How to determine that a child has a spasm in the abdomen: symptoms of a spasm of the stomach, intestines
The main sign of spasm of the stomach and intestines is pain. During a spasm, it appears suddenly, its intensity may increase. An attack of pain can be triggered by active movements, running, jumping, or eating. Its most common location is the upper abdomen, although pain may also be present in other parts of the intestine.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal muscle tension.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach and intestines.
- Vomit.
- Weakness, increased fatigue.
- Lack of stool and gas production.
- Bloating.
- Temperature increase.
If a child develops diarrhea during a spasm, it can bring temporary relief, although the pain remains. The consistency of stool should be uniform, without inclusions or foreign impurities. The appearance of mucus and fat particles in them is a sign of impaired digestion of food.
Clinical picture
As a rule, colic occurs and gets worse suddenly. Attacks become more frequent after eating, physical activity, or running. Abdominal pain syndrome manifests itself as pain.
Irritation of nerve fibers belonging to the abdominal cavity provokes the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- headache;
- flatulence and bloating;
- constipation;
- high blood pressure.
Against the background of a spasm, diarrhea may begin, which will bring relief. In this case, the nagging pain syndrome, as a rule, persists for some time.
According to the recommendations of the pediatrician Komarovsky, it is necessary to pay attention to the child’s stool - its color, consistency, presence or absence of impurities. If there are mucous and fatty compounds in the stool, the cause of cramps is most likely due to improper digestion of food products. This disorder causes discomfort, lack of appetite and poor motor activity.
Colic is accompanied by the following clinical picture: severe pain, severe tension in the abdominal muscles, diarrhea. The nature of colic is periodic and short-term. In the case of intestinal colic, body temperature may remain within normal limits if the cause of the condition is not an intestinal infection.
Colic and abdominal cramps in a child may accompany the course or exacerbation of diseases such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, pathologies of the pancreas or liver. With such ailments, food is not fully digested. Residues of food products penetrate into the intestines, which provokes severe painful spasms.
Similar symptoms are often observed in children with cholera, salmonellosis and typhoid fever, as well as dysentery. These ailments have a detrimental effect on the motor function of the organ. One of the most common causes of pain is helminthic infestation. Parasites irritate the nerve endings, which causes colic and intestinal obstruction. Not only children experience spasms; spasmodic pain is also not uncommon in adults.
Diagnosis of diseases associated with abdominal cramps in a child
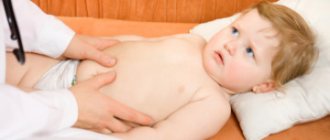
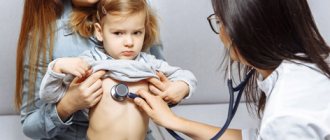
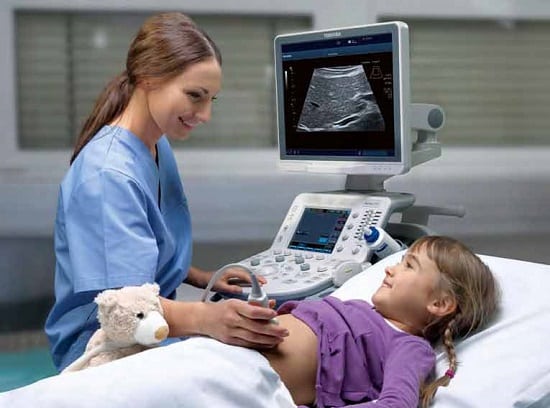
To determine the cause of spasms in a small child, you should contact a pediatrician, pediatric surgeon, gastroenterologist, or neurologist. The doctor, with the help of the parents, will collect anamnesis, conduct a visual examination, and palpate the abdomen in the projection of the stomach and intestines.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- Bacterial culture of stool.
- Fecal analysis for helminths.
- Coprogram.
- Radiography.
- FEGDS.
The doctor analyzes the examination results and prescribes treatment accordingly.
Why does abdominal spasm occur in a child and how to treat it: causes and treatment
At 2-3 years old, a child can already show the location of the pain, which facilitates the diagnosis of painful sensations. By this age, the child’s intestines and stomach are mostly formed and have sufficient functionality.
- ARVI, influenza, rotavirus infection . In addition to spasms, symptoms such as hyperthermia, rhinitis, weakness, and headache may occur.
- Umbilical hernia . Additionally, acute pain is felt in the navel area, nausea and vomiting appear, the navel stands out above the surface of the abdomen and becomes swollen.
- Constipation . Diagnosed by a long break between bowel movements.
- Gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by incomplete digestion of food.
- Food poisoning . Additional symptoms are diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, pale skin, cold sweat.
- Helminthiasis . When infected with worms, the baby's tummy swells from excessive gas formation, pain appears in the form of acute attacks, and sometimes there is itching in the anal area. Additionally, underweight may be observed with excellent appetite.
- Stress, nervous shock . Appears with severe fear, emotional shock, in the form of a kind of protection from unwanted actions. This is not a simulation, but actual pain.
- Acute intestinal obstruction . Caused by blockage of the intestinal ducts, it causes intoxication of the body by the decomposition products of feces. Nausea and vomiting do not alleviate the child's condition. The pain may stop due to muscle fatigue, but most often peritonitis begins.
- Violation of the usual diet.
- Binge eating.
- Poisoning with poisons, mushrooms.
What to do if a child has abdominal cramps: diagnosis and treatment
Abdominal pain quite often appears in children 2-3 years old for no apparent reason. If it is in the nature of spasms, children experience extremely negative sensations. It is important to know the probable cause of pain of this nature in order to alleviate the condition of a small child and not miss the onset of a serious pathology.
How to determine that a child has a spasm in the abdomen: symptoms of a spasm of the stomach, intestines
The main sign of spasm of the stomach and intestines is pain. During a spasm, it appears suddenly, its intensity may increase. An attack of pain can be triggered by active movements, running, jumping, or eating. Its most common location is the upper abdomen, although pain may also be present in other parts of the intestine.
In addition to pain, a child may experience the following symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal muscle tension.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach and intestines.
- Vomit.
- Weakness, increased fatigue.
- Lack of stool and gas production.
- Bloating.
- Temperature increase.
If a child develops diarrhea during a spasm, it can bring temporary relief, although the pain remains. The consistency of stool should be uniform, without inclusions or foreign impurities. The appearance of mucus and fat particles in them is a sign of impaired digestion of food.
Diagnosis of diseases associated with abdominal cramps in a child
To determine the cause of spasms in a small child, you should contact a pediatrician, pediatric surgeon, gastroenterologist, or neurologist. The doctor, with the help of the parents, will collect anamnesis, conduct a visual examination, and palpate the abdomen in the projection of the stomach and intestines.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following examinations are carried out:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- Bacterial culture of stool.
- Fecal analysis for helminths.
- Coprogram.
- Radiography.
- FEGDS.
The doctor analyzes the examination results and prescribes treatment accordingly.
Why does abdominal spasm occur in a child and how to treat it: causes and treatment
At 2-3 years old, a child can already show the location of the pain, which facilitates the diagnosis of painful sensations. By this age, the child’s intestines and stomach are mostly formed and have sufficient functionality.
The main causes of spasms:
- ARVI, influenza, rotavirus infection . In addition to spasms, symptoms such as hyperthermia, rhinitis, weakness, and headache may occur.
- Umbilical hernia . Additionally, acute pain is felt in the navel area, nausea and vomiting appear, the navel stands out above the surface of the abdomen and becomes swollen.
- Constipation . Diagnosed by a long break between bowel movements.
- Gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by incomplete digestion of food.
- Food poisoning . Additional symptoms are diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, pale skin, cold sweat.
- Helminthiasis . When infected with worms, the baby's tummy swells from excessive gas formation, pain appears in the form of acute attacks, and sometimes there is itching in the anal area. Additionally, underweight may be observed with excellent appetite.
- Stress, nervous shock . Appears with severe fear, emotional shock, in the form of a kind of protection from unwanted actions. This is not a simulation, but actual pain.
- Acute intestinal obstruction . Caused by blockage of the intestinal ducts, it causes intoxication of the body by the decomposition products of feces. Nausea and vomiting do not alleviate the child's condition. The pain may stop due to muscle fatigue, but most often peritonitis begins.
- Violation of the usual diet.
- Binge eating.
- Poisoning with poisons, mushrooms.
What is prescribed for children 2-3 years old for abdominal cramps?
Based on reviews from parents, it can be determined that pediatricians most often prescribe the following drugs in such cases (the site does not advertise these products).
A doctor should prescribe medication to eliminate the cause of the spasm, because self-medication of children by parents can lead to serious complications. Children should not be given medications intended for adults, and when using “children’s” medications, the dosage and frequency of administration should be strictly observed.
Drugs to eliminate the causes of spasms
| Name | Indications | Contraindications |
| Nurofen | ARVI, abdominal pain | bleeding in the stomach, hemophilia, bleeding disorders |
| Linex | dysbacteriosis | allergy to the components of the drug |
| Papaverine | spasm of smooth muscles of the stomach and intestines | glaucoma, liver failure |
| Smecta | bloating | intestinal obstruction |
| Phosphalugel | stomach and intestinal disorders | renal failure |
| Enterofuril | gastrointestinal diseases, rotavirus infection | fructose intolerance |
| Hamomilla (homeopathic remedy) | with spasms in the navel area, accompanied by belching and rumbling | individual intolerance |
If the cause of stomach and intestinal spasms is mild functional impairment, after consulting a doctor, you can use folk remedies: honey with warm water, chamomile tea, cabbage juice, fennel fruit infusion.
When should you urgently call a doctor if your child has abdominal cramps?
The main criterion for seeking medical help is the so-called “acute abdomen,” when a child feels severe pain, accompanied by vomiting and fever.
If acute spasmodic pain in the abdomen appears in a child 2-3 years old, you should immediately call an ambulance. It is forbidden to use anything to stop the symptoms, give the child medicine, or apply heat or cold to the stomach.
Less pronounced spasms of an unstable nature that do not disappear within an hour are another reason to consult a doctor. It is possible that their cause does not require immediate medical attention, but it must be determined solely by a doctor .
Deterioration of the condition in young children can occur in a matter of minutes, and it is best if the child is under the supervision of a specialist during this time.
Before the ambulance arrives, you are allowed to drink plenty of fluids and are prohibited from taking painkillers so that the picture of the disease is clear.
Share with friends:
Source: https://baragozik.ru/zdorovyj-malysh/chto-delat-esli-u-rebenka-spazmy-v-zhivote-diagnostika-i-lechenie.html
What is prescribed for children 2-3 years old for abdominal cramps?
Based on reviews from parents, it can be determined that pediatricians most often prescribe the following drugs in such cases (the site does not advertise these products).

| Name | Indications | Contraindications |
| Nurofen | ARVI, abdominal pain | bleeding in the stomach, hemophilia, bleeding disorders |
| Linex | dysbacteriosis | allergy to the components of the drug |
| Papaverine | spasm of smooth muscles of the stomach and intestines | glaucoma, liver failure |
| Smecta | bloating | intestinal obstruction |
| Phosphalugel | stomach and intestinal disorders | renal failure |
| Enterofuril | gastrointestinal diseases, rotavirus infection | fructose intolerance |
| Hamomilla (homeopathic remedy) | with spasms in the navel area, accompanied by belching and rumbling | individual intolerance |
If the cause of stomach and intestinal spasms is mild functional impairment, after consulting a doctor, you can use folk remedies: honey with warm water, chamomile tea, cabbage juice, fennel fruit infusion.
What to pay attention to if your child has a stomach ache
If a child at the age of 5 periodically has a stomach ache, then parents need to monitor exactly when the symptom occurs. Particular attention should be paid to whether there is a relationship with food intake, its quality and quantity, as well as with bowel movements and time of day.
If, after eating a certain food, abdominal pain, nausea, stool problems, and flatulence appear, then perhaps these are signs of fermentopathy. In this group of diseases, not enough enzyme is synthesized that breaks down a certain compound, or it is labile, that is, it is destroyed when exposed to provoking factors.
The pathology does not always appear immediately after birth, for example, with constitutional lactase deficiency, lactase ceases to be synthesized from 3-5 years (as studies show, about 50% of adult Europeans cannot tolerate milk, although this was not observed in early childhood).
Food allergies do not only appear in infancy; they can also develop in children as young as five years old. Therefore, if a child has a stomach ache every day for a week and at the same time he eats chocolate every day for a year, then an allergic reaction cannot be ruled out.
Moreover, the disease does not always have skin manifestations (rash, redness, dry skin); digestive disorders often occur, such as abdominal pain, colic, nausea, vomiting, bowel dysfunction, flatulence, as well as respiratory symptoms (rhinitis, asthma) or swelling.

An immune reaction can occur not only to a specific product, but also to all red or orange vegetables, to a preservative
If a child experiences abdominal pain at night, this may be due to a disease of the anatomical structure, which should protect against the reflux of gastric or intestinal contents back into the esophagus. Due to reflux, the walls of the esophagus become inflamed, which causes pain, heartburn, belching, and difficulty swallowing.
In preschool children, GERD is sometimes accompanied by vomiting streaked with blood. Pathology occurs as a result of impaired motility of the stomach and intestines, insufficiency of the esophageal sphincter. The provoking factor is obesity, diaphragmatic hernia, dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Parents should not make the diagnosis themselves. Only a doctor, after examining, palpating the abdomen and conducting a laboratory examination, will be able to tell why the baby’s tummy often hurts.
When should you urgently call a doctor if your child has abdominal cramps?
The main criterion for seeking medical help is the so-called “acute abdomen,” when a child feels severe pain, accompanied by vomiting and fever.
Less pronounced spasms of an unstable nature that do not disappear within an hour are another reason to consult a doctor. It is possible that their cause does not require immediate medical attention, but it must be determined solely by a doctor . Deterioration of the condition in young children can occur in a matter of minutes, and it is best if the child is under the supervision of a specialist during this time. Before the ambulance arrives, you are allowed to drink plenty of fluids and are prohibited from taking painkillers so that the picture of the disease is clear.
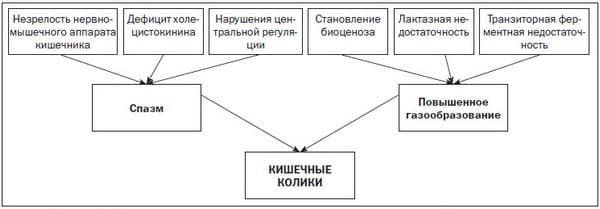
Intestinal colic is a common phenomenon characteristic of infants in the first months of life, but it often occurs in older children. This is not a diagnosis, not a disease. This is a symptom, a spasm, a special pain sensation that can accompany various diseases. It is advisable for parents to understand the causes of colic in order to provide their child with timely and competent help or contact a specialist to establish a diagnosis.

Features of intestinal colic in infants
In the third week from birth, the baby may experience painful cramps in the abdomen, to which he reacts with a loud, high-pitched, long cry. The baby's tummy swells and hardens. The child wiggles his legs and becomes restless. Most often, such spasms appear in newborns in the late afternoon (colic time is after 18:00), can last up to 3 hours and end suddenly. The causes of infant colic are not fully understood. It is known that it can be caused by increased gas formation, imperfection of the nerve endings of the newborn’s intestines, due to the certain composition and enzymes of breast milk, which change during the day.
Intestinal colic in such babies is not considered a pathology. The phenomenon disappears without any treatment, on its own, by 3-4 months of life. It is believed that male infants are more likely to suffer from colic.
Only a doctor can reliably determine whether colic in a baby is a symptom of a congenital pathology, and which one. If the child is healthy, then no treatment will be required in this case. Parents will just have to be patient. Over time, the baby's digestive and nervous system improves, and intestinal colic goes away. You can alleviate the baby's condition by laying it on the stomach, lightly massaging the tummy, or applying a warm diaper. A nursing mother's diet or formula should be carefully selected and not provoke increased gas formation, which leads to intestinal colic.
Intestinal colic in preschool children
Acute abdominal pain of a spastic nature can also occur in preschoolers, that is, in children older than 1-2 years, disturbing them, causing fear and tears. And if this condition in infants does not cause concern to doctors and colic goes away by 3-4 months, then intestinal pain in children older than one year can be caused by various reasons.

These include:
- Activity of helminths. For example, a ball of roundworms can block the intestinal lumen and cause pain due to obstruction in this place.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines, gastrointestinal tract.
- Eating disorders, dry food, unhealthy foods.
- Excessive impressionability.
- Congenital pathologies of the digestive organs.
- Appendicular colic.
- Intestinal infection.
- IBS – irritable bowel syndrome.
Colic appears suddenly and is usually followed by loose stools mixed with mucus. If colic is caused by an inflammatory process or infection in the gastrointestinal tract, the child may develop a fever. The pain and burning usually lasts 2-3 minutes, then goes away.
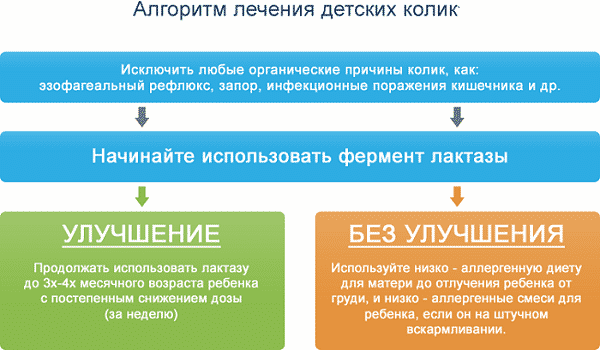
If spasms occur frequently, then it is necessary to examine the child and consult a specialist. After establishing the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment.
If a strong spasm or colic is caused by increased excitability or excessive impressionability, it is enough to calm the baby, eliminate the cause of the excitement, give him tea with mint, chamomile, valerian, and distract him. And the pain will go away. But it is better to consult a doctor in a timely manner. In case of severe cramps and additional symptoms (vomiting, diarrhea, fever, stomach pain, pain in the side), you must call an ambulance. Before her arrival, no medications, enemas or heating pads should be used to eliminate pain, so as not to blur the clinical picture of the disease and not cause harm.
Causes of pain
Pain in a child can occur due to damage to organ tissue, that is, if a pathological process occurs in the tissues, causing it to change. The cell adapts to the actions of various factors and reaches a stable state, allowing it to adapt to new conditions.
If the cell's adaptive capabilities are exhausted, then damage occurs, which can still be reversible. If the unfavorable factor acts constantly or is very strong, then the cell dies.
The following causes of cell damage are identified:
- hypoxia (occurs when blood flow decreases or the blood is unable to transport oxygen);
- physical effects (trauma, overheating, cold);
- chemical agents and medications (dust, asbestos, high doses of medications, alcohol have a destructive effect on tissue);
- infectious agents;
- immune response;
- genetic disorders;
- unbalanced diet (cell damage is often caused by a lack of protein and vitamins in the diet).
Abdominal pain in a 5-year-old child most often occurs as a result of:
- improper nutrition. Overeating, eating fatty, spicy foods. A lack of microelements and vitamins leads to a deterioration in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and other body systems. Due to an unbalanced diet and lack of nutritional regimen, dysbiosis, iron deficiency anemia, rickets, hypovitaminosis, obesity, diabetes mellitus, gastritis may develop;
- lack of hygiene skills. Often children of primary school age are diagnosed with diseases that are considered diseases of dirty hands. These are hepatitis A, dysentery, influenza, salmonellosis, typhoid fever, parasite infection;
- taking medications. Some medications can irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa, which can lead to inflammatory processes. Taking broad-spectrum antibacterial agents destroys both bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which is why intestinal dysbiosis develops;
- emotional stress. Children of five years of age often experience severe stomach pain in stressful situations, which may result in nausea, increased temperature and blood pressure. During diagnosis, no pathologies are detected that could provoke such symptoms. These pains are psychogenic in nature, usually manifesting themselves in the form of colic in the abdomen or pain in the area around the navel;
- congenital or hereditary pathologies of the abdominal organs. Diverticula, hernias, fermentopathy, celiac disease (celiac disease), stenosis of the intestinal tube, neurogenic ileus, anomalies of intestinal rotation are genetically determined and develop under certain conditions. Some diseases are detected in the first days or weeks after birth, others may appear years later. For example, intestinal diverticula are detected only when they are inflamed; an umbilical hernia causes discomfort when it reaches a certain size.
Intestinal colic in school-age children
Intestinal colic in school-age children can also be caused by various diseases, pathologies in the digestive system, infections and helminths.
In addition, it can be provoked by:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress caused by increased study load associated with exams, difficult relationships in the team;
- poisoning of the body with heavy metals;
- excessive stress during sports training;
- eating disorders - fast food, irregular meals, energy carbonated drinks.
Frequent, severe, painful abdominal cramps in children aged 7-10 years and older should alert parents and force them to see a doctor. He will conduct a survey about the nature of the pain, when it appeared, and will palpate the indicated location. It will be necessary to take tests of the child’s blood, stool, and urine. Based on the first results of the examination, additional diagnostic measures may be prescribed: ultrasound, tomography, X-ray, colonoscopy, FEGDS. Depending on the data obtained, a diagnosis is established and treatment is prescribed: from medication to surgery.
If intestinal colic was eliminated at home, but recurrences occur, then you cannot risk the child’s health. Without timely consultation with a doctor, you can miss or develop a serious illness - from pancreatitis and appendicitis to a malignant tumor.
In some cases, you can miss time and provoke complications, for example, peritonitis as a result of a ruptured appendix, metastases from a malignant tumor, death of the pancreas - pancreatic necrosis.
Prevention and treatment
Preventive measures to reduce the frequency and severity of intestinal colic in infants are:
- high-quality nutrition for a nursing mother, excluding foods that can cause increased gas formation - cabbage, apples, legumes, baked goods, sweets;
- correct attachment to the breast;
- correct selection of nutritional mixture and its dilution (with artificial feeding);
- a hole in the bottle of small diameter;
- laying on the stomach;
- give the baby the opportunity to burp air by standing the baby upright after feeding.
For children of preschool and school age, recommendations for the prevention of intestinal colic are as follows:
- nutrition according to age, without abuse of “harmful” foods and drinks;
- proper drinking regime, taking enough liquid;
- active lifestyle;
- timely medical examinations, age-appropriate vaccinations;
- periodic examination for helminths;
- preventing or mitigating stressful situations related to studies, relationships in the family and children's team;
- training in sports sections should carry a moderate load;
- compliance with hygiene rules in everyday life (clean hands, clothes, use only individual personal hygiene items).
You can eliminate intestinal colic on your own in an older, non-infantile child only with full confidence in the absence of pathology, infection or disease. If, after consulting a doctor, nothing serious was discovered, then to alleviate the condition, you can give the child or schoolchild two tablets of No-Shpa (Drotaverine) or a Spazmalgon tablet. Anxiety and the effects of stress are relieved with mint or chamomile tea, infusion or decoction of valerian.
If you are bloated, you can put a warm heating pad on your lower abdomen and drink tea with fennel or dill water. Enemas with herbal decoctions are used carefully to cleanse the intestines of gases and feces.
When intestinal colic appears in children, it is mandatory to adjust the diet; a period of fasting (up to 12 hours) is possible and useful, when the child is given only tea with crackers without additives. During and after colic, the diet should be gentle, excluding fried, fatty, spicy foods, baked goods, yeast baked goods, large quantities of sweets, and carbonated drinks.
For what reasons do they arise?
Abdominal cramps in a child can usually spread not only to the intestines, but also to the stomach area.
The baby may have problems due to:
- Response to inappropriate infant formula. Most often, this problem affects infants, since their bodies do not yet have enough lactase, which affects the breakdown of food. As a result, the following is observed: loose stools, a sharp decrease in weight gain, bloating as a result of the accumulation of gases. You can notice bloating in a baby immediately after feeding;
- Development of pyloric stenosis - permanent or temporary spasm of the sphincter, which is located at the border of the stomach and duodenum. This problem affects mainly three-month-old children and is expressed in painful sensations. You can notice the problem by: an increase in the baby’s anxiety level, an exacerbation of the gag reflex, dehydration and systematic regurgitation. This is due to the fact that food enters the stomach through the esophagus, but does not enter the intestines or enters with difficulty;
- Dysbacteriosis, which manifests itself in children as a result of feeding on the milk of a mother who is undergoing antibiotic treatment. In addition to painful sensations, the baby experiences an increase in gas production. There is mucus and blood in the stool or other changes in the stool. On palpation, hardening of the child's tummy is noted.
Self-medication of children of such a young age should be done with extreme caution. The baby’s body is still quite vulnerable and it is recommended that if a problem arises, consult a specialist.
Stomach spasm: why it happens and how it is expressed
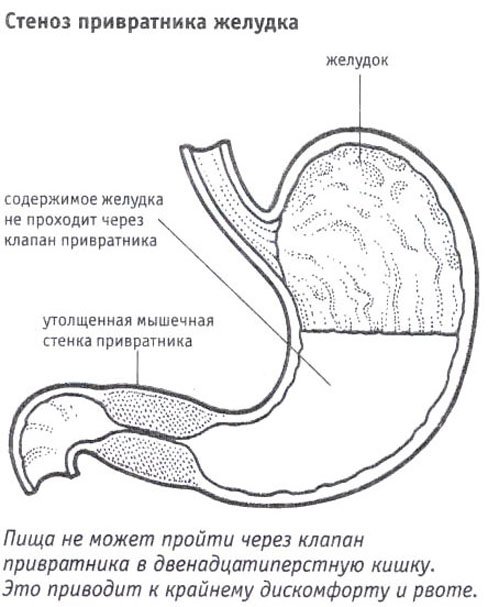
Abdominal cramps in a small child can affect not only the intestines, but also the stomach. Often the problem occurs in infants who have been switched to unadapted milk formulas. The lack of the lactase enzyme affects the breakdown of food, as a result of which the baby produces loose stools, the baby does not gain weight well, and gases accumulate in his stomach. Bloating is observed immediately after feeding.
If a child has a stomach ache during the first 3 months of life, most likely he has developed pyloric stenosis. This is a constant or one-time spasm of the sphincter separating the stomach and duodenum. Food masses do not reach the intestines or reach it with difficulty. The baby’s health is affected by regurgitation, gag reflex, anxiety, and dehydration.
Spasms of the stomach and intestines in children under one year of age often occur due to dysbiosis developed due to the use of antibiotics by a nursing woman. The sensations are accompanied by increased gas formation, the release of blood and mucus with feces, and a seemingly unreasonable change in the character of the stool. Palpation determines a hard abdomen.
As the child grows up, spastic sensations arise against the background of various pathologies:
- appendicitis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- biliary and pancreatic colic;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- tract damage by helminthic infestations.
Abdominal cramps in children older than one year and younger preschool age
Painful sensations in children in the abdominal area have a number of their own characteristics and difficulties, depending both on the characteristics of the problem and on age-related characteristics. One of the main problems with spasms in two-year-old children is the fact that they cannot yet say exactly what exactly is hurting them.

In this case, parents should not forget that abdominal cramps in a 2-year-old child can be noticed by the baby’s behavior. He will be capricious and refuse food. The main reason may be unsuitable or low-quality products.
Abdominal cramps in a 3-year-old child can be caused by the same problems and diseases as in adults - poisoning, appendicitis.
Is it possible that “adult” diseases, which are associated with the accumulation of heterogeneous elements in the body - stones in the kidneys and urinary system, cirrhosis of the liver, are not typical for younger people.
Abdominal cramps in a 5-year-old child, as in a three-year-old child, arise as a result of the same diseases as in adults, with rare exceptions. A small advantage of spasms at this age is the fact that the child can tell what exactly is bothering him.
Most often, in children 3 and 5 years of age, sharp pain in the abdominal area is caused by diseases such as:
- Umbilical hernia – characterized by acute painful sensations in the navel area. You can visually determine by the swelling of the navel, it becomes tighter, and the tummy sticks out a little above it. In addition, the child suffers from nausea and systematic vomiting;
- ODS, in which, in combination with abdominal cramps, there is an increase in temperature, sore throat and headache, general weakness of the body, runny nose;
- Problems with bowel movements, particularly constipation. Most often, cramps disappear as soon as constipation problems are eliminated;
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract, which can most often occur in children over 3 years of age. With this problem, pain may also occur during urination. In addition, there is an increase in the child’s body temperature and external lethargy;
- Poisoning – characterized by too liquid stool, pale skin, systematic vomiting or nausea. All this is accompanied by attacks of abdominal cramps;
- The presence of helminths is accompanied by increased gas formation and, accordingly, bloating. In this case, abdominal cramps in a baby may be accompanied by a feeling of itching in the anus and a sharp decrease in body weight while maintaining normal appetite.
However, it is important to remember that only a specialist can diagnose any disease with high accuracy. Therefore, if problems arise, it is recommended to consult a doctor who, after a preliminary examination and based on tests, will determine which treatment plan is suitable for a particular patient.
Abdominal cramps in a child, reasons, how to provide first aid
It’s rare that any parent manages to avoid problems with their child’s health.
These include childhood infectious diseases, colds, and often the little ones have stomach problems. For example, abdominal cramps in a child are a consequence of problems with the digestive system. These may include both banal overeating and more serious problems: poisoning, appendicitis. Each age has its own characteristics of the occurrence and treatment of spasms.
For what reasons do they arise?
Abdominal cramps in a child can usually spread not only to the intestines, but also to the stomach area.
The baby may have problems due to:
- Response to inappropriate infant formula. Most often, this problem affects infants, since their bodies do not yet have enough lactase, which affects the breakdown of food. As a result, the following is observed: loose stools, a sharp decrease in weight gain, bloating as a result of the accumulation of gases. You can notice bloating in a baby immediately after feeding;
- Development of pyloric stenosis - permanent or temporary spasm of the sphincter, which is located at the border of the stomach and duodenum. This problem affects mainly three-month-old children and is expressed in painful sensations. You can notice the problem by: an increase in the baby’s anxiety level, an exacerbation of the gag reflex, dehydration and systematic regurgitation. This is due to the fact that food enters the stomach through the esophagus, but does not enter the intestines or enters with difficulty;
- Dysbacteriosis, which manifests itself in children as a result of feeding on the milk of a mother who is undergoing antibiotic treatment. In addition to painful sensations, the baby experiences an increase in gas production. There is mucus and blood in the stool or other changes in the stool. On palpation, hardening of the child's tummy is noted.
Self-medication of children of such a young age should be done with extreme caution. The baby’s body is still quite vulnerable and it is recommended that if a problem arises, consult a specialist.
Abdominal cramps in children older than one year and younger preschool age
Painful sensations in children in the abdominal area have a number of their own characteristics and difficulties, depending both on the characteristics of the problem and on age-related characteristics. One of the main problems with spasms in two-year-old children is the fact that they cannot yet say exactly what exactly is hurting them.
In this case, parents should not forget that abdominal cramps in a 2-year-old child can be noticed by the baby’s behavior. He will be capricious and refuse food. The main reason may be unsuitable or low-quality products.
Abdominal cramps in a 3-year-old child can be caused by the same problems and diseases as in adults - poisoning, appendicitis.
Is it possible that “adult” diseases, which are associated with the accumulation of heterogeneous elements in the body - stones in the kidneys and urinary system, cirrhosis of the liver, are not typical for younger people.
Abdominal cramps in a 5-year-old child, as in a three-year-old child, arise as a result of the same diseases as in adults, with rare exceptions. A small advantage of spasms at this age is the fact that the child can tell what exactly is bothering him.
Most often, in children 3 and 5 years of age, sharp pain in the abdominal area is caused by diseases such as:
- Umbilical hernia – characterized by acute painful sensations in the navel area. You can visually determine by the swelling of the navel, it becomes tighter, and the tummy sticks out a little above it. In addition, the child suffers from nausea and systematic vomiting;
- ODS, in which, in combination with abdominal cramps, there is an increase in temperature, sore throat and headache, general weakness of the body, runny nose;
- Problems with bowel movements, particularly constipation. Most often, cramps disappear as soon as constipation problems are eliminated;
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract, which can most often occur in children over 3 years of age. With this problem, pain may also occur during urination. In addition, there is an increase in the child’s body temperature and external lethargy;
- Poisoning – characterized by too liquid stool, pale skin, systematic vomiting or nausea. All this is accompanied by attacks of abdominal cramps;
- The presence of helminths is accompanied by increased gas formation and, accordingly, bloating. In this case, abdominal cramps in a baby may be accompanied by a feeling of itching in the anus and a sharp decrease in body weight while maintaining normal appetite.
However, it is important to remember that only a specialist can diagnose any disease with high accuracy. Therefore, if problems arise, it is recommended to consult a doctor who, after a preliminary examination and based on tests, will determine which treatment plan is suitable for a particular patient.
Abdominal cramps in school and adolescence
A feature of spasms at this age is the likelihood of functional pain. When spasms of this nature occur, it is not possible to accurately determine the cause of their occurrence, since they are not associated with any specific disease.
In this case, there is no need to worry, such pain goes away on its own, without any specialized therapy.
In the process of studying the problem, doctors have established a division of functional pain according to their characteristic features, which include:
- Dyspeptic syndrome;
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- Emotional spasm of the intestines and stomach.
In addition, the occurrence of abdominal pain in a ten-year-old child may indicate inflammatory processes in the appendix.
It is important to remember that in any case, you should not be negligent about the baby’s health, because this can lead to serious consequences. If a problem occurs, it is better to consult a doctor before starting treatment.
What symptoms should be considered particularly dangerous, and in which cases should you immediately consult a doctor?
There are a number of symptoms, the occurrence of which signals the need to immediately call an ambulance.
These include:
- A feeling of severe acute pain, which is accompanied by a feeling of nausea and systematic vomiting, and a sharp increase in temperature. In this case, it is strictly not recommended to relieve symptoms with any medications. You can only apply something cold to your stomach to calm the pain a little;
- Not strong, systematic painful sensations that do not subside within an hour;
- A sharp deterioration in the well-being of children. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance. It is not recommended to relieve symptoms with painkillers; it is better to give the child something to drink. The use of medications can delay diagnosis, which can negatively affect the child's well-being.
- In addition, if there is any serious deterioration in the baby’s well-being, it is recommended to consult a specialist as soon as possible in order to minimize the likelihood of developing more serious problems.
What to do if a child has abdominal pain with cramps, how to provide first aid
Often, the condition can be alleviated without contacting a doctor. However, it is important to understand that if nausea or vomiting occurs, accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, you should not abuse self-medication.
To relieve pain, it is not recommended to use any medications without first consulting a specialist.
However, you can:
- If you have problems with stool, give an enema. However, this does not apply to infants; an enema without the permission of a pediatrician is prohibited at this age;
- For diarrhea, it is recommended to give your child as much fluid as possible. You should drink often, but in small portions;
- If the cause of a child’s spasms is constipation, it is worth diversifying the baby’s diet with fresh fruits, vegetables and herbs;
- In case of an eating disorder, it is recommended to minimize or completely exclude from the child’s diet all foods that activate gas formation processes: dairy products, legumes, flour products, pickles, mushrooms and kvass. Introduce as much fiber into the menu as possible;
- If the spasms are of a neurotic nature, it is recommended to give the child tinctures of valerian officinalis and motherwort. In addition, warm milk with honey, which should be given to the baby before bed, will not be amiss. To reduce stress, it is worth including regular walks in the fresh air in your daily routine, minimizing time in front of the TV and computer, and taking a contrast shower.
If you cannot fix the problem on your own, it is still recommended to seek advice from a specialist.
What can you eat if you have abdominal cramps?
If the pain was caused by poisoning or malfunction of the digestive system, after eliminating the problem, you should pay special attention to creating a menu.
So, for spasms, it is worth including in it:
- Liquid porridges;
- Honey;
- Light vegetable soups;
- Decoctions and teas;
- Boiled vegetables (except cabbage);
- Not hard boiled eggs;
- A small amount of crackers;
- Baked fruits;
- Lean fish;
- Kissel.
A week after poisoning, you can also include lean meat in the menu. Don't put too much strain on your digestive system at first.
Treatment of abdominal cramps with medications and traditional methods
You should use medications to treat a child only after prior agreement with your doctor.
For painful sensations the following are most often used:
- Disflatil; No-shpa; Mezim;
- Espumisan; Festal; Lactovit;
- Activated carbon; Enterosgel; Linux.
These are relatively mild drugs that have minimal effects on the body. However, you should not give them to your child without permission.
In addition to drug treatment of spasms, treatment with traditional methods is often used.
The most popular recipes include:
- A teaspoon of honey should be dissolved in a glass of heated water and drunk an hour before meals. This will help moderate the pain and eliminate the feeling of heaviness;
- Cabbage juice also helps relieve stomach cramps. To do this, you need to drink a tablespoon of warmed juice three times a day;
- Chamomile tea, which can be prepared by pouring boiled water over a teaspoon of dried chamomile, will also moderate spasms. Let the liquids sit for fifteen minutes, filter and drink a third of a glass before meals;
- An infusion of fennel fruits and dandelion roots will relieve pain. A tablespoon of dried raw materials should be poured with hot water and left for twenty minutes. Drink three times a day before meals.
However, before starting treatment, you should make sure that the child is not allergic to any of the components of the recipe. To do this, you should consult your doctor.
Abdominal cramps in a child can be either a cause of banal overeating or poisoning, or a symptom of a serious illness. It is not recommended to overuse self-medication, because a child’s body is not as resistant to the harmful effects of medications as an adult’s body and there is a high probability of the situation worsening.
Also, if the baby’s condition sharply worsens, you should not delay providing assistance: first of all, call an ambulance.
Useful information for parents - watch the video:
Source: https://VekZhivu.com/article/2987-spazmy-v-zhivote-u-rebenka-prichiny-kak-okazat-pervuyu-pomoshch
What to do if a child has abdominal pain with cramps, how to provide first aid
Often, the condition can be alleviated without contacting a doctor. However, it is important to understand that if nausea or vomiting occurs, accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, you should not abuse self-medication.
To relieve pain, it is not recommended to use any medications without first consulting a specialist.
- If you have problems with stool, give an enema. However, this does not apply to infants; an enema without the permission of a pediatrician is prohibited at this age;
- For diarrhea, it is recommended to give your child as much fluid as possible. You should drink often, but in small portions;
- If the cause of a child’s spasms is constipation, it is worth diversifying the baby’s diet with fresh fruits, vegetables and herbs;
- In case of an eating disorder, it is recommended to minimize or completely exclude from the child’s diet all foods that activate gas formation processes: dairy products, legumes, flour products, pickles, mushrooms and kvass. Introduce as much fiber into the menu as possible;
- If the spasms are of a neurotic nature, it is recommended to give the child tinctures of valerian officinalis and motherwort. In addition, warm milk with honey, which should be given to the baby before bed, will not be amiss. To reduce stress, it is worth including regular walks in the fresh air in your daily routine, minimizing time in front of the TV and computer, and taking a contrast shower.
If you cannot fix the problem on your own, it is still recommended to seek advice from a specialist.
A 2-year-old child has abdominal pain with cramps
Probably every parent has heard at least once in his life from his child that he has a stomach ache. Despite the prevalence of this symptom, few people know how to properly deal with it, what medications can be given, and which drugs should be strictly avoided.
A variety of disorders in the body can provoke painful sensations: pancreatitis, gastritis, ulcers, constipation, appendicitis. The causes are not always related to dyspeptic disorders; discomfort can be caused by allergies, infectious diseases, helminthic infestations, kidney problems, and more.
The pathological process can be caused by exposure to both internal and external factors. In most cases, unwashed hands can provoke the development of an infectious process. Incompatible products, expired food, injuries, stressful situations - these are not all the reasons that can cause abdominal pain.
It is extremely important not to miss a condition that requires emergency medical attention. This is why you should not self-diagnose, but rather entrust your child’s health to a professional.
Diseases with abdominal pain in children
Next, we consider the main pathologies that manifest themselves as abdominal pain syndrome.
Acute appendicitis as a cause of pain
As a result of inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, unbearable pain occurs. According to statistics, in seventy percent of cases the cause of complaints of abdominal pain in pediatric practice is appendicitis.
With appendicitis, pain first appears in the navel area, and then moves to the right area
Abdominal discomfort is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and fever. Sometimes children develop diarrhea in response to increased intestinal contractions. During examination, the specialist may pay attention to the coated tongue.
Painful sensations become constant and aching. Discomfort forces the child to look for a body position that could relieve his pain. Lying on the left side only increases the pain, so the child lies on his back or on his right side.
The clinical picture of acute appendicitis in children can vary greatly, this is due to the location of the appendix. For example, if the appendage is located in the pelvic area, then the child may experience frequent, painful urination.
If it is located near the rectum, then the urge to defecate will be painful. The process may also be located in the liver area. In this case, intense pain appears in the right hypochondrium, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
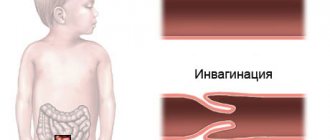
Intussusception
The mechanism of the pathological process is associated with the introduction of one section of the intestine into another. The disease is quite rare and appears mainly in boys. Improper introduction of complementary foods can cause disturbances in peristalsis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HYUfjceQ-Fk
The disease appears suddenly. Against the background of complete calm, the child becomes restless, he screams, cries and presses his legs to his tummy. The face becomes pale and covered in cold sweat. The child develops cramping pain.
The attack is accompanied by vomiting and fever. First, the child vomits food debris, and then the vomit becomes fecal in nature.
Source: https://menchov.ru/u-rebenka-2-goda-bolit-zhivot-spazmami/
What can you eat if you have abdominal cramps?
If the pain was caused by poisoning or malfunction of the digestive system, after eliminating the problem, you should pay special attention to creating a menu.

So, for spasms, it is worth including in it:
- Liquid porridges;
- Honey;
- Light vegetable soups;
- Decoctions and teas;
- Boiled vegetables (except cabbage);
- Not hard boiled eggs;
- A small amount of crackers;
- Baked fruits;
- Lean fish;
- Kissel.
A week after poisoning, you can also include lean meat in the menu. Don't put too much strain on your digestive system at first.