Leakage from the ear is a symptom of most diseases of the hearing organ, requiring urgent attention to an ENT doctor. People with ear problems often wonder: what to do when the ear is leaking? Self-medication with ear drops and heating is strictly prohibited. Only after consulting a specialist, you can apply these or other medications topically and take them orally.
In official medicine, leakage from the ear is defined by the term “otorrhea.” This is not an independent pathology, but a symptom of a pathological process in the ears. The causes of otorrhea are very varied and varied: infection, trauma, neoplasms. Ear discharge can be serous, purulent, bloody, sanguineous, and have a different color, consistency, and smell. Most often, exudate is formed due to the accumulation of microbes that cause local inflammation.
The appearance of drainage from the ear is often accompanied by additional clinical signs - tingling, shooting pain, general malaise, weakness. If the cause of otorrhea is not determined in time and the pathology is not treated, fluid will constantly accumulate inside. This will lead to a deterioration in the health and well-being of the patient.
Young children are most susceptible to the development of inflammatory ear diseases. This is due to frequent runny nose and inability to blow your nose. While crying, the child begins to sniffle. Bacteria penetrate the narrow auditory tube, it becomes inflamed and swollen, pressure in the ear cavity increases, and pain occurs.
Often, in people with ear leakage, not only ear pathology is detected, but also dysfunction of the respiratory organs - throat and nose, which is explained by the anatomical connection between them.
Etiology
Diseases in which fluid leaks from the ear:
- External otitis develops as a result of the penetration of bacteria under the skin in people who have microtraumas of the ear cavity. Such damage can be caused by overuse of bathing procedures, frequent swimming, skin diseases, and the use of improvised means and cotton swabs to clean the ears. Earwax is washed out of the ear, its protective function is weakened, and the body's resistance is reduced. Otitis externa manifests itself as hyperemia, itching, ear pain, and hearing loss.
One of the symptoms of otitis media is also otorrhea. In this case, purulent fluid usually flows from the ear. Otitis can be acute, accompanied by fever, and sluggish with a temporary cessation of symptoms. The acute form is manifested by pain, unpleasant sensations in the ear, and decreased perception of sounds. The sluggish form is characterized by the disappearance of clinical signs and their reappearance. In the absence of timely treatment, inflammation from the tympanic cavity spreads to the inner ear, and labyrinthitis develops.- Violation of the integrity of the eardrum is caused by an acute inflammatory process, traumatic injury, foreign bodies, and high pressure when diving to depth. A torn membrane ceases to perform protective and sound-conducting functions. Patients develop otitis media, hearing loss, and serous fluid flows from the ear.
- Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the cellular structures and cave of the mastoid process of the temporal bone, located behind the ear and containing air-filled bone cavities. The disease is manifested by suppuration, redness of the ear, peeling and itching. Local hyperthermia and tissue swelling are signs of inflammation. Common symptoms of mastoiditis are headache and fever.
- Furunculosis of the ear develops against the background of microbial exposure and is observed in people with a hereditary predisposition. Purulent boils in the ear canal cause pain that increases with chewing. The boil is visible to the naked eye if it is located shallowly. When it ruptures, pus flows from the patient's ear.
- Watery discharge from the ears is observed with allergic otitis media. The disease develops in response to various irritants - allergens. Transudate begins to be actively synthesized, which accumulates in the middle ear and, after perforation of the membrane, comes out. Allergic otitis media is a common manifestation of general allergization of the body. The flow of colorless fluid from the ears is accompanied by itching and congestion. Antihistamines will help get rid of such symptoms.
- Cholesteatoma is a tumor of the epithelial cells of the middle ear. It can be congenital and secondary or acquired. Cholesteatoma develops after chronic inflammation or trauma to the ear structures. Patients with a tumor complain of dizziness, a feeling of fullness or pressure in the middle ear, headache, nausea, loss of performance, and severe fatigue. The pathology is manifested by a flow from the ear with a sharp, unpleasant odor and constant pain. In severe cases, patients lose their hearing and may become completely deaf.
- Ear dermatitis is accompanied by profuse drainage from the ear. The affected ear hurts greatly, the external canal swells. Patients complain of unbearable itching, swelling and flaking of the skin, the formation of weeping wounds, flowing pus and sticky liquid.
- Otomycosis is a fungal inflammation of the hearing organ, which develops as a result of long-term use of hormones or antibiotics. The disease is manifested by itching, white discharge with a yellowish or greenish tint. To treat fungal otitis, antimycotic drops are used.
- TBI is often accompanied by a rupture of the dura mater and leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose and ears, which has a watery consistency and a transparent color. This is an emergency condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Untreated ARVI often spreads to the hearing organ. With influenza and ARVI, body temperature rises, runny nose, sore throat and ears, and general signs of intoxication. In the absence of adequate treatment for a respiratory infection, hearing acuity will gradually decrease until the ability to perceive sound is completely lost.
- Adenoids in children, sinusitis , tonsillitis also affect the condition of the middle ear.
Leakage of fluid from the ears is one of the main symptoms of ear pathology. It is often combined with the following symptoms: fever, chills, hearing loss, dizziness, regional lymphadenitis, shooting ear pain, hyperemia of the auricle.
Other causes of otorrhea include the following:
- Hypothermia.
- Intense and harmful effects of tobacco products.
- Contaminated water entering a swimmer's ear.
- High air temperature and high humidity.
- Improper ear cleaning, damaging the outer ear.
- Wearing hearing aids.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Immunodeficiency states.
Causes of excessive sulfur secretion
In young children, there may be a slight disruption in the functioning of some systems, including the production of sulfur. In this case, too little or, conversely, too much is released. The latter is due to the activation of the sulfur glands located in the human ears. With more significant deviations, the consistency of the secretion changes. Sometimes it simply flows because its composition is disrupted, which leads to the liquefaction of the secretions.
A child may also have a lot of earwax due to other factors. The most common reasons are:
- evacuation of contaminants and accumulated secretions;
- cold;
- hormonal factors;
- softening of sulfur.
In most cases, when no pathology is observed, sulfur is released naturally and helps cleanse the ear canal. Activation of this process occurs during a cold. In this case, sulfur performs a protective function in the child’s ears, preventing infection from penetrating into the hearing organs as much as possible.

At a certain age, hormonal changes begin. In children, this can also be expressed in changes in the functioning of the sulfur glands. Another reason is water getting into the ear canal. It softens the secretion and, already in a liquid state, it is removed out.
Character of the current
Transparent discharge is a sign of aseptic inflammation and injury. A colorless and odorless course is a symptomatic manifestation of exudative otitis media, in which serous effusion accumulates in the tympanic cavity. It puts a certain pressure on the eardrum, it ruptures, and fluid flows out of the ear. When allergic irritation of the skin of the ear canal occurs, bubbles appear, which spontaneously open, and a clear liquid flows from the ear. A fracture of the base of the skull is manifested by the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, which is also transparent. If the disease is not treated, secondary infection will occur. The discharge becomes purulent, smells bad, and the patient’s condition worsens.
Yellow liquid flowing from the ears is an alarming sign indicating a serious disease of the hearing organ. The cause of yellow discharge is fungi and bacteria. Streptococcal and staphylococcal infections cause purulent otitis media with perforation of the eardrum and inflammation of surrounding tissues. Patients develop fever, weakness, headache, and nausea. If these symptoms are ignored, the patient may develop mastoiditis, brain abscess, and sepsis. If your ear is leaking yellow, thick fluid, it may be earwax leaking from your ear. When heated and the temperature rises, the wax plug may melt and leak out.
Brownish discharge from the ear is a sign of a violation of the integrity of the capillaries. Hemorrhage and tissue destruction are caused by acute inflammation of the ear, the formation of tumors, rupture of the eardrum, bullous otitis, and myringitis. Blood with pus indicates polyps or an advanced infection. Similar changes in ear secretion occur when ingested by an insect or are the result of an ear injury. The blood is secreted and darkens as it clots. Then it is mixed with sulfur, which gives it such an unusual shade.
Black discharge from the ears appears when the patient has otomycosis caused by mold and yeast-like fungi. This symptom of the disease is accompanied by severe itching inside the ear and pain.
If ear drainage is ignored and left untreated, serious complications can occur:
- Hearing loss
- Perforation of the eardrum,
- brain abscess,
- Sepsis,
- Disability,
- Death.
Wax in a child's ears: causes and methods of cleaning
Very often, parents pay attention to the fact that wax forms in their children’s ears, and in fairly large quantities. This does not look very attractive and ultimately leads to the appearance of ear plugs. To get rid of wax, parents should know why it appears and how to clean the ears of a newborn.
What is the norm for sulfur formation?
Wax in a child's ears has a protective function. Thanks to sulfur, the eardrum is protected from various external negative factors. However, if sulfur is released in large quantities, then the child’s parents should sound the alarm.
- If previously wax rarely appeared in the ears, and then began to increase in volume, this indicates that the child is experiencing intoxication. Through sulfur, various harmful substances are removed from the body.
- Dried sulfur discharge indicates that the child has encountered skin diseases. Perhaps he has psoriasis, neurodermatitis or an allergic reaction. It is important to consult a doctor to determine what kind of deviation occurred.
- Liquid sulfur is a common symptom of otitis media. In this case, it is important to start treatment as quickly as possible so as not to worsen the situation. Subsequently, the child may develop a fever.
- Black wax in the ears. In this case, parents need to monitor the child. If this was a one-time incident, then perhaps the baby just got dirt in his ear. When the process of the appearance of black sulfur becomes constant, you should consult a doctor - most likely, the child has developed purulent inflammation.
- Dark brown sulfur is not a cause for concern. This color is the norm for healthy people.
It is dark brown sulfur that is an indicator of the normal functioning of the baby’s body. If you don't like the color of wax from an aesthetic point of view, you can clean your child's ears once a week to keep them looking well-groomed.
How to clean your child's ears
Any mother can independently learn how to clean wax for a child at home. If the color of sulfur and its volume are normal, then in this case you do not need to contact doctors for help.
Increased sulfur release can lead to the appearance of sulfur plugs, which are removed under stationary conditions.
In some cases, wax plugs can cause numerous complications.
- Ear cleaning should be done regularly. A suitable frequency is several times a week. If sulfur accumulates in a large volume, then the protective function is lost. It begins to put pressure on the walls of the ear and provokes inflammation. Often, due to increased secretion of sulfur, chronic skin diseases of the ear canal appear.
- To clean your child's ears, you need a special tool. For example, to prevent wax from accumulating in the baby’s ears, you need to clean them with special swabs soaked in hydrogen peroxide or an oil solution. Cotton swabs are only allowed to be used from two years of age. It is best to take sticks with a limiter, which will help avoid excessive insertion into the ear canal.
- The auricle should be gently pulled back. Next, pull down a little so that the ear canal remains open. Using circular movements, we begin to remove sulfur. It is better not to make sudden movements, as this can drive the wax deep inside and scratch the walls of the passage.
- If your baby has a sulfur plug, then it is better not to perform independent manipulations and immediately contact a specialist. It will help relieve your baby of excessive discharge.
Sulfur deposits pose numerous dangers. For example, a child may subsequently face serious illnesses and hearing impairments. It is very important to take action in time.
Why wax plugs may appear in babies
Pathologies do not appear just like that. There are always reasons for the appearance of wax plugs. Let's look at why unpleasant wax plugs can occur in the ears of newborns:
- Excessive attention to ear hygiene. Many parents over-clean their children's ears, which leads to even more wax production. As a result, a sulfur plug forms over time. The frequency of cleaning earwax from ears should not exceed one to two times a week.
- Using cotton swabs. Sticks should not be used to clean ears, and their manufacturers notify us of this. You can always find a similar warning on the packaging of cotton swabs. The sticks only push the sulfur deeper, which negatively affects the baby’s well-being and leads to the appearance of traffic jams.
- Dry indoor air. If the air is too dry, children may develop wax plugs. And this is not the only problem: dry air also leads to children experiencing headaches, runny nose, etc. Optimal humidity levels in the room where the child is located are about 60-70%.
- Anatomical structure of the ear. Sometimes children have structural features of the ear that lead to worsening of wax removal. In this case, additional ear care is required.
- Genetic predisposition to sulfur plugs. This also happens - and it is inherited. When parents have such a problem, it is important to monitor the child and promptly eliminate the consequences of excessive sulfur secretion.
- Careless hair washing. If washing the child's hair unsuccessfully, water may get into the child's ear, as a result of which the wax begins to swell and is difficult to remove from the ears. Over time, a plug forms in the ear.
- Foreign bodies in the ear. Children often put small objects in different places. Initially, this does not cause any discomfort, so the child quickly forgets about the object. But over time, it becomes a source of inflammation. It is not recommended to remove objects yourself; it is best to contact a specialist for this.
- Frequent wearing of headphones. This is already typical for teenagers who actively use headphones. Mechanical pushing of sulfur deeper leads to the formation of a plug. The ear canal is also blocked.
How to understand that a sulfur plug has appeared
Diagnosing wax plugs is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. Even if there is quite a lot of sulfur, it may not show itself in the form of additional symptoms.
Discomfort appears only when the ear canal is completely blocked. Hearing begins to decline.
Exposure to water during bathing causes the plug to swell and, as a result, the ability to hear sounds is lost.
Other symptoms of wax plugs in children:
- noise in ears;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- sensation of fullness in the ears;
- headache.
Sulfur plugs can negatively affect the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Hearing loss is far from the most dangerous complication for a child.
Diagnosis of wax plugs is made by pediatricians during a visual examination of the patient. The final diagnosis is made by an otolaryngologist. The doctor assesses the stage of the pathology, checks for the presence of other diseases, foreign bodies in the ears, etc.
Preparations for clearing ear wax
Medicines are rarely prescribed to children. Doctors advise using a solution of furatsilin or ordinary boiled water to clean ear plugs.
The manipulation must be repeated several times, which will lead to the dissolution of the plug and its removal. An antiseptic helps disinfect the ear canal to avoid inflammation.
If furatsilin does not help, then you can use drops of Remo-Vax or A-Cerumen. Be sure to read the instructions for the medications.
Hydrogen peroxide is another well-known method for clearing earwax. The procedure is very simple and effective. To remove sulfur plugs, it is necessary to use hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 3%. This is the only option that is safe for your baby’s ears.
To remove the formation, place the child on his side and drop 2-4 drops of the product into the ear. If the baby begins to be capricious and complain of pain, then it is better to consult a doctor. If there are no side effects, then you need to lie on your side for about 10-15 minutes, then roll over to the other side so that all the peroxide comes out of the ear. The procedure should be repeated for a couple of days.
Constantly cleaning your ears with hydrogen peroxide is not recommended. It is worth remembering that sulfur has protective functions, and therefore in certain quantities it is important and needed by the body.
Source: https://OdmDetka.ru/article/sera_v_ushakh_rebenka_prichiny_poyavleniya_i_sposoby_ochistki.htm
Diagnostics
An ENT doctor is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases manifested by ear discharge. Before making a diagnosis, he collects anamnesis, listens to complaints, examines the patient and prescribes the necessary tests.
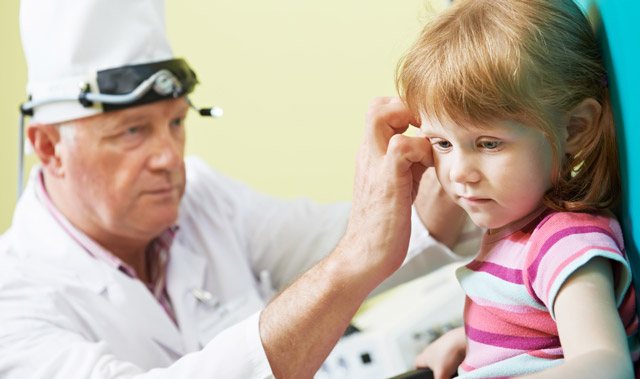
To determine whether a baby's ear hurts, you need to press on the tragus. This action puts pressure on the eardrum, and if it is inflamed, pain occurs. The baby constantly cries, does not take the breast, and does not sleep. This diagnostic method is applicable only to infants, since their bone part of the auditory analyzer has not yet fully formed.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics include:
- A general clinical blood test reveals signs of inflammation - leukocytosis with a shift to the left, increased ESR.
- Bacteriological examination of leakage from the ear makes it possible to determine the causative agent of the pathology and its sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
- Otoscopy is an instrumental technique that allows you to examine the external auditory canal and eardrum to determine the integrity of the structures and inflammatory processes using an otoscope, a refractometer and ear specula.
- Audiometry is the study of hearing acuity using special equipment.
- Tympanometry is the measurement of pressure inside the ear.
- CT and radiography are auxiliary methods that detect violations of bone structures, the presence of tumors and other changes.
How to fix
Since the reasons that led to profuse discharge from the ear are different, the methods also differ. The most common cause is the formation of sulfur plugs. While it is easy for adults to remove it, it is better to take children to the doctor, since it is much easier for them to be harmed.
At home
If no pathological processes are detected in the ear, ensuring ear hygiene will be sufficient. For babies, parents should remove excess wax. At school age, this responsibility falls on the shoulders of the teenager. It is important to explain all the rules for safe cleaning of the ear canal.
At home you should:
- Avoid using vacuum headphones. If the cause is a hearing aid, then you need to carefully monitor its hygiene.
- If the reason was visiting dusty premises, then nothing should be done. Excess secretion indicates that the child’s body is functioning normally.
- When a sulfur plug forms, rinsing is carried out. First, it can be dissolved by dropping 3% hydrogen peroxide into the ear.
How to properly clean ear wax
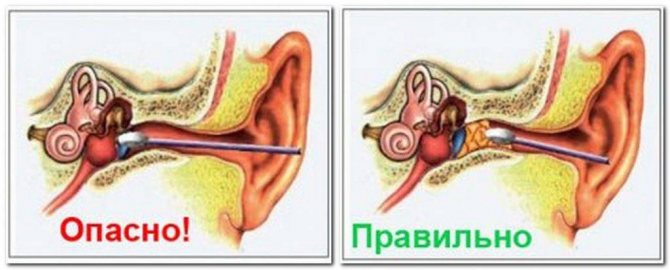
Medication
You can buy Remo-Vax at the pharmacy to wash your ears. It softens and removes excess wax from the ear cavity. Can be used to prevent increased sulfur production or when using hearing aids or headphones.
The medical institution will offer to rinse the ear using a special Janet syringe. The procedure should only be performed by a doctor, since improper water pressure can damage the eardrum. You should not warm up the ear if a large amount of wax is released. This can lead to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora.
If the excessive formation of wax in a child is associated with inflammation of the middle ear, then treatment is carried out with local or systemic drugs. In this case, after the course and recovery, the amount of secretion is normalized.
How to clean your child's ears, watch our video:
Source: gidmed.com
Treatment
In order for patients to stop leaking from the ear, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease. Treatment of any pathology begins with the removal of any discharge in the external auditory canal.
Traditional medicine
Conservative treatment consists of the use of antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and restorative agents.
- Local treatment of otitis involves the use of ear drops with glucocorticoids - "Garazon", "Combinil-Duo", with NSAIDs - "Otipax", "Otinum", with antibiotics - "Anauran", "Otofa", "Fugentin", "Tsipromed" , with an antifungal component - “Candibiotic”, with an antiseptic - “Miramistin”. Before use, the drops must be warmed in your hand. The auricle is pulled back and up in adults, back and down in children.
- The general treatment of purulent otitis consists of antibacterial therapy. To do this, use wide-spectrum drugs in the form of tablets or injections that penetrate well into the tympanic cavity. Patients are prescribed Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin, Suprax, Augmentin, Flemoclav. After opening the boil, antibiotic therapy is carried out using a turunda soaked in medicine and inserted into the ear.
- To reduce pain around the ear, doctors recommend applying Fastum Gel or Diclofenac.
- To prevent dysbacteriosis, take Lactobacterin, Linex, Bifiform.
- Desensitizing drugs for relieving edema - Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin.
- Antimycotic drugs for otomycosis for oral administration - Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Nystatin.
Physiotherapy is carried out after the symptoms of acute inflammation have reduced. It consists of conducting and using UHF therapy, UV irradiation, Sollux, and Minin lamp.
Surgical treatment is carried out in cases where conservative therapy does not give the expected result. During the operation, the integrity of the eardrum is restored and infected tissue is removed.
ethnoscience
There are a large number of effective folk recipes for treating patients with leaking ears.

- Plantain juice, a decoction of mint with honey, fresh aloe juice mixed with water, and an alcohol tincture of propolis or calendula are instilled into the ear.
- Warming semi-alcohol compresses are placed on the ear area. They improve blood supply to the middle ear, which promotes a speedy recovery.
- To wash the ear, use a decoction of chamomile, and to clean it, use a cotton swab moistened with hydrogen peroxide.
- Melted wax allows you to get rid of purulent discharge. Melted wax is applied to linen cloth, rolled into a tube, one end of which is inserted into the sore ear, and the other is set on fire. When the fabric burns down to the ear, the procedure is stopped. The effect of such an unusual treatment occurs very quickly.
- Aromatherapy is carried out with chamomile oil diluted with boiling water. The ears are washed with this product. Lavender and olive oils are no less effective. This mixture is instilled into the sore ears and cotton swabs are inserted into them.
To prevent the development of ear pathology, manifested by progression and pain, it is necessary to avoid drafts, the entry of harmful substances and foreign bodies into the ears, and head injuries. If water gets into your ears, it must be removed immediately. Hygiene procedures should not be carried out with cotton swabs. It is better to wash the ear with soap and clean water.
If your ear is leaking, you should see a doctor. This is a symptom of one of the infectious diseases, which without medical care will lead to severe complications and death. Self-medication, even in the initial stages of pathology, can end in failure. Therefore, if you notice symptoms of ear pathology, consult an ENT doctor. Take prescribed medications and keep your ears clean.
Deviations from the norm
In principle, wax in a child’s ear performs a very important and positive function—protective. It is thanks to it that the eardrum is reliably protected from all kinds of harmful influences from the outside. However, in large quantities and with certain features in the baby’s condition, sulfur can become an alarm signal for parents:
- if earlier wax rarely appeared in the child’s ears, but at some point its production increased several times, this may indicate intoxication of the small organism: in this way it will remove pathological, harmful substances;
- dry wax in a child’s ears most often becomes a symptom of various skin diseases that affect the epidermis of the ear canal - this could be psoriasis, neurodermatitis, some allergic reactions;
- if liquid wax is found in a child’s ears, it is one of the first harbingers of any inflammation: otitis, for example - in this case, you must definitely show the baby to a doctor to begin timely and correct treatment, so as not to lead to high temperatures;
- sometimes black wax appears in the child’s ears, and then parents need to observe especially carefully for some time: usually this is a one-time phenomenon due to the fact that dirt has gotten into the baby’s ear and is now coming out of it in this way; however, if this occurs for several (2-3) days, you should consult a doctor to rule out a purulent inflammatory process;
- the usual dark brown wax in a child’s ears is an indicator of the norm: this is the color of discharge from the ear canal in healthy people, so in this case there is no need to worry about your child.