What weather factors affect an infant?
Outdoor temperature
The influence is not specifically hot or frosty weather, but a sharp change in temperature. Even an adult body often reacts negatively to this weather phenomenon, let alone babies in their first year of life.
Atmosphere pressure
Normal atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. But as practice shows, such pressure rarely occurs. Increased atmospheric pressure greatly affects the cardiovascular system of the infant. The blood vessels of babies are much weaker and less permeable than those of adults, so even small fluctuations in atmospheric pressure can significantly affect the child’s well-being. The baby may suffer from headaches, dizziness and general weakness.
Wind
Indicators such as wind strength and speed are very important. It is known that children feel much worse in windy and cold weather. Symptoms: increased excitability, anxiety, tearfulness. Doctors characterize this behavior as meteoneurosis.
Air humidity
A decrease in air humidity leads to profuse sweating in the baby. This, in turn, leads to dehydration. Dehydration causes blood thickening, changes in heart rate, and poor circulation. This condition is very dangerous for infants: if you do not help the child in time, then sad consequences, even death, are possible.
If the humidity rises sharply, then this is also bad. In summer, this phenomenon can cause heat stroke, and in winter, rapid hypothermia.
Geomagnetic conditions
Magnetic storms have a strong effect even on adults, although many consider them an invention of grandmothers. In fact, this phenomenon is recognized by both scientists and doctors. A magnetic surge can cause stress in a baby, which lasts up to 8 hours. The child is very irritable and capricious on such days. Moreover, if the baby is very weather dependent, then he can experience the consequences of magnetic stress for several days.
What is child overheating?
Overheating is a painful condition of the body that can develop from a person’s prolonged exposure to elevated ambient temperatures. The condition is dangerous, especially for children. Babies in their first year of life suffer most from it.
A quick consequence of overheating can be heatstroke, and this is an extremely dangerous condition. Mortality of children from heatstroke is recorded in 30% of cases. If your child has signs indicating that the baby is overheated, you must urgently provide him with first aid and call an ambulance.
Be careful and regularly monitor your child for possible symptoms of heat and sunstroke. In advanced forms, this condition is extremely dangerous.
Which children are more dependent on the weather?
The greatest impact of the weather is felt by babies who were born prematurely, during multiple pregnancies or by caesarean section. The thing is that such babies already have difficulty getting used to life outside the mother’s womb, and the changeable climate only aggravates the situation.
Even if the baby was born on time naturally, he may also be affected by the weather. This usually happens to children who have some health problems. It has also been noted that children with light hair color are more sensitive to weather conditions.
At risk are infants who have recently undergone surgery, treatment with strong medications, or serious stress (for example, moving and changing environment or conflict in the family). It is worth paying attention to children after vaccination; this factor can also affect weather dependence.

If mommy notices that the baby is reacting too strongly to weather conditions, then this may be an incentive for a thorough medical examination. Particular attention should be paid to the baby’s cardiovascular and nervous systems
We are growing and developing!
Every person is affected to a certain extent by weather changes. Among children, a negative reaction to weather dependence is very widespread. The health of babies is primarily affected by magnetic storms, humidity and solar activity, as well as changes in atmospheric pressure and oxygen concentration in the air. Meteosensitivity manifests itself to a greater extent in children under seven years of age. Moreover, those who live in cities are more susceptible to weather dependence than their peers living in rural areas. In large administrative centers, during magnetic storms and atmospheric fluctuations, 50% of children experience a general decrease in body tone. They develop weakness, causeless irritability, and headaches.

How the weather affects children suffering from various diseases
The most acute reaction of children to the weather is manifested in children with diseases of the respiratory system, digestive organs, and congenital heart defects. These babies need to be given increased attention during sudden changes in atmospheric pressure and changes in the geomagnetic background. Children with heart defects suffer from high humidity. The well-being of children with respiratory problems directly depends on the level of oxygen in the air. For children with bronchial asthma, the most dangerous time is when atmospheric fronts pass. Diseases of the digestive system worsen during geomagnetic storms.
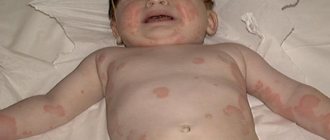
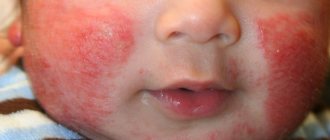
A child reacts to the weather if he suffers from eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis. Here, an exacerbation can be provoked by high humidity and sharp fluctuations in weather factors during the day. For most skin diseases, prolonged thaws, severe frosts and high air humidity are extremely unfavorable. Sometimes the cause of weather dependence can be colds, sudden weight gain, or head trauma. Weather sensitivity can be inherited. If, for example, one of the parents is susceptible to vegetative-vascular dystonia, then the baby will feel the approach of bad weather much earlier than the weather forecasters report it.
When is the impact of weather on children especially pronounced?
The poor health of children has a certain seasonal dependence. The influence of weather on children is especially great in early spring and autumn than in other periods of the year. In total, there are three types of reactions to the weather. The easiest option is when a healthy child feels slight discomfort with increased solar activity, changes in atmospheric pressure, and temperature changes. In this case, there is drowsiness, slight weakness, and worsening mood. The following reaction is referred to as meteopathy. It affects children with chronic cardiovascular diseases, neuropsychic disorders, bronchial asthma, and those who have suffered a head injury.
Children suffering from meteoneurosis are in the most difficult situation. This is a severe form of nervous disorder in which the child reacts very strongly to the weather. Magnetic storms, temperature changes, changes in atmospheric pressure, and high humidity lead to attacks of suffocation, cardiac complications, and increased irritability. As a rule, children with impaired metabolism and a weakened immune system, as well as extremely impressionable and psychologically vulnerable children, are prone to meteoneurosis.
How to reduce children's reactions to the weather
Dealing with weather addiction in children is difficult, but it is possible. First of all, it is necessary to increase the defenses of a small organism. Good nutrition and physical activity play an important role in this. Hardening also helps combat weather dependence. Diet can reduce the severity of unpleasant sensations from “weather vagaries”. It is necessary to exclude fatty, smoked and fried foods from the baby’s diet. You need to feed your child food rich in vitamins C, E, B. There are especially many of them in citrus fruits, spinach, and nuts. These vitamins effectively fight the disease.
The main cure for weather addiction is undoubtedly fresh air. The child should be in nature as often as possible. This will protect it from pressure changes and magnetic storms. There is no better therapy than walking in the woods and playing in the park. Unfortunately, these days there are no universal remedies that can once and for all rid a little person of meteosensitivity. But there are drugs - adaptogens. They help improve the child's health.
Diseases associated with weather dependence of the infant
If the baby is weather-sensitive, this can lead to exacerbation of chronic diseases, and also signal the following diseases:
- Rheumatism. A child’s complaints about pain in the legs during bad weather should not be ignored: this is a reason to examine the baby.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (vegetative-vascular dystonia, heart disease, pressure inside the skull). Whims in bad weather in children with these diseases are not just bad behavior, but suffering from pain and discomfort.
- Gastrointestinal ailments. It is in bad weather that children most often experience exacerbations of gastritis, colitis and biliary dyskinesia.
- Skin diseases (atopic dermatitis, eczema, etc.). Any dermatologist knows that in cold weather and low humidity, all skin diseases in children sharply worsen and are less treatable.
- Kidney diseases. High air humidity and low temperatures can have a dramatic negative impact on kidney health. In such weather, children may have difficulty urinating, pain in the abdomen and lumbar region, and various complications of kidney disease, for example, intoxication.
- Asthma. Sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, high humidity, and low oxygen levels immediately affect asthmatic children. During this period, they experience shortness of breath, weakness, cold sweat, dizziness, and possible loss of consciousness.
- Neurology. Children with diagnoses such as hyperactivity and ADD (attention deficit disorder) suffer greatly from changing weather. They become more excitable and capricious or, conversely, depressed and lethargic.

If the baby shows anxiety and causes a lot of trouble in bad weather, then you need to understand that it is not his fault. You need to treat a weather-dependent child with understanding and be patient
Weather dependence in a child: how to help your baby survive heat and magnetic storms
– Is there a connection between the human body and natural phenomena?
– Today, the results of joint scientific research by doctors, climatologists, and pediatricians give the right to assert that the state of human health, almost from the first days of birth, depends on the influence of specific weather, geophysical and cosmic factors. One of the signs of a decrease in the immune and protective forces of a child’s body is the occurrence of meteodependence, meteosensitivity, or meteoneurosis.
Weather sensitivity is the body's predisposition to adverse reactions caused by the weather. But the changes themselves that occur in the child’s body in response to changing weather are called meteopathic reactions, or meteoneurosis. The appearance of meteoneurosis in a child may indicate a weakening of protective, adaptive processes or the presence of some hidden pathological process.
Based on the nature of the child’s meteopathic reactions, one can guess what kind of disease the child is latently or openly suffering from. By the way, according to a number of scientists, weather dependence in a child is almost three times higher among residents of large cities, especially among children, than among residents of rural areas.
– Is it a mistake to call meteoneurosis a disease?
– Once again it is worth emphasizing that meteoneurosis in a child is not a disease. It is evidence of a weakening of the protective-adaptive and immune forces of the child’s body after an illness, stress, improper hardening regime or the virtual absence of health-improving procedures in the child’s life, etc.
– Can meteoneurosis be called a seasonal phenomenon?
- Of course not. Meteoneurosis in a child can acutely manifest itself during sharp abnormal fluctuations in weather conditions (sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, high humidity, fluctuations in air temperature, high geomagnetic background).
Most often, meteopathic reactions in a child occur during the transitional seasons of the year, when fluctuations in meteorological parameters are especially noticeable for the child, as well as on days with the formation of weather conditions of “external” air hypoxia - hypoxic type of weather (oxygen content in the air is below the climatic norm).
– Children with what diseases react faster than others to weather changes?
– The weather significantly affects the well-being of children with congenital heart defects. Children suffering from respiratory diseases also react sharply to weather fluctuations. For them, days with high humidity, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, and low oxygen content in the air are stressful.
During this period, the child may experience unexplained weakness, suffocation, and cough associated with lack of air. The same can be observed in the formation of weather with stuffiness and overheating in the summer, when there is a sharp decrease in oxygen content in the air (especially such weather conditions are stressful for children with asthmatic conditions).
Parents should be concerned about general weakness, shortness of breath, and the appearance of symptoms of suffocation and coughing in the baby. All this may indicate a decrease in the vital capacity of the child’s lungs. In the winter and autumn seasons, in damp and cool weather, ailments, exacerbations, anxiety and depression may occur in children with diseases of the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys.
Very often, under the influence of unfavorable weather conditions, especially in spring and summer, intractable skin diseases - eczema, psoriasis, various neurodermatitis and other allergic disorders - come to life. Prolonged exposure to the sun in young children can trigger solar urticaria.
– What treatment can the doctor suggest?
– To correct psycho-emotional instability, increased excitability and dysfunction of the autonomic regulation centers, the attending physician may prescribe sedatives and sometimes hypnotics.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are very useful for such children - medicinal electrophoresis on the collar area, electrosleep. For pronounced meteorological neuroses, especially in adolescents, it is useful, in consultation with a doctor, to use vitamins, adaptogens, antihistamines and neurotropic drugs.
In cases where the oxygen deficiency already existing in the child’s body (cardiac dysfunction, bronchial asthma) is superimposed by weather hypoxia, it is advisable to carry out aerotherapy. Walking before bed, breathing exercises, and oxygen cocktails are especially useful.
– What are your tips for preventing meteoneurosis in a child?
– Weather vagaries are not so terrible, and you should not expect the inevitable appearance of symptoms of deterioration. Knowing about upcoming adverse weather conditions and possible manifestations of meteoneurosis, it is necessary to use medications recommended by your doctor in advance.
The most important thing in the prevention of meteoneurosis is hardening: sun, air baths, hydrotherapy. Previously, in children's health institutions there was a so-called “health path”, where children began hardening procedures with physical exercises in the air, then walked along the “health path”, which was doused with water on both sides with a gradually decreasing temperature.
These kids responded well to weather changes and suffered from colds less often. Rational hardening using sun, air baths, and hydrotherapy methods will help to easily cope with the manifestations of meteoneurosis in a child, increase the overall resistance of the child’s body, help improve the regulation of metabolic processes, and strengthen the nervous system.
Famous Russian pediatrician G.N. Speransky believed that hardening a child should begin from the first day of his life. The mildest means of hardening are air baths, which should be started from two months of age at room temperature (20–22°C), starting from two to three minutes and gradually increasing to 15–30 minutes.
In the warm season, air baths can be carried out outdoors and combined with solar ones. The air temperature in the shade should be at least 20°C, the duration under comfortable indifferent weather conditions can be from five and increase to 15–25 minutes a day.
Follow the rules for caring for newborns at home and perform water procedures. They can be started at home by rubbing with a soft towel or mitten for seven to ten days, then wet rubbing at 30°C and gradually lowering the temperature to 20°C, and then starting water procedures.