High temperature in a child
Thus, if a child at 5 months has a body temperature of 37 degrees, there is no need to worry.
Examine the baby - does he look painful? Does he eat and sleep well? Does he show interest in the world around him? If you answered yes to these questions, rest assured that everything is fine with your child. This temperature can persist for the first year or two of life, gradually approaching “adult temperature.” If the body temperature of a 5-month-old child exceeds 37.5 C, it is necessary to consider the possibility of overheating or illness.
If the living conditions are comfortable (the room is not stuffy, the air temperature is not higher than 22 C, the child is dressed in light clothing, eats well enough, drinks water), the reason probably lies in a disease that needs to be identified as soon as possible.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
Important! If a child has a fever without any symptoms, and this is not associated with proven overheating, then calling a doctor becomes a necessity. This situation may occur in the case of a bacterial infection or a focus of bacterial inflammation. The mother needs to undergo a urine and blood test so that the doctor can clarify the picture and prescribe the correct medication.
There are situations when a mother needs to drop everything and immediately call an ambulance. If the child has:
- Cramps.
- Sharp pain in the abdomen.
- The baby was given antipyretic drugs, but the fever never subsided.
- Severe pallor and lethargy.
In this condition, the child should not be left alone without supervision. The mother is obliged to provide help to the child so that he copes with the unusual condition, as well as to establish the reason that contributed to it.
Causes of fever
Thus, thermometry readings reaching 38 degrees almost 100% indicate illness. The cause of fever can be determined based on the accompanying symptoms:
- if the baby is drooling, his gums are red and swollen, and he is capricious and constantly cries, he is probably teething;
- indigestion indicates poisoning, intestinal infection, or ordinary indigestion - constipation in infants is often accompanied by an increase in temperature;
- the appearance of a rash, plaque on the tongue, throat, or a specific cough may indicate so-called childhood infections, such as rubella, measles, whooping cough, scarlet fever;
a runny nose, red throat against a background of a temperature not exceeding 38.5 C in an infant indicates a viral infection - a cold;- a very high temperature is a symptom of an acute bacterial infection, which often does not have visible external manifestations (for example, otitis media and inflammation of the kidneys in an infant can only be detected by a doctor, because the child is still too young to complain of pain in the ear or back).
The symptoms of many diseases in infants are blurred, without a clear clinical picture. Very often this makes diagnosis difficult. At the same time, many diseases of infants develop rapidly, so not a minute can be lost.
Temperature 37°C: what can provoke it?
In most cases, when the thermometer increases to 37°C, the patient also experiences various catarrhal symptoms. These include sore throat, nasal congestion, coughing, sneezing, headache and others. What can provoke such indicators in children without visible symptoms? These conditions may be:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Girls become pregnant.
- Chronic, sluggish infection in the body.
- Physical exhaustion.
- Stress, severe nervous tension.
- Venereal diseases.
You might be interested in: White coating on the tongue in children
If this temperature persists for 2-3 days, but no further symptoms occur, you should undergo a medical examination to determine the causes and prescribe appropriate treatment.
1246847579

Under no circumstances should you attempt to independently diagnose and prescribe treatment. This is extremely dangerous for your child.
Treatment
When trying to treat a fever, you need to realize that a high temperature is just a symptom and not a disease.
In most cases, relieving fever is not a cure, and sometimes even worsens the course of the disease.
Thus, pediatricians recommend lowering the temperature in infants from three months old if it reaches 39 degrees. If a child has a disease of the heart or nervous system, you need to bring it down to 38.5 C. What to do if a child at 5 months has a temperature of 38 C? Treat the underlying disease. So, if a patient has otitis media, pneumonia or kidney inflammation, antibiotics are needed. They must be prescribed by a doctor! By the way, it is strongly not recommended to take an antipyretic drug and antibiotics at the same time. The reasons for this are simple - an antipyretic will reduce the temperature to normal, regardless of whether the bacterial focus is destroyed. In such a situation, it becomes very difficult to understand whether the antibiotic is effective. If antibiotics work, then within the first 3 days of treatment the temperature should drop to normal levels.
You can also use physical methods of cooling - drinking plenty of fluids, fresh air, getting rid of excess clothes and blankets. Use rubbing only after consulting a pediatrician - not all doctors approve of this method, because in some situations it can only cause harm.
If you cannot determine the cause of your baby’s fever, seek help from your pediatrician. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable - do not experiment with your child’s health.
The main causes of fever in a baby at 5 months
Before figuring out what to do if a child develops a fever, it is necessary to consider the main reasons that provoke a febrile state in children. The main causes and corresponding symptoms of fever are due to the following reasons:
- Teething. The first thing parents should consider when a temperature of 37.5 degrees is detected in a child at the age of 5 months is teething. It is from 4-5 months that children begin to develop their first teeth, which cause a lot of inconvenience not only to the child, but also to the parents. The process of teething for each baby proceeds individually, so some experience pain and develop a strong fever, while others experience only a slight increase in body temperature. It will not be difficult for parents to determine that a 5-month-old child’s temperature of 38 indicates teething. To do this, it is enough to examine the oral cavity, and if symptoms of redness and swelling of the gums are detected, then this is the reason. In addition, when teething, the child becomes capricious, sleeps poorly, and also has excessive saliva secretion from the mouth.
- Children's infectious diseases. The temperature of a child aged 5 months may increase due to the development of infectious diseases such as measles, chickenpox, rubella, and whooping cough. Most of these illnesses occur with the development of additional symptoms, such as cough or rash on the body. If signs of illness are detected, the baby will need to be hospitalized in the emergency room, since these types of illnesses are contagious.
- Viral diseases. With the development of a viral disease in children, the temperature rises to 38.5-39 degrees. Occasionally, at the initial stage, the fever may increase slightly: first to 37.5-38 degrees, and in the late afternoon or at night to 39 degrees. Viral diseases include: influenza, ARVI, colds and other types of colds. A cold causes symptoms such as cough, runny nose, sore throat, and nasal congestion. Only a doctor has the right to determine the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. It is important for parents to know that treating colds with antibiotics is strictly prohibited.
- Poisoning and intestinal infection. At 5 months, the mother begins to gradually introduce new types of complementary foods into the child’s diet. Despite the fact that such complementary foods are intended directly for children of a certain age, they can occasionally provoke the development of poisoning and intestinal infections. The main symptoms of poisoning and intestinal infections are: constipation, frequent regurgitation, vomiting, fever. The fever can remain at a subfebrile level up to 38 degrees, and also rise to 39-40 degrees, which depends on the cause of poisoning.
- Bacterial diseases. In addition to viral microorganisms, bacterial parasites can enter the body of babies. Most bacteria live in the body of every person, including children. While the immune system maintains defense, these bacteria are in an inactive state, but as soon as the baby gets cold, overeats or overheats, these microorganisms become active. To treat bacterial diseases, you will need to resort to antibiotics. It is impossible to cure a bacterial disease with antiviral drugs, just as it is impossible to kill viruses with antibiotics. When the body is infected with bacterial parasites, the body temperature rises. If the fever is maintained for a long time (2-3 days), then antibiotic therapy should be resorted to. Initially, it is necessary to take the small patient to the hospital so that he can be examined by a doctor.
How to choose an antipyretic drug?

In your home medicine cabinet it is worth keeping in stock effective antipyretic drugs approved for use in infancy. These drugs include paracetamol and ibuprofen. At the same time, ibuprofen is considered a stronger substance (but also has more side effects).
Recommendations for choosing and taking antipyretics for infants:
- resort to using antipyretics only if necessary, do not give the child a pill “just in case” if he has 37.6 C;
- if at 38.5 C the baby behaves normally (does not refuse food, does not cry, is calm), it is not necessary to lower the temperature;
- if the patient is vomiting (in infants this is a common reaction to fever), use an antipyretic drug in the form of rectal suppositories, if diarrhea - in the form of syrup;
- strictly adhere to the dosage calculated based on the patient’s age and weight;
- syrups begin to act the fastest (after 20-30 minutes), but their effect lasts for 3-4 hours;
- rectal suppositories work more slowly, but their effect lasts longer;
- If you couldn’t relieve the fever, and the child’s temperature is 39 C, call a doctor.
Thus, fever in infants does not occur out of nowhere and requires careful attention. At the same time, in most cases, simply reducing the fever is not enough - treatment is necessary, aimed at the cause of the disease.
Is fever always bad?
Increased temperature (fever) is not an independent disease, although this symptom can accompany many diseases. All fevers can be divided into:
- infectious (the cause of an increase in body temperature is various pathogenic viruses and bacteria);
- non-infectious (functional), the cause of which can be a variety of factors affecting the functioning of the thermoregulation center. An increase in temperature can occur with various endocrine diseases as a result of the action of certain hormones, with dehydration, neuroses, increased physical and emotional activity, etc.
The thermoregulation center is part of the central nervous system, located in the hypothalamus part of the brain and regulates the processes of heat generation and heat transfer, being responsible for maintaining a constant normal body temperature.
In infectious fevers, an increase in body temperature plays a protective role. It is under such conditions that the growth and reproduction of bacteria decreases; for many viruses, the only destructive factor is high temperature. With a fever of up to 39°C, the human body actively produces immune defense proteins - immunoglobulins, and metabolic processes are activated. However, when a certain threshold is exceeded (it is individual for each person, but on average it is about 39-39.5 ° C), the protective function of the temperature reaction weakens. Under such conditions, the supply of oxygen to tissues is reduced, and the basic processes of metabolism and vital activity of many cells of the body, primarily the central nervous and cardiovascular systems, suffer. Therefore, up to a certain level, fever itself is a protective factor, and only when this threshold is reached and exceeded is it necessary to use antipyretic methods that are part of symptomatic (i.e., eliminating painful symptoms) therapy.
In cases of non-infectious fevers, elevated body temperature is only a response of the thermoregulation center to the influence of various factors (hormones, biologically active substances) and, as a rule, is not protective or compensatory in nature. Such fevers usually cannot be treated with antipyretics, so therapy is aimed at eliminating the provoking factor (elimination of hormonal imbalance, sedatives, etc.).
What temperature is considered normal?
In a newly born baby, most of the body systems, although formed, are functionally immature. This is true both for the central nervous system and for its part - the thermoregulation center. Therefore, the processes of heat formation and release are also imperfect. Newborns, especially premature ones, are extremely sensitive to environmental conditions - they easily overheat and easily freeze.
Normal body temperature in newborns ranges from 37.0+0.5°C and depends on the place and time of measurement. The highest temperatures are recorded from 18 to 22 pm, and the lowest body temperature is characteristic of the early morning hours. You can measure temperature in the rectum (rectal temperature), in the armpit (axillary), in the mouth (oral), in the inguinal fold. The highest temperature is determined in the rectum; on average it does not exceed 37.6°C, although sometimes it can normally reach 38.0°C. This is approximately 1°C higher than the axillary (axillary) temperature and 0.3-0.4°C higher than the temperature in the oral cavity. However, for each baby there is an individual temperature norm, which may differ from the general average. To determine your baby's individual norm, you should measure his temperature when he is healthy and calm (in the absence of signs of malaise or illness) 3 times a day (morning, afternoon and evening). Babies up to 5-6 months are recommended to measure rectal temperature.
Thermometers
The most accurate instrument for determining temperature remains a mercury thermometer. To measure rectal temperature, thermometers with a thick round mercury-containing flask are used. Modern electronic thermometers are faster and safer, but they can distort temperature readings by several tenths of a degree. When using ear thermometers, the sensor must be positioned correctly in the auricle, otherwise incorrect data may be obtained. Liquid crystal plate thermometers provide only approximate information about body temperature. Oral thermometers (for measuring temperature in the oral cavity) can only be used from the age of 4-5 years, and the problem of “chewing the device” remains relevant.
General events
All processes in newborns develop rapidly, and deterioration of the condition can occur very quickly. Therefore, in case of any alarming symptom (and an increase in temperature is certainly one), you should immediately contact and consult with your pediatrician or call an ambulance.
It is imperative to call an ambulance if the measured temperature in the armpit is 39.0-39.5°C, and the rectal temperature exceeds 40.0°C. It must be said that even with an established diagnosis, a very high temperature is still dangerous due to the likelihood of developing the so-called hyperthermic syndrome. In this case, there is a rapid and inadequate increase in body temperature, accompanied by disturbances in the supply of blood to organs and tissues due to impaired circulation in small vessels, up to disruption of the function of vital organs (brain, heart). One of the most striking manifestations of this syndrome is seizures. Therefore, a significant increase in the baby’s temperature requires special attention.
In order to make the child feel better, before the doctor arrives and consults, parents can independently perform a number of activities.
The first thing to do is to create comfortable environmental conditions for the baby. The room needs to be ventilated. The room temperature should be about 20°C (19-21°C). Due to imperfect thermoregulation processes in a newborn, increased temperature and humidity in the room can lead to overheating of the child. You can use a fan or air conditioner, avoiding the direct direction of the air stream on the baby.
A baby with a fever should not be wrapped. On the contrary, the child must be uncovered and put on a light cotton blouse or overalls. It is important to remember that a disposable diaper can cover up to 30% of the child’s body surface, preventing normal sweating and heat exchange. Therefore, especially if it is not possible to reduce the temperature in the room, it is better to remove the diaper from the newborn.
How to measure temperature correctly
It should be remembered that the temperature should be measured when the baby is calm, since crying, agitation, overheating, and physical activity contribute to an increase in body temperature. When measuring temperature in the natural folds of the body (groin, armpit), they must be thoroughly wiped, since moisture lowers the thermometer’s readings. After crying, emotional or physical arousal of the child, you must wait at least 30 minutes. And measure the temperature in a calm state.
To determine the rectal temperature of a newborn, you should put the baby on his back (you can on your lap), lift and move his legs, as when washing, lubricate the skin of the anus with baby cream (you can also lubricate the thermometer flask with a thin layer of cream, but you must remember that a thick layer of lubricant can distort the performance of the device). Having first shaken off the mercury column below 36°C, you need to insert the thermometer into the anus to a depth of about 2 cm. Then the baby’s legs need to be brought together and held in this position for at least 3 minutes.
If you cannot measure the rectal temperature, the baby is crying, calm him down, and after a while measure the temperature in the armpit. In this case, the child can be in your arms. The measured temperature and the time of measurement must be recorded in order to then show it to the treating pediatrician: a compiled temperature graph (temperature curve) can help in making a diagnosis.
How to help a child
To provide effective and at the same time competent assistance to a child with hyperthermia, parents must adhere to the following principles.
Principle one
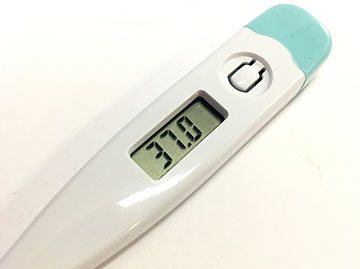
It is advisable not to measure your baby’s temperature with an electronic thermometer, as it gives inaccurate results.
It is not advisable to use mercury thermometers, since they are easy to break, and everyone knows about the dangers of mercury fumes.
The best solution would be to purchase a glass mercury-free thermometer, which, like its “dangerous” analogue, always gives accurate readings.
You should not trust your lips and palms; these are not accurate “measuring instruments”.
Principle two
If the temperature rises at the onset of the disease, it is necessary to ensure that the child is examined by a doctor, since a favorable outcome of treatment directly depends on the timeliness and correctness of the diagnosis.
You should immediately consult a doctor (call an ambulance) if:

- the temperature rose to 39.5 degrees when measured in the armpit;
- after taking antipyretic drugs at a temperature of 39 degrees for 30-40 minutes, no decrease is observed;
- if all recommendations and prescriptions are followed, the temperature rises daily for 4 days;
- any of the following symptoms are present: rash, severe headache, vomiting (not associated with food intake), pale skin, seizures, the child does not urinate;
- The temperature has risen in a baby under 3 months old.
Principle three
It is necessary to provide the most comfortable conditions for the child:

- It is better to put the baby to bed;
- The child's clothing should be made from natural fabrics, comfortable and breathable. It is better to remove the diaper;
- make sure that the baby is “dry”, immediately change clothes and bedding if he sweats or wets himself;
- The room in which the patient is located must be constantly ventilated. Make sure it doesn't get too hot. The optimal temperature is 18-20 degrees;
- a child with a fever should not be cold or hot; it is better to have a blanket or blanket on hand and act on the principle of cold - cover, hot - open slightly.
Drink
With increased fluid loss, which is often observed with fever, and can also be aggravated by the presence of vomiting and diarrhea, newborns quickly develop dehydration. Dehydration itself can contribute to an increase in your child's body temperature. Supplementation is the main method of combating dehydration. Breastfed babies need to be put to the breast more often (there is a lot of water in human milk). If a baby refuses milk, as well as babies who are bottle-fed, fennel tea and boiled water should be offered. Liquid should be given in small quantities (for a baby of the first month - one teaspoon every 20-30 minutes), since drinking a large volume of liquid at the same time can independently provoke vomiting as a result of overstretching the walls of the stomach. In case of severe dehydration, the doctor may prescribe special saline solutions for newborns. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
Physical methods of reducing temperature
Various physical methods of reducing temperature are widely used as first aid for children with fever. These methods are based on increasing heat transfer.
The most common non-medicinal way to reduce fever is rubbing. The newborn is undressed and his body is wiped with napkins soaked in water at a temperature of 36-37°C. Sponging with water at a lower temperature can cause shivering, which in turn only contributes to an additional increase in body temperature.
The baby is laid out on a diaper with an oilcloth laid underneath. Water at the required temperature is placed nearby. Having wetted the napkin, you should wring it out, and then with careful, non-rubbing movements, wipe the child’s body from the periphery (starting with the arms, legs) to the center. Light friction promotes reflex expansion of blood vessels, which improves heat transfer, and evaporation of water enhances this process. The water should be periodically diluted with warmer water, preventing it from cooling significantly and maintaining the water temperature close to normal body temperature.
Wiping with solutions of alcohol, vinegar or vodka is currently not recommended, since inhaling the vapors of these substances may be unsafe for the child, and intense evaporation can provoke muscle tremors and increase the temperature.
You can put a cool compress on the baby’s forehead - a napkin soaked in water at room temperature. It is necessary to periodically moisten the napkin with water so that the compress does not turn into a warming one.
Currently, wet sheet wraps are practically not used, as this impedes sweating - a natural way of heat transfer. Body temperature will drop faster with exposed skin. Cool water enemas are also rarely used.
In cases of very high temperatures (above 39.5°C), pieces of ice wrapped in cloth are placed on the area of large vessels (in the groin, armpits, popliteal and elbow folds, on the temporal and carotid arteries) to increase and accelerate heat transfer. There are special freezing gels, bags or heating pads that can also be used in such situations.
Drug treatment
The main rule is that medications can be given to a newborn only on the recommendation of the treating pediatrician. Under no circumstances should you be guided by your personal, previous experience or the extensive experience of grandmothers, neighbors and acquaintances. Each situation must be assessed by a pediatrician and, taking into account all indications and contraindications, prescribe appropriate treatment in the required dosage.
In cases of non-infectious fever, this may include recommendations on the regimen, care of the newborn, correction of feeding, drinking regimen, etc. Sometimes additional diagnostics may be required to determine the cause of a fever in a newborn.
For infectious fevers, the doctor will prescribe treatment aimed at suppressing the pathogenic agent - viruses or bacteria. For viral diseases, this may be the prescription of Interferon or drugs that enhance the production of Interferon in the body; For diseases caused by bacteria, antibiotics are prescribed. The question of the need to use antipyretics (antipyretics) in a baby under 1 month (newborn) is decided by the attending physician.
Currently, in pediatric practice, the most commonly used antipyretic drugs, the active ingredient in which is either Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. These are the safest (especially ibuprofen), effective and well-studied antipyretics approved for use in children from 6 months. For children under this age, the question of using Paracetamol or Ibuprofen is decided by the attending physician, depending on the specific situation. The drugs are used in the form of suspensions, syrups or rectal suppositories.
Particular attention should be paid to the single and daily dosage of the drug (it is calculated based on the actual weight of the baby). Exceeding the dose of a drug can cause various, sometimes very severe, side effects and toxic reactions. For example, an overdose of Paracetamol causes toxic damage to the liver and kidneys.
Previously, acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) was widely used in pediatric practice, but scientific research data have revealed a relationship between taking Aspirin for viral diseases in children and the development of Reye's syndrome - severe damage to the brain and liver. Therefore, Aspirin is not currently recommended for the treatment of children under 15 years of age.
Analgin (metamizole) is still produced by Russian pharmaceutical companies, although in many countries around the world the use of this drug is prohibited or sharply limited. This is due to severe adverse reactions caused by Analgin: serious hematopoietic disorders, anaphylactic shock (allergic shock reaction), immune damage to the liver, lungs, and kidneys. Since 1992, the Pharmaceutical Committee of the Russian Federation decided to limit the use of metamizole for children and adolescents under 18 years of age. However, it should be noted that ambulance and emergency doctors, if necessary, successfully use this drug for infants.
Amidopyrine and Phenacetin have been removed from the list of antipyretic drugs since the 60s of the 20th century due to severe toxic reactions and inhibition of hematopoiesis associated with their use. However, the production of these drugs in our country has not yet been stopped.
The effect of antipyretic drugs can be assessed after 30-40 minutes. after taking them. On average, they reduce the temperature by 0.5-1.5°C, but the effect largely depends on individual sensitivity to the drug.
Once again, it should be recalled that fever is only a symptom that indicates a change in the functioning of the body’s thermoregulatory mechanisms. Therefore, therapy should first of all be aimed at eliminating the causes of fever. Antipyretics are an auxiliary, symptomatic treatment that improves the patient’s well-being.
Marina Besedina pediatrician, St. Vladimir Children's City Clinical Hospital, Moscow
The first thing parents notice when their child gets sick is fever and increased anxiety. What should a mother do if her child has a temperature of 38, but doctors do not recommend bringing it down? Proper treatment can prevent an emergency call to the pediatrician's house.
Increased temperature due to viral and bacterial infections
If a child suddenly develops a high temperature, it often means that his immune system is desperately “fighting” the pathogen that has penetrated and multiplied in the child’s body. An increase in temperature to high values (above 38-39 degrees) without signs of a cold or other complaints may indicate that an acute infection has begun. These can be either bacteria or viruses, but viral infections are more common in childhood. The absence of a runny nose, cough, sore throat and redness is due to the fact that the immune system responded by quickly activating its defenses. Often, fever, lethargy, weakness, moodiness due to headache, joint or muscle pain are the first signs of the disease. Sometimes other symptoms appear after 2-4 hours, but they can appear within a day. Also, reactions to the presence of viruses in the body can be acute and short-term if the immune system has actively encountered the pathogen. At the same time, by bringing down any temperature with an antipyretic, we prevent the immune system from fighting viruses and bacteria and producing antibodies. That is, we ourselves weaken the child’s immunity.
Quite often, as a pediatrician, I observe a picture - if parents immediately begin an active fight against hyperthermia at its first appearance - the child gets sick longer and more difficult.
I always recommend that parents start lowering the temperature only after 38.5 and with a tendency to increase (except for young children, or children with serious concomitant pathologies, if there was a history of convulsions against a background of elevated temperature)!
But at the same time, you should always consult a doctor, preferably a doctor who constantly monitors and knows the baby - this is an important aspect of the treatment of any pathological condition in a child.
So, ARVI is the main and most common cause of spontaneous temperature rise.
But there are others:
- enterovirus, rotavirus, parovirus infection;
- angina;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- pneumonia or bronchitis caused by atypical pathogens;
- any inflammatory process in the body, bacteremia
- overheat;
- teething;
- inflammatory diseases of the nervous system – meningitis, encephalitis;
- psychosomatic fever (thermoneurosis);
- autoimmune diseases;
- tumors of the nervous system;
- blood diseases, including cancer.
You can read about how to bring down the temperature at home in the article - “Elevated temperature in a child - how to bring it down at home.”
Other causes of fever during inflammation in the body
Most often, the causes of a spontaneous one-time or subsequently sustained increase in temperature are considered to be:
- Viral infections
(enterovirus, rotavirus, parovirus infection, herpes viruses, infectious mononucleosis) - in this case, an acute onset in the form of hyperthermia and weakness is possible, followed by the manifestation of other characteristic symptoms - loose frequent stools, vomiting, rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, conjunctivitis, enlarged lymph nodes , liver, spleen. With these diseases, the temperature can be persistent and prolonged, which is typical for most of these viral infections. Only a doctor can clarify the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, so you should not self-medicate, this is especially dangerous for children with diarrhea and vomiting, which, combined with a high temperature, provoke severe dehydration.
- Sore throat or acute tonsillitis
is the second most common cause of fever without accompanying symptoms in the first hours of illness. Hyperthermia and intoxication caused by the activation of pathogenic microorganisms in the throat (staphylococcus, streptococcus and others) appear in a child with a sore throat before the enlargement and inflammation of the tonsils, and sometimes simultaneously, but parents do not have the opportunity to look at the throat, especially in children under 6 years of age. A sore throat appears later, but the child cannot always explain this symptom - he refuses to eat, becomes whiny, lethargic, and only a doctor can understand that the cause is inflammation of the tonsils. - Inflammatory diseases of the urinary system
(cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis) - it is these pathologies that can be asymptomatic for a long time with an increase in temperature to high numbers, so any pediatrician should prescribe a blood and urine test when the temperature rises. About 20% of all cases of high fever for no apparent reason are due to pyelonephritis and cystitis; children simply cannot explain where and what hurts them. And urination disorders, their frequency and the baby’s crying during urination are not always noticeable. But if these symptoms appear, there is a change in the color and smell of urine, you should immediately consult a doctor. - Inflammatory diseases of the nervous system
– meningitis, encephalitis. When the first symptoms of meningitis or encephalitis appear in a child, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help - only with proper and timely treatment can the consequences of this complex disease be avoided. But often the first sign is a high temperature, which is difficult to bring down due to its central genesis and overstimulation of the thermohegulation center.
Characteristics of high thermometer readings
Babies tend to react sensitively to any viruses or bacteria. Their penetration into the body and further reproduction causes a natural activation of immune processes. During the destruction of foreign bodies, the temperature rises. Acceptable mercury values should be considered as a protective reaction. If a child has a temperature of 38, then this is not a reason to panic.
The increase may be accompanied by weakness, sore throat, febrile convulsions, etc. Autoimmune diseases caused by some internal complications are much less common. In particular, if the fever lasts for 3 or more days, then a fungal infection is quite likely. Basically, fever is caused by viral (the same flu/ARVI) or bacterial (sore throat) infections.

It should also be remembered that children tolerate high temperatures somewhat easier than adults. This is a natural restructuring of the body’s thermoregulation in response to irritants that die in the process. Suppressing it with medications will lead to stopping immune processes, stopping the production of interferon (reducing defenses) and prolonging the duration of the disease. Temperature increases can be classified as follows:
- values up to 38 degrees are called low-grade fever;
- from 38 to 39 - considered moderate febrile;
- if it is above 39, then we are talking about high febrile;
- and, finally, 41+ are dangerous hyperpyrexic values.
An immediate emergency call should be made in the last 2 cases. Since such values are hardly “normal” for a child’s body. In this case, you can begin to reduce the temperature yourself, even before the arrival of a professional doctor.
If a child has a temperature of 39 for 5 days
High values of temperature measurements, which are observed for five or more days, may indicate that the child’s body is not able to independently suppress the infectious or inflammatory process.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of such prolonged hyperthermia, based on examination and tests performed.
It is reckless and very risky for parents to engage in self-diagnosis without professional knowledge.
As a rule, elevated temperature is accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms and conditions:
- cough;
- sore throat;
- indifference to food;
- feeling unwell, lethargic.

Signs of specific inflammatory and infectious processes include:
- vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- ear pain;
- burning when urinating;
- convulsions;
- skin rash;
- neck stiffness.
The listed symptoms individually and collectively indicate the presence of diseases that can cause enormous damage to the child’s health or even lead to death if diagnosed untimely or incorrectly and prescribed treatment.
Thus, if a temperature of 39 degrees lasts for 5 days, you cannot do without professional help from doctors, tests and medications. The possibility of hospital treatment should also not be ruled out.
According to statistics, about 70% of ambulance and local doctor calls to children happen precisely for this reason.
First aid
If the child’s health is satisfactory and the temperature is normal, there is no need to resort to pharmaceuticals. If the baby finds it difficult to perceive the heating of his own body or suffers from a neurological factor, then this can be considered as an exception - and an antipyretic should be given immediately.
Attention! It is forbidden to give your child aspirin or analgin, since these drugs cause complications in a number of cases.
Doctors often recommend Nurofen and Panadol in various forms. This can be either syrup or candles. The only exception is attacks of vomiting, then there is no choice. An effective component in most medications is Paracetamol. Its dosage should be calculated based on the baby’s weight (approximately 15 mg per 1 kg), however, administration by different methods should not occur simultaneously. That is, one of two things - either syrup or candles. It is also worth remembering the need for a sufficient interval between taking the medicine. As a rule, about 3-4 hours pass before a new increase. The result from the administration of the drug should occur within half an hour.
Advice. Preparations in the form of suppositories are recommended for use at night. Their effect is longer lasting, and the effect occurs somewhat later. This form of medication will make it easier for your baby to fall asleep.
If even after repeated use of the drug there is no improvement, then you can resort to the help of Nurofen, the dosage of which should be 2-3 times less. This is due to the fact that the drug can cause some gastrointestinal complications. You should not prescribe it to your baby yourself; it is better to consult an experienced pediatrician.
Features of treatment
Before treating the disease, parents must make sure that their own diagnosis is correct. To do this, you should consult a doctor who will confirm or refute the diagnosis predicted by the parents. Based on the diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
When a child is teething, therapy is not required, but only if the symptoms proceed without complications. If the baby has a strong fever, then you need to give him an antipyretic, and if the gums are sore, you can use special dental anesthetic drugs.
In case of infectious diseases, it is necessary to take the baby to the hospital, where the doctor will prescribe appropriate medications to alleviate the symptoms of the ongoing type of disease. Treating diseases such as measles, rubella, chickenpox, whooping cough and others at home is prohibited. For viral illnesses, the child is prescribed antiviral drugs, as well as medications to eliminate additional symptoms such as runny nose, cough and sore throat.

If a child’s fever does not subside for the fifth day, this indicates a bacterial illness. It is not recommended to take antibiotics and antipyretic drugs at the same time, as an overdose and side symptoms may occur. If on day 2-3 there are no changes in a positive direction, then you should resort to using an antibiotic from another group.
It is important to know! Whatever the temperature, after taking antibiotics it is strictly prohibited to bring it down with antipyretics, since they contain components that have antipyretic properties.
Symptoms at a temperature of 38 degrees
When a child has a temperature of 38, the following symptoms are most often observed:
- A sore throat, dry cough, congestion in the nasal mucosa, the effect of lactic acid in the muscles - all this indicates a common cold (ARVI) and, among other things, requires drinking plenty of fluids;
- If, in addition to cold symptoms, pain in the ears and discharge from them are added, then one can suspect an increase in temperature from otitis media (inflammation of the ear);
- If a rash appears on the child’s body, plaque appears on the tonsils, and the lymph nodes in the neck are enlarged, then it’s time to talk about chickenpox or some other infection (from tonsillitis to mononucleosis);
- An infection may also be indicated by bad odor from the baby's urine or painful sensations when urinating. In particular, in the stomach or lower back area. In this case, antibiotics may be needed;
- But manifestations of nausea and abdominal cramps (vomiting, loose stools) indicate viral gastroenteritis.
All these symptoms one way or another require calling a pediatrician. His consultation is necessary because the parents may have missed something important during the panic attack. It is also important to remember that it is not recommended to use antipyretics for longer than 2-3 days. Because in this way you can suppress the manifestation of the symptoms of a dangerous disease. For example, a fever a few days later may indicate a disease such as pneumonia. The latter must be combated with antibiotics. And one more thing - these drugs cannot be taken at the same time, since then diagnosing the course of the disease will be seriously difficult. It will simply be unclear why the condition improved. In general, a temporary increase in the value of the mercury column should reduce the period of the disease.
Causes of increased body temperature
If an elevated temperature in a child is the only symptom, and no other signs occur, we may be talking about one of the conditions described below.
Heatstroke
In young children, especially under one year old, too hot a climate, warm clothing and intense physical activity can cause the thermometer to rise. This is due to the fact that the control center in such children still does not work well. In addition, fever may occur if the baby is overheated in the sun. In this case, the temperature rises for a short period, and other signs may not be observed.

To prevent such an unpleasant situation, it is important to monitor the microclimate in the room and dress the baby according to the weather.
Allergic reaction
Another fairly common reason for an increase in thermometer readings in children is contact with an allergen. If the baby suffers from an allergic reaction to any substances, then upon contact with them the body temperature may rise to 37-38°C.

In this case, symptoms such as dry cough, nasal congestion, sore throat, increased lacrimation, and sneezing may also occur. If you notice such manifestations in your child, it is important to find the irritant and limit the baby’s contact with it.
Transient fever
In the first weeks of life, the baby’s body temperature may increase due to imperfect heat exchange in the body and instability of the water-salt balance. In other words, this is how the child’s body can adapt to environmental conditions.
This condition, as practice shows, can last from several hours to several days. At this time, it is very important to prevent overheating or dehydration of the small body.
Response to vaccination
Often, an increase in body temperature to 38°C occurs in children after vaccination. Other symptoms may be completely absent. This reaction of the body to vaccination is considered normal. Contacting a specialist is required in cases where the elevated temperature lasts for more than 3 days, and the baby develops weakness, apathy, loss of appetite and other alarming signs.
Teething
Many parents have experienced elevated thermometer readings in their children during teething. This is a completely normal reaction of the body that goes away on its own. In this case, there is no need to reduce the temperature. Practice shows that after 1-2 days the baby’s indicators normalize on their own. Teething can be recognized by signs such as increased salivation, nasal congestion, redness and swelling of the gums. To alleviate the condition of the newborn, it is recommended to use various painkillers and cooling gels.
You might be interested in: Apgar score for newborns in the table
During teething, the baby every now and then strives to take something in his mouth. These could be toys, items of clothing, or just fingers. During this period, it is advisable to especially carefully monitor hygiene.
Infectious diseases of the genitourinary system
In young and older children, high body temperature can occur when the genitourinary system is damaged by various infectious agents. In this case, for the first 3-4 days, any signs may be absent. Later, the baby begins to complain of pain in the back or lower abdomen, burning and stinging during urination, and discomfort in the groin area.
Incubation period for bacterial and viral infections
It often happens that the first sign of acute respiratory viral infection, flu or sore throat is an elevated body temperature. After 2-3 days, other manifestations of a particular disease may appear, for example, cough, runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, redness of the throat, and others.

For the timely detection of viral and bacterial pathologies, it is important to carefully monitor the general well-being of the baby.
Oncological diseases
An increase in body temperature in a child to 38°C or higher can be observed if there are malignant tumors in the body. However, other signs may be absent for a long time. To prevent serious complications, it is important to seek medical help as soon as such a symptom is detected.
Endocrine diseases
Various diseases of endocrine origin, for example, thyrotoxicosis, can cause an increase in thermometer readings in children. Treatment of this condition requires the use of hormonal drugs according to a special regimen.
Caring for your baby at elevated temperatures
When a child has a temperature of 38, he requires special care. You should try to put him to bed to reduce physical activity. Healthy sleep is best for gaining strength. He will still need them to fight the disease. At this time, you can distract him with something, be it cartoons or a science fiction book. Outdoor games are not recommended. The food should be easily digestible so that a sudden attack of vomiting does not bring all the food back. No meat or other fatty foods. There is also no talk about canned food or sweets. It is much more important to provide your baby with plenty of fluids to flush out toxins. Light tea with a spoon of jam or a slice of lemon is allowed. Various herbal decoctions, fruit drinks and baked milk are also used. You can add a little natural honey to the drink.

Advice. Drinking is also good because you can discreetly add medicinal syrups to it.
At the same time, do not forget about ventilating the room and humidifying the air. It is enough to place an open container with clean water somewhere nearby. The room should not be too hot. Maximum - 22-23 degrees.
You should treat your little one's clothes calmly - no piles of blankets or hundreds of pajamas. Such actions will only aggravate further heating, or even lead to heat stroke. Light clothing and a loose blanket are sufficient. You should not wipe your baby with alcohol. The skin will easily absorb alcohol fumes and cause intoxication of the body. Also, you should not use cold compresses, even if the child has a temperature of 38 or higher. The exception is the situation when the baby himself is hot, but his limbs are noticeably cold. In this case, you can limit yourself to a slight change in temperature: apply a cold one to your head, and wrap your arms and legs tightly. This will help balance the temperature.
Some experts argue that the child should not be placed in a horizontal position, as this will complicate ventilation of the lungs. For deeper breathing, active laughter and movement are recommended. Bed rest can lead to unnecessary swelling. After temporary relief, you can place the baby in the prepared bath. Not only the skin will warm up, but also the lymph nodes. The runny nose will noticeably decrease, and the cough will become more wet.
Attention! Do not let it cool down suddenly after water procedures. You will need to wrap him up and prepare him for bed.
If an annoying cough prevents your child from falling asleep, then you should choose the right mixture. They come both from the cough itself and to facilitate the coughing process. If the first remedies are needed for dry coughs, then the second ones are needed for wet coughs. It is also useful to place hot chamomile tea in the room. It has a pronounced antiseptic property. Even simply filling a room with healing steam will have a positive effect.

Even after successfully fighting the disease, you should not rush to send your child to kindergarten. He, like any other person, needs rehabilitation.
Some doctors argue that it is absolutely not necessary to reduce the temperature to 39 degrees. Allegedly, it is not dangerous to children’s health, but it is fatal to harmful microorganisms. However, this recommendation is inappropriate when the baby is shaking with chills. In this case, after consulting with a doctor by phone, you must give an antipyretic drug, and then wait for his arrival to determine further treatment.
High temperature in a child without symptoms
In infants, and in children under 3 years of age, the body’s thermoregulation has not yet been established. Therefore, temperature changes in a baby from 36.3 to 37.5 degrees are normal, provided that the temperature drops on its own and nothing bothers the child. But when the temperature rises higher and lasts throughout the day, it becomes more serious. The main causes of elevated temperature: Overheating You should not wrap babies too much, because they do not yet know how to sweat, so they quickly overheat. And too high a temperature in the apartment is also bad. Pediatricians advise maintaining the temperature in the apartment no higher than 20 degrees, then the baby will be comfortable. Let your child drink plain water more often, not just breast milk. And don’t forget to take air baths from time to time, laying him naked on a diaper - this is both a cooling and hardening procedure at the same time. Teeth cutting In babies, this period begins at about four months. If an elevated temperature is accompanied by whims, screams, anxiety, and often profuse drooling, then teeth may begin to erupt. Sometimes children react to teeth with a runny nose and changes in stool (it becomes thin and watery). It is quite difficult to visually see swollen and reddened gums. Only an experienced pediatrician can determine this. Consulting a doctor is all the more important because these symptoms can also accompany an inflammatory process in the mouth (stomatitis, thrush and just a sore throat). Most often, high temperature during teething occurs from 6 to 12 months, when the incisors appear, and also at 1.5 years when the molars erupt. Then the temperature can rise to 39 degrees. On such days, children sleep poorly and often refuse to eat. The temperature during teething should be lowered depending on the condition of the child. For example, the temperature is low (around 37.3 degrees), but the child is crying and very capricious, which means that painkillers need to be given. However, some children calmly react to temperatures even higher. Often, fever due to teething can last from one to seven days. After the tooth comes out, it will go away on its own. The best thing to do these days is not to overexcite the child, put him to the breast more often, and hug him. Don't play loud music, let him sleep more. Be sure to observe the temperature regime (no higher than +20 in the room). Dress your child in loose clothing that does not restrict movement. It is advisable, when the temperature is elevated, to leave the baby without a diaper so that the skin can breathe and there is no overheating. And then the temperature will subside without medication. IMPORTANT! Be sure to call a doctor if your high temperature (39 degrees or higher) lasts longer than a day, is difficult to control with antipyretics, or rises too quickly after taking medications. It is especially important if the baby constantly cries monotonously, spits up more than usual, vomits, and is constantly lethargic. “It is very important to exclude urinary tract infections in asymptomatic temperatures in infants,” warns pediatrician Evgeniy Timakov. — Particularly dangerous is asymptomatic renal dysfunction, which is accompanied only by elevated temperature. Therefore, first of all, if you have a fever, I recommend taking a general urine test, which can tell the doctor a lot.
Why can the temperature last for 2 days?
The first obvious answer is a viral infection. Dr. Komarovsky is convinced that 2 days of 38℃ or higher with this diagnosis is quite normal. But this doctor, popular in the post-Soviet space, is also sure that on the 3rd day the temperature should begin to decrease. 2 days no higher than 38℃, and if on the third 38.2, this can no longer be considered a normal situation.
It is imperative to make an initial call to the doctor if, for some unknown reason, he was not invited to your home on the first day of illness.
And if the pediatrician has already been called, then if there is no improvement, when the temperature lasts 3 days and rises even more, it needs to be done again. Possible causes of temperature 38℃ for 2 days
| Cause | What are the symptoms other than fever? | What to do? |
| Pyelonephritis and other diseases of the urinary system | No signs of a cold or any other infection. | Do a urine test. Contact a pediatric nephrologist. |
| Reaction to vaccination | It is possible that mild symptoms of the disease for which the vaccine was given may occur. | Knock down from 38℃. |
| Teething in children aged 6 months to 2.5 years | Inflamed and swollen gums, excessive salivation. | Do not let them chew on crackers and crusts, only use special teethers. Apply a special anesthetic gel to your gums. |
| Stomatitis | Redness of the oral mucosa, coating on the tongue, drooling. | Visit the pediatric dentist. |
| ARVI | May begin without signs of a cold. 2 days after the temperature rises to 38 - runny nose, cough, aching joints, weakness. | Avoid dehydration. |
| Sudden exanthema (roseola), most common in children under 2 years of age | 5 days no symptoms except fever and enlarged occipital lymph nodes. | Active drinking regime. When after 5 days the temperature becomes normal and a pink rash appears, call the doctor again to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes. |
| Flu | In addition to the signs of ARVI - headache, watery and red eyes. | Be sure to call a doctor. Drinking with vitamin C. |
| Intestinal infection | Vomiting, diarrhea, nausea. | Be sure to call a doctor. Activated carbon. |
| Appendicitis | Stomach pain, hard abdominal muscles. | Be sure to call a doctor. Do not give painkillers. |
| Angina | Sore throat, changes in the mucous membrane. | Be sure to call a doctor. Gargling. |
| Pharyngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis | Cough, wheezing. | Be sure to call a doctor. Herbal decoctions with an expectorant effect: licorice, plantain. |
| Meningococcal infection, measles, rubella, scarlet fever, chickenpox, herpes. | A rash specific to this infection. | Be sure to call a doctor. Limit contact with other people, especially pregnant women. |
| Mumps (mumps) | Unilateral and then bilateral enlargement of the parotid salivary glands (cheeks near the ears). | Call the doctor. Only liquid food - it hurts the child to chew. Don’t force him to eat, if he doesn’t want to, he’d better drink more. |
| Otitis | Earache | Call the doctor. Do not use a heating pad. Ear drops only after a doctor's prescription. Use cotton swabs to remove discharge only from the auricle, do not go into the ear canal. |
| Myocarditis | Heartache | Call the doctor. Do not use painkillers unless prescribed. |