Tracheitis - etiology
Infectious tracheitis is caused by the same pathogens that lead to the development of pharyngitis, laryngitis and rhinitis: streptococci, staphylococci. If these diseases are not treated (or treated incorrectly), the inflammatory process can spread to the trachea. Tracheitis can be acute or chronic.
There is also a non-infectious form of tracheitis, which develops as a result of hypothermia of the upper respiratory tract or the harmful effects of chemical suspensions, dust, and steam.
The development of tracheitis may be influenced by the following factors:
- inflammatory processes in the nasal passages and nasopharynx;
- smoking tobacco;
- regular inhalation of toxic substances;
- frequent hypothermia;
- chronic respiratory diseases;
- Constantly breathing in air that is too hot or too cold.
Tracheitis in children: 5 main symptoms and a review of 7 principles of treatment from a pediatrician
According to Dr. Komarovsky, tracheitis is caused by a virus or bacteria that affects the respiratory tract. First, they are localized in the larynx and nasopharynx, and then descend into the trachea. The causes of the disease are pathogenic organisms, but Dr. Komarovsky identifies certain risk factors that provoke it:
- constant contact with the allergen;
- hypothermia;
- poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency;
- mechanical injuries of the respiratory system;
- unfavorable environment, air pollution;
- passive smoking.
In order to cure tracheitis in time, Komarovsky advises monitoring the child when the first symptoms appear. The main symptom of the disease is a sudden paroxysmal cough. It can be caused by laughter, crying or simply cold air. Other symptoms that help prevent a cough, which mainly occurs at night:
- hoarseness of voice;
- sneezing;
- temperature increase;
- chest pain.
Komarovsky also identifies the following signs of tracheitis in a child:
From the nervous system:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- moodiness;
- tearfulness;
- loss of appetite.
The most important for treatment are the first three days. If you ignore the symptoms and let the disease take its course, tracheitis becomes chronic.
Treatment of tracheitis in children according to Komarovsky
As Dr. Komarovsky says, the treatment of tracheitis in children is to ensure the correct regimen. Antibacterial drugs are used only in very severe cases of the disease. The body can overcome a viral infection on its own without the help of medications. If the doctor detects the presence of bacteria, then special medications are prescribed. When medications are needed:
- For the bacteriological form of the disease, antibiotics are prescribed;
- Atypical clinical signs - no fever or weakness. Typically, this is how allergic tracheitis occurs.
If the doctor has diagnosed viral tracheitis, all that is needed is bed rest, fasting and the correct microclimate in the room. Also the main task is to eliminate cough.
What is required from parents:
- Ensuring the correct microclimate in the room: temperature 20-22 ° C, air humidity from 50 to 70%, regular ventilation. To humidify the air, it is recommended to purchase a special preparation. If this is not possible, then you can hang wet towels in the room or put a bowl of water.
- Do wet cleaning daily to prevent dust particles from entering the respiratory system.
- If there is no fever, it is advisable to take warm medicinal baths. The procedure stops the inflammatory process and moisturizes the mucous membrane.
- Maintaining bed rest. But the baby should not lie in bed around the clock. A short nap at lunchtime and rest during the day is enough. In general, the child needs to change position frequently.
Often tracheitis occurs against the background of other diseases, such as nasopharyngitis or laryngitis. In such cases, treatment is complex.
Drugs
The main task of treating tracheitis in a child, according to Komarovsky, is to transform a non-productive cough into a productive one. In some cases, not only the trachea, but also the bronchi are affected, then the disease develops into tracheobronchitis. The symptoms of this disease are almost identical, but it carries a threat in the form of pneumonia and laryngeal edema.
What medications does the doctor prescribe:
- Centrally acting antitussives. They reduce the excitability of the cough center and temporarily stop attacks: Pertussin, Gerbion, Bronholitin, Gedelix.
- Antitussives with expectorant effect: Sinekod, Stoptusin, Linex, Libexin.
- Expectorants soften sputum and remove it from the respiratory tract: ACC, Althea, Codelac Broncho, Lazolvan, Ascoril.
- Antihistamines to reduce swelling: Claritin, Erius.
- Antipyretics: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol.
- Immunomodulators: Nazoferon, Immunal.
Although Dr. Komarovsky believes that expectorants are needed only for bronchitis and pneumonia. These medications only worsen the cough, activating the production of sputum. The body can turn a dry cough into a wet one if the following conditions are present:
- clean, cool and humid air;
- drinking plenty of fluids.
Compliance with these points will ensure a quick recovery. Otherwise, tracheitis may develop into a bacteriological form, which requires antibiotics.
If your child's symptoms become more severe, this is a sign that the bacteria is present. Only a doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial drugs, which lasts from 3 to 7 days.
Changing the dose or duration of therapy is strictly prohibited. Which drugs are most effective:
- Augmentin;
- Flemoclav;
- Amoxicillin;
- Amoxiclav.
This is a group of penicillins. If the patient has individual intolerance, macrolides are prescribed:
- Clarithromycin;
- Azithromycin.
In severe cases, cephalosporins are prescribed:
- Ceftriaxone;
- Suprax;
- Cefazolin.
It is advisable to take antibiotics at the same time, without interruption. If there is no improvement within 3-4 days, this indicates that the bacterium is immune to this medicine and needs to be replaced.
Herbs against tracheitis
How to treat tracheitis in a child? As Dr. Komarovsky advises, the use of herbal therapy will be very useful. What they use:
- rinsing;
- compresses;
- bathing with essential oils;
- rubbing;
- decoctions of medicinal herbs.
If the baby does not know how to gargle, he should be given a lot and often to drink:
- chamomile and linden tea;
- milk with honey and butter;
- fruit drinks and compotes.
Which herbal decoctions give good results in treating cough:
- chamomile;
- coltsfoot;
- marshmallow;
- ivy;
- liquorice root.
Here are some useful recipes:
- Pour boiling water (half a liter) over two tablespoons of blackberry leaves. Cover with a lid and leave for an hour. Then strain. Use as tea.
- Pour 15 pine buds with hot water (2 cups) and cook over low heat. Leave to infuse, strain. Take the decoction warm, a spoonful 4-5 times a day.
- Pour boiling water (150 ml) over 2-3 tablespoons of thyme and leave for an hour. Consume no more than a glass of decoction per day; it is better to divide it into several doses.
- Pour a tablespoon of mallow into two glasses of boiling water. Cover and wait 2 hours. It is advisable to drink the decoction during the day.
Other folk methods will also help eliminate cough:
- Black radish juice. Make a hole in the vegetable and pour honey into it. Leave for several hours. The juice that has begun to secrete should be drunk three times a day, one teaspoon at a time.
- Make sugar syrup and mix with freshly squeezed carrot juice. Drink warm three times a day, one spoon.
- Pour a spoonful of dry and crushed plantain into a cup of boiling water. After 2 hours, strain and drink a spoon three times a day.
- Honey (5 grams) + anise seeds (30 grams) + salt (2 grams). Mix all ingredients thoroughly, add water and bring to a boil. Strain. Drink a teaspoon twice a day.
If the child is already big and can gargle, herbal decoctions will also be very useful. Although, according to Dr. Komarovsky, all these procedures are additional means that only help strengthen the immune system. The child’s body will be able to destroy the virus on its own.
Inhalations
Inhalations will help eliminate symptoms and strengthen the main course of treatment. It is advisable to use a nebulizer; if you don’t have one, you can breathe over the steam. Important! Inhalations should not be carried out at elevated temperatures.
Treatments with essential oils give good results:
- eucalyptus;
- cypress;
- tea tree;
- cedar;
- fir;
- pine;
- lemon.
But first the patient should be tested for an allergic reaction. For example, in young children, obstruction may occur immediately. For dry coughs, eucalyptus, lemon, mint and anise oils will give the best results.
They can be used as a single ingredient and in compositions. Herbal decoctions are also used for inhalation. Chamomile or eucalyptus is used as a base. Herbs cannot be used in a nebulizer; it is better to purchase a steam inhaler.
What herbs are effective for tracheitis:
- raspberry leaves;
- St. John's wort;
- coltsfoot;
- calendula;
- fir;
- mint.
Parents often use an ancient folk method - breathing over potato vapor. Potatoes should be boiled in their skins until a characteristic smell appears. The duration of the procedure is up to 10 minutes.
The following pharmaceutical preparations are used as a medicine for the nebulizer:
- Ambrobene;
- Rotokan;
- Berodual;
- Interferon;
- saline solution
But Dr. Komarovsky himself considers the nebulizer to be an ineffective drug. As the doctor says, it is effective only in case of lung diseases.
The drug can provoke the spread of infection from the upper respiratory tract to the lower and, as a result, relapse of the disease. And breathing above the fumes is dangerous for small children.
The steam increases the size of sputum, which can cause bronchospasm.
Other means
Tracheitis is a disease that can be treated with heat. But it is important to remember that thermal procedures cannot be carried out if there is a high temperature. Application of compresses and rubbing is recommended only after consultation with a doctor. Products used for rubbing:
- Doctor Mom;
- Star;
- badger fat;
- a solution of apple cider vinegar and water.
You should first make sure that the little patient is not allergic to these drugs. Then you can treat the front and back of the sore area and feet. It is recommended to do massage with honey.
Warm compresses will be helpful. What products are recommended to be used to prepare compresses:
- goose fat;
- potato;
- vodka or diluted alcohol;
- essential oils;
- mustard.
You can pour dry mustard directly into your socks and go to bed to warm up. There may be a slight burning sensation. Foot baths with mustard will also be useful.
One of the remedies for treating tracheitis is propolis. It can be chewed in its pure form or used as an inhalant. Other folk recipes that help in therapy:
- Wash the black radish thoroughly, peel and cut. Add sugar and bake in the oven for two hours. The resulting liquid should be drained and taken twice a day, one teaspoon.
- Put the milk to boil and throw in a few figs. Drink one glass before bed.
- Pour boiling water over dried viburnum berries and boil. Another way is to cover the viburnum berries with sugar (in layers) and leave for several days. Dilute the resulting juice with water and drink it as tea.
It is important that the baby drinks a lot. This can be ordinary filtered water, weak tea, compotes.
Tracheitis in a child - Komarovsky recommends
Dr. Komarovsky always encourages parents to listen to common sense. Vivid advertising of medicines is not always a guarantee of their effectiveness and quality.
To begin with, you should not panic and stuff your child with all available means. If parents notice the symptoms in time, treatment of tracheitis will be successful.
What Dr. Komarovsky advises parents to do at the first signs of illness:
- Give the child warm tea, milk with soda or Borjomi water.
- ensure peace, control physical activity;
- monitor the cleanliness and humidity of the air and room.
If there is no fever or loss of appetite, no antibiotics or antivirals are required. The above mentioned treatments will be sufficient. If the temperature rises and the baby begins to act up, you should visit a doctor. These signs may also indicate a more serious pathology:
At the first symptoms of viral tracheitis, you need to boost your immunity. Immunomodulators, vitamins and proper nutrition will help with this.
Prevention
You need to strengthen your immune system from birth. Mother's milk helps babies with this. Over time, the child can be accustomed to hardening. Other preventive measures:
- healthy eating;
- daily walks;
- physical activity;
- drink enough water;
- good sleep;
- hardening;
- timely treatment of colds.
The family atmosphere is also very important. Quarrels and conflicts are the cause of stress, which leaves its mark on the state of the body.
The baby should be dressed according to the season, avoid hypothermia and vice versa. If you have any chronic diseases, you need to regularly visit a doctor and undergo a routine examination. Oral hygiene and healthy teeth are another factor in preventing respiratory diseases, including tracheitis.
During epidemics, you should avoid large gatherings of people, do not go to the market and shops with your baby, and reduce the number of trips in minibuses. A vacation at sea or in a medical sanatorium will help improve your body’s health.
Source:
Causes of the disease in children
Most often, tracheitis occurs against the background of respiratory diseases that were not treated in a timely manner. This respiratory tract pathology is most common in young children (from six months to 3 years). This is due to the immune system not being fully formed and lack of contact with viruses (in particular, the influenza virus) in the past.
Treatment of tracheitis of infectious origin is complicated by the fact that the child’s body has already been weakened by an untreated disease. Therefore, during flu epidemics, it is important to closely monitor your health and get the vaccinations recommended by doctors.
Tracheitis in a child: how to properly treat the disease, what methods are used for children
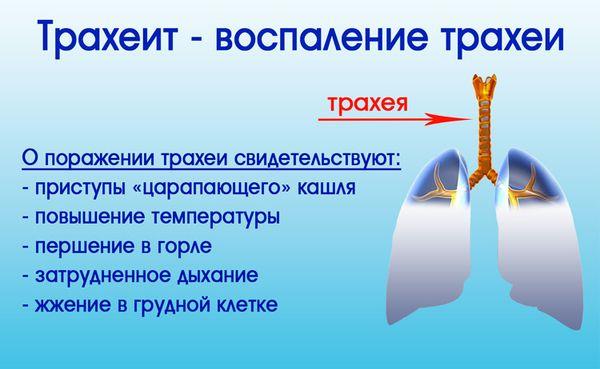
Tracheitis is a disease from the group of acute respiratory diseases. It can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. The diagnosis is made when the inflammatory process is localized in the tracheal area.
What is tracheitis
Tracheitis is an acute inflammation of the tracheal mucosa. In a child, this pathology often complements laryngitis, bronchitis and other acute respiratory infections. In such a situation, the diagnosis sounds like tracheobronchitis, tracheolaryngitis, rhinotracheitis, rhinopharyngotracheitis, etc. The course of the disease brings a lot of discomfort to the baby’s life.
But if the lesion is detected in a timely manner and proper treatment is organized, the disease ends quickly and without consequences. It is believed that tracheitis most often affects children at an older age - after 5 years. In a child under 5 years of age, as a rule, inflammation spreads to all upper organs of the respiratory system.
The symptoms of tracheitis are similar to rhinitis, bronchitis and pharyngitis; frequent attacks of unproductive obsessive coughing occur.
Classification of pathology
Tracheitis in a child usually becomes a consequence of the process of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract and occurs as a descending infection.
The pathology is less often isolated and is often combined with rhinitis, sore throat, laryngitis and other diseases of the respiratory system. In groups of children, the disease develops in outbreaks during the cold season - usually in autumn and spring.
In addition to influenza viruses, the causes of infection include measles, whooping cough, and, less commonly, typhus.
Tracheitis is an infectious disease that affects the internal mucosa of the trachea. The pathology is contagious and transmitted by airborne droplets. According to the course of tracheitis, it is classified into 2 types:
- acute – accompanied by a barking, sharp cough;
- chronic - develops as a result of frequent acute lesions of the trachea.
The chronic form can develop according to the atrophic or hypertrophic type. Hypertrophic tracheitis is characterized by thickening and proliferation of the mucosa.
With atrophic laryngitis, the mucous membrane gradually becomes thinner and even disappears in some areas.
Acute damage in addition to viruses and bacteria can provoke hypersensitivity.
Antihistamines are prescribed for therapy.
Symptoms
When the trachea becomes inflamed, receptors and viruses are irritated. In this regard, a severe cough of a non-productive nature develops. It provokes pain and a decrease in the timbre of the voice.
The disease begins with a common sore throat and frequent coughing. Then the coughing becomes obsessive and noticeably intensifies.
Typically, attacks occur in the morning and at night, and then the child complains of pain in the chest.
Symptoms of tracheitis in a child are:
- when coughing, sputum does not come out, or the way out is minimal;
- temperature rises;
- hoarseness and hoarseness appear, rhinitis develops;
- Chest pain and headache occur.
It is prohibited to take any measures on your own to treat tracheal diseases. There are many similar diseases, but their treatment is different. Lost time will worsen health problems. Symptoms and treatment of tracheitis in children can only be determined by a doctor. He will choose treatment methods and prescribe the necessary medications.
Organization of treatment
Treatment of symptoms of tracheitis should be comprehensive. Many body functions are weakened due to illness, and exhaustion occurs due to a painful cough. The acute form of tracheitis, if diagnosed in a timely manner, responds well to treatment. Complex therapy includes several stages that answer the question of how to treat tracheitis in a child:
- Mandatory plenty of warm drinks - tea with rose hips, lemon, a variety of fruit drinks, etc.
- Organization of distracting procedures - compresses, mustard plasters, rubbing.
- Inhalations – for safety reasons, it is recommended to carry out procedures using a nebulizer.
- Drug treatment with expectorants and antibiotics as needed.
- Maintaining normal humidity in the room, air temperature - optimally 20 degrees.
- Organization of daily wet cleaning.
- Refusal to use any irritating fragrances; it is also necessary to ensure that tobacco smoke does not penetrate into the room.
- It is forbidden to strain the ligaments - talk, cry, etc.
Inhalations and any distracting procedures can only be carried out with the permission of a doctor. If implemented incorrectly, they provoke an attack of croup.
Tracheitis requires urgent treatment, especially with coughing attacks at night. In a child’s body, the inflammatory process quickly penetrates the lungs, causing pneumonia.
If all the rules established by the doctor are followed, complete recovery occurs in 1–2 weeks.
Features of treatment of tracheitis in children
There are some features of how to treat tracheitis in children:
- Antitussives should be given only in the form of syrups.
- From the very beginning of infection, it is recommended to carry out antiviral therapy with Viferon, Interferon or Arbidol.
- In rare cases, but antibiotics may still be required, children with tracheitis are most often prescribed Sumamed, which is produced in the form of a suspension.
- To stop the process of inflammation in the larynx and trachea, inhalations with a nebulizer are required.
- If the temperature is normal, then therapy can be supplemented with heating of the trachea and upper part of the bronchi, rubbing and compresses.
- Additionally, it is necessary to strengthen the baby’s immunity so that he can cope with the pathology faster - for this, the doctor prescribes immunomodulators, vitamins and herbal medicine.
If tracheitis is diagnosed in an infant, then therapy is carried out under the supervision of a specialist in a hospital.
Treatment tactics for different forms
Approaches to how to treat tracheitis of viral and bacterial origin in a child may differ slightly. It is important to visit a doctor to clarify the diagnosis and the nature of the developing pathology.
Bacterial
Bacterial tracheitis, as a rule, is a secondary lesion; they develop with a long-term weakened state of the baby’s immunity.
In such a situation, it is necessary to use antibacterial agents, the minimum course of which is 3 to 5 days. Only a doctor should select a specific drug.
During antibiotic therapy, it is permissible to simultaneously give probiotics in order to maintain the normal functioning of the digestive organs - these are Creon, Bifiform, Linex, etc.
Allergic
Allergic tracheitis in a child is characterized by an atypical clinical picture - often the condition is not accompanied by high fever.
Pathology must be treated by eliminating the irritant and taking antihistamines.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes immunity-supporting therapy - nutritious nutrition, frequent walks, a favorable psychological atmosphere.
Viral
Viral tracheitis is primary, occurs actively, is accompanied by high fever, lethargy and irritability. The body, as a rule, resists viruses itself, which is expressed in increased temperature and prolonged sleep. Parents will be required to follow simple rules:
- maintaining the air humidity level at no less than 60%;
- maintaining cleanliness in the premises;
- frequent ventilation;
- bathing the child, provided that the temperature is normal, and changing underwear and bed linen every day.
Medicines for tracheitis
Any antibiotics for tracheitis and the need for their use should be determined by a doctor. As a rule, children with bacterial infections benefit from broad-spectrum drugs at a dosage of 20–40 mg per 1 kg of weight. Treatment is carried out for 2 weeks.
For children under 12 years of age, the dosage is increased to 30–70 mg per 1 kg of weight. The main rule is not to cause harm with antibacterial agents and use them only when really necessary.
In addition to antibacterial drugs, therapy with expectorants and antiseptics is carried out:
- In case of viral infection - children's Viferon, Kagocel, Grippferon.
- To relieve a painful non-productive cough - chest mixture, licorice root syrup, Stoptussin - these drugs will help transform the cough into a wet one.
- ACC, Ambrobene and Lazolvan - will help thin the mucus during a wet cough and make it easier to clear.
- To normalize the temperature, Nurofen in syrup or suppositories and Paracetamol are used.
- Rinsing with sea water Aqualor, Aquamaris will help with rhinitis, they are allowed even for infants. If congestion is severe, your doctor may prescribe vasoconstrictor drops, especially before bed.
- Taking multivitamins and ascorbic acid will eliminate fatigue and improve immunity.
Inhalation procedures
Another effective way to treat children with tracheitis is inhalation of medicinal vapors. It is best to carry out the procedure using a nebulizer. It breaks down the drug into microscopic particles, which then quickly penetrate into the places where inflammation is localized.
Inhalation allows you to deliver the medicine directly to the lesion, bypassing the esophagus. This approach significantly improves the treatment outcome. Herbal medicinal decoctions, saline solution, Miramistin, Chlorophyllipt, Lazolvan, Ambrobene, Derinat are used as medicinal solutions.
So, any form of tracheitis can be treated if the parents noticed a violation of the child’s condition in time and consulted a doctor. After recovery, you should be attentive to the baby’s health, because even a common cold can develop into a new inflammation of the trachea.
Parents should maintain a friendly atmosphere in the house, walk with their child more often and properly organize his diet. In this case, the risks of infection are minimized.
You can find even more useful articles about ENT diseases on the website https://lor-uhogorlonos.ru/
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/59f9a0235a104fe1e0d6eaf6/5b14d9889b403ce2e4f20f57
Classification of tracheitis
Experts distinguish two main forms of the disease: acute and chronic. Sometimes an allergic form of tracheitis is also identified, the development of which is caused by a reaction to various irritants. Children living in environmentally unfavorable areas are at risk.
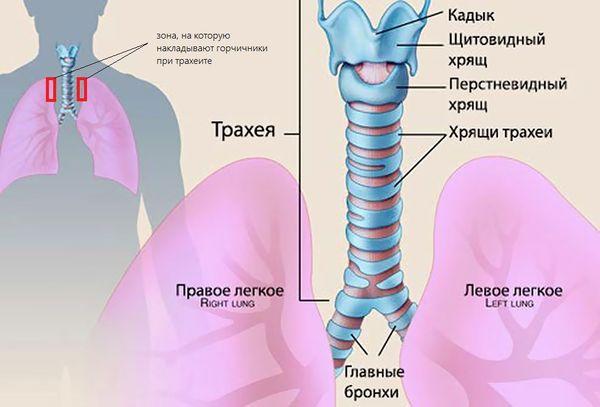
Spicy
The most common cause of acute tracheitis is a bacterial or viral infection. There are secondary reasons that can affect the penetration of infection into the child’s body:
- general or local hypothermia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- low air humidity in the room;
- regular inhalation of tobacco smoke;
- unfavorable environmental situation.
Chronic
The chronic form of tracheitis develops against the background of prolonged respiratory diseases, the prolonged treatment of which has not yielded results. Often it becomes a consequence of inflammation of the bronchi if the inflammatory process spreads to the trachea (the disease is called tracheobronchitis). The following factors may influence the appearance of chronic tracheitis:
- chronic forms of tonsillitis, rhinitis;
- passive smoking;
- caries not cured in time;
- adenoids.

Causes
The main reasons for the development of acute tracheitis among children is the aggressive influence of viruses or bacteria. Most often, the pathological process is provoked by influenza viruses, pneumococci and very rarely staphylococci.
- An acute form of tracheitis can occur as a result of increased dry air in the room where the baby is present, severe hypothermia, allergic reactions and some cardiac diseases. Poor ecology has a negative impact, as does the child’s presence near people who smoke.
- Chronic tracheitis is provoked by untreated (or late diagnosed) respiratory infections, as well as a combination of inflammatory processes developing in the bronchi. In addition, adenoiditis, carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis and passive smoking can lead to the disease.
- For the development of an allergic form of tracheitis, the presence of external or internal irritants is necessary, which are perceived by the immune system as a foreign protein.
Most often, allergic tracheitis is provoked by pet hair, dust mites, food, or taking certain medications.
Symptoms of tracheitis in a child
The main symptom is a dry cough, attacks of which become more pronounced at night and in the morning. The following signs of the disease are also identified:
- disturbance of normal breathing, shortness of breath, oxygen deficiency;
- increased body temperature;
- change or complete loss of voice;
- burning and pain in the sternum;
- characteristic noises when inhaling;
- loss of appetite;
- regular headaches;
- gagging during severe coughing attacks;
- childhood weakness, deterioration of health, exhaustion of the body.
If a child suffers from attacks of dry cough, this may indicate the presence of tracheitis, but only a doctor can confidently diagnose this disease.
Baby
Clinical manifestations of tracheitis in infants require special attention, since the baby is not yet able to independently report his feelings. This disease occurs even in the youngest children, who are from 1-2 months to 1 year, and can be recognized by shallow breathing and low muffled sounds. In some cases, an increase in body temperature is observed. The cough reflex develops only by 5 months, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult.
From 1 to 4 years
A one-year-old child already has a cough, but it is characterized by unproductivity and poor sputum production. Children who are 3 years old also cough unproductively, since their respiratory system is not yet fully developed. Attacks most often occur at night.
From 5 and older
In children over 5 years of age, hypersecretion predominates, due to which cough with tracheitis quickly transforms from dry to wet. At the age of 12, the disease often progresses without fever.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of each type of disease are different, but all of them have a number of characteristic symptoms:
- A dry cough, which after 3-4 days turns into a wet cough, with the release of a small amount of mucous sputum. The average duration of this condition is 10-14 days.
- Pain behind the sternum that occurs during a coughing attack and persists after it.
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels.
- Signs of intoxication - headache, irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbance.
- Symptoms of concomitant diseases are sneezing, nasal congestion and runny nose with rhinitis, sore throat with pharyngitis, conjunctivitis with allergies.
It is not difficult to recognize tracheitis, but you should not make this diagnosis yourself and self-medicate.
The doctor diagnoses the disease and prescribes appropriate medications based on complaints, examination and laboratory test data. A cough can be a sign not only of inflammation of the tracheal mucosa, but also of other conditions, including quite serious ones.
Diagnostic methods
Cough is quite common, but dangerous for a child, so if it appears, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. Self-medication in this case is contraindicated, since identifying the symptoms of tracheitis at home is not always possible, and delaying therapy can lead to complications.
See also
What to do if your throat hurts for a long time and does not go away without fever and nothing helps
Read

Characteristic of tracheitis is the gradual development of a coughing attack: first the child feels a sore throat, then a slight cough appears, and only after that it develops into a severe attack. Sputum is poorly separated and has an excessively viscous consistency. Cough - croaking or barking, causing severe discomfort or pain in the chest area.
To obtain a clearer picture, the following types of diagnostic studies are carried out:
- endoscopy;
- blood analysis;
- laryngotracheoscopy;
- X-ray of respiratory organs;
- bacteriological analysis of material from the child’s nose and throat.
What tests and examinations are needed for tracheitis?
At the first signs of pathology, parents turn to the treating pediatrician, who, based on the clinical picture, makes a preliminary conclusion and refers them for consultation to specialized specialists. A qualified pediatric otolaryngologist or pulmonologist can diagnose and prescribe appropriate therapy for a child.
At the initial appointment, the doctor asks the parents about the manifestations of the disease in the child, how long ago and how severe, in their opinion, the inflammatory process of the trachea has been occurring. What symptoms bother the little patient most often, at what time of day.
Next, a visual inspection is carried out. The color of the skin is assessed; if the functioning of the respiratory organs is impaired, the skin may have a grayish color. The patient's chest must be palpated. Swelling or its absence in the area of the lymph nodes is assessed.
Experienced doctors from the first minutes of examination pay special attention to the baby’s nasal breathing. Sometimes the doctor detects a runny nose, which occurs in combination with tracheitis.
After a visual examination, an instrumental examination of the throat is carried out using a spatula and the chest with a phonendoscope. Thanks to the instruments, the doctor is able to see redness in the oropharynx area, which indicates concomitant pharyngitis. During auscultation, breathing is heard, wheezing and its characteristics are determined.
Additionally, young patients are referred for laboratory tests:
- General blood analysis.
- Chest X-ray.
- Endoscopic examinations are practiced: laryngotracheoscopy, tracheobronchoscopy.
- Parents are recommended to take a swab from the nose and throat (bacteriological examination) to identify pathogens and their resistance to certain antibacterial drugs.
- Culture and bacteriological examination of sputum.
In case of severe disease or in case of doubt about the diagnosis, otolaryngologists refer young patients for consultation with colleagues (allergists, immunologists, pulmonologists) with a narrow profile.
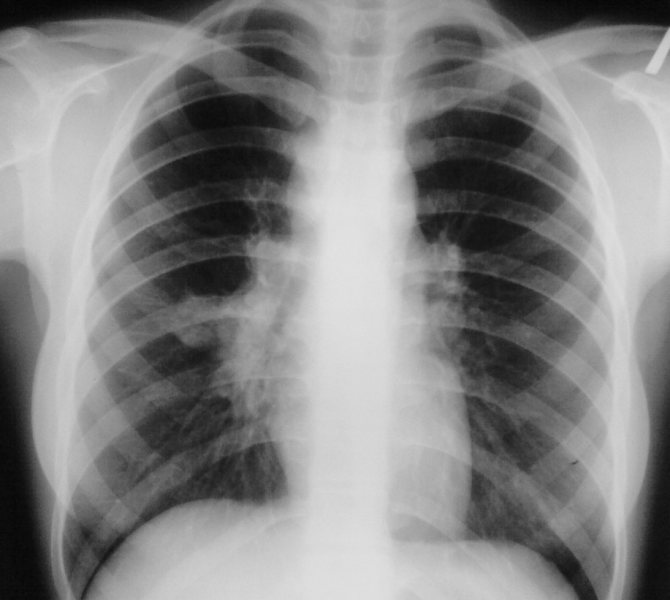
Chest X-ray.
Treatment of tracheitis in children
Tracheitis must be treated under the supervision of a pediatrician. If there are complications, you may need the help of a pulmonologist who treats diseases of the lungs and respiratory tract. Therapy for tracheitis includes medicinal and non-medicinal methods, the effective combination of which can quickly cope with the disease and alleviate the child’s condition. For example, to get rid of a dry cough, you can use electrophoresis procedures in parallel with inhalations and mucolytic agents.

Medications
Therapy for tracheitis depends on the nature of the disease. Tracheitis, which has a viral etiology, is treated with antiviral drugs suitable for children. The dosage regimen is prescribed by the treating pediatrician, and the main effect of the medications is aimed at eliminating concomitant diseases.
If the disease is bacterial in nature or signs of bronchitis are observed, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. The most commonly used topical antibiotics are for the nose and throat. Taking antibiotics is considered justified in case of exacerbation of tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media or during prolonged treatment of tracheitis.
For mild cases of the disease, the doctor may recommend therapy without the use of such drugs. In this case, the child is under constant observation, and treatment is adjusted as the condition worsens. The main efforts are aimed at relieving coughing attacks. To do this, the child is prescribed mucolytic tablets, which help thin and remove mucus.

The use of cough remedies based on medicinal plants with expectorant, anti-inflammatory and mucolytic effects is widespread. They may come in the form of tablets, lozenges, lozenges or syrups.
Inhalations
Inhalations make a great contribution to the treatment of tracheitis. They have a positive effect on health, help moisturize and soften the laryngeal mucosa, which allows you to cure the disease much faster. In modern medicine, nebulizers are regularly used - devices with a heating element and a container for a special medicinal solution. During the heating process, the medicine is converted into a fine suspension, which is inhaled by the patient.

ethnoscience
The oldest and generation-tested treatment for tracheitis with folk remedies is the use of home inhalations. It has little in common with using a nebulizer with special drug solutions, but can be very beneficial.
Home inhalations are carried out as simply as possible: hot vapors are inhaled over a pan of water and various herbs. For tracheitis, linden, thyme, chamomile, St. John's wort, eucalyptus, lemon balm and coltsfoot are recommended. They effectively reduce swelling and reduce inflammation. Instead of herbal preparations, you can use essential oils (2-3 drops per 1 liter of water).
Home inhalations have the following contraindications:
- bronchial asthma;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- increase in body temperature.
In addition to inhalations, there are several effective folk remedies for tracheitis:
- chamomile tea;
- gargling with herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula, sage);
- plenty of warm drinks;
- compresses on the chest (apply only after the cough has become wet).
To soften the throat and alleviate the child's condition during illness, you can use butter. It is best to add it to warm milk along with ginger powder, which boosts immunity. This drink will help relieve irritation and temporarily get rid of coughing attacks.
If your cough bothers you at night and prevents you from falling asleep, hot milk will help. A small amount of sugar should be dissolved in a glass of hot milk and given to the child before bedtime. You can use fresh honey instead of sugar, but be careful if your child is prone to allergies. This is the simplest and most accessible home mucolytic remedy, thanks to which you can maintain healthy sleep during treatment of the disease.

If the child does not have a fever, alcohol compresses can be used at night. They are not applied to the throat, but to the upper chest area.
See also
How is surgery to remove adenoids performed in children, is it painful?
Read
Even very young children, for whom hot inhalations are currently contraindicated, will benefit from aromatherapy. Fir, pine, eucalyptus, juniper and ginger oils are best suited for it. To fill a room with aroma, just heat water in a saucepan and add a few drops of your chosen essential oil. This method also has an additional effect: in the absence of a humidifier, it will help create a healthier microclimate in the apartment to combat respiratory diseases.
There are other options, for example, using a special aroma lamp in the children's room or adding oil to the aroma pendant.
Treatment of tracheitis with folk remedies can bring positive results, but it is recommended to first coordinate it with a specialist. Some herbs have side effects, some cause allergies in children. In addition, therapy for this disease cannot be considered complete without the use of pharmaceutical drugs, and even relief from symptoms for a long period does not mean that tracheitis has passed.
Massotherapy
As a concomitant treatment at home, you can resort to therapeutic massage. It helps normalize the functioning of the immune system and suppress coughing attacks. To perform a massage, it is necessary to study acupuncture points that activate the body's defenses.
Massage for tracheitis is carried out with stroking movements directed from the middle of the chest upward, or with pressing, vibrating movements. It is most effective for treating young children.
Massage procedures are contraindicated for blood diseases and elevated body temperature. Before using this treatment method on your own, it is recommended to consult your pediatrician.
How to treat tracheitis in children under one year old and older children?
First, tracheitis is treated without taking antibiotics, unless, of course, the cause of the disease is a bacterial infection. This disease “exhausts” many body functions that, for example, are not fully developed in children, so treatment should be comprehensive, but as gentle as possible. If acute tracheitis is diagnosed on time, then it is much easier to treat than chronic tracheitis, which is not always treatable.
Stages of treatment of tracheitis in children:
- Elimination of the cause (ARVI, bacterial infection, allergy) that provokes inflammation of the tracheal mucosa.
- Elimination of various symptoms of the disease. Antipyretic drugs are used at high temperatures, expectorants are used to remove mucus and ease breathing, eliminating a dry “barking” cough.
- An effective way to treat tracheitis is physiotherapeutic procedures and inhalations.
- Strengthening the immune system.
Treatment for tracheitis is quite long. The specialist gives recommendations that need to be followed, especially when it comes to infants, for whom tracheitis poses a great danger due to the lack of a cough reflex and the threat of asphyxia.
Organization of space for a patient with tracheitis:
- clean, fresh air;
- daily wet cleaning;
- exclusion of irritating factors: cigarette smoke (if parents smoke), various cleaning products, fragrances;
- Pay attention to the child, especially the infant, try to prevent crying, as it can irritate the tracheal mucosa.
Use of medications:
- Antibiotics are prescribed only for tracheitis caused by a bacterial infection; in other cases, doctors do without them. If we are talking about just such a source of the disease, then Bioparox is used (contraindicated for children under three years of age). In addition, an antibiotic may be prescribed in case of protracted illness complicated by otitis media and sinusitis. In this case, the modern drug Azithromycin, which is also approved for use in infants, may be recommended.
- To treat tracheitis that is not bacterial in nature, expectorants : Lazolvan (can be prescribed as a mucolytic even to newborns), Ambrobene, Ambrohexal, Flavamed, Brombegsin, ACC, Doctor MOM, Gedelix. Antipyretics, based on paracetamol, are also prescribed.
- For tracheitis caused by viruses, antiviral agents : Viferon, Kipferon, Anaferon, Immunal and others.
An effective way to combat inflammation of the trachea is inhalation with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile and calendula) and essential oils (fir, geranium, juniper). Inhalation time is no more than 10 minutes. If the child’s tracheitis is allergic in nature, then such procedures can be carried out only after consultation with a specialist (allergist-immunologist).
Features of infant treatment
Treatment of tracheitis in infants under one year of age is complicated by the fact that many medications are contraindicated for them. In addition, folk remedies are not used in most cases to treat newborns. Not so long ago it was not possible to carry out inhalations for small children, but today in pharmacies you can purchase special nebulizers for infants, with which you can alleviate the condition and speed up treatment.

A pediatrician can recommend special medicinal ointments that are used for respiratory diseases and promote normal breathing and cough relief.
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment for tracheitis depends on its form and the age of the patient. In school-age children, with timely and properly selected treatment, the disease resolves within 2 weeks. With incorrectly selected therapy or hypothermia, symptoms may not subside for 3-4 weeks.
Protracted, chronic tracheitis, complicated by concomitant diseases of the respiratory system, takes the longest to treat.
Preschoolers and infants have a weak cough reflex and an incompetent immune system, so tracheitis in them is not treated so quickly. Therapy for the disease can take 4-5 weeks, with few symptoms, poor sputum production and a cough that weakens over time. How long treatment lasts largely depends on timely contact with a doctor, who will make a diagnosis and give the first recommendations.

What is contraindicated to do with this disease?
To speed up the treatment process and prevent complications, it is recommended to follow some rules. For tracheitis the following are contraindicated:
- Visiting baths and saunas in case of acute disease and elevated body temperature.
- Eating fatty and fried foods.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Staying in cold air and drafts.
- Eating food that is too hot or too cold.
- Overstrain of the vocal cords.
It is better to consult a specialist about whether it is possible to walk with one form or another of the disease. In most cases, if the child's condition allows and it is not cold outside, short walks in the fresh air are beneficial.

How to distinguish tracheitis from other diseases?
In order for treatment of tracheitis in children to proceed without complications, diseases with similar symptoms should be excluded.
A dry or barking cough occurs due to various processes in the respiratory organs, so diagnosis requires attention.
- With tracheitis, a child’s cough necessarily develops into a productive one and does not have a barking sound, which is a feature of laryngitis.
- With pharyngitis, the baby has a very sore throat, and with tracheitis, the unpleasant sensations are concentrated in the clavicular area.
- With bronchitis, there is a high temperature, and wheezing in the chest is more pronounced, dangerous spasms and shortness of breath may occur.
- Tracheitis differs from whooping cough by its short duration and absence of wheezing. The baby has no signs of intoxication with the decay products of the virus, his condition is stable.
- With pneumonia, temperature, fever, and chills are constantly present. Wheezing is heard in the lungs, not in the trachea.
- Tuberculosis is distinguished by the nature of the cough: attacks are mild and short, and do not depend on the position of the body. The baby is rapidly losing weight.
- If a foreign body enters, the child cannot inhale air, the skin around the lips turns blue, and respiratory function is impaired.
What is a cough with tracheitis in children? When sputum accumulates, the child has an attack of up to 15–20 tremors. In the first days it is dry, painful, with tingling in the chest and a gag reflex. Gradually there is a transition to a wet form with abundant secretion of sputum and mucus, which improves the process of coughing.
Drugs for the treatment of tracheitis
Treatment of tracheitis in children has a number of features: all medications must be strictly age appropriate. You should not use alcohol-based formulations, which can damage the inflamed trachea and cause a burn to the mucous membrane.
If the disease is viral in nature, it is treated with anti-infective drugs:
- Kagocel;
- Nazoveron;
- Aflubin;
- Cytovir-3;
- Novirin,
- Amiksin.
You can treat acute tracheitis in children with the antiviral drug Interferon. It is instilled 3-5 times a day into each nostril. The product reaches the larynx and trachea, stimulating the production of natural immunity. A positive effect is observed after 1–2 days. With timely treatment, the intensity of cough is reduced, the temperature drops, and recovery is accelerated.
An antibiotic for tracheitis in children is selected by a pediatrician after collecting an anamnesis and tests.
To reduce tracheal irritation, the following are used:
- Klacid;
- Cefosine;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Clubax.
How to treat tracheitis in a child with a painful cough depends on the stage of the disease. The best effect is provided by mucolytics: Ambrobene, Ambroxol, ACC. They improve sputum discharge and normalize the condition of the lungs, but are not recommended for children under 2 years of age: the absence of a cough reflex will only worsen the situation and increase inflammation.
Antitussives are recommended if sputum does not clear on its own. This syrup is easy to use, has a pleasant taste, stops coughing and alleviates soreness in the trachea.
The following remedies help treat tracheitis in a 6-year-old child:
- Sinekod.
- Bronholitin.
- Gerbion.
They envelop the mucous membrane, reduce swelling, and antibiotics complement the treatment.
Antipyretic medicine for tracheitis for children should be selected based on Paracetamol or Ibuprofen: Panadol, Nimulid, Nurofen. These components are relatively safe for children's health; they last for several hours with minimal risk of complications. This ensures the child sleeps soundly and maintains his strength.
Is it possible for a child with tracheitis to walk in winter? Doctors recommend not to give up spending time in the fresh air if the disease is not in the acute phase. Walks should not be accompanied by jogging and active play. It is better to ensure a quiet pastime, sleeping in a stroller. But a sick baby should not go out into the cold if the temperature has dropped to -10°C.
Preventive actions
The key measure to prevent the disease is to strengthen the child’s immunity. Nonspecific preventive measures include:
- hardening;
- to give up smoking;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- complete healthy diet;
- timely treatment of respiratory diseases.
Treatment of the chronic form of tracheitis requires a lot of time and effort, so at the first symptoms it is recommended to consult a specialist. This will allow you to cure the disease as soon as possible and completely get rid of the painful dry cough that it causes.
Tracheitis in an infant: symptoms and treatment
Reading time: 4 minutes
AA
The trachea is one of the organs of the respiratory system, through which the bronchi and larynx are connected .
This organ is lined from the inside with mucous membrane, which can become inflamed under the influence of various factors , in which case the specialist diagnoses “tracheitis”.
What is tracheitis?
Reference! In infants
tracheitis
in most cases, it develops against the background of any respiratory diseases, in which the infection spreads from the nasopharynx to the lower respiratory tract.
Mostly in childhood, this pathology develops when affected by influenza viruses, whooping cough, measles and adenoviruses.
Pathology of a bacterial nature in infancy is rare and occurs in no more than two percent of cases, when respiratory diseases are accompanied by damage by pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci and other anaerobic bacteria.
Tracheitis is rarely isolated as an independent disease and is mainly combined with bronchitis, pharyngitis and laryngitis.
The mucous membrane of the trachea is damaged, on the inside of which a layer of mucus accumulates; often, as the disease becomes more complicated, pinpoint hemorrhages are observed on the surface of the tissues of this organ.
Symptoms of tracheitis in infants
Attention! Infants with tracheitis do not have specific symptoms, and the development of the pathology can be judged by the general deterioration in the child’s well-being, who becomes lethargic, refuses to breastfeed, and spits up more often than usual.
Other signs of the disease include:
- low-grade fever ;
- dry cough;
- runny nose;
- wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Depending on what disease the pathology is combined with, the cough can become productive (with tracheobronchitis) or remain dry (with pharyngitis).
Causes of the disease
The cause of tracheitis in infants is damage to the tracheal mucosa by pathogenic microflora , which spreads after influenza or ARVI .
Predisposing factors to the development of the disease are:
- prolonged stay in a room with excessively dry air;
- hypothermia;
- exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke;
- weakened immune system;
- pathological processes of the respiratory system.
Keep in mind! In some cases, the disease is of allergic origin, which requires a special approach to treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of tracheitis in infancy may be limited to a simple visual examination and listening to the respiratory organs.
a general blood test may be prescribed .
In case of infectious inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract, a blood test will show increased levels of leukocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils and ESR.
If developing pneumonia an x-ray is performed .
Treatment for infants
Know! At any age, the goals of treating tracheitis are the same. This is the elimination of inflammatory processes, stopping the spread of infection and relieving symptoms.
Treatment is complex and involves:
- Drink plenty of warm drinks to thin the mucus;
- taking immunostimulating and restorative drugs;
- rubbing, mustard plasters, compresses and other distracting procedures that eliminate cough;
- drug treatment.
Rubbing has no contraindications in infancy, but only if certain means are used, although the procedure can be performed simply with a cloth without the use of any means.
During rubbing circulation improves and the body activates protective mechanisms that begin to fight infection.
To enhance the effectiveness, you can use vegetable oil with the addition of a drop of pine essential oil per tablespoon of vegetable oil.
When applying compresses for infants, not all products can be used: mustard plasters and alcohol-containing compounds should be excluded.
You can moisten gauze in a composition that contains camphor, Provençal oil and vinegar in equal proportions.
The compress is applied to the neck, covering the chest area, covered with plastic wrap and left for one hour.
Attention! Another option is honey heated to a temperature of 40 degrees, which is used to lubricate the throat and chest area, after which the child is wrapped in a warm sheet or diaper and left for one hour.
This recipe is suitable only if the child is not allergic to honey.
For viral etiology of tracheitis, the otolaryngologist may prescribe one of the following antiviral drugs :
- nazoferon;
- novirin;
- cytovir;
- remantadine;
- oscillococcinum;
- aflubin;
- amiksin.
is of bacterial origin, cefuroxime, amoxiclav, cefotaxime, flemoklav, sumamed are prescribed.
At the age of up to three months, with a low-grade fever, the use of antipyretics is permissible.
You should know! For children older than three months, it is recommended to lower the temperature when the level rises to 38.5 degrees.
Possible complications
The most dangerous complication of tracheitis in infancy is inflammation of the bronchi.
And since the child’s cough reflexes are not developed in the first months of life, this consequence is fraught with accumulation of sputum.
As a result, mucus not only makes breathing difficult, but also becomes a source of proliferation of pathogenic microflora, which spreads to the lower respiratory tract.
As a result asphyxia may occur due to respiratory failure.
Prevention
Preventive measures for tracheitis in infancy primarily include maintaining a normal level of humidity in the room .
To do this, you need to either purchase a special humidifier, or do wet cleaning and ventilation in the room at least once every two days.
Remember! Both during illness and to prevent it, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia in the child. In such cases, you can reduce the risk of developing the disease and eliminate complications.
From this video you will learn all about the symptoms and treatment of tracheitis:
Any viral and infectious diseases must be treated in a timely manner and strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician.
Author of the article
ENT (otolaryngologist), 11 years of experience
Source: https://galinavladi.ru/traheit-u-mladenca-simptomy-i-lechenie.html