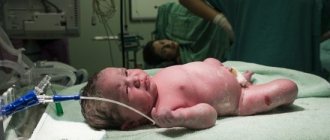
Jaundice is the most common form of hemolytic disease of newborns. Most often, jaundice in newborns develops as a result of a Rh conflict between the mother and the fetus (negative Rh in the woman and positive in the fetus), or a conflict between blood groups (first blood group in the woman and second or third in the fetus). Usually, during childbirth, the blood of mother and child mixes, antibodies to the child’s blood cells are formed in the mother’s body, these antibodies, in turn, enter the child’s blood and cause the destruction of his blood cells. The bilirubin (tissue poison) formed as a result of breakdown is excreted through the liver, but if the rate of its formation is higher than the rate of excretion, then it accumulates in the child’s blood and stains the tissues. As bilirubin intoxication increases, the child’s condition worsens: lethargy, drowsiness appear, and convulsions may occur. When bilirubin levels are high, kernicterus occurs, which damages the brain. Jaundice in newborns appears in the first few days after birth, and the earlier it appears, the more severe the hemolytic disease. Doctors consider jaundice that appears in the first 12 hours after birth to be pathological and take urgent measures to rehabilitate the newborn: drugs are prescribed that increase the detoxification function of the liver (for example, phenobarbital), phototherapy is performed - the child is placed under a lamp, under the influence of radiation which causes oxidation and decay bilirubin. Also, to slow down the adsorption of bilirubin in the intestines, cleansing enemas and activated charcoal are prescribed. In severe cases, they resort to replacement blood transfusion. Physiological jaundice in newborns usually appears on the 3rd day after birth, is not accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition of the child and goes away within two weeks without medical intervention. To prevent jaundice in newborns, the antenatal clinic identifies pregnant women at risk: those who have a history of miscarriages; abortions; blood transfusions; previous child born with hemolytic disease. They undergo blood tests several times during pregnancy to determine the titer of anti-Rhesus antibodies. In this case, the dynamics of titer changes are taken into account, and if the risk of an immune conflict is established, additional examinations are carried out - amniocentesis, ultrasound. On the first day after the birth of a child with Rh positive in an Rh negative mother, she is given an injection of immunoglobulin to prevent the synthesis of anti-Rh antibodies and to avoid immune conflict in subsequent pregnancies.
Jaundice is a common disease during which the baby's skin, as well as visible mucous membranes and the whites of the eyes, acquire a yellowish-dark tint. Why does jaundice occur in a newborn? What can this disease be fraught with and how to treat it? Later in the article we will consider all these issues in detail and give practical recommendations.
Physiological
Conjugative (physiological, neonatal) jaundice in a newborn is a very common phenomenon, from which, according to statistics, about 60-70% of infants suffer in the first days of their lives. This is due to the immaturity of the newborn’s body systems responsible for the metabolism of a substance such as bilirubin, a pigment that has a red-yellow color and is formed during the destruction of hemoglobin. Gradually accumulating in the skin, this pigment helps it acquire a yellowish tint.

With conjugation jaundice, the general condition of newborns does not undergo serious deterioration. The exception is jaundice, which is very pronounced. In such cases, newborns experience excessive drowsiness, lack of appetite, and vomiting. However, the severity of jaundice is determined not by external manifestations, but by the level of direct bilirubin in the blood.
Pathological
If jaundice in a newborn does not go away after three to four weeks, then most likely it has a pathological form. But you shouldn’t jump to conclusions and panic. You will learn a reliable diagnosis only after consulting a qualified pediatrician and carrying out all the necessary tests that will help not only establish the form of the disease, but also its type. Pathological jaundice occurs:
- Nuclear. This type of jaundice is accompanied by a high amount of indirect bilirubin in the blood, which, when entering the brain, affects its cell nuclei. The lack of effective timely treatment leads to such catastrophic consequences as delayed physical and mental development, cerebral palsy (CP), deafness, decreased vision and even blindness. In addition, the activity of the entire nervous system may be disrupted and a serious neurological defect may occur.
- Hemolytic. This type occurs when mother and newborn are incompatible by blood type and/or Rh factor. Hemolytic jaundice is accompanied by massive destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis). It often occurs if the mother has blood group I, and her child has blood group II (less often III). Doctors say that with each subsequent pregnancy, the risk of this type of complication increases, which makes abortion very dangerous, especially for women with a negative Rh factor.

Why is activated carbon used for an infant?
As your baby grows and develops inside your womb, its intestinal environment is considered completely sterile. After birth, it is populated by diverse microorganisms characteristic of the intestinal environment of a mature adult.
However, not all of them are equally beneficial - some bacteria are opportunistic, and not only do not contribute to the favorable functioning of the convoluted organ, but also seriously disrupt it. It is not for nothing that infants so often suffer from stool disorders, including constipation and diarrhea, as well as intestinal colic and other uncomfortable and painful phenomena.
Childhood dysbiosis often develops if a newborn is put to the mother's breast late, or is transferred to artificial feeding early. This phenomenon is also more than likely if antibiotic therapy took place after birth. Acute intestinal infections also provoke a change from “beneficial” flora to “harmful” flora.
The use of activated carbon in this case is quite advisable. The natural adsorbent absorbs gases and waste products of pathogenic microorganisms, significantly making life easier for the baby. However, this remark is worth especially emphasizing - it only makes life easier, but does not cure it completely. Alas, in order for your child to get rid of the cause of the disorder, stopping its symptoms will clearly not be enough.
In order for the child’s body to be completely freed from toxic substances, it is important to carry out adequate targeted therapy, which should be agreed upon with the local pediatrician. By the way, using charcoal too often is also not recommended, although many new parents break this rule, considering the “harmless” drug to be something of a panacea for all ills.
Causes of jaundice in newborns
The occurrence of transient conjugation jaundice in most healthy newborns in the first days of life is associated with the following factors:
- The content of a special type of hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the fetus - fetal (hemoglobin F), the gradual destruction of these red blood cells after the birth of the child.
- Deficiency of a special protein in newborns, which ensures the transport of bilirubin through the cell membranes of the liver.
- Excessive accumulation of bilirubin, resulting from the defective functioning of the immature enzymatic systems of the newborn’s liver, which are involved in the conversion of indirect bilirubin into direct bilirubin.
- Low excretory capacity of the liver in newborns, which affects the rate of excretion of bilirubin from the body.
As for pathological jaundice in newborns, the main cause of its occurrence generally does not differ from those listed above. The occurrence of this disease is caused by excess bilirubin in the child’s blood, which happens when there are no enzymes in the baby’s body that supply this pigment to the liver. But in this case, the absence of such enzymes is not associated with a delay in the formation of liver systems, but with massive hemorrhages on the skin and head of the child, prematurity or very pronounced jaundice in previous children, if any.

How to give activated carbon to a baby: dosage regimens and analogues
Infants have health problems that require the use of sorbents, and then parents are faced with the question of how to give activated charcoal to their infants. Information about the medicine
Coal is produced in flat, round, slightly rough tablets. Their color is black, they have a chamfer and a risk. The medication is produced by several companies, so it may have a different composition of indifferent components.
Activated carbon is an enterosorbent and polyvalent physicochemical antidote, which binds harmful substances and allergens on its surface and removes them from the body.
It prevents the absorption of medications from the digestive tract, including antimicrobial agents, salts of heavy metals, drugs, microorganisms and their waste products, gases, plant and animal toxic compounds, phenol-containing substances, and hydrocyanic acid.
Coal binds metabolic products on its surface, which can cause poisoning and the development of pathological conditions in the body. These are substances such as cholesterol, urea, bilirubin.
It binds alkalis and acids poorly: iron salts and hydrocyanic acid, monoethylene glycol, karbofos, methyl alcohol. It can be used as a sorbent during hemoperfusion, a medical procedure during which the blood is cleansed of poisons and toxins.
The drug does not irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Once in the body, it is not absorbed into the bloodstream and is completely evacuated from the digestive tract within a day.
Is it possible to give activated carbon to infants?
Is it possible for an infant to use activated charcoal? You need to check in the annotation that comes with the medication. The age at which sorbent can be given to children depends on the manufacturer. For example, a drug from the Vifitech company can be used by infants from birth, while a drug from the Usolye-Sibirsky Chemical Pharmaceutical Plant is allowed only for patients over 3 years of age.
Application area
Activated carbon can be given to a baby if he or she has the following health problems:
- Poisoning caused by substances that form in the body or enter it from the outside.
- Acute infections of the digestive tract caused by consumption of foods contaminated with pathogenic microflora. Coal can be given to infants in combination with other medications for dysentery and salmonellosis.
- Intoxication with drugs, including those that affect the central nervous system, drugs, heavy metal compounds, alkaloids and other poisons.
- Pathologies of the digestive system, in which dyspeptic disorders and increased gas formation are observed; You can give activated charcoal for colic in a baby.
- The sorbent helps with increased levels in the blood of nitrogen-containing products that are formed during the breakdown of protein. This condition is observed against the background of renal failure.
- The drug helps with high levels of bilirubin in the blood, so you can give activated charcoal for jaundice in newborns and viral liver inflammation.
- Allergies triggered by medications or food.
It is recommended to give the adsorbent to the child to remove gas bubbles before diagnostic tests such as ultrasound and radiography. This allows for a clearer image and a more accurate diagnosis.
Contraindications
Activated carbon for newborns is contraindicated if the following pathologies are identified:
- allergy to active and inactive components of the drug;
- erosive and ulcerative damage to the gastrointestinal tract, including gastric and duodenal ulcers, UC;
- bleeding from the digestive organs;
- hypotonicity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Activated carbon is prohibited for infants if they are simultaneously prescribed antitoxic medications, the effect of which begins after their absorption. These are drugs such as Methionine.
If a child is diagnosed with diabetes, or a low-carbohydrate diet is recommended for an infant, then the sorbent should be given to him with caution.
Rules and regimens for taking activated carbon for infants
Activated carbon for babies must first be crushed into powder and mixed with water. Give the resulting suspension to the baby 1-2 hours before or after feeding.
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor for each child individually, depending on the diagnosis:
- For pathologies in the acute stage, the duration of therapy can vary from 3 to 5 days.
- Newborns with allergies and chronic diseases should drink activated carbon for up to 2 weeks. After consultation with a doctor, a second course of therapy is possible after a 14-day break.
- For colic, activated charcoal can be given to a baby for up to 1 week.
During treatment, parents should consider the following:
- Despite the fact that to date there have been no cases of overdose of activated carbon, it should not be given to infants in dosages exceeding those recommended by the instructions.
- The sorbent reduces the adsorption and effectiveness of medications that are taken simultaneously. The time interval between taking the sorbent and other medications should be 2 hours.
- If you give a sorbent during feeding, it binds the contents of the gastrointestinal tract on its surface, and the therapeutic effect of activated carbon decreases.
- If the course of therapy lasts more than 2 weeks, then the baby should be given multivitamins and calcium-containing medications.
- Parents of diabetic children or babies prescribed a low-carbohydrate diet should take into account that 1 tablet contains 0.004 XE.
- The adsorbent must be stored in a dry place, at temperatures up to 25 degrees, separately from compounds that emit gases or vapors into the atmosphere, since otherwise the drug loses its sorption abilities.
- You should not give your baby medication that has expired.
The shelf life of the adsorbent should be checked on the packaging, since it may vary depending on the manufacturer. For example, tablets produced at the Usolye-Sibirsky Chemical-Pharmaceutical Plant are good for 36 months, but the drug from Lumi LLC can be stored for only 2 years.
Adverse reactions to charcoal in children
Taking an adsorbent can cause the following undesirable effects in an infant:
Coal analogues for infants
There are drugs on sale that are substitutes for activated carbon in the therapeutic group:
- Medicines based on simethicone. You can replace activated charcoal in a newborn with colic with Espumisan in drops or suspension, or with Sab Simplex. These medications can be given to infants for as long as required. They are allowed from birth. Children over 28 days old with colic are allowed Bobotik.
- Baby Calm. This is a dietary supplement that is recommended to be given to infants when there is an accumulation of gases in the intestines. The effect of the dietary supplement is explained by mint, fennel and dill oil.
- Filtrum-STI. The drug is available in tablets that contain lignin as the main component. The medicine is used in the same cases as activated carbon. For infants, a single dose of Filtrum-STI is ½ tablet. The frequency of administration is 3 or 4 times a day.
Whether activated carbon can be used for infants, or whether it is better to replace it with an analogue, the doctor must decide, since each medication has its own characteristics.
Despite its over-the-counter availability, the sorbent should not be given to infants without a doctor’s recommendation. The doctor will tell you whether newborns can take charcoal and select a treatment regimen. You should not try to independently diagnose a baby, since green diarrhea is not always associated with pathology; perhaps the mother simply ate something; she needs to adjust her diet, and everything will return to normal for the baby.
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first symptoms, consult a doctor! Self-medication is dangerous to health!
Source: https://otravilsya.com/deti/aktivirovannyy-ugol-dlya-grudnichka/
Symptoms of jaundice in newborns
Conjugation jaundice in newborns usually occurs on the second to fourth days after birth. Its main symptom is that the baby acquires a yellow-orange skin color. As for the general condition of the child, the concentration of hemoglobin in his blood, as well as the color of urine and feces, these indicators remain normal. Physiological jaundice disappears on average in three to four weeks, but the extinction of the disease, i.e. The disappearance of a noticeable yellow tint to the skin should begin by the end of the first week of the child's life.
Unlike physiological jaundice, which has a pathological form, is expressed already in the first 24 hours after the birth of a baby and lasts more than three weeks. During this period, in addition to the characteristic yellow color, the newborn baby has a high level of bilirubin in the blood. Also, the distinctive signs of pathological jaundice include:
- Refusal of the newborn to feed, suppression of the sucking reflex, lethargy, excessive drowsiness and lethargy of the baby. Such obvious symptoms as a monotonous cry of a baby and muscle hypertonicity - a violation of the muscle tone of the body, expressed in muscle overstrain - can also indicate the pathological nature of jaundice in a newborn.
- An orange-yellow tint of the skin and visible mucous membranes on the child’s body that does not change for four or more weeks, discoloration of his feces, darkening of the urine. These symptoms can be noticed directly by the parents of the newborn, spending time with him outside the maternity hospital and hospital. However, if all the above-mentioned signs of a pathological disease were not detected in time, much more serious symptoms may appear - convulsions, bradycardia, high-pitched screams, stupor and even coma.

Carbon tablets in the treatment of newborns
The drug is one of the available adsorbents; it well absorbs toxic substances that enter the body or are released during the digestion of food. Activated carbon is prescribed to infants for a number of diseases. This medication is considered safe as it rarely causes side effects. Thanks to black powder, all harmful substances are quickly removed from the body, thereby strengthening the immune system.

The pharmaceutical industry produces activated carbon in four dosage forms - tablets, capsules, powder and black paste. The attending physician usually selects the form of the drug based on the age of the young patient. Infants are most often prescribed powder, which is first diluted with water.
If there is no charcoal powder in the pharmacy, then it doesn’t matter. It is quite possible to prepare it yourself. To do this, roll a rolling pin over the blister of tablets and the medicine for a child under 2 years of age is ready. It is diluted in a small volume of water to a suspension, and then given to a small child.
This adsorbent successfully treats diarrhea, which is caused by intestinal infections and many poisonings. The substance consists of many pores that attract toxic substances, like a sponge, and prevent them from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
It must be remembered that activated carbon is not able to help with poisoning by concentrated acid or alkali.
Activated charcoal quickly eliminates cutting pain in the tummy and bloating, and also reduces colic in an infant in a matter of minutes. In case of dysbacteriosis, doctors try not to prescribe this sorbent to children, since it is not characterized by selective activity and removes both useful and harmful substances from the body. In this case, it would be more appropriate to prescribe enterosgel and probiotics.
Norm of bilirubin in infants
Bilirubin is a substance formed during the breakdown of red blood cells. While in the mother's womb, the child's body contains a very large percentage of red blood cells that carry hemoglobin. But after birth, the newborn no longer needs such a volume of them, and therefore they are subject to destruction. The normal bilirubin level in infants is distributed as follows:
- A newly born baby – no more than 51-60 µmol/l.
- Child from 3 to 7 days - no higher than 205 µmol/l (in premature babies, the bilirubin level should not exceed 170 µmol/l).
- Children from 2 to 3 weeks – 8.5-20.5 µmol/l.

How to give activated carbon to children under one year old?
Almost all parents are faced with digestive problems in their child. Is it possible to give activated carbon to children under one year of age for poisoning and other gastrointestinal pathologies? This is one of the safest drugs, which, however, has nuances in the treatment of newborns and will only be effective if used correctly.
Is it possible to give activated carbon to a baby?
Activated carbon is an adsorbent that absorbs toxins that enter the body. Its main advantage is a minimal set of adverse reactions and, as a result, safety of use in all age groups. The main advantages of the drug:
- Multiple forms: powder, tablets, granules or paste. For small children, it is more convenient to use a powder that quickly dissolves in water, forming a suspension.
- Versatility: the drug is used for jaundice, poisoning with abdominal pain and high temperature, stool disorders and increased gas formation, colic and allergies.
- It has a low price, is always available for sale, and does not require a prescription.
The drug can be given to infants only on the recommendation of a pediatrician after examination and subject to the prescribed dosage. Unfortunately, activated carbon is not selective only for toxins or harmful microbes - this is the main drawback of the product when treating infants.
While in the womb, the baby's intestines are sterile, and only after the baby is born does it begin to fill with beneficial bacteria. Immediately after birth, it is recommended to place the baby on the mother’s breast as early as possible: colostrum (first milk) activates the proliferation of beneficial microflora in the gastrointestinal tract.
The intestine of a newborn is the most vulnerable place at the beginning of life. Therefore, colic, increased gas production, bloating, and dysbacteriosis are frequent companions of the first months.
Another cause of the disorder is the entry into the body of various intestinal infections and pathogenic microbes.
From the very beginning, the baby learns about the world, constantly putting his hands and toys into his mouth, increasing the risk of introducing dangerous bacteria.
Activated carbon for newborns will help absorb harmful substances and remove them out. However, along with toxins, coal will bind and remove beneficial microflora .
An adult, unlike a baby, will not feel the negative effects of enterosorbent, having restored the microflora naturally from food.
That is why, especially in the first months of life, charcoal is prescribed infrequently , and if it is used, it must be used with pro- and prebiotics in order to minimize the negative effect.
If an artificial formula is used to feed the child or the parents have already switched to complementary feeding, this stimulates the production of enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the stressful effect of activated carbon on the baby’s microflora will not be so significant.
What ailments does activated carbon help with?
In addition to the problems mentioned above (mild poisoning, jaundice), activated charcoal for newborns is given for various allergic reactions .
For example, atopic dermatitis can occur due to a change in formula, or a change in the mother's diet, or due to the characteristics of the body (for example, due to an allergy to cow's milk protein).
In this case, the sorbent will help bind and get rid of toxins.
Almost every baby after birth develops physiological jaundice, which in most cases goes away on its own. But if the bilirubin level is much higher than normal, then a sorbent is prescribed as an addition to the main therapy. If the disease is not treated in time, high levels of bilirubin can adversely affect brain cells.
There are cases when activated carbon is completely useless - these are various types of chemical poisoning.
How to give activated charcoal to a baby?
Dosage and application features:
- the universal formula “1 tablet (0.25 g) per 10 kilograms of weight” is relevant for both children and adults;
- consumption 2 hours before or 2 hours after meals, so that the newborn’s body has time to absorb beneficial substances from breast milk or complementary foods;
- application 3 times a day.
It is recommended that infants be given activated carbon in the form of a suspension (the tablet is kneaded and dissolved in water to the consistency of a cream). The mixture should be homogeneous, without the inclusion of large crystals. You can administer the composition to your baby through a syringe without a needle or give it from a spoon. After swallowing, give 20-30 ml of clean water.
The treatment period for colic is 4 days, dermatitis and jaundice is about a week. Longer exposure to the sorbent is more likely to harm the baby’s body.
Do not self-medicate . Any therapy for a child is used as prescribed by a doctor.
Symptoms associated with discomfort in the digestive system can be the result of serious pathologies, so a pediatrician should diagnose the disease.
He will also give recommendations on the use of charcoal to treat a child, taking into account age, supplementing therapy with probiotic drugs if necessary.
Source: https://esliotravilsya.ru/pomosh/kak-davat-aktivirovannyj-ugol-detyam-do-goda
How dangerous is jaundice and when does it go away?
Conjugation jaundice, which resolves without any complications two to three weeks after the baby is born, does not entail any serious consequences that would affect the vital functions of the newborn’s body. If, while in the maternity hospital, doctors determine that the baby has jaundice, but he is not capricious and does not refuse breastfeeding, then there is no reason to worry.
As for pathological jaundice, in particular nuclear and hemolytic, these diseases pose a much greater danger. The fact is that both of these types of jaundice do not allow bilirubin to be excreted from the body, thereby facilitating its penetration into the blood and further effects on all vital organs. Because of this, all newborns who have suffered pathological jaundice visit a neurologist, orthopedist and ophthalmologist monthly throughout the year. In addition, they are given a medical exemption from vaccinations for one year.

Is it necessary to treat physiological jaundice?
The translation of the article “Jaundice in breastfed newborns”, Lawrence M. Gartner, MD, Kwang-sun Lee, MD, talks about various studies of children on breastfeeding and artificial comparison, and the effect of breastfeeding on the course of jaundice. These studies revealed that frequent breastfeeding (more than 8-12 times a day) helps to heal the baby.
“Increasing the frequency of breastfeeding from 6 to 12 times per day during each of the first 3 days of life was associated with lower serum bilirubin concentrations measured on the third day of life.”
“At the same time, with an average interval between breastfeedings of 4 hours during the first 3 days of life, the average serum bilirubin on the third day of life was twice the value of serum bilirubin in bottle-fed children.”
That is, against the background of rare breastfeeding, a complication occurs, which is called breastfeeding jaundice - it is solved by establishing guards. Moreover, the article states that medical staff must monitor the correctness of organized breastfeeding. Much to my regret, this is rare in our maternity hospitals. And even in some parts of our country, the idea of supplementing babies with water to prevent dehydration is still preserved.
Meanwhile, “when breastfed infants were supplemented with water or glucose water, serum bilirubin concentrations became higher than in infants receiving breast milk.”
And the World Health Organization talks about the need for exclusive breastfeeding up to 6 months, for a minute.
The concept of a protracted course of the disease due to mother's milk is widespread. So.
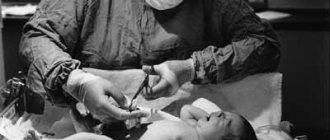
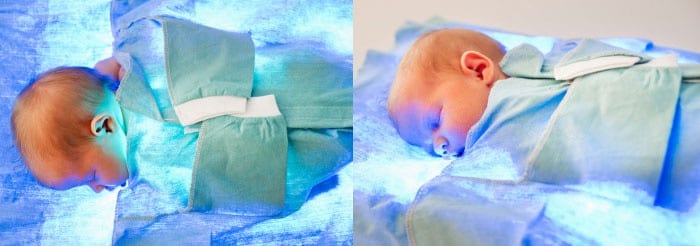
Phototherapy
One of the most common and effective ways to treat jaundice in newborns is phototherapy. This therapy involves irradiating the baby with ultraviolet rays, the effect of which makes toxic bilirubin a harmless substance soluble in water. The phototherapy procedure in the hospital is carried out according to the following scheme:
- A protective bandage is put on the newborn's eyes.
- The baby is placed under special lamps.
- The doctor clearly regulates the duration of the procedure to prevent the formation of burns, overheating or dehydration of the newborn.
How to properly give adsorbent to a newborn
Treatment of young children with activated carbon has its own characteristics. First of all, it is very important to properly prepare and give the medicine to your baby:
- If there is no ready-made coal powder, then grind the tablets well. The resulting mass should not contain large granules, as the baby may choke
. - The resulting powder is diluted with a small volume of boiled water to the consistency of sour cream.
- The resulting mixture is given to the infant from a teaspoon or using a disposable syringe with the needle removed.
- The baby must be given 50 ml of water to drink the adsorbent, so the medicine will get into the stomach faster.
- The daily dose of the drug is divided into 2-3 doses and given at regular intervals.
The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician, but usually treatment ranges from 2 to 5 days
. Longer treatment is undesirable, as it can lead to vitamin deficiency in the baby.
If the baby has a tendency to constipation, then it is better to give preference to another adsorbent.
Treatment at home
Often, jaundice in newborns can appear after mother and baby are discharged from the hospital. In such cases, young parents can independently carry out all the necessary procedures to treat the baby. Daylight can completely replace a medical ultraviolet lamp. However, direct sunlight should be avoided on the delicate skin of the newborn in order to avoid the formation of burns.

The nuances of taking activated carbon in an infant
Giving an infant activated charcoal too often is a real crime against his health on your part. Even when treating adults, it is recommended to maintain adequate dosages and not overuse such “safe” therapy. And all because this adsorbent, in addition to toxins and other harmful substances, actively removes vitamins, trace elements and minerals from the body. And if an adult can still replenish them naturally or artificially, then the baby needs them especially urgently, despite exactly how he eats.
In this regard, it is easier for “artificial” formulas - special milk formulas are quite fatty, dense and nutritious, they contain micronutrients in high concentrations.
But mother's milk may not be so enriched with valuable elements.
What can we say about complementary foods, if any. Please note that modern products, even if they are considered the healthiest, do not contain vitamins and minerals in their “pristine” form.
It is often treated with chemicals and several other compounds that strip it of its true nutritional value.
In medical practice, charcoal is prescribed to children in fairly rare cases. Pediatricians usually advise young parents to use probiotics and prebiotics to improve the health of the baby. But in general, this well-known medication is quite capable of helping the baby eliminate flatulence, colic and bloating when these symptoms cause him concern. If we talk about probiotics and prebiotics, the former stimulate the growth of their own beneficial flora in the baby’s intestines, and the latter already contain live beneficial lactobacilli and bifidobacteria.
Pharmaceutical drugs for treatment
Often, jaundice in a newborn goes away on its own, but in some cases when complications arise, it requires increased attention from the treating doctor and young parents. Sometimes phototherapy alone is not enough and you have to resort to the use of medications. The most effective medicines include hepel, ursofalk, ursosan, hofitol, and activated carbon.
The composition of this drug contains the following components of plant origin:
- Great celandine.
- Thistle.
- Nutmeg.
- Cinchona.
- Moss club-shaped.
- White hellebore.
- Bitter gourd.
- White phosphorus.
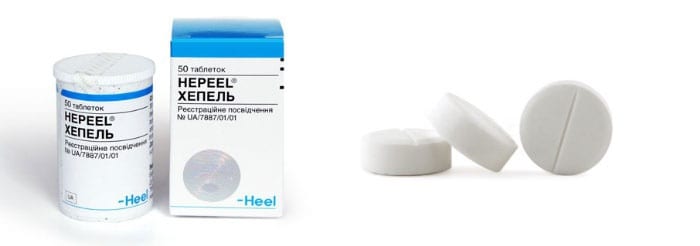
Hepel is a homeopathic remedy that is designed to improve the functioning of the gallbladder and liver. It is indicated for use to achieve the following goals:
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
- Removing toxins and poisons from the newborn’s body.
- Normalization of newborn stool.
- Activation of bile excretion.
As for the dosage of a drug such as hepel, when treating jaundice in infants, children should be given 1/4 of a tablet, first grinding it to a powder and diluting it with breast milk/formula. Due to the fact that the newborn is not yet able to take the medicine from a spoon, the mixed medicine is dripped onto the oral mucosa two to three times a day, an hour after meals or half an hour before meals.
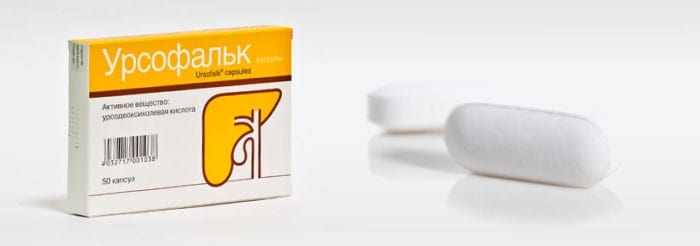
The active ingredient of this drug is ursodeoxycholic acid, which has a pronounced immunomodulatory, choleretic, cholelithiasis and hypocholesterolemic effect. According to the instructions for Ursofalk, the recommended dose for newborns is up to 40 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day. The list of indications for use of this product includes:
- Toxic damage to the liver and spleen of newborns.
- Hepatitis of various origins.
- Biliary dyskinesia.
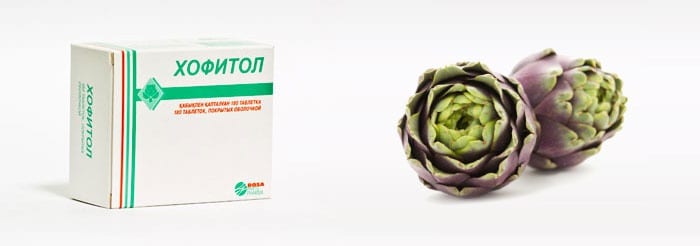
Hofitol for newborns is a herbal medicine, the composition of which consists of an extract of field artichoke leaves. The dose required to take the drug is always calculated by the attending physician. Newborn babies are given 5-10 drops of hophytol three times a day on an empty stomach, which were previously diluted in 5 ml of water. Indications for the use of this medicinal drug include:
- Constipation caused by gallbladder diseases.
- Normalization of metabolic processes in the body of a newborn.
Activated carbon is an inexpensive product that helps remove pathogenic flora from the body and causes virtually no side effects. The required dose of coal is calculated taking into account the weight of the baby. Newborns weighing less than 3 kg should take no more than 1/4 tablet at a time. And children whose weight is 3-5 kg are given 1/3 of the tablet.
The list of indications for the use of activated carbon includes:
- Atopic dermatitis and colic.
- Intestinal dysbiosis in a newborn, accompanied by bloating and diarrhea.
- Prolonged jaundice.

The comparative cost of the above drugs, which are prescribed by experienced pediatricians when jaundice occurs, is as follows:
- Hepel – 240-270 rub.
- Ursofalk - from 205 to 2200 rubles.
- Chofitol – 275-630 rub.
- Activated carbon – 6-10 rub.
Allergy treatment
Activated carbon can also help with a number of allergic diseases. This sorbent successfully treats the following conditions:
- atopic dermatitis;
- bronchial asthma triggered by allergens;
- allergic rhinitis;
- conjunctivitis of allergic origin.
In addition, the sorbent is used in the recovery period, after treating allergies of various origins.
Coal is most active in case of an allergic reaction to certain foods . In this case, the intestines are unable to completely remove all waste products from the body; they accumulate, which is manifested by a skin rash.
Activated carbon is a universal sorbent that is found in almost every home medicine cabinet. This drug has almost no contraindications or side effects, so it is allowed even for newborns.
Activated carbon has long been considered the safest and most effective remedy that is taken during various types of poisoning - poisoning with alcohol, drugs or chemicals.
The drug is prescribed to adults and children; can it be used for infants?