What is a food allergy?
Pathogens that can lead to various reactions are called allergens. In food, proteins perform this role. During thermal or other processing, allergens may lose their properties completely or partially; some, on the contrary, become more active.
The allergic reaction mechanism is launched almost immediately after the pathogen enters the body. The production of immunoglobulin E begins, which triggers a series of reactions that result in allergy symptoms. Depending on the activity of the pathogen, as well as the degree of reaction to a particular allergen, the first reactions can occur either immediately after eating or be extended over a certain period of time.
Preventive actions
Treating food allergies in children is a painstaking process. You know that it is easier to prevent a disease than to eliminate it later.
Guided by this rule, gradually expand the child’s diet. Do not give carbonated drinks, candy, crackers, chips and other questionable foods. Thus, you only provoke the development of allergies.
Keep a food diary. Gradually introduce foods and monitor the body's reaction. This will allow you to independently exclude a potentially dangerous allergen.
Select mixtures carefully, give preference to hypoallergenic types.
If an allergic reaction develops, visit an allergist. An experienced specialist will help you resolve the current situation and give recommendations.
Symptoms of food allergies
The body's response to pathogens is not the same and is divided between different types of organs and tissues, which makes it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis when the problem is not obvious. Answer the question “what does a food allergy look like in a baby?” A clear knowledge of existing symptoms, the mechanics of allergies and the diet itself will help.
On the skin side, the disease manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- rashes of any kind;
- redness;
- diathesis of the cheek area;
- the occurrence of diaper rash;
- profuse sweating;
- hives;
- peeling of the scalp;
- Quincke's edema.
Gastrointestinal symptoms:
- regurgitation;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- constipation,
- flatulence.
There are also combinations of various symptoms, among which the most dangerous are Quincke's edema and bronchospasm. Answer to the question: “How do severe food allergies manifest in infants?” - such. In both cases, suffocation develops with attacks of dry cough, the complexion changes, and if the baby does not respond in a timely manner, the baby may suffocate.
First aid for bronchospasm:
- Immediately call an ambulance and call for a squad, and ask what actions need to be taken before the ambulance arrives;
- Find out what dose of antihistamine medication available on hand should be given to your baby;
- Give the baby medication following the recommendations of the ambulance;
- Wait for the ambulance to arrive.
Countless allergens
Allergic reactions, in particular food ones, are increasingly common in children. The most common allergens that cause this reaction are dust (containing microscopic mites), pollen, feathers and animal hair, medications, cosmetics and food. Allergies manifest themselves in various acute or chronic ailments: urticaria, eczema, swelling, diarrhea, vomiting, cough, rhinitis...
Some allergies go away over time (this is often the case with childhood food allergies), but some children develop sensitivity to other substances, such as dust, pollen, or dead skin cells and animal dander.
Truth or lie?
Asthma is an allergic disease.
Lie. Asthma affects the bronchi and respiratory system. The risk of developing asthma is higher in people with allergies, and asthmatics often experience a variety of allergic reactions.
Causes of the disease
As we have already said, the source of pathogens entering the child’s body is either the mother’s breast milk or artificial milk. In the case of breastfeeding, it is contained in those products that the nursing mother consumes, otherwise it is worth carefully studying the composition of artificial nutrition.
The risk of a child suffering from some form of allergy primarily depends on heredity. If one of the parents suffers from food allergies, then the risk of passing this problem on to the child is 37%; when both parents are allergic, then the chance of passing on the allergy from them is more than 60%. In addition to heredity, developed abnormalities, previous acute respiratory viral infections and intestinal diseases contribute to this.
Food allergies in children under one year of age occur primarily due to functional limitations of the digestive tract. Enzymes have low activity, protective antibodies of the mucous membranes are produced at a low rate. Coupled with the high permeability of the mucous membranes, this leads to the fact that pathogens easily enter the bloodstream.
Note. The development of allergies is greatly influenced by the period of pregnancy. Factors such as: smoking can contribute to the development of the problem; past illnesses; use of antibiotics; eating strong allergens such as chocolate, coffee, cow's milk, honey and others. It is also dangerous for the mother to be exposed to environmental allergens, especially in the summer.
Causes and/or risk factors
- Heredity. The presence of any allergy in parents, grandparents and other relatives may indicate a hereditary predisposition of the child to immediate hypersensitivity reactions.
- Violation of the mother's diet during the prenatal and lactation periods. An unprepared child’s body is faced with food products that it essentially cannot identify, which is perceived as foreign and rejected by the body through the formation of an allergic reaction.
- Dysbacteriosis. An imbalance of beneficial microflora in relation to pathogenic microflora leads to impaired digestion. At certain parts of the digestive tract, undigested food is perceived by the immune system as an allergen.
- Enzyme deficiency. It is very important for infants to introduce complementary foods correctly; early introduction of new food leads to the formation of an allergy to it, since the enzymes necessary for its digestion have not yet been produced. Allergies can also occur as a result of diseases of the pancreas, in which its function is reduced.
- Pathology of the intestinal mucosa. Congenital or acquired intestinal diseases also disrupt the normal digestion of food, which leads to the formation of allergic reactions.
We recommend reading:
Pylorospasm: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment (nutrition, medications and physiotherapy)
Diagnostics
If you observe the symptoms described earlier in your baby, you should consult a doctor for advice. In case of severe allergic reactions with the development of several signs or difficulty breathing, the child should be hospitalized immediately.
Diagnosis of the disease in medical institutions occurs as follows:
- information provided by parents is collected;
- a connection between the occurrence of certain symptoms and food intake is established;
- a general examination of the child takes place;
- a blood test is taken;
- An ultrasound examination is performed to exclude a possible non-allergic component of the problem.
The existence of the disease may be indicated by the fact that after stopping taking certain foods, allergic reactions stopped, as well as an improvement in the baby’s condition after taking medications.
After confirming the diagnosis, an equally important question arises - which product caused the reaction? This knowledge will help in the future to avoid a product or products that can not only harm the body, but also lead to death. To find out, a special analysis is carried out. Blood is taken from infants for testing. And in older children, a special test of skin reactions to a number of possible pathogens is carried out.
The procedure is carried out before the start of treatment, but the causes can also be identified indirectly. By studying the mother's food diary, you can identify new foods in the diet; if they strictly describe all types of food and liquid, then this greatly simplifies the diagnosis.
What to do?
If you notice that your child is sensitive to some substance or product or time of year, such as spring, you need to undergo special testing. This is done by an allergist: a patch is applied to the skin or a tiny injection is given.
Substances suspected of causing allergies applied in this way may or may not cause a skin reaction.
A diagnosis of food allergy means the need to follow a diet with the obligatory exclusion of foods that cause allergies. Therefore, treatment is prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. Skin tests cannot be completely trusted when it comes to food allergies (you can get a positive reaction to a food that you will not have an allergic reaction to if you consume it). Special blood tests (which detect antibodies to food allergens) are expensive and also do not provide a 100% guarantee at an early age.
If your child has an allergic reaction, you should contact your pediatrician and follow his advice. Especially in the case of Quincke's edema. This is a serious reaction (significant difficulty breathing and swelling of the larynx) and should be treated immediately.
During an attack, antihistamines or medications with cortisone will soften the allergic reaction.
Treatment may be needed to reduce sensitivity. If possible, potential allergens should be completely eliminated.
Treatment
The general treatment regimen for the problem consists of switching the mother’s diet to a new diet that excludes one or more foods that cause reactions or can cause them in the baby. In the case of artificial feeding, alternative formula options are selected. As an additional measure, your doctor may prescribe medications or various local medications.
Remember! It is prohibited to independently treat food allergies in a child! In trying to cure the disease, you can not only harm the child, but also cause irreversible consequences.
How to cope with allergies
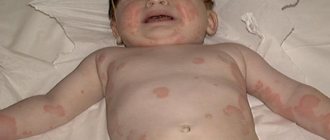
Photos of food allergies in children show rashes and redness on the skin.
Another visual manifestation is severe swelling of the face and neck. Some children experience watery eyes and rhinitis.
In this case, the child needs complex treatment. First you need to adjust your diet.
If the baby is breastfed, the mother is recommended to “go on a diet.” When a child feeds independently, he is switched to a hypoallergenic diet.
Hypoallergenic products for children are:
- adapted mixtures based on isolate;
- special fertilizers with elements of milk protein hydrolysates;
- monocomponent purees (based on one berry, fruit or vegetable);
- cereals without milk;
- canned meat;
- special water for children.
If you are a nursing mother, exclude fish and dairy products from your diet, do not eat nuts, eggs, chocolate, pineapples, kiwis and citrus fruits.
Avoid sauerkraut, seafood, smoked cheeses, alcohol and spices. Pickles and spicy foods are prohibited.
It is recommended to feed the child with special infant formulas, in particular Nutrilon Pepti, HiPP, Nutrilak, Humana and Frisopep.

This will reduce the risk of developing an allergic reaction.
If your baby has an acute allergy, use antihistamines. The most popular are Claritin, Zodak, Suprastin, Zyrtec and Diazolin. Don't hesitate to call an ambulance, this will help you avoid trouble!
Artificial feeding
Most often, in this case, all sorts of reactions can occur due to cow's milk proteins. The problem is solved by replacing with alternative options, for example, hypoallergenic mixtures. The latter uses soy milk or complex milk processing, breaking it down into amino acids. In both cases, the chance of an allergy for children is zero.
Among the disadvantages of the approach, it can be noted that a child may develop intolerance to soy protein, and hydrolyzed mixtures are very expensive and have low taste characteristics. Therefore, when the symptoms decrease, the standard diet, including cow's milk and its various variations, is reintroduced. Hypoallergenic nutrition lasts up to 3 months, then the diet is expanded again, excluding the use of mixtures with strong allergens and a minimal amount of the original pathogen.
Causes of allergies in children
Unfortunately, the number of children susceptible to allergic reactions is steadily increasing.
Today the incidence rate in Russia is 30%. This figure is approximately the same for all European countries, indicating the international scope of the problem.
The main reasons are: difficult environmental conditions, hereditary predisposition, seasonal epidemics, illnesses of parents, stress, peculiarities of pregnancy and the mother’s breastfeeding period, etc.
Most often, in the first year of life, allergies are expressed in the form of rashes, redness and peeling on the child’s skin. Sometimes this manifests itself in the form of intestinal colic, stool instability, gas, and respiratory disorders.
Yes, this is all serious. But don’t be discouraged just because your little one happened to be born in an era of urbanization and thousands of environmental disasters. The mother’s task is not to be afraid, but to do everything possible to protect her baby from allergies.
Breast-feeding
When breastfeeding, the mother is transferred to a new diet. To do this, for the next 7-14 days, exclude all possible dangers from the diet - canned foods and foods containing preservatives, animal fats, dyes, seafood, brightly colored fruits and berries, spices. The intake of milk, flour products and pasta is limited, also in limited quantities semolina and any milk-based cereals are consumed. Sugar and salt may be allowed in minimal quantities.
Fermented milk products are allowed, including hard cheeses and yoghurts without flavorings, dyes or flavorings. Among the cereals, it is recommended to eat buckwheat, rice, corn and oatmeal. Vegetables and fruits are selected according to their appearance; they must be green or white in color. Poultry, pork or beef is allowed boiled, steamed or dried.
You can get a more precise diet from your doctor. It will consist not only of the general recommendations described above, but will also take into account all the characteristics of the mother’s body, as well as the baby’s reaction to a particular pathogen. It is very important for the child to continue breastfeeding, so at the first signs of reactions, seek advice and adjust the diet.
How can you tell if your child is prone to allergies?
Most often, this reaction occurs in children at risk. GEM is an abbreviation for three main factors that put children at risk - genetics, environment, mother.
Everything is passed on from parents to child - both good and not so good. If both mom and dad have allergies, you need to be on guard.
In this case, the risk of an allergy in a child is 90%.
If only the mother is susceptible to allergies - 80%, if the father - 30%. If you do not suffer from allergies, but your parents (grandparents) do, the likelihood of your baby getting sick is reduced to 20%.
The ecological situation in the place where the mother grew up, where her pregnancy took place, and where the baby appeared and is growing is of great importance. In big cities, the situation is rarely favorable - tobacco smoke, smog, and many allergens from plants and trees accumulate in the air.
Well, if before the child was born, the father or mother worked in hazardous work, then this factor can have a detrimental effect not only on their health, but also indirectly on the body of the unborn child.
Sometimes people are not free to choose where they live and work. But parents are always obliged to take care of the health of their offspring, to the best of their ability.
Alas, it is not always the case that pregnancy proceeds calmly and serenely. If the mother took antibiotics during this period, or there was a threat of miscarriage, then most likely in the future this will affect the occurrence of allergic manifestations in the child.
It happens that expectant mothers are addicted to eating chocolate, citrus fruits, fish, nuts or other allergenic foods. And if they smoke and continue to do so during lactation, then the baby’s risk of developing allergies increases to 50%! Moreover, passive smoking affects this exactly to the same extent as active smoking.
But the main cause of allergies in babies in the first year of life is still poor nutrition. We will tell you below how to protect your baby, even with a high probability of illness (if you found several matches at once) and about treatment methods.
Drug treatment
Various medications are used as an auxiliary treatment; they are very often used if they are faced with serious manifestations of allergic reactions. Prescribe antihistamine tablets or drops, absorbents, various gels and ointments for topical use. Some topical medications contain hormones, and in rare advanced cases, hormones are given intravenously. To restore the baby’s intestinal microflora, a medicine containing lactobacilli and bifidobacteria is prescribed.
How to treat allergies?
Currently, the only effective way to treat food allergies is to avoid those foods.
Any suspicion of such a reaction should be brought to the attention of a specialist - an allergist. Anyone with food allergies should always have injectable adrenaline with them. If you accidentally eat an allergenic product, you can be brought out of allergic shock with the help of this drug. People who are aware of their abnormal sensitivity to certain products should always wear a keychain with information about their own disease. Then you should immediately call an ambulance, they will take you to the nearest medical facility.
Anaphylaxis is the most severe allergic lesion, often life-threatening. This manifestation does not occur in all patients, so the need for injectable adrenaline should be discussed with a doctor.
The obvious danger of food allergies is the complications they provoke. Experience shows that breastfeeding can reliably protect you and your baby from such troubles.
To reduce the risk of allergies, you should avoid eating foods to which you have an acute reaction. It happens that such products accidentally end up on your table along with other food, so it is still necessary to know about the time intervals after which allergies appear.
If we talk about the time of manifestation of these symptoms, then it makes sense to divide the process of an allergic reaction into two stages:
- First. Contact of the body with an allergen. At this stage, the immune system produces specific antibodies to the product, but no painful symptoms are observed.
- At the second stage, the body encounters an already familiar product and a ready-made reaction pattern to it. It is at this stage that allergies occur.
There are times when the immune system mistakes a harmless product for an infection and begins to actively produce antibodies to it.
Given these factors, it is worth noting that the reaction time of different people to the action of an allergen varies greatly.
One organism needs 1-2 minutes, while another organism may show allergy symptoms only after a few hours.
How to prevent allergic reactions?
Alas, if your child is allergic to a particular product, then during breastfeeding the best treatment is to avoid the pathogen, as well as products related to it. There are also general tips on diet and feeding that will help prevent serious consequences after adding new products containing active allergens for the baby. Below, we have provided useful tips to help avoid or minimize allergic reactions.
- Complementary feeding should not be given to children under 6 months of age;
- The first complementary foods should be single-ingredient;
- Products containing strong allergens are best introduced no earlier than at the age of 1 year;
- Any new food product at an early age can cause allergies;
- Timely bowel movement of a child is an important factor in protecting against allergens in the intestines;
- It is better to replace various medications with a large number of dyes with analogues without flavors and dyes;
- Keep a food diary, this guarantees not only complete and proper nutrition for the mother, but also important data that will help the doctor identify among all the products a product with an allergen that is dangerous for the child;
- Watch the composition of detergents for pacifiers and other things that enter the baby's mouth, but it is best to avoid them completely.
Root cause of allergies
The main purpose of the immune system is to maximally protect the body from a variety of threats coming from outside. The category of such threats usually includes potentially dangerous microorganisms in the form of viruses, bacteria or toxins. An overreaction to a threat is understood as the immune response to completely harmless substances, for example, certain foods.
The culprit of this reaction is immunoglobulin produced by the immune system. In ordinary language, these are antibodies to certain foods.
As practice shows, absolutely any product can be an allergen. A number of products that are especially dangerous in this regard:
- eggs;
- dairy products;
- some nuts, especially peanuts;
- shrimp, crabs, lobsters and other crustaceans;
- foods high in soy;
- a number of grain crops.
Food allergies first appear in early childhood, but can strike you at any age. Usually, most food allergens cease to be such when the child is 5 years old. But the remaining allergens will most likely accompany you throughout your life. This primarily applies to nuts, crustaceans and molluscs.
Nowadays, it is very difficult to imagine products that are completely free of food additives, dyes, preservatives and the like. These substances may cause allergies in some people. It is necessary to distinguish between two fundamentally different concepts such as allergy and individual intolerance. Statistics show that true food allergies are not that common - only 1% of all cases. In most cases, people experience individual intolerance to certain foods:
- corn-based products;
- milk and dairy products;
- grains, and more specifically grains with a high gluten content.
Useful tips
To protect your baby from this disease, follow some tips:
- Keep your child's bedding clean.
- For your baby's personal hygiene, use only hypoallergenic cosmetics.
- Eat only freshly prepared food; eating yesterday's food is unacceptable.
- Do not allow your baby to interact with animals.
- Ventilate the room regularly.
- Get rid of bad habits, don't overeat.
- Introduce complementary foods to your baby no earlier than six months of age, starting with green vegetables and fruits, then yellow, pink and red.
- Use only proven hypoallergenic milk formulas.
- Prepare porridge only with goat's milk (not cow's milk).