Carrying a child is accompanied by significant changes in a woman’s body, so mild dizziness during pregnancy is considered normal in most cases.
Typically, vertigo occurs due to cerebral circulation disorders, anemia, and toxicosis, characteristic of pregnant women. If you rarely feel dizzy, there is no vomiting or fainting, there is no need to worry about the health of the expectant mother.
Frequent attacks accompanied by a sharp deterioration in condition and loss of consciousness require immediate medical attention. In this case, dizziness is an alarming symptom, indicating pathological processes in the body. Based on the results of the examination, appropriate treatment is prescribed taking into account pregnancy.
Why do pregnant women feel dizzy?
Most expectant mothers experience dizziness throughout pregnancy. Often this sign indicates conception, especially in those women who have not previously experienced vertigo.
Additionally, periodic attacks of nausea, weakness, drowsiness, or problems falling asleep may occur. Such symptoms are characteristic of toxicosis caused by hormonal changes.
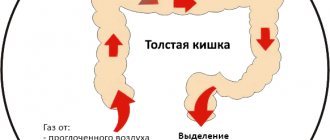
In the second and third trimester, paroxysms of dizziness are most often a consequence of deterioration of cerebral circulation. The growing uterus accounts for about a third of the total volume of circulating blood; accordingly, the nutrition of brain tissue deteriorates.
For reference. Another common cause is iron deficiency anemia, often diagnosed in pregnant women.
Thus, dizziness during pregnancy occurs in the following cases:
- changes in hormonal levels associated with bearing a child;
- lack of hemoglobin in the blood and, accordingly, oxygen starvation;
- osteochondrosis of the neck, as a result of softening of cartilage tissue;
- increased blood sugar and cholesterol levels due to dietary errors;
- redistribution of blood supply as the uterus grows;
- overwork, stress and other psycho-emotional overloads.
The listed factors cause malaise in generally healthy women, so it occurs sporadically and can be corrected with the help of diet, organizing a daily routine, and creating a calm environment.
Frequent and severe dizziness during pregnancy can be a symptom of serious illnesses.
Important. Often, intense attacks occur against the background of chronic infections, vascular or nerve diseases, and vestibular disorders. In this case, there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, the occurrence of defects and anomalies in the fetus, and premature birth.
Harbingers of childbirth
These changes are called precursors of childbirth . Precursors include such signs as:
- lowering of the abdomen;
- false contractions;
- stabilization or reduction of maternal weight;
- discharge of the mucus plug;
- sudden changes in mood and nesting instinct;
- frequent urge to urinate and defecate.
experiences 2-3 signs several weeks before giving birth . In some cases, especially among first-time mothers, there are no precursors of labor at all, or the woman simply does not recognize them.
When do the precursors of labor begin and how long do they last?
Everything is very individual, for some women 3-4 weeks before giving birth , for others just a couple of days . In fact, already at 35-36 weeks of pregnancy, the harbingers of labor can make themselves felt. A lot depends on whether a woman is giving birth for the first time. In the second and third births, the precursors are usually more obvious and are observed closer to the beginning of labor. Despite the fact that the precursors of the onset of labor are not at all necessary, it is still worth talking about them in more detail so that women are prepared for them and know about them. what this or that sign says.
Descent of the abdomen
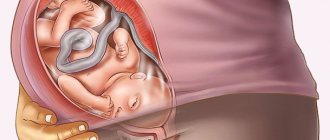
Not only is the woman preparing for childbirth, her baby is also in a hurry to be born. 10-20 days before the onset of labor, the fetus can radically change its position - move closer to the pelvis. Together with it, the fundus of the uterus, and therefore the woman’s abdomen, also descends. It moves lower and changes shape. Following this, the pressure on the stomach and diaphragm decreases. It becomes easier for a woman to breathe and eat, but it is now more difficult for her to walk and sit. Like many other precursors of childbirth, in multiparous women, lowering of the abdomen occurs later, sometimes literally on the eve of childbirth. Approximately, lowering of the abdomen, as a harbinger of labor, occurs at 37 weeks for primiparous women, and at 39-40 weeks for multiparous women.
Increased urge to urinate and defecate
The prolapsed uterus puts pressure on the bladder, causing it to be emptied more often. In addition, hormonal changes affect the intestines and the rate at which fluid is eliminated from the body. All this leads to the fact that a pregnant woman has to go to the toilet more often.
Since this phenomenon is directly related to the descent of the abdomen, this harbinger of labor in first-time mothers is usually observed at 37-38 weeks.
Stabilization or weight loss
Another harbinger of an approaching birth may be stabilization of the pregnant woman’s weight. As mentioned above, fluid is removed from a woman’s body before childbirth at a faster rate, while her appetite decreases, and sometimes she doesn’t feel like eating at all.
This leads to the fact that the pregnant woman’s weight stays at one value, and sometimes decreases by 1-2 kg. However, only those women who weigh themselves regularly can notice this.

Instability of emotional state
Sudden changes in mood can also be a harbinger of the onset of labor. The woman becomes anxious, apathy may suddenly give way to a thirst for vigorous activity.
Often during this period, a pregnant woman begins to clean the apartment, sort children's things, and in especially acute cases even starts renovations. Or, on the contrary, she tries to seclude herself, hide from everyone.
All this is called the nesting instinct. Thus, a woman instinctively prepares for the arrival of a baby; she wants not only her, but also the “nest,” that is, the apartment, to be ready for his birth.
False contractions
Many women experience the phenomenon of false or training contractions. The uterus is preparing for the birth process. For this organ, it is associated with prolonged and intense stress.
Under the influence of the hormone oxytocin, 2-3 weeks before delivery, the uterus begins to voluntarily contract from time to time. These contractions feel similar to contractions. Many women get scared and immediately begin to get ready for the maternity hospital.
It is necessary to make sure that we are talking specifically about labor, and not about the harbingers before childbirth. Doing this is both simple and difficult at the same time.
It's best to calm down and try to relax first. You can lie in a warm bath; false contractions from such a procedure usually either disappear completely or become less sensitive.
There is one more significant difference: training contractions, unlike real ones, are not regular, and moreover, the interval between them is not shortened. It is necessary to count the breaks between contractions and their duration.
Mucus plug
The surest harbinger of an early birth is, perhaps, the release of the mucus plug. This usually happens 1-2 days before labor begins. The plug may come out immediately - a dense mucous lump, brownish in color, or in the form of a spotting discharge. This harbinger of childbirth can make both primiparous and multiparous women happy at 40-41 weeks.
Causes of dizziness at different times
The main influence on the state of a pregnant woman’s body is caused by significant changes in hormonal levels.
At the beginning of pregnancy, it is necessary to prevent rejection of the fetus, in the middle - to ensure its growth and development, and in the last months - to prepare for delivery. Hormones regulate the activity of all systems and organs, so fluctuations in their concentration in the blood often manifest themselves as pathological symptoms.

In case of ailments of any kind, you must consult a doctor immediately. However, understanding the processes occurring in the body will help a woman distinguish a dangerous pathological condition from transient minor disorders.
First trimester
Dizziness during early pregnancy is most often the result of hormonal changes. Immediately after fertilization of the egg, the mechanism of its preservation is launched: the concentration of estogens sharply decreases, the amount of progesterone and prolactin hormones increases.
As a result, the menstrual cycle is interrupted and the woman’s immunity is partially suppressed (to prevent fetal rejection). Such drastic changes inevitably affect the well-being of the expectant mother, causing toxicosis, dizziness, and weakness.
Why do I get dizzy due to hormonal fluctuations? The optimal tone of the arteries of the brain is maintained through neurohumoral regulation: hormones ensure contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles of the vascular wall, maintaining stable blood pressure.
With any deviations, spasm or uncontrolled expansion of cerebral vessels occurs and, accordingly, blood pressure rises or falls. Pregnant women often experience hypotension, against the background of which the blood supply to the brain deteriorates, dizziness, visual and coordination disorders, and paresthesia appear.
Second trimester
The period from the fourth to the sixth months of gestation is the most favorable from the point of view of the well-being of the expectant mother. On the one hand, her body has already adapted to the new operating conditions, toxicosis has passed, and the state of the nervous system has stabilized.
On the other hand, the size of the uterus (and, accordingly, the abdomen) does not limit physical mobility and does not significantly affect the activity of internal organs. But even at this time, not all women manage to avoid problems with health and well-being.

During the second trimester, dizziness can occur for several reasons, the most common of which is iron deficiency anemia. To ensure the growth of the uterus, the functioning of the placenta and the development of the fetus, an additional network of blood vessels is formed in the pelvic area of the pregnant woman. As a result, the volume of circulating blood increases and the need for oxygen to nourish tissues increases.
Dizziness during pregnancy - causes, symptoms, danger
Dizziness during pregnancy is a common unpleasant condition. It causes a feeling of loss of orientation in space. Such a violation can be caused by many reasons, which the expectant mother needs to know about.
What it is
Dizziness occurs suddenly during pregnancy. The expectant mother experiences something like a push and begins to be “led” from side to side. In other cases, there may be a sensation of movement of familiar objects.
The condition reaches a critical point, and in order to stay on your feet, you have to hold on to objects.
Pathology manifests itself in 2 types.
- Lung. The expectant mother feels discomfort, which goes away on its own. To ease its course, just go out into the fresh air.
- Strong. Accompanied by nausea, loss of coordination and even loss of consciousness.
Most often, the violation is provoked by being in a stuffy room or changes in atmospheric pressure. While carrying a child, a woman feels changes in the weather, and the usual rhythm of life can cause discomfort.
Causes
A weak manifestation should not cause panic. Its reason is the anxiety of the expectant mother, as well as the changes occurring in the body. If you feel dizzy often or severely during pregnancy, then this is a reason to consult a doctor.
The causes of dizziness during pregnancy are different for each trimester. But, for each character period, one of them is a large influx of circulating blood. By the end of gestation, blood volume increases to 20%.
Dizziness during early pregnancy is normal. The expectant mother begins to feel unwell in an unventilated room, and also gets motion sickness in transport. The condition worsens in hot weather.
Dizziness during pregnancy in the second and third trimesters is also acceptable. But, if accompanied by darkening of the eyes, this is an alarming symptom. Sometimes it is triggered by an uncomfortable posture or sudden movements. Poor nutrition is also a cause. With an inadequate diet, the level of glucose in the blood decreases.
Before giving birth, this feeling may also arise. This is explained by the restructuring of the body and its preparation for childbirth. Blood rushes to the pelvic organs, causing the cerebral cortex to experience oxygen starvation.
In medical terminology, there are 3 causes of illness.
- Physiological. This reason lies precisely in sudden movements, a feeling of stuffiness in the air and travel in public transport. Often trips in transport end with an attack of vomiting.
- Non-systemic. Accompanied by increased anxiety and depression. The expectant mother is under constant stress while carrying a child and worries about the outcome of the birth.
- Systemic. This reason is the most dangerous and requires specialist consultation. Triggered by the presence of latent or indolent diseases.
In any case, it seems that dizziness during pregnancy appears for no reason.
Symptoms
Light cloudiness does not pose a health hazard. But, it is recommended to know what causes it in order to protect yourself.
The onset of an attack is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- pulsation in the ears and temples;
- vision becomes “blurry”;
- cold sweat;
- weakness;
- numbness.
If symptoms are detected, it is recommended to take a horizontal position and raise your legs up. This will allow blood to flow to the brain and make the expectant mother feel better.
When does it occur
Among the provoking factors are the following.
- Low hemoglobin. An insufficient level provokes loss of consciousness. To bring it back to normal, you need to see a doctor who can prescribe therapy.
- Toxicosis. This phenomenon is considered common. According to statistics, every second woman experiences toxicosis. As a rule, it goes away by the middle of the second trimester.
- Low blood pressure and weakness with vomiting.
- Decreased glucose levels. It is provoked by irregular eating or sweet snacks.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun. This action provokes overheating of the body, which leads to a feeling of loss in space.
- Late gestation period, when the uterus has increased in size and puts pressure on the organs.
What is the danger
Since dizziness and nausea during pregnancy are a constant companion for women, you should know whether this is dangerous for the health of the expectant mother and baby. The main danger is loss of consciousness.
It occurs suddenly, as a result of which the woman loses her balance and falls. If a fall occurs, there is a risk of harm to the fetus.
You should consult a doctor if the condition is accompanied by:
How to prevent
Its mild occurrence does not pose a health hazard. But, it is recommended to know how to prevent such ailment.
At the first signs of discomfort, a woman needs to lie down and raise her legs up. If it is not possible to take a horizontal position, then you should sit down.
While sitting, you need to lower your head as low as possible. This action will improve your well-being.
Preventing an attack is not difficult. It is enough to avoid stuffy rooms, but if this is not possible, then go out into the air more often.
Ventilating the room will also help. If a pregnant woman experiences dizziness on public transport, you should ask to give up your seat.
If a woman knows that she is susceptible to low blood pressure, then she can drink a caffeine-based drink. Since coffee is harmful for pregnant women, you should consult a gynecologist.
When and which doctor to contact
Pathology can be suspected at an early stage. However, a mild occurrence is not a reason to seek help from a specialist. For more severe cases, consultation with a therapist or neurologist is required.
Treatment consists of a thorough examination and selection of medications. Procedures must be carried out after consultation with a specialist.
Diagnosis and treatment
Since this unpleasant condition can accompany fainting, there is a risk of harm to the baby’s health. This may occur due to falling onto a hard surface and receiving a strong impact. If the phenomenon recurs regularly, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
At the appointment, the doctor will write a referral, which will include:
If a more thorough diagnosis is required, the doctor will refer you to other specialists for consultation. In any case, the treatment complex should be carried out on the recommendation of a doctor.
If the attack ends in fainting, first aid is necessary. You need to lay the woman on her back and raise her legs up. Next, loosen your clothes and sprinkle your face with water.
To alleviate the condition, you can wipe your face with a damp towel or give ammonia a sniff. After the woman regains consciousness, it is advisable for her to take valerian or Corvalol.
If fainting occurs due to skipping a meal, you should drink sweet tea and lie down. If you have vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is permissible to drink soothing herbal teas. For anemia, take measures to increase hemoglobin levels.
Treatment and prevention
Avoiding the condition is not difficult. It is enough to follow the general recommendations.
- If you are in a sitting or lying position, you should not stand up suddenly. You need to get up gradually, first lower your legs to the surface, and then, after a few seconds, rise.
- If you have to spend a long time sitting or standing, then you need to do exercises.
- Avoid crowds of people.
- Arrange ventilation of the room.
- Eat several times a day, without allowing a long break in meals.
- On the appointed day, come to the gynecologist for an appointment to monitor the progress of pregnancy.
- Avoid taking a bath.
- If you have toxicosis, have a snack in the morning, before you need to get out of bed.
- In the third trimester, do not lie on your back for a long time or in one position.
- Spend time outdoors.
Thus, dizziness during pregnancy can be caused by many factors. In order to avoid it, you need to be careful about your health. And the main thing to remember is that the future of the baby depends on the health of the mother.
The material was prepared specifically for the website kakrodit.ru, edited by doctor O.V. Klochkova. Specialty: obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category.
Source: https://kakrodit.ru/golovokruzhenie-pri-beremennosti/
Diagnostics
All ailments must be reported to the gynecologist during routine examinations or contact a therapist if attacks of dizziness occur frequently. Particularly dangerous are paroxysms accompanied by severe vomiting, disturbances of perception, and loss of consciousness.
After a physical examination and medical history, the doctor prescribes laboratory and instrumental examinations for the pregnant woman.

A study of blood composition allows us to identify changes in its formula, indicating iron deficiency anemia. Biochemical analysis provides complete information about the concentration of cholesterol, sugar, and microelements.
For reference. Instrumental diagnostics are carried out to identify or exclude cerebrovascular, neurological and other organic disorders.
Treatment
The set of therapeutic measures depends on the cause of the pathological symptoms. In addition, it is necessary to take into account all the characteristics of the body in this condition, as well as the potential harm of many medications.
If dizziness and nausea during early pregnancy are a consequence of toxicosis, it is recommended to rest more, walk, and take Cerucal to stop gagging.
Organizing a daily routine with the correct alternation of phases of work and rest, as well as a long, restful night’s sleep, helps to cope with illness. To calm the nervous system, mild sedatives of plant origin are indicated.

Based on the test results, vitamin complexes and iron supplements may be prescribed to compensate for their deficiency. A diet containing a lot of protein, fiber, vitamins is also required, and the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates and fats should be limited.
Moderate regular physical activity and daily walks help normalize blood circulation.
For reference. Specialized drug treatment is indicated only when specific pathologies that cause dizziness are identified. These include skull injuries, vestibular neuronitis, and infectious diseases.
For benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, vestibular exercises are recommended for pregnant women. In some cases, in case of severe vascular diseases or the presence of tumors, surgery is performed.
Consequences and prevention
Mild, infrequent attacks of dizziness are not dangerous for pregnant women. They usually go away after stabilization of hormonal levels, as well as under the condition of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and good nutrition.
Only systematic severe paroxysms in combination with vomiting and fainting, indicating serious pathologies, can lead to serious consequences.
For reference. You can prevent dizziness at the planning stage by undergoing a full examination and, if necessary, treating chronic pathologies.
The lifestyle of the expectant mother also influences the course of pregnancy.
Precursors of labor in multiparous women
The purpose of a woman is to give life to a new person. And if there is more than one child in the family, the parents are doubly (triplely, etc.) happy. And every time pregnancy is perceived as some kind of magic or sacrament.
A multiparous woman considers herself experienced enough to easily withstand 40 weeks of an “interesting position” and the subsequent birth . It would seem that everything is familiar and experienced to her.
But each subsequent pregnancy will never be similar to the previous one. Likewise, the precursors of labor , which occur at a more accelerated pace during the second pregnancy.
What are the warning signs of labor in multiparous women?
An experienced woman already knows what the warning signs of childbirth may be for multiparous women . This includes the release of water surrounding the fetus, cramping contractions of the muscles of the uterus, and prolapse of the abdomen.
Every pregnant woman who gave birth for the first time went through all this. And even if a significant period of time has passed between the births of children, a multiparous woman is confident that she will meet the approaching birth .
But the fact is that the harbingers of the first birth may differ significantly from those that will foreshadow subsequent labor. And the whole point is that a woman who has given birth has her organs already prepared for the birth of her second baby.
The first harbingers of labor in multiparous women
While an inexperienced pregnant woman may still be mistaken that all the precursors appear immediately before childbirth, a multiparous woman knows that the first “bells” can appear long before the baby’s desire to be born.
This article is very often read:
- 37 weeks of pregnancy - harbingers of labor
- Precursors of labor at 38 weeks of pregnancy
- 39 weeks of pregnancy harbingers of labor
- 40 weeks of pregnancy harbingers of labor
The expectant mother can feel false contractions even in the early stages of pregnancy, which confuses the firstborn. But an experienced woman may not feel these false contractions (or not pay attention to them), because her uterus seems to have no need to prepare the cervix for the upcoming process in advance.
Precursors of labor in multiparous women
Therefore, the first harbingers of labor in multiparous women include abdominal prolapse. It is also accompanied by strong pressure from the uterus on the bladder, prostate gland and rectum. But the diaphragm is relieved of pressure, and it becomes easier for mommy to breathe.
It is at this stage (about 2-3 weeks before giving birth) that a woman not only constantly wants to go to the toilet, but she may experience involuntary (usually drip) urination.
Precursors of childbirth in multiparous women. Discharge
The drooping of the abdomen already indicates that the baby has taken the desired position and is ready to be born any day now. The fetal head “targets” the exit from the cervix, exerting pressure on it with the entire body weight.
It is under such “pressure” that the cork comes off, giving way to the baby. The firstborn may not even know about this sign. And the mucous or bloody discharge that follows rejection sometimes frightens an inexperienced pregnant woman.
A knowledgeable woman may miss the exit of the traffic jam (not notice). Therefore, you should not watch the moment of its rejection, but consider the discharge that appears on your panties (or pad) as a harbinger of labor in multiparous women
If a pregnant woman is regularly seen by an obstetrician-gynecologist, the doctor will definitely notice such changes, determine the nature of the discharge and be able to say with greater accuracy about the due date of the baby’s birth.
How long do the precursors of labor last for multiparous women?
Contractions are considered to be the most important harbingers of the birth of a child Real, prenatal, muscle spasms differ from false contractions in that the dynamics of true contractions tend to increase: pain intensifies over time, pressure on the lower abdomen increases, and the time between spasms decreases.
How long can the precursors of labor last for multiparous women ? Are these periods different from those during the first pregnancy? Yes, they differ, and significantly. A nulliparous uterus will have to spend more effort to release the baby into the world. Therefore, during the first birth, the whole process takes longer.
Due to the fact that the cervix of a primigravida is not yet elastic enough, cramping warning signs can “torture” a woman for 12 hours or more. In multiparous women, this process goes faster due to the “experience” of the uterus. And the intervals between cramping pains will be much shorter - up to several seconds.
In labor practice, there is even such a thing as “rapid labor” - a woman in labor in this situation does not even have time to tune in to the very moment of the birth of the child. Therefore, those giving birth not for the first time should not sit until the last minute and count the minutes of the break between contractions. When the first false warning signs of labor appear, it is advisable for multiparas to go to the hospital.
Childbirth in multiparous women
The moment when a pregnant woman shows signs of labor is called the first phase in obstetrics. This is the longest period even for those who give life not for the first time. Contractions of the uterus are necessary so that the cervix can fully open.
But even this diameter of 10 cm is not enough for the child to freely leave the mother’s womb. The second phase of labor begins, when the uterus, continuing to contract, pushes the fetus towards exit.
Childbirth in a multiparous woman (as, in fact, in a first-born woman) will be considered completed only after the end of the third phase, i.e. after expulsion of the placenta from the uterus.
Also, watch a video on this topic: