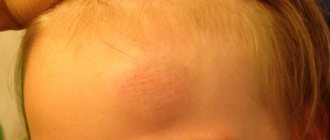
Why do babies often fall?
It is very difficult to protect a child from falls
Children are restless and inquisitive, so they often fall. Not a single parent has ever been able to completely avoid injuries and bruises.
Due to their structure, babies often hit their heads. Young children's heads are large relative to other parts of the body. Therefore, when they lose balance, they hit their heads. Children under 10 months are more likely to hit their foreheads against walls, cabinets and doors. In the process of mastering walking, one-year-old babies can hit the back of their head, temple, or chin on the floor or asphalt, or get hit by swings on playgrounds.
First aid
- First of all, calm the child down, immobilize him, and inspect the site of the impact.
- Apply cold to the injured area, especially if there is hematoma and swelling. Can be used:
- ice from the refrigerator, but always wrapped in a cloth, otherwise a cold burn cannot be avoided;
- cold objects;
- a cloth soaked in cold water.
- If the child has abrasions on the outer part of the ear, treat them with hydrogen peroxide, and if necessary, apply a sterile bandage.
- If the blow was so strong that the middle ear was damaged and blood appears, you must carefully insert a cotton swab moistened with hydrogen peroxide to stop the bleeding. After some time, carefully remove it, but it is better to moisten it with water first so that it comes out easier and does not damage the integrity of the dried blood clots.
My son, at the age of three, hit his ear on the corner of the table and immediately began to cry a lot. My ear instantly turned red and swollen a little, so I immediately applied ice. A minute later the child calmed down and sat calmly in his arms. After seven to ten minutes, I removed the cold, the ear looked almost normal. A few hours later there was no trace left of the blow. And the child, after getting out of his arms, did not remember about the sore ear, apparently there was practically no pain, and I did not remind him of it.

Are child falls from height always dangerous?
The brain in children is reliably protected from injury. The bones of the skull are soft and mobile thanks to the fontanel and sutures. Cerebrospinal fluid acts as a shock absorber. Falling off the couch is more worrying for parents than it is for the child.
If a baby at 5-7 months old falls off the sofa, hits a door frame, or falls out of the crib, you need to keep an eye on him. At first the baby will cry, but more from fear than from pain. If the baby has calmed down after half an hour, there are no deviations in behavior and no cause for concern. Most often, only a lump that forms immediately after the injury reminds of an unpleasant incident.
Often, after falling and crying, the child can fall asleep. You need to wake up the baby slightly once every 2-3 hours, assess the condition of the pupils and motor functions. It is worth periodically examining the head and paying attention to the fontanel. If it begins to change, pulsates, bulges, veins are visible, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Most falls and head impacts occur between 8 and 12 months, when children are learning to walk. To minimize the likelihood of bruises, it is necessary for the child to first learn to crawl, and then be able to stand.
The larger the fontanel, the less likely the child will experience dangerous consequences after hitting his head.
if a child hits his forehead
There are mothers who complain that their child fell... from the sofa, bed, when they, the mothers, turned away or walked away for just a couple of seconds... What to do in a situation when a child has fallen?
A child's skull is a more fragile and vulnerable structure. The likelihood of brain injury from a head impact is much higher in children than in adults. Especially in the first year of life, when the bones of the skull have not yet fused and are easily displaced upon impact. We, adults, are obliged to know where the baby is in danger. Falling onto the floor from a changing table or falling out of a stroller is a “hobby” for infants. Older children master the world by testing its strength with their own foreheads. The young traveler doesn’t even need sharp corners - he will hit a bump literally out of the blue. And it’s good if there’s a bump. And when the baby grows up and starts running, it is not known who grabs his head more often - the frightened mother or himself. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely protect a child from injury. If your child rarely falls, are you trembling too much over him? Babies most often roll onto the floor from changing tables, so you need to swaddle your baby not on the table, but, for example, on the sofa. He's shorter. Also, to cushion a possible fall, place a rug under a table or next to a sofa. Three more simple recommendations:
- do not take your eyes off the baby for a second while swaddling;
- try to hold it with your hand;
- If you need to go away (to get a bottle, or pick up the phone, or open the door), take the baby with you. Otherwise, he can turn over from his back to his stomach at any moment (it’s better not to think about the consequences of such an acrobatic sketch).
You have to keep an eye on the baby even when he lies quietly in his crib. However, lying down is half the battle. As soon as he starts to sit down, keep your eyes open. If your fidget has already mastered the art of sitting, urgently buy a low, stroller. And definitely mobile, that is, one in which the child can sit and lie down. It is more difficult for him to get out of such a stroller, and it is safer to fall. Special socks with “brakes” (these are rubberized inserts in the sole of the sock that reduce slipping) can protect your child from falling in the apartment. Place rugs in places where your baby usually travels (but so that they lie tightly and do not slide on the floor). For the first time, wrap some thick material around the sharp corners of furniture and door jambs. Remove chairs and other furniture from windows - this will keep an inquisitive little person from wanting to climb onto the windowsill or, scary to think, open the window. And if you do fall... If an accident happens and the child falls, hitting his head, the main thing is not to panic, not to find out who is to blame. All attention to the baby. Your task is to quickly find out how serious the injury is. The easiest injury is a bruise of the soft tissues of the head (not to be confused with a brain contusion!). In this case, the brain does not suffer in any way. There may be a small abrasion or bump at the site of the impact. The child, after crying for 10-20 minutes, calms down and behaves as usual. In this case, you do not need to see a doctor. With a concussion, everything is much more serious: a short-term loss of consciousness may occur, vomiting begins (in children under 3 months - multiple times), the skin turns pale, and cold sweat appears. The child is lethargic, drowsy, refuses to eat; those who are older and capable of some information about themselves complain of headaches and tinnitus. An even more serious injury is cerebral contusion . In this case, immediately after the injury, a prolonged blackout of consciousness is possible (sometimes it is absent for more than an hour). In especially severe cases, respiratory and cardiac problems occur. In case of a skull fracture, in addition to the general serious condition of the child, blood or light fluid (CSF) may leak from the nose or ear, and bruises may form around the eyes (a symptom of glasses). It is very important to know that with skull fractures, symptoms do not appear immediately, but several hours after the injury. Therefore, rule number one is that after a bruise (damage) to the head, you must monitor the child’s condition very carefully. Any doubts that “everything is okay” is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. If signs of a concussion or brain injury appear, call a doctor immediately. What can be done If there is no obvious damage to the bones of the skull, apply a cloth moistened with cold water or ice in a rag to the site of the impact. This will reduce pain and stop tissue swelling and bleeding. Bleeding can be stopped in this way - by applying a thick piece of dry cloth (tampon) to the wound. If it becomes saturated with blood, place a second one on top of the first tampon. Attention! If bleeding continues after 15 minutes, call a doctor immediately. After any head injury, the child needs rest, but do not let him fall asleep for an hour, otherwise you will not understand how serious his condition is. Wake up your baby at night too. If he does not answer simple questions, or has poor coordination of movements, or vomiting repeatedly, call a doctor immediately. Pay attention to the pupils: their unequal size indicates severe brain damage. If you suspect a serious injury, and the baby has fallen asleep, do not wait until he wakes up: call a doctor. If a child has lost consciousness after hitting his head and you have already called an ambulance, lay the baby on his side so that vomit does not enter the respiratory tract. If you suspect that, in addition to the brain, the spine has been damaged (from a fall from a height onto the head or back), the child must be turned extremely carefully and so that the body and head are on the same axis: this will help avoid additional injury. But still, the most important thing that is required of you if a child is injured is to remain calm. Too much depends on the adequacy of your reactions - the health of a little person depends.
How to give first aid
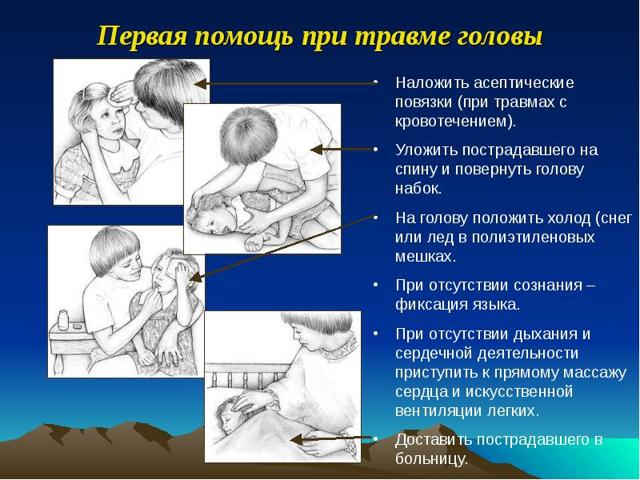
If the baby fell from the bed, changing table and hit his head, the mother needs to assess the extent of the damage and pay attention to the general condition.
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic. It is better to treat with solutions without alcohol - peroxide, Chlorhexidine.
- If the skin is not damaged, apply ice after wrapping it in several layers of fabric. Hold for no more than 3 minutes. Repeat the procedures at intervals of 10-5 minutes for an hour.
- Calm me down and let me sleep if I want.
- If the length of the wound is more than 7 cm, you must go to the emergency room. The doctor will put several stitches.
- In case of an open head injury, the wound should not be compressed to stop the bleeding. Place ice around the damaged area and call an ambulance.
- If dizziness or vomiting occurs, place the child on his side and raise the upper body slightly. Call an ambulance.
Even in the absence of serious violations in the first day after a fall, it is advisable to provide the baby with peace, limit outdoor games, and protect him from loud sounds.
Treatment
- The doctor examines the patient and identifies the consequences of the blow.
- If there is injury to the skin, the wound is treated with hydrogen peroxide.
- When a hematoma appears, heparin ointment is prescribed. If it does not produce results, they do an opening and cleaning. After surgery, a sterile dressing is applied.
- If deformation of the auricle cartilage occurs, restoration surgery will be performed.
- In the case where there was a “dirty blow” with partial damage to the skin, the child will be prescribed antibacterial ointments.
- If the pain is severe, the specialist will prescribe analgesics, such as ibuprofen.
- If the blow was so strong that it resulted in injury to the ear drum, the wound will be swabbed and disinfected. If surgery is not required, the child will have a sterile bandage placed on the ear.

When you need to see a doctor urgently
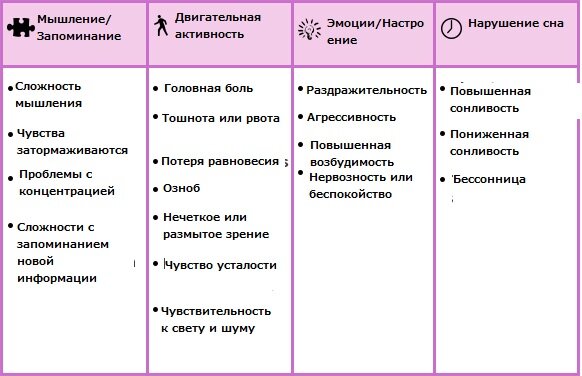
Signs of a concussion
Traumatic brain injuries - concussions and bruises, compression of brain tissue - are manifested by a variety of symptoms. If a baby between the ages of 2 months and one year appears at least 1 alarming sign, you should immediately consult a doctor. You need to start with your pediatrician. If necessary, you will have to visit a pediatric neurologist. You should not try to independently determine the severity and type of injury; you should not give painkillers and other medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Signs of head injuries:
- single or multiple clouding, loss of consciousness, the duration of the attack does not matter - the main symptom of a concussion;
- the child has trouble falling asleep or becomes drowsy;
- changes in behavior;
- crying lasts an hour or longer - this may be due to a headache that the child cannot yet talk about;
- repeated bouts of vomiting or frequent regurgitation begin;
- pale skin, blurred vision;
- pupils of different sizes, no reaction to light;
- convulsions;
- the child cannot move his arms or legs due to weakness;
- discharge of any kind from the nose or ears is a sign of a fracture of the skull bones;
- bruises under the eyes and behind the ears on both sides;
- In infants, the temperature often rises due to traumatic brain injuries.
When the brain tissue is squeezed due to compression, severe vomiting is a concern. After loss of consciousness, the child can behave as usual for up to 2 days. But this condition is extremely dangerous, as it can lead to cerebral edema.
You should definitely consult a doctor if you are injured or hit in the temporal region. Here the bone is thin, fragments can injure the brain, and there is a high probability of internal bleeding.
Alarming symptoms
Regardless of whether the child has a bump on his forehead or not, after the injury we recommend showing the baby to a specialist. At a minimum, you should call your doctor and discuss what happened. In the future, it is necessary to monitor the baby very carefully.
Actually, these are the actions you need to start with if a child hits his forehead and gets a big bump. That is, if you see that the baby was just hit hard, but the situation does not pose any danger, then simply apply a cold compress to the site of the injury and continue to observe. Keep in mind that the bruise is more dangerous the younger the child. Accordingly, if this is an infant, there is no need to observe - immediately call a doctor at home for a full medical examination.
There are also some alarming signs that parents should not hesitate to visit a pediatrician if they find them:
- At the site of the bruise, not a lump, but a depression appeared.
- The child cries constantly.
- The baby started vomiting and felt sick.
- The baby behaves in a way that is unusual for him: he is too calm or, on the contrary, too irritable.
- The child is very weak, his skin turns white or his lips turn blue, he is drowsy and breathes heavily in his sleep.
- The pupils are different in size, the eyes squint.
- The child hit his forehead, and the lump rapidly increases in size.
- The child lost consciousness (even if it only lasted a few seconds).
- The child has seizures.
- The child is disoriented: speaks with difficulty, is inhibited.
- The child cannot move normally and experiences pain when trying to turn/tilt his head and stand up.
- There is bleeding from the ears and nose.
Symptoms such as these indicate severe brain injury. If you observe any of the above signs, call the children's emergency room. Remember that these symptoms may not appear immediately, but within 24 hours or later after the incident, so do not leave your baby unattended. And for medicinal purposes, the reaction and behavior of the baby after a bruise is more important, and not the bruise itself.
How is the treatment carried out?

In his videos, Dr. Komarovsky says that there is no need to treat a concussion. It is enough to sleep more for 2-3 days and maintain bed rest. But if there are signs of a bruise or swelling of the brain, you cannot do without drug therapy. To relieve an acute condition, droppers and injections are prescribed. After 5-7 days, depending on the child’s condition, they switch to suspensions, syrups, and powders.
Drugs for the treatment of traumatic brain injuries in children:
- Sedatives. They soothe and prolong sleep, which allows the brain to recover faster.
- Antihistamines and diuretics. Prescribed to prevent or eliminate symptoms of cerebral edema.
- Nootropics. Improves microcirculation in brain tissue and promotes restoration of neural connections.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are needed at elevated temperatures.
- Painkillers relieve headaches.
- Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants – prevention of thrombosis.
- Anti-epileptic drugs – necessary for seizures.
Sometimes unloading spinal taps are prescribed to reduce the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid on the brain. In case of severe bruises or compression of the brain, a neurosurgical operation is performed.
Maintaining strict bed rest and prolonged sleep are prerequisites for a speedy recovery after head injuries.
Ear contusion: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
It is easy to injure the ear, since this part of the body is extremely vulnerable: it protrudes strongly above the surface of the head. A significant part of injuries to the auricle - the outer ear - is also accompanied by damage to the middle and inner ear, which can lead to severe hearing impairment.
Causes
Most often, a bruise to the outer ear occurs when a person falls or is hit by another person. A sharp mechanical impact shakes soft tissues and cartilage, damaging small vessels of the organ. Sometimes, when a bruise occurs on the auricle, abrasions and lacerations occur. In this case, treatment under the supervision of an ENT doctor is necessary.
Symptoms of injury
This type of damage can be easily recognized by its characteristic signs:
- the fact of physical impact on the ear;
- redness;
- swelling;
- pain when touched;
- later - the appearance of a bruise on the ear.
First aid
In the first minutes after the injury, apply something cold to the sore ear. At home, a bag of food from the freezer or a piece of ice is suitable for these purposes. Be sure to wrap the cold object in a towel to avoid overcooling your ear. Cold helps to narrow the capillaries in the ear and thereby prevent the formation of a hematoma - a large accumulation of blood in the ear tissue.
If the victim is bothered by pain, you can give him a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Ibuprofen, Ketorolac, etc.).
After the manipulations, it would be a good idea to see a doctor about the injury. This is especially true in cases where the ear has become even redder, or the hematoma is rapidly growing.
Diagnosis and treatment
In case of minor bruises, it is enough to examine an ENT doctor (to exclude possible complications) and follow his instructions. Most often, these prescriptions come down to taking anti-inflammatory drugs for several days. Sometimes external agents are prescribed to speed up healing - ointments with heparin, Troxevasin.
At the first visit, the patient should describe in detail how and what he hit. You should not miss scheduled visits to the clinic, as the doctor must assess how the bruise is progressing during treatment.
If all recommendations are followed, recovery occurs on average 5-7 days from the moment of injury.
Further examination and treatment in a hospital setting is necessary in the following cases:
- The ear hematoma is large, extends to the ear canal, the skin over it is tense and bluish. If the accumulation of blood is not removed in time, this is fraught with complications;
- if infection of the ear tissue is suspected;
- when damage to the structures of the inner or middle ear is possible;
- if you suspect a fracture of the skull bones;
- when blood and cerebrospinal fluid leak out of the ear canal.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor performs an otoscopy (examination of the inner and middle ear); may prescribe an x-ray examination, as well as an MRI. These types of studies will allow us to determine an accurate diagnosis and, accordingly, further treatment tactics.
If there is an otohematoma (hematoma of the auricle), anti-inflammatory therapy, compresses, and physical therapy are prescribed. Spontaneous resorption of the hematoma is also possible. Sometimes they resort to surgical treatment - the accumulation of blood is removed, followed by the prescription of antibiotics.
If the bruise is accompanied by a violation of the anatomical integrity of the organ, rupture of the auricle, reconstructive surgery cannot be avoided.
Consequences and complications
Even the most harmless ear injuries can become a prerequisite for the development of conditions such as:
- decreased hearing acuity up to complete deafness in one ear;
- damage to the vestibular apparatus;
- infectious complications - chronic otitis media, abscess, osteomyelitis of the skull bones;
- from the nervous system - meningitis, encephalitis, neuritis of the auditory or facial nerves, paralysis of the facial muscles;
- sepsis.
Doctors remind: if you have an ear injury, it is better to see a doctor right away and not treat it yourself.
It is necessary to contact an ENT doctor, as well as a neurologist, if the following changes in health occur:
- fever not associated with a respiratory infection;
- changes in hearing (decreased hearing or the appearance of hyperacusis, when even quiet sounds are perceived painfully);
- nausea, dizziness, severe weakness, double vision;
- taking painkillers does not bring relief, the pain becomes stronger;
- the bruise on the ear suddenly changed color and size.
Self-medication in such situations is unacceptable.
The help of a qualified specialist is required. After all, an ear bruise can be accompanied by a concussion, a fracture of the temporal bone or other bones of the skull.
First aid for a child with a blow to the ear. How to act correctly?
Source: https://TravmoVed.com/ushiby/ushib-uha/
What are the dangers of head injuries for a child?
With a traumatic brain injury, brain functions are impaired. Without proper and timely treatment, changes in tissues can be irreversible.
Dangerous consequences of head injuries in children:
- skull fracture, hematoma, internal bleeding;
- neurological disorders - epilepsy, coordination problems;
- retardation in physical and mental development, impaired cognitive functions;
- post-traumatic encephalopathy
- paralysis;
- the consequences of head injuries in infancy can appear at the age of 16, when the formation of the frontal lobes ends, which leads to problems with speech and memory.
The most dangerous consequences are stopping breathing and heartbeat. Pathologies often occur during sleep. Therefore, it is important to monitor the child in the first day after the fall, regularly wake him up, and check his reflexes.
First aid
In the case of only external damage, treatment may be limited to first aid. If the auricle is damaged and there is slight bleeding, it is necessary to treat the damaged area with hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine bigluconate or any other antiseptic.
In case of more significant injuries, the victim must be provided not only with first aid, but also taken to a clinic, emergency room or ENT department of a hospital as soon as possible. If blood comes from the ear canal, it is necessary to insert shallow sterile cotton wool (tampons) inside and then apply a bandage. This will help stop the bleeding and get to the doctor faster.
It is better to provide rest to the victim and under no circumstances should you rinse or clean the ear canal yourself after an ear injury.
After a bruise, the ear swells, what to do in this situation? Often a bluish swelling appears at the site of the bruise due to hemorrhage of the affected vessels. Due to swelling of the tissues in the area of the passage, hearing difficulties may occur, and accumulated air and fluid may also escape from the ear. Cold compresses will help relieve swelling and reduce hematoma (cold exposure can be carried out for no longer than 20 minutes per procedure).
If the auditory organ is severely injured, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible in order to receive professional help, including prompt suturing of the auricle. There are times when a part of the ear is completely torn off.
In this case, it is important to create sterile cold conditions for this part (a container with ice or a dampened cloth) and transport it along with the victim to the hospital as soon as possible. If everything is done correctly and an operation to reattach the severed ear is performed within 10 hours after the incident, the hearing organ will most likely be completely restored.
How to get rid of a lump

If the baby bumps, but there are no dangerous consequences of falling and hitting his head, treatment at home consists of eliminating bumps and bruises. To lubricate the damaged area in a child, heparin ointment or Rescue Balm is suitable.
Folk remedies for treating bumps and scratches on the head:
- Fresh green onion juice has a pronounced absorbent effect. Lubricate the bruised area or make compresses.
- Plantain cures abrasions and shallow scratches well. Mash fresh leaves until juice appears.
- Wormwood quickly relieves pain. Grind fresh leaves, add water until a thick paste is obtained. Apply to hematomas 3-4 times a day.
There are no special rules for preventing head injuries. But to prevent a child at 4-12 months from hitting his head, parents need to think through in advance all the dangerous situations when the baby might bump or fall headfirst. Children who begin to crawl should only be left alone in a playpen with high sides. If the baby begins to walk, you need to remove all carpets and hard objects from the floor, buy special socks with an anti-slip coating, and cover the corners of the furniture with pads. In the toilet and bath, put special rubber mats on the tiles and strengthen the sink well.
Prevention of head injuries in children
Try to do everything possible to make your baby’s time as safe as possible:
- Take care of special pads on the corners of furniture.
- Wash the floors when the child is not at home or is sleeping.
- When there is ice outside, put on special shoes for your child and yourself that will resist falls.
- Get rid of paths in the apartment that can “ride” across the floor, thereby putting your child in danger.
- If your toddler moves around the apartment with the help of a walker, monitor his movements.
- Do not leave your baby unattended on the bed. If you leave the room, it is better to sit him on the floor. At the same time, you need to be absolutely sure that all corners in the room are safe and nothing poses a threat to the child’s health.
- If your child is learning to skate, roller skate or bike, make sure to purchase special equipment, including a helmet.