What is epidural anesthesia?
Let's figure out what the epidural space is. This is a certain area of the spine, in the lumbar region. Exact location: inside the spinal canal, between the dura mater of the spinal cord and the outer wall. It is here that all nerve impulses coming from the pelvic organs (including the uterus) are transmitted.
Painkillers that are administered orally block the transmission of pain impulses to the brain. Thus, the woman does not feel the pain of contractions. The drug must be strictly dosed, one dose is calculated in such a way that the pregnant woman does not feel anything below the belt, but at the same time moves independently.
This anesthesia allows the woman in labor to be fully conscious. Unless there are special medical indications, the effect of epidural anesthesia is intended only for the period of cervical dilatation and contractions. The woman experiences pushing and the birth process itself without pain relief.
Epidural and spinal anesthesia: what is the difference?
Very often these two types of anesthesia are confused, because they are similar in appearance. Spinal anesthesia differs in its mechanism of action: an anesthetic is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid with a very thin needle. The localization of the injection is below the level of the spinal cord. In addition, epidural anesthesia is recognized as much safer than spinal anesthesia - the risk of complications is much lower.
Price
If there are medical indications for the procedure, it should be free. If a woman in labor independently made a decision about pain relief, the cost will range from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles, depending on the type of maternity hospital.
Epidural anesthesia: what expectant mothers need to know
There are many rumors and speculations about epidural anesthesia. To some, it seems like a relief from labor pains, while others are sure that this is a very dangerous procedure that can leave you disabled for life. What is epidural anesthesia?
Epidural anesthesia: what is it?
The spinal cord and its roots are covered with a special membrane, which we call the dura mater. A medicinal substance is injected into a small space around this membrane (epidural or peridural) through a special catheter, which leads to loss of pain and general sensitivity, as well as muscle relaxation.
Epidural anesthesia: who is it indicated for?
The purpose of any anesthesia is pain relief, and nothing more.
Epidural anesthesia can be used for local anesthesia, as an addition to general anesthesia (anesthesia), as complete anesthesia during a caesarean section, for example.
But this type of anesthesia can also be used in people suffering from back pain in the postoperative period to relieve pain. It is always carried out at the request and consent of the person, including the woman in labor.
Fear of pain or fashion?
Previously, women became pregnant and gave birth a lot, so pain during childbirth was often endured as a norm of life. Although with repeated childbirth the pain may be insignificant or even absent.
Now many women give birth to only 1-2 children, concentrating a lot of attention not so much on pregnancy, but on fears, often imposed by other people.
There is often pressure from the outside: why endure pain if you can give birth without pain.
To some extent, this is a tribute to fashion and the imposition of convenient stereotypes by the medical staff themselves - this type of pain relief is not cheap. But I will not argue that a woman in childbirth should suffer because of pain.
After all, the sensation of pain depends on the individual pain threshold: someone can endure severe pain and not complain, someone loses consciousness even from minor pain. There are no reliable methods for assessing pain in medicine.
There are women who perceive childbirth due to severe pain as an extremely negative moment in life and refuse subsequent pregnancies and childbirth due to the psycho-emotional trauma they have suffered.
Epidural anesthesia: getting rid of myths
A doctor’s duty is to provide truthful, accurate, up-to-date information on any topic requested by his patient, including a pregnant woman. When working with a pregnant woman and preparing her for childbirth, it is important to follow three stages.
- Stage 1
– discussion of the topic of pain relief during childbirth. This is usually done at the beginning of the third trimester. What is important here is not the imposition of stereotyped views, but the provision of information about all types of anesthesia used in modern obstetrics, as well as an explanation of when and what type of anesthesia can be used. - Stage 2
– depending on the type of anesthesia chosen, a consultation with an anesthesiologist can be arranged.
If, for example, a woman chooses epidural anesthesia
, the anesthesiologist must determine the presence of contraindications, as well as explain the complications of such anesthesia. - Stage 3
– adjusting the woman’s desires directly during childbirth. After all, women often do not have time to take advantage of pain relief. Many women in labor prefer to try natural childbirth without pain relief, but if the pain is severe, they can switch to epidural anesthesia if conditions allow it.
Is it true that during childbirth with epidural anesthesia a woman will not feel pain?
Epidural anesthesia is performed specifically for the purpose of pain relief. If such anesthesia is performed correctly, there should be no pain. The sensation of pain may be associated with errors in the epidural, an insufficient dose of the drug, or other reasons.
Is it true that if a doctor injects an epidural anesthesia incorrectly, you can remain disabled? And even lose the ability to walk?
There are about 50 complications of epidural anesthesia and overall the overall complication rate is 23 percent. In other words, almost every 4th woman will experience some kind of complication due to EA.
Complications from the nervous system, including loss of sensation and motor skills, also occur after epidural anesthesia. For example, paresthesia (loss of sensation) occurs in 1.6 per 1000, with permanent neuropathy in 0.04 percent of women.
Loss of sensitivity and numbness can occur not only in the legs, but also in the arms, fingers, lower back, and buttocks (up to 3 percent). For some women this can be a permanent complication.
Indeed, cases of paralysis after epidural anesthesia in women have been described in medicine. In one clinical study of 108 women with nonfatal complications, permanent paralysis was observed in 5.
Disability can also occur due to spinal arachnoiditis, and infection has nothing to do with it - it is most often a reaction to a drug or catheter (as a foreign body).
Is it true that epidural anesthesia has a negative effect on the child? And is it better to agree to a cesarean rather than an EA?
Children whose mothers use EA are more likely to experience so-called fetal distress, bradycardia (decreased heart rate), and newborns have breathing problems, in general, a lack of oxygen in the blood and tissues. However, a caesarean section will one way or another require good anesthesia, so it is not rational to carry out surgical delivery if there is no indication for this.
Epidural anesthesia: advantages
In fact, we have already touched on some of the disadvantages of epidural anesthesia.
- The biggest plus is that this type of pain relief is very effective if done correctly.
- Also, the complication rate is lower than with general anesthesia. When contraindications are taken into account and epidural anesthesia is administered professionally, the rate of serious complications is extremely low.
- Modern epidurals make it possible to control the amount of medication administered by the woman herself (for example, only when she feels contractions), which reduces the negative impact of the drug (the dose is reduced).
Epidural anesthesia: advice from a gynecologist
Epidural anesthesia is not a death sentence or an obligation. 1.
The physician should discuss alternative pain management methods with the woman, taking into account contraindications, level of complications, and the woman's wishes.
2.
If a woman nevertheless chooses epidural anesthesia, she should be familiarized with the most common types of complications and their level, and only after receiving all the answers to her questions can she sign a written consent for pain relief. 3.
Don't be afraid to ask your doctors questions.
It is their responsibility to provide you with information to make a decision. After all, it’s not just your health and your body. This is your child's health.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/acush/epiduralnaia-anesteziia-chto-nujno-znat-buduscim-mamam-5afc680148c85e85e6733deb
How do they do it?
So, how does this procedure happen:
- In order for the doctor to make the correct puncture, the woman in labor is asked to sit down and bend her back or take a horizontal position on the couch and curl up in a ball. In other words: provide maximum access to the desired area of the spine. You cannot move, even if it hurts: try not to pull away or arch your back. The sensations will be unpleasant, but short-lived. Doctors recommend turning off your consciousness for a few seconds and thinking about the birth of a healthy child - if something goes wrong during the puncture, the risk of complications is very high.
- The puncture site must be thoroughly treated with an antiseptic and disinfected.
- The patient is first injected with an anesthetic to remove the sensitivity of the skin and tissue (subcutaneous fat) at the site of the future puncture.
- The anesthesiologist makes a puncture and inserts a needle into the space of the spine. A prerequisite is that it must reach the dura mater of the spinal cord. If a woman feels that a contraction may occur during a puncture, she should immediately tell the doctor about it! The main task is not to move. It is worth paying attention to other possible symptoms: numbness of the tongue, nausea, dizziness, you cannot feel your legs or a very sore head. All these signs can be eliminated without problems only at the initial stage of the procedure
- A very thin silicone tube is guided along the needle - a special catheter that allows drugs to flow into the epidural space. This catheter will remain in place as long as it takes for the pain medication to work. Avoid sudden movements while walking to avoid accidentally knocking off the device. The catheter should be in the back of the pregnant woman during childbirth. If during insertion of the catheter a woman feels pain radiating to her leg or back, it means that the needle has caught the nerve ending - the root.
- The needle is removed and the tube is secured with adhesive tape to the back.
- You must first test the tolerance and reaction of the body using a small amount of the drug.
- When the birth process is over, the tube is removed from the young mother’s back, and the puncture site is hidden under an adhesive bandage. In this case, you will need to remain in a lying position for a long time in order to minimize the possible risks of complications.
Catheter placement
The procedure itself (puncture and installation of the catheter) takes a short amount of time - about 10 minutes. The effect of the drugs begins 20 minutes after administration. Many women are very frightened by possible manipulations with the spine, and the word “puncture” sounds very scary.
Experts rush to reassure women in labor: short-term sensations are quite tolerable, lasting only a few seconds. The catheter is not felt at all during movements.
There are 2 modes that allow you to administer drugs:
- In small doses, but continuously, at minimal intervals.
- Once. If necessary, the procedure is repeated after 2 hours. Until the dose takes effect, the woman in labor must take a lying position: the vessels in the legs dilate, and if the woman stands up suddenly, blood may flow to them and loss of consciousness may occur.
What drugs are used for epidural anesthesia?
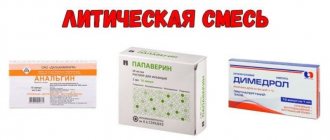
The most commonly used drugs are those that do not penetrate the placental barrier: Novocaine, Lidocaine, Bupivacaine.
Instruments for administering epidural anesthesia
Does epidural anesthesia affect the baby's health and labor?
The anesthetics that are administered do not affect the child, since they do not penetrate the placenta. Epidural anesthesia does not harm the baby's health! However, the final conclusion about the harmlessness of the procedure is ambiguous: many experts agree that there is no effect on the first stage of labor, but the efforts are less pronounced.
Injections in the delivery room: let’s lift the curtain
Without exception, all pregnant women admitted to the maternity ward are given blood tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis.
During pregnancy, you have already had to take this test at least twice, but when you enter the maternity hospital, you will have to do it again.
Even if a woman is admitted to the maternity ward from the pregnancy pathology department, the analysis will have to be repeated. Blood is drawn by the maternity ward midwife shortly after admission.
Before carrying out epidural anesthesia (which will be discussed below) and in case of bleeding, blood is taken from the mother's finger. The amount of hemoglobin, red blood cells and white blood cells, as well as blood clotting time and bleeding time are determined.
To carry out epidural anesthesia, it is important that there are no disruptions in the functioning of the blood coagulation system.
In case of bleeding, these tests are important for choosing therapy, deciding on the need for blood transfusions and blood substitutes, as well as for predicting the condition of the woman in labor.
Preparing the cervix for childbirth
One of the important factors that indicates the body’s readiness for childbirth is the condition of the cervix. Before birth, the cervix should be soft, shortened, and the cervical canal should be slightly dilated.
In cases where the waters have already been poured out, but labor has not yet occurred (premature rupture of amniotic fluid), the drug ENZAPROST
with the antispasmodic drug
NO-SHPA.
The fact is that after the rupture of amniotic fluid, no more than 12 hours should pass before the baby is born.
After all, after the integrity of the membranes is broken, the baby is no longer protected by the membranes from infection from the vagina. After the administration of SINESTROL,
regular contractions may appear.
Pain relief for childbirth
Within the walls of the maternity ward, you can often hear from women whose contractions are in full swing: “Give me some kind of injection!” We will not talk about breathing techniques, massage, or behavior during childbirth that could help you without injections. Let's talk about those cases when it finally came to injection.
Narcotic analgesics are administered intramuscularly or intravenously - drugs that interact with special receptors in the central nervous system. The main narcotic analgesic used for labor pain relief is PROMEDOL.
During childbirth PROMEDOL
is administered when the opening of the cervix is 5-6 cm (no later than 2 hours before the expected birth of the baby).
It is at this time that the drug is administered, because the narcotic analgesic penetrates through the placenta to the fetus, affecting its respiratory center, therefore, if less than two to three hours have passed between the last injection and the birth of the baby, the newborn’s breathing is depressed.
After such an injection, a woman in labor may vomit.
The degree of analgesic effect of PROMEDOL
very individual. For some, it almost completely relieves labor pain, for others it has virtually no effect. For some women, this drug has a very weak analgesic effect. This method does not work on women who have previously used drugs.
Epidural anesthesia is administered using an injection in the back.
The essence of the method is that the doctor inserts a needle into the lumbar region, the needle enters the spinal canal into the space above the hard shell of the spinal cord (epidural space) - just where the nerve roots pass that carry pain impulses from the uterus.
To make the procedure painless, before the injection, the skin at the site of the intended injection is anesthetized - for this, a local anesthetic (for example, NOVOCAINE) is injected into the skin of the lumbar region.
Then a special needle is inserted into which a thin silicone tube (catheter) is inserted; (MARCAINE, ROPIVACAINE, ULTRACAINE) is injected into it
Medication can be added through the catheter as needed.
Indications for epidural anesthesia are determined by the obstetrician together with the anesthesiologist, depending on the obstetric situation (opening of the cervix, strength of contractions, fetal position, etc.) and the needs of the woman in labor.
During epidural anesthesia, the patient is in the most bent position: lying on her stomach, bent over, or sitting, bending over - in this position, the bony outgrowths of the vertebrae are maximally separated, the space between them is sufficient for successful needle insertion.
After administration of the drug, pain relief develops within 10-20 minutes.
Pain sensations are completely blocked in all women - only a feeling of pressure may persist during contractions or during a vaginal examination. The analgesic effect can be extended up to 24-36 hours. Blocking the pain nerve roots does not affect uterine contractions - childbirth occurs as usual. The local anesthetic does not enter the mother’s blood at all and is therefore harmless to the fetus.
When the catheter is inserted, it may touch a nerve, causing a brief shooting sensation in the leg. Another thing that can accompany anesthesia is sometimes a feeling of numbness, weakness and heaviness in the legs.
During epidural anesthesia, the woman is not allowed to get out of bed due to the possibility of developing muscle weakness and the possibility of falling. It is also not recommended to lie on your back because of the possible decrease in blood pressure in this position.
To prevent this effect, the woman is injected with saline intravenously, that is, when performing epidural anesthesia, an injection in the back is accompanied by the placement of a dropper.
In order to alleviate the suffering of women in labor, intramuscular injections of NO-SHPA are also used.
Such injections are usually given at the beginning of the first stage of labor.
Since NO-SPA
is an antispasmodic drug, that is, it eliminates spasms of smooth muscles, this medicine helps to open the cervix, the basis of which is precisely these muscles.
After the medication is administered, contractions may become slightly less painful.
Stimulation of labor
Stimulation is necessary when labor is weak. There are primary and secondary weakness of labor.
With primary weakness of labor, contractions from the beginning of labor are weak and ineffective, while with secondary, the strength and duration of contractions are initially sufficient, but then throughout labor the contractions gradually weaken, become less frequent and shorter, and further dilatation of the cervix does not occur.
The diagnosis of “weak labor” is made when contractions are weak and the cervix does not dilate.
The main non-drug method to enhance labor is also a kind of injection - puncture of the amniotic sac, or amniotomy. This manipulation is carried out when the cervix is dilated by 2 cm or more. Then the woman in labor is observed for 2-3 hours.
In some patients, as a result of amniotomy, labor increases. For example, with polyhydramnios, the uterine muscles are overstretched, and the discharge of amniotic fluid helps to reduce the intrauterine volume and the beginning of correct and sufficient contraction of the uterine muscles.
If the desired effect from amniotomy is not obtained, then the use of medications is necessary.
It must be emphasized that the main method of treating weakness of labor forces is the use of uterotonics - drugs that enhance the contractile activity of the uterus.
OXYTOCIN is used for this purpose.
and prostaglandins: they are administered intravenously by drip or using special devices - infusion pumps, which ensure strictly dosed administration of drugs. A syringe is inserted into this device and, using a special tube, it is connected to a needle or catheter inserted into a vein.
The plunger of this syringe gradually pumps a predetermined amount of medication into the vein. At the same time, the condition of the fetus is monitored using a cardiac monitor1.
OXYTOCIN
does not have an adverse effect on a healthy fetus. However, in case of chronic suffering of the fetus, which often occurs in the presence of any complications of pregnancy (preeclampsia, prolonged threat of miscarriage, placental insufficiency, etc.
), administration of OXYTOCIN
may worsen the condition of the fetus.
Therefore, before starting labor stimulation, its condition is carefully assessed based on the nature of the amniotic fluid (with chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia, the water may be green) and according to the results of cardiac monitoring.
It should be noted that delaying labor in case of development of labor weakness entails serious consequences for the mother and fetus, therefore, if indicated, timely stimulation will be the key to a successful outcome of childbirth.
Medication-induced sleep-rest
If a woman enters the maternity unit with vague pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, and these pains are irregular, prolonged, but not productive, then we are talking about preliminary pain that precedes the development of regular contractions, but does not lead to the opening of the cervix.
When such pain appears, the woman gets tired, and the contractions that begin after this are often weak. To prevent weakness, the woman in labor needs to rest, especially if preliminary pain occurs in the evening and lasts all night.
To do this, the expectant mother is administered intravenously the narcotic analgesic PROMEDOL,
which causes the so-called medicinal sleep-rest.
It should be noted that during prolonged labor and when the woman in labor is tired, in order to treat the weakness of labor, medicinal sleep-rest can also be used, during which the woman restores the strength and energy resources of the uterus. After awakening, labor intensifies in some patients. Sleep comes quite quickly and lasts on average 2 hours.
Prevention of bleeding
When a woman is pushing, that is, already in the second stage of labor, at the moment of eruption of the head or immediately after the birth of the placenta, in most maternity hospitals it is customary for all women in labor to inject the drug METHYLERUMETHRINE into a vein to prevent bleeding.
This drug causes the uterus to contract, which allows the muscle fibers of the uterus to compress the vessels that rupture when the placenta is separated.
During surgery
If, for one reason or another, childbirth is carried out by cesarean section, then there is no way to do without injections. In the case of an operation under epidural anesthesia, the same manipulations are performed as for pain relief during childbirth. But the operation can also be performed under general anesthesia, in which case the anesthetic is administered intravenously.
In any case, during the operation, drugs are administered intravenously to provide complete pain relief and provide the woman with maximum comfort during the operation.
To prevent infectious complications, antibacterial drugs (antibiotics) are administered.
Since blood loss during surgery is slightly greater than during normal childbirth, special solutions are administered during surgery to replenish lost fluid.
It should be noted that all injections - both during childbirth and during a cesarean section - can be carried out by inserting a needle or (if long-term administration of medications) a catheter - a thin plastic tube - into a vein.
If there is a needle in the vein, then, despite the fact that it is fixed on the skin with a plaster, this still somewhat limits the patient’s mobility, since with inaccurate movements the needle can come out of the vein. If there is a catheter in the vein, then movements are almost unlimited.
Listed here are many, but not all, of the injections that may be needed during childbirth. We hope that you will encounter a minimum number of them. However, if you still have to deal with such manipulations, remember that they are all designed to help you and the baby.
Photo source: Shutterstock
Source: https://www.9months.ru/rodybase/724/ukoly-v-rodzale-priotkroem-zavesu
Indications for use
In what situations is epidural anesthesia needed:
- if the pregnancy is premature. With the help of epidural anesthesia during labor, the woman's pelvic floor muscles relax. This means that during childbirth the child will experience much less resistance than without the use of drugs;
- if the mother's blood pressure is much higher than necessary. With the help of anesthesia, these inflated rates can be reduced;
- if childbirth is very long and difficult;
- if there is a need for an emergency caesarean section or it is not possible to give general anesthesia. The reason for surgery may be a too large fetus or multiple pregnancy;
- improper contraction of the muscles of the uterus, which in medicine is called “discoordination of labor.” In this case, the cervix does not dilate.
In Western clinics, this procedure is often performed without medical indications - to relieve unpleasant symptoms and eliminate discomfort. But domestic medicine is more categorical on this issue.
Many women are afraid of contractions
What are the indications for epidural anesthesia?
So, let's touch on the main reasons that may be indications for the use of epidural anesthesia:
- Various kidney diseases;
- Increased blood pressure, while the use of epidural anesthesia will reduce the pressure of the woman in labor;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, in which any stress on the heart is contraindicated;
- Low pain threshold, which was already mentioned above, and, accordingly, unbearable pain during childbirth, as a result of which it happens that women even lose consciousness and then doctors have to save the life of not only the expectant mother, but also the child;
- Slow dilatation of the cervix;
- The need for a caesarean section.
In some cases, epidural anesthesia may also be necessary for postpartum procedures, such as tubal ligation.
Epidural anesthesia blocks pain in the lower part of the mother's body
Effect on the fetus
Because anesthetics do not cross the placental barrier, simply blocking nerve impulses, anesthesia is not believed to cause any harm to the fetus. The drug does not enter the blood. However, you need to take into account that during childbirth, your baby feels pain no less than the mother. He is under a lot of stress, so taking painkillers is not advisable.
The desired refusal of anesthesia is explained by the fact that pain during labor helps to produce endorphin in the body. This is a very desirable process, because the baby’s body cannot yet produce it. If the mother’s body does not need to produce the hormone, the child is left without natural pain relief - the substance does not reach him through the placenta.
Contraindications
Of course, any medical intervention in the natural process of childbirth has its contraindications. Epidural anesthesia is no exception:
- Abnormal pressure surges may occur: cranial pressure may increase or blood pressure may decrease;
- spinal deformation and, as a consequence, difficult access for catheter insertion;
- Inflammatory processes may occur at the puncture site;
- the drug should not be administered if the woman is intolerant to it;
- if there is a risk of obstetric hemorrhage;
- if the woman in labor is unconscious or has neurological or mental illness;
- vascular and heart diseases: the doctor individually considers the issue of anesthesia.
Of course, the procedure is not carried out if the woman has written a refusal.
Where is the needle inserted during anesthesia?
Allergy is the main contraindication
First of all, for pain relief during childbirth, regional anesthesia is used; this is the main method; if for some reason it cannot be used, and pain relief is necessary, then general anesthesia is already used.
To identify contraindications, our first question is about allergies: 99% of people have had their teeth treated, if there are no contraindications, then, as a rule, there are no regional anesthesia.
Contraindications for regional anesthesia:
- Patient refusal.
- Allergy to medications used.
- Infection at the injection site and severe general infections.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Severe dehydration or blood loss.
- Some heart diseases.
- Tattoo at the injection site.
Consequences and complications after epidural anesthesia during childbirth
Complications can arise if the anesthetic gets into the venous bed of the epidural space. This creates a greater risk of the drug entering the bloodstream. If, after inserting a catheter, a woman in labor feels unpleasant symptoms (numbness of the tongue, upper and lower extremities, nausea, dizziness, taste in the mouth), she should immediately inform the doctor.
Allergic reactions can often occur, so the anesthesiologist must first do a test test: inject a small amount of the drug to check the body’s reaction.
There is a risk of breathing difficulties. This may occur due to the effect of the drug on the nerve endings that go to the muscles located between the ribs.
Another problem that may arise after using an epidural is severe headache or back pain. The cause may be the process of puncture of the dura mater of the spinal cord or the entry of a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid into the epidural space.
Both headache and back pain can go away within one day, or can last for several months. In order to remove it, a medicinal method is used. As a last resort, the puncture can be repeated - inject some of the mother’s blood into the “leakage” area. This will “seal” the puncture.
A decrease in blood pressure may occur. Vivid symptoms in this case: dots before the eyes, vomiting, dizziness and nausea. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to remain in a lying position for some time after the administration of the anesthetic, do not make sudden movements, and insert an IV.
Epidural anesthesia is also dangerous due to the occurrence of hypotonicity of the bladder muscles, and as a result – problems with urination. Please note that sometimes paralysis of the lower extremities can occur - probably the most unpleasant and terrible complication after pain relief.
But don’t panic: if you follow the doctor’s recommendations and do not move during the puncture, you will easily endure both the procedure itself and childbirth.
Failed epidural anesthesia
According to medical statistics, out of 100% of cases of using epidural anesthesia, 5% end in ineffective administration of the drug (no pain relief occurs at all), and 15% result in partial delivery. This may occur due to the fact that it is not always possible to perfectly enter the epidural space.
This can happen due to the inexperience of the anesthesiologist (an extremely rare case, because inexperienced young specialists must carry out such manipulations under the supervision of experienced colleagues). Possible spinal abnormalities or the fatness (obesity) of the pregnant woman may also affect this.
Not uncommon common case: mosaic anesthesia. What is meant? This occurs when the connecting septa within the epidural space interfere with the flow and distribution of the drug.
The condition of a woman with epidural anesthesia is constantly monitored by specialists
In this case, you will have to increase the amount and concentration of the medication. The woman in labor will need to lie on the side on which the anesthesia did not work, and the doctor will make another puncture.
Theory of emotional connection between mother and child during childbirth
A huge number of women have undergone the procedure of epidural anesthesia. This happened differently for everyone, but the result was the same: their babies were safely born healthy.
The most important thing is a positive attitude.
Talk to your baby, encourage him to work, ask for his help, remember the proper breathing technique that you were taught in courses for pregnant women. Try to create a connection with your child - this will definitely help you avoid many difficulties.
Every minute of pain is accompanied by the release of the hormone of happiness – endorphin – into the blood. If a woman in labor goes through this pain on her own, she understands how happy she is when she gives birth to her baby strong and healthy. If the pain syndrome is minor, the joy of the upcoming meeting with your baby will be fully felt.
Is anesthesia needed during childbirth?
In fact, labor pain during physiological labor is quite tolerable, and there is no need to resort to pain relief. Pain is the body’s physical signals about problems, a kind of warning to a woman, and if it is drowned out, it means going against nature.
Therefore, all doctors unanimously say that a woman is well prepared for childbirth, who has consciously and responsibly approached the issues of pregnancy and the birth of a baby. goes to give birth with her husband, practically no anesthesia is required. Pain occurs due to fear and pressure on the body.
The muscles go into spasm from the release of adrenaline and you feel pain. Therefore, physical and psychoprophylactic preparation for childbirth in courses for pregnant women is very important, then you will not need anesthesia.
Pain relief is indicated in cases of: • labor disturbances (including prolonged labor); • pain of a special type (true pain associated with the pathological course of labor); • birth of a large fetus; • premature birth; • gestosis (edema, high blood pressure, protein in the urine); • surgical interventions.
Reviews from real patients
If you are worried about how your birth will go, whether you need pain relief and in what cases it is better to refuse it, go to the women's forum and look at reviews about the epidural anesthesia procedure. According to them, many women used this method of pain relief without risk to their health and the health of their baby.
You should weigh the risks before using an epidural.
It doesn’t matter what kind of birth you have: most often the whole process occurs without problems if you follow the doctor’s recommendations. Some patients agree to give birth exclusively using this type of pain relief.
Here is a review from Olga, a girl who experienced childbirth with an epidural: “I didn’t expect that the first birth would be so difficult and painful! To relieve the pain a little, the doctor advised making a puncture and injecting an anesthetic. Minor discomfort during the administration of the drug is negligible compared to the severe pain that was experienced before.”