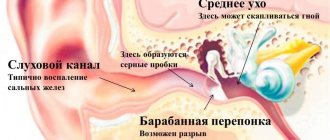
An abscess is a limited accumulation of pus in tissues
A limited accumulation of pus in tissues is called an abscess (abscess or ulcer). It can form in any part of the body, for example, in internal organs, bones, muscles and even in the brain.
Abscesses in a child most often form in the subcutaneous tissue. They are caused by the entry of microbes through various skin lesions.
Formation occurs gradually, as first painful redness of the skin appears, then swelling, and only then the abscess itself.
The causes of abscesses in children can be various factors, but in general it is the ingestion of viruses or bacteria when the integrity of the skin is damaged.
Children most often suffer from abscesses due to scratches, cuts, abrasions, punctures and bruises.
Abscesses appear in children and on the mucous membrane. The consequences of an ingrown nail or bruise of the nail plate when Staphylococcus aureus gets into the wound is an abscess. Flux in case of gum injury is also suppuration. And any suppuration is an abscess.
Treatment strategy for boils in children
A boil develops after the penetration of pyogenic bacteria into the hair follicle. They cause damage to the follicle, sebaceous gland and subcutaneous fat tissue. The causative agents of the disease can be different bacteria. Most often, a boil is formed as a result of the activity of Staphylococcus aureus or white.
Children's skin is not sterile. It constantly contains different types of microorganisms, including pyogenic ones. However, they do not cause the development of pyoderma (pustular disease). The proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms is inhibited by beneficial microflora. The intact stratum corneum and the presence of a positive electrical charge on it do not allow pathogens to penetrate the hair follicles and form lesions. But even if bacteria manage to penetrate into the deeper layers of the epidermis as a result of trauma to the skin, they are destroyed by the cells of the child’s immune system.
Certain conditions are necessary for the development of boils. They are formed when local and general damaging factors appear simultaneously. Local factors include skin injury, a critical decrease in the number of beneficial microflora and destruction of the skin's protective barrier. A common factor that provokes pyoderma is decreased immunity. Overwork (physical and psychological), stress, chronic illness, endocrine disorders and poor nutrition can weaken the child’s body’s defenses.
The goal of boil therapy is to destroy the causative agent of the disease and eliminate factors contributing to the development of pustular disease. If weakened immunity is associated with the presence of concomitant diseases, additional medications are prescribed to treat them. When a decrease in the body's defenses is caused by stress or nervous strain, sedatives are used.
If the factors that provoked the weakening of the child’s immunity are not eliminated, after some time a new boil may form. When ulcers appear regularly, furunculosis is diagnosed. Pyogenic bacteria produce toxic substances that suppress the immune system. Therefore, furunculosis poses a serious danger to the child.
Local therapy for boils at the maturation stage
The sooner treatment is started, the less likely there will be complications. At the ripening stage, the boil is treated with an alcohol solution of salicylic acid (1%), camphor alcohol (2%), aniline dyes (fucorcin, 1% brilliant green, 0.1% potassium permanganate) or hydrogen peroxide (3%). It is necessary to treat not only the abscess itself, but also the skin around it at a distance of several centimeters. If local therapy was started when the first signs of boil formation appeared, it may resolve without reaching the maturation stage.
When several boils appear, external preparations with antibiotics and sulfonamides are used (2% fucidin ointment or cream, 2% mupirocin or bactroban ointment, bacitracin + neomycin, levomekol ointment, heliomycin ointment 4%, lincomycin ointment 2%, gentamicin ointment 0.1% ).
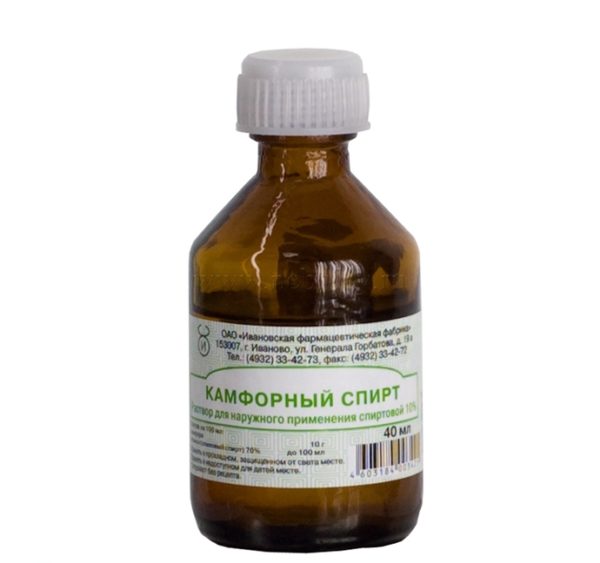

Camphor alcohol is used to treat a boil at the ripening stage
If the development of the purulent process continues, you need to wait until the boil opens. To speed up the maturation of the abscess, some doctors recommend using dry heat. Indeed, warming accelerates the development of the pathological process. But if the heat is excessive, pyogenic bacteria can spread deep into the tissues of the epidermis and beyond. Overheating often causes severe purulent diseases - an abscess or phlegmon. They are characterized by extensive damage to body tissues. Therefore, you should not heat the boil.
You cannot cut or puncture the top of the abscess to speed up its breakthrough. Such actions can cause infection of the affected tissues with other types of pathogenic microorganisms and complicate the pathological process.
Other types of treatment for boils on the arm
Treatment of boils is carried out using ultra-high frequency therapy. It consists of exposing the lesion to high and ultra-high frequency currents (from 10 to 300 MHz). UHF therapy has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, bacteriostatic and immunostimulating effects. To treat a boil, electrodes are placed in close proximity to the affected area. If the boil develops quickly, an athermic dose of UHF therapy is first used. Towards the end of treatment, switch to a subthermal dose. To accelerate the sluggish purulent-inflammatory process, a thermal dose of UHF therapy is used. Procedures are done daily in the morning.

To cure a boil, ultraviolet therapy is used. The mechanism of action of ultraviolet rays is based on the ability of atoms and molecules of skin tissue to absorb light energy. Ultraviolet radiation triggers photochemical processes in the epidermis, accompanied by the release of biologically active substances. Penetrating into the blood, they cause vasodilation and migration of leukocytes to the lesion. Ultraviolet rays have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, trophic-regenerative and analgesic effects. Several sessions of UV therapy can stop the purulent-necrotic process and cause the boil to disappear. At the stage of maturation of the abscess, procedures are carried out after 2-3 days. After opening it, ultraviolet radiation is used to accelerate the rejection of disintegrated tissue. The session is prescribed immediately after the purulent contents are released, then every 3-5 days.
Treatment of the boil after opening
As soon as the abscess matures and opens, its cavity is washed with hydrogen peroxide (3%). To thoroughly treat the inner surface of the boil capsule, you can use a syringe without a needle. Hydrogen peroxide is taken into it and the liquid is released into the wound without touching it. After washing, the cavity is treated with nitrofural (0.1%), an alcohol solution of chlorhexidine (0.5%) or an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine bigluconate (1%). Dioxidine, eucalyptus leaf extract and microcide are used to treat the wound.

After opening, the boil is treated with dioxidine
The wound needs to be treated daily. After each procedure, the bandage must be changed. Squeezing pus out of a boil or trying to remove the rod from it yourself is strictly prohibited. Pressure on the pyogenic capsule can lead to its rupture and spread of infection into the deeper layers of the epidermis. The purulent-necrotic rod is rejected on its own after 1-2 days. Treatment continues until the wound heals completely.
Treatment for dull and brittle hair
At home, without harm to lactation and the health of the mother, you can use the following folk recipes for hair:
- Beer mask.
Accelerates hair growth. Apply the drink to your hair every day, hold for 10 minutes, and rinse thoroughly. After 1-2 weeks, the hair will become noticeably thicker and the hair will be shiny.
- Egg mask.
Take 1 yolk, add a drop of burdock oil and lemon juice to it. Apply on your head for 20 minutes, rinse. Repeat 3-4 times a week for at least a month. Hair will gain strength and shine.
Advertisement
If your hair was not cut or dyed during pregnancy, go to the hairdresser. It is better to shorten long hair or remove only the split ends with a short haircut.
Systemic therapy for boils
If local treatment is ineffective, systemic antibiotics are prescribed. Systemic therapy is used in cases where the axillary or ulnar lymph nodes have enlarged and become painful. Taking antibiotics orally is recommended if very large or multiple boils are detected.
For antibacterial therapy to be successful, drugs that are highly active against boil pathogens are used. If the pathogen cannot be identified, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used.
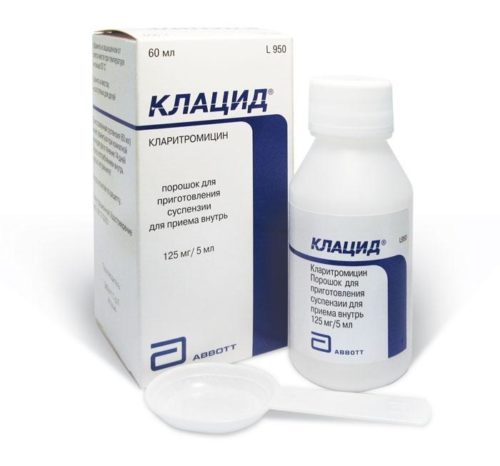
To treat severe forms of boils, antibiotics from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines or cephalosporins are used. Children are prescribed Klacid, Azithromycin, Josamycin, Vilprafen, Unidox - Solutab or Zinnat. Antibiotics come in pharmaceutical forms in the form of a powder for the preparation of a suspension or syrup. Therefore, they are convenient to give to preschool children. The course of treatment usually lasts from 7 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the disease.
Treatment of weakened children is carried out with the help of immunomodulatory agents (Isoprinosine, Taktivin).
Having seen such an abscess on a child’s finger, almost every mother believes that we are talking about a serious inflammatory process, when in fact the fault is an incorrectly done manicure, after which the growing corner of the nail plate digs into the delicate skin of the periungual fold, thereby provoking the formation of a purulent sac.
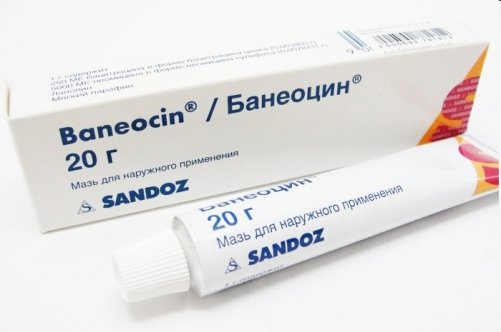
In this case, the abscess near the baby’s nail opens up within a few days, after which recovery occurs, but this does not mean that the process should be left to chance, waiting until the problem resolves itself. The fact is that an abscess on a finger near a baby’s nail can develop into a serious inflammation if it is not treated with antiseptic agents and an alcohol tincture of calendula is best suited for these purposes, which should be used in consultation with the pediatrician. If a purulent sac forms, the doctor may prescribe more serious drugs such as local antibiotics (Bactroban ointment, Baneocin in powder form, etc.), the daily use of which will help draw the pus to the surface within a few days, as well as relieve the inflammation process without any serious consequences for the health of the baby itself. Naturally, during the treatment period, the child’s nail and periungual fold should be covered with a plaster or a sterile gauze bandage, putting scratches on top (special mittens for newborns), so that the baby does not accidentally swallow medications applied to the wound.
In addition, we should not forget about preventive measures, which boil down to proper trimming of nails with the obligatory rounding of the corners of the plate and treating the fingers and the instruments used with a children's antiseptic (alternatively, you can use the same alcohol tincture of calendula). Such simple measures, applied every time the mother gives her baby a manicure, help to avoid infection and the development of an inflammatory process, so neglecting them is strictly contraindicated.
If an abscess on a child’s finger or foot is formed due to the ingrowth of the nail plate, which happens quite often, then it is necessary to carefully trim the corner of the nail that irritates the delicate skin, remove it with tweezers or any other convenient-to-use object and treat the inflamed area with a weak alcohol tincture or peroxide hydrogen or any other antiseptic. If you don’t have anything like that at hand, then it is recommended to wash the inflamed finger with boiled clean water and baby soap, dry it and smear it with brilliant green, using a regular ear stick for these purposes.
Zelenka will dry the wound and neutralize all pathogenic bacteria, and usually after its use the problem goes away within a few days. Things will be much more serious if a purulent panaritium has formed on the child’s finger, usually accompanied by acute pain, severe redness and unnatural swelling. Treatment of this pathology in infants is carried out under the strict supervision of a pediatrician, despite the fact that its local type is relevant only if the disease is in its initial stage. In this situation, the doctor may prescribe daily warm baths with manganese, antiseptic compresses and lotions. Traditional methods of treatment can also be included in the therapeutic complex, but only in agreement with the pediatrician.
In case of progression of the inflammatory process (increase in temperature and worsening of the general symptoms of the pathology), surgical intervention is urgently performed, which involves cleaning the canal formed from pus, its disinfection and antibiotic therapy.

Surgical treatment of boils
If a child has a large boil on his arm that causes severe pain, it is opened. The operation to open the abscess is performed under local anesthesia, so it does not cause pain. The doctor (surgeon) excises the top of the boil and removes the accumulated pus using a syringe or catheter.
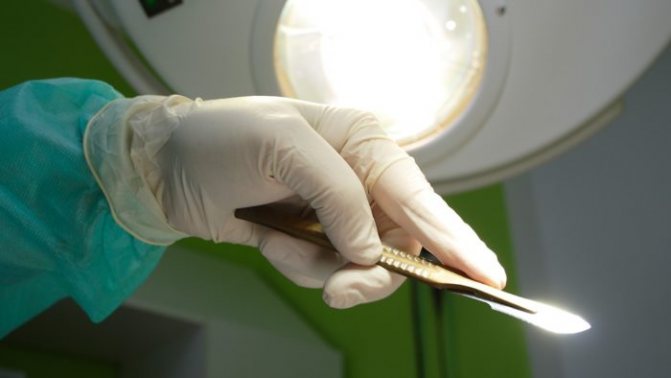
The operation to open the abscess is performed under local anesthesia
The cavity cleared of pus is washed with antiseptic solutions. An antibiotic (Levomycetin) and a rubber strip folded in several layers to drain the wound are injected into it. The rubber strip will not allow the wound to heal until all the pus has drained out. A bandage soaked in hypertonic sodium chloride solution is applied to the wound. A hypertonic solution will help the cavity quickly get rid of purulent-necrotic contents.
When the cavity is clean, the rubber strip is removed. A bandage with Vishnevsky ointment is applied to the wound. The surgeon initially treats the wound and bandages daily, and when the cavity is cleared, after 2-3 days.
How are abscesses treated?
To treat an abscess, you must contact a surgeon.
When abscesses in children have already formed, you need to contact a surgeon, and here home remedies will no longer help.
The abscess must be opened, the pus removed and antiseptic dressings applied until the wound heals. Moreover, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to stop the inflammatory process.
But in the initial stages of abscess formation, you can use home remedies and try not to bring the disease to surgical intervention. First of all, try not to overcool the abscess; it may harden, and then you will definitely need to open it.
Aloe leaf softens and draws out pus well. Just cut it and bandage it to the abscess with the pulp inside. Change the bandage every 2-3 hours.
Another folk remedy for drawing out pus is a mixture of grated laundry soap and baked onions. The mixture is applied to the site of inflammation. Change every 4 hours.
There is a treatment with honey. In this case, a mixture of honey, alcohol and Vishnevsky ointment is made, applied as a bandage to the inflammation and left for 12 hours. Using this method, the abscess disappears in 2-3 days.
You can use proven medications, such as Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment or Levomikol ointment. You can use the drug Silica, which will help the abscess to mature.
It is imperative to keep the site of inflammation clean, so you should periodically treat it with a solution of potassium permanganate, furatsilin or chlorhexidine. These drugs will not cause discomfort or pain, unlike alcohol-containing products.
Only a doctor can prescribe medication. Antibiotics may be used if complications arise.
Laser therapy for boils
The operation to open the boil can be performed using a laser. Laser therapy is prescribed for children from 6 years of age. Excision of the lesion occurs under the influence of a focused beam of electromagnetic waves of a certain spectrum, which are emitted by a laser. The laser beam quickly heats the intercellular and intracellular fluid of tissues, causing it to boil. During the process of vaporization, tissue cells are destroyed.
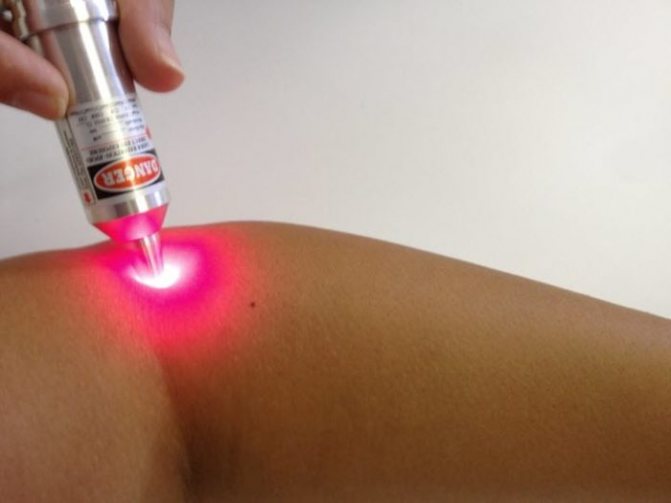
Laser therapy for boils
A directed, focused beam of waves allows you to make a perfectly even cut. Tissue dissection is accompanied by sealing of blood vessels, so the operation is bloodless and practically does not cause tissue swelling. After laser opening of the boil, healing occurs much faster than after excision of the abscess with a scalpel. Since the laser does not come into contact with the skin, the chance of infection during surgery is zero.
Opening the abscess and removing the purulent-necrotic core occurs painlessly in 5-15 minutes. After the operation, the wound is washed with an antiseptic and a bandage is applied.
Sick child mode
Since a sick child has a weakened immune system, it is necessary to avoid injuring healthy areas of the skin. In people with pustular skin diseases, the composition of the bacterial flora changes not only in the area of the lesions, but also in areas of the body remote from them. Pyogenic bacteria that caused the appearance of a boil quickly spread over the entire surface of the skin of a sick child. They can cause the appearance of new pathological foci.
Healthy skin should be kept clean and washed regularly. Particular attention should be paid to skin folds. They contain the most pathogenic microorganisms. The boil itself and the skin around it should not be wetted. When taking a shower, you need to cover your hand with waterproof material so that water does not accidentally get on the boil. It is not recommended to give your child a bath. If he is in hot water, his body will overheat. Overheating will also occur in the affected area, even if the child’s hand is not immersed in water. Cold water can cause hypothermia in the body and weaken its defenses.

Baby's healthy skin should be kept clean and washed regularly
In order not to cause the spread of infection, you need to cut the baby’s fingernails short until it is completely cured. In addition to skin folds, pathogenic bacteria are found in large numbers in the subungual spaces. It is recommended to treat them daily with an alcohol solution of iodine (2%). To prevent the child from touching the boil with his hands, the abscess must be covered with a bandage.
It is necessary to pay attention to the patient's nutrition. It should be complete, regular, rich in vitamins and microelements. It is necessary to exclude sweets, cakes, pastries and other confectionery products from the baby’s menu. It is also recommended to limit salt intake. Staphylococci reproduce well in sweet and salty environments.
Ways to solve problems with nails, hair and skin after childbirth
If your appearance after childbirth upsets you, take the following general steps to improve your health:
- Take vitamins as prescribed by your pediatrician or gynecologist.
Self-prescription of dietary supplements is not recommended, especially during lactation .
- Eat right and regularly.
Eat more fruits and vegetables, meat, drink milk.
- Drink plenty of clean water.
This helps improve lactation and remove toxins.
- Get enough sleep.
This is difficult to do if the baby is restless, but you can entrust the baby to the father or grandmother once a day to rest for a while.
- Spend more time outside.
This is beneficial for mother and baby.
- Use protective equipment when your skin comes into contact with water and aggressive environments.
These are hand gloves, water-repellent creams (silicone based).
And, of course, use cosmetics to care for your skin and nails. You don’t have to go to a salon or buy expensive cosmetics; grandma’s recipes are more than enough.
Precautionary measures
It is not recommended to independently treat multiple and large boils in children. Antibiotics and sulfa drugs can only be used after consultation with a doctor and under his supervision. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor if the boil quickly increases in size, causes severe pain and an increase in body temperature to 38°C or higher.

Boils in children are best treated under the close supervision of a physician.
A doctor's consultation is necessary when treatment of a boil is ineffective. Warning signs include enlarged and painful lymph nodes. Surgical opening of the boil is necessary if a bubble with purulent contents does not form at its top. This sign may indicate the development of an abscess or phlegmon.
Causes of abscesses in children
This disease can be harmless, or it can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, it is better not to hope for “maybe”, but to consult a doctor in a timely manner for help.
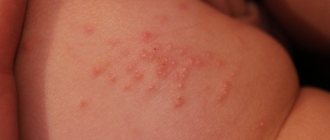
External symptoms of an abscess
- redness in the area of suppuration
- dense swelling of the tissue around the abscess
- obvious presence of pus
The initial stage of abscess development is the most painful process. At this time, severe pain, twitching spasms, accumulation of pus and the release of ichor are felt.
Suppuration is provoked by the body itself, as this is done to remove negative substances and to reject foreign bodies.
During the formation of an abscess capsule, the child may experience an increase in body temperature, fatigue, and nervousness.
Read: Signs of bronchial asthma in a child, how to recognize? Effective treatment and diagnosis