured during childbirth.
- The nurse visits the newborn every day for 10 days. Then she will come only on the 14th and 21st days of the child’s life.
- If development proceeds normally, there is no need for further visits.
For the first time, a young pregnant girl will meet the clinic staff while she is still carrying her baby. The first visit to a pregnant woman by a health worker is made immediately after the woman has registered with the antenatal clinic.
The nurse’s task during the first visit to a pregnant woman is to assess the conditions in which the expectant mother lives and will live for 9 months, as well as talk with the pregnant woman and provide her with advice that can help the expectant young mother.
The next time the nurse will visit the pregnant woman in the third trimester, she will check whether the woman is following the recommendations that were discussed during the first meeting.
The nurse also conducts a consultation with the mother and tells her how to properly care for the baby, everything about breastfeeding and the postpartum period in general.
Learn about the peculiarities of the gestation period and the birth itself. She needs to study the documents for the baby that were issued at the maternity hospital. The nurse also creates a medical record for the child and fills it out according to the rules.
During patronage, the nurse assesses the psychological and nervous state of the baby. The baby’s existing reflexes are noted, and the work of the analyzers is assessed.
After ten days of life, it is checked whether the baby can keep a moving object in his field of vision. At 20 days, the child should fix his gaze on an object that does not move, and already at 1-3 months, the visiting nurse notes the baby’s ability to lift and hold his head when he is lying on his stomach, etc.
The mother receives from the health worker various kinds of advice and recommendations that will help to monitor the umbilical wound, etc. And also, if there are indications that the child needs to undergo examination by specialists, the mother is notified about this.
The nurse also shows various gymnastics exercises for infants, and also explains to the mother how to massage.
Inspect and evaluate housing and family relationships. The nurse can also recommend something to improve the baby's living conditions.
Find out from the mother how she feeds the baby. If the baby feeds on the mother's breast, then the nurse examines her, looks at how the baby grasps the nipple correctly or not.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Sanitary log sample filling
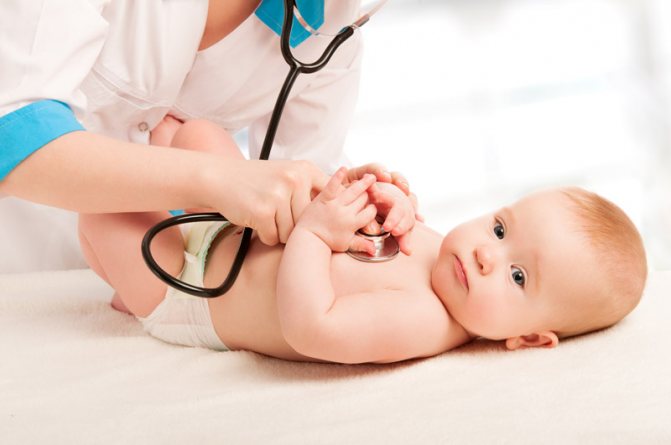
The nurse provides consultation regarding feeding regimen, breast hygiene, nutrition for the mother, etc. If the child is fed formula, then the nurse should provide consultation regarding everything related to this topic.
Newborn patronage is the observation of a child in the first month of his life by a doctor and nurse. It is provided free of charge to all children without exception. Such observation is carried out at the place of residence of the mother and child. It doesn’t matter where they are registered, a pediatric nurse or pediatrician comes to the mother’s place of residence.
Newborn patronage is carried out during the first month of the baby’s life. This is stipulated in the legislation of the Russian Federation.
All young mothers are wondering what nursing care for a newborn is, and why should a nurse or doctor come home? After all, parents can call the clinic by phone and report the child’s health status.
Important: Only through the efforts of a mother who follows a healthy lifestyle will the baby grow up healthy and strong. Good care and breastfeeding will help him quickly adapt to living conditions, build immunity, and the acquired potential will help him develop all vital functions and intelligence.
Mandatory patronage of a newborn is specified in the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated June 1, 2010. This Order was issued on the basis of Article 37.1 of the “Law of the Russian Federation on the Protection of Citizens’ Health,” adopted on July 22, 1993.
When a nurse comes for the first time to the home where a mother and her newborn live, she fills out a special form. Entries are made on the basis of the discharge summary issued by the maternity hospital and other documents.
First, the passport part is filled out: date, last name and first name of the baby, date of birth, address and place of work of the mother and father. If you were admitted to the hospital after maternity hospital, you must indicate the date and referral diagnosis.

Newborn care form
The next part of the form indicates data if there are complaints or the baby was treated in a hospital after the maternity hospital. This part of the form must be filled out by the doctor during initial patronage.
The nurse makes entries in this part of the form. She indicates whether there were threats of termination of pregnancy, illnesses of the mother, whether there were abortions, miscarriages.
Patronage form and sample filling
Next, the nurse asks about bad habits during pregnancy and makes a note on the form. Complications during childbirth and when the baby cried must be indicated. The baby's weight, head and chest circumference, and when he was latched to the breast are recorded.
Newborn care form and filling it out
The nurse should record the vaccinations given in the maternity hospital. Then the date of discharge is noted, and how the newborn period progresses.
Newborn care form
All other entries in this form are made by the doctor in the first year of the child’s life. He will note how psychomotor development proceeds, the nature of feeding, the timing and sequence of introducing complementary foods.
A young mother must remember that she must tell the nurse about all the problems that arise in the baby. If you do everything correctly and quickly, it will be easier to deal with problems. Abdominal colic, regurgitation and constant crying of the baby will disappear.
Many young parents do not understand the importance of caring for a newborn. When discharged from the maternity hospital, they ask the question: “how many times a week is patronage for a newborn carried out, and is it necessary?” But as described above, the visiting nurse will come every day for the first 10 days of the baby’s life. Then on days 14, 21 and the last visit on day 28.
How often are patronage visits carried out?
The first time the doctor comes is one of the first three days after discharge and the maternity hospital. If the baby is the first-born, was born later or earlier than expected, or has any congenital diseases, then the pediatrician examines him directly on the day of discharge.
For the first ten days, the pediatrician or visiting nurse should come every day. They can come together, separately, or on different days altogether.
During the first visit, the doctor gets acquainted with the living conditions of the baby and his parents. He also finds out the worries and problems of the family associated with the birth of a child and is interested in the mother’s well-being and mental state.
Next, the doctor finds out how the pregnancy went - whether the mother was in conservancy, whether there was toxicosis. He is interested in the course of labor, namely: the child was born naturally or by caesarean section, how the newborn felt. All this information is contained in the exchange card that the young mother receives upon discharge from the maternity hospital.
The baby's pedigree is being collected. Information is collected about the health status of parents and other close relatives. This is done in order to determine the risk of hereditary diseases.
The next stage is examining the baby. He is literally examined from head to toe - skin color, head shape, eye reaction to light, position of the ears, structure of the hard and soft palate, shape of the chest, abdomen and genitals, position of the arms and legs.
At the end of the visit, the doctor examines the mother’s breasts and gives recommendations on feeding. Attention is also paid to the hygienic care of the newborn.
At the second and subsequent visits, the doctor examines the baby again to assess development. Possible problems of the growing baby (regurgitation, colic) are discussed with the mother, and a conversation is held about the prevention of rickets.
When is patronage carried out and how many times?
The term “patronage” is literally translated from French as “patronage” (patronaqe). In medicine, it means a set of activities carried out by a doctor or nurse at the patient’s home, the tasks of which are to treat the patient, prevent him from various diseases, as well as educate him.
On the first to third day of your stay, a pediatrician will come home to the newborn.
IMPORTANT: One of the most important tasks of public medicine (and medicine in general) is raising healthy, strong children with strong immune systems. Local doctors and nurses must not only treat young patients, but also take all possible measures to prevent them from possible diseases and developmental disorders
During visits as part of prenatal care, as well as patronage for newborns, the nurse must identify and prevent unfavorable environmental factors (internal and external) that can negatively affect the health and normal development of the baby who has just been born.
IMPORTANT: A woman’s first acquaintance with the staff of a children’s clinic occurs during her pregnancy. The first time a pediatric nurse visits her immediately after registering with the antenatal clinic in order to assess the conditions under which the pregnancy will proceed and the child will be born, as well as give the pregnant woman some recommendations.
Later, in the middle of the third trimester, the nurse will come again to check that her recommendations have been followed. She will advise the expectant mother on issues of caring for the newborn, breastfeeding, and organizing the postpartum period in general.
Patronage is not only a medical intervention, it also aims to support a young mother and help her learn how to care for a newborn.
Responsibilities of a doctor
Patronage for a newborn is carried out by two people: a doctor and a nurse. During the first visit, the doctor is responsible directly for the child - he conducts an examination and assesses the general condition of the baby to ensure that it meets normal parameters.
This inspection includes:
- observation of reflexes;
- visual assessment of the condition of the skin;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- examination of the fontanelle;
- inspection of the umbilical cord cutting site.
The child’s feeding activity is also monitored.
In the case of unfavorable family genetics, it is imperative to notify the doctor about the possibility of hereditary diseases.
Diseases in children (borderline conditions)
c) wash your hands;
Medical professionals necessarily recommend that the mother of a premature baby visit specialists, and most often these are: a cardiologist, a neurologist and an orthopedist to get advice.
All necessary tests and examinations are carried out there to make a final and accurate diagnosis. If there is a need for treatment, the child is treated.
Is it possible to refuse patronage?
Every mother often needs help caring for her baby, especially if she has her first child. However, many parents do not want to receive this assistance in local clinics and prefer private medical institutions.
Yes, parents can refuse. If there is no desire and no need for help and advice from doctors, parents can write a refusal and confirm the correctness of their actions with the help of arguments.
If the refusal is accepted, the health and proper development of the newborn depends entirely on the parents.
In general, patronage of a newborn child consists of active monitoring of a baby who has come to his own home for the first time in his life.
These procedures free the new mother from constant trips to the clinic with her baby during the first month of the baby’s life, as this is dangerous for the child’s life, because his body is still vulnerable to infections.
Therefore, we hope that this article was useful, especially for those who are soon expecting a child. We told you what patronage is and why it is needed.
You should not inspire yourself with bad thoughts that with the birth of a child you will be left alone. And don’t be afraid of the baby; in any case, they will always give you a helping hand, and they will tell and show you everything.
Health to you and your kids!
2poloski.com
Algorithm for carrying out the procedure for patronage of newborns
A proven sequence of actions when caring for infants allows parents to understand exactly what and how will happen during the procedure. The atmosphere is always friendly and correct, conducive to communication and obtaining the necessary information.
What happens when caring for an infant:
- first visit to the visiting nurse and pediatrician;
- examination of the child and mother;
- filling out the necessary documents (form for the first patronage of a newborn);
- consultation with parents in question-answer mode, demonstration of proper child care techniques;
- scheduling your next visit.
The simplicity and accessibility of the procedure for patronage of newborns does not in any way detract from its effectiveness and positive impact from the process.
Thanks to patronage, even inexperienced parents are instilled with confidence in their own abilities, which helps them take care of a new person as correctly as possible, making smart decisions, fully aware of the responsibility for a new life.