How many days does it take for a baby to have a runny nose?
How long rhinitis treatment will take depends on several factors, among which the cause of such a symptom is one of the first places.
Swelling of the mucous membrane during ARVI
How long does a runny nose last during ARVI? Experienced mothers and pediatricians will say that viral rhinitis can be diagnosed in babies up to 5-6 times a year. This is due to both the imperfect immune system and the structural features of the airways.
An increase in the amount of mucus secreted from the nose when viruses enter the body is a protective reaction to the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms. If the baby’s immunity is not further weakened by concomitant pathologies, then usually in 5-6 days it is possible to cope with the infection and not a trace remains of the liquid discharge from the nose.
Physiological runny nose
After birth, the baby is protected by antibodies inherited from the mother, but by six months this protection is weakened. The child is forced to independently cope with attacks from viruses and bacteria.
Physiological rhinitis is a completely normal phenomenon, which indicates the child’s adaptation to new conditions. For some, it disappears within a couple of months, and may accompany the child for about three months. The duration often also depends on the care of the baby's nose.
Allergic nature of discharge
Nasal discharge due to an allergic reaction can accompany children for a long time, until the irritating factor is eliminated. If such a pathology is detected, then it is necessary to try to identify the allergen and, if possible, reduce the baby’s contact with it.
Running nose when teething
When a baby starts teething, runny nasal discharge worries many mothers. But children's specialists argue that the cause is not the process itself, but a decrease in immunity against its background.
This leads to:
- The body's defenses decline.
- The immune system cannot cope with bacteria and viruses that penetrate the child's body.
But there is another reason, which physiologists easily explain. The mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and mouth have a common blood circulation. When teeth begin to cut, an inflammatory process occurs in the gums and blood flow increases. At the same time, in the nasal cavity, the cells of the mucous membrane begin to work hard and secrete a small amount of mucus.
The duration of a runny nose during teething depends on how quickly the tooth appears on the surface.

How to treat a persistent runny nose in a child?
To treat a long-term runny nose in a baby, first of all, you need to contact a pediatrician or pediatric otolaryngologist to conduct a thorough and comprehensive examination of the baby, because rhinitis can accompany quite serious diseases.
Should you warm your nose if you have a runny nose? - We recommend reading.
With reduced immunity
If a prolonged runny nose due to a cold in a child is caused by a decrease in immunity, then immunomodulators should be taken. For example, the drug IRS-19 contains a complex of lysates of bacteria that are the most common causative agents of respiratory diseases. The antigens contained in the drug cause protective reactions in the mucous membrane, similar to those that occur during infection with the corresponding pathogens. There is an increased proliferation of immunocompetent cells, and the level of lysozyme and interferon, which are destructive to pathogens, in the mucosal secretion increases. The activity of phagocytes increases, the number of antibodies increases.
Use of various drugs
You should not prescribe all kinds of advertised drops to your newborn on your own. If you have been prescribed such drugs, then treat the dosage with all possible care. Correctly measure the number of drops for the baby and use the drug for no more than the specified period.
When a newborn has a runny nose, there are three types of drops with different effects:
- Vasoconstrictors. The name speaks for itself. Designed to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane. It is better to use them before the child goes to bed to remove swelling. The action does not begin immediately, that is, in the next minute after the drop is applied, the nose will not breathe, however, this is not a reason to immediately repeat the procedure;
- Antibacterial. Used for infectious causes of runny nose;
- Immunomodulatory and antiviral. These solutions activate the child’s immunity to fight the disease. They are used both prophylactically and for treatment.
Read more about cold drops for newborns>>>
Important! Do not get carried away with self-medication and remember that if you have at least one of the symptoms described below, you must definitely show your child to a doctor!
- Increased body temperature of the baby. 37.5 for children under one year of age and 38 for older children;
- The duration of a runny nose is more than two weeks;
- The newborn's appetite, stool, and sleep are disturbed;
- A runny nose appeared after contact with a suspected allergen;
- The baby does not eat and is rapidly weakening;
- The runny nose was accompanied by redness of the throat;
- We noticed wheezing in the child.
Additional measures taken for a runny nose
A child under one year old can only breathe through his nose, so imagine the difficulties he faces when he starts to have a runny nose. Not only breathing becomes difficult, but also sucking. And, accordingly, your newborn baby will not be full.
- Therefore, your task for these days will be to regularly clean your nose using the above methods and apply frequent breastfeeding. If the child is already drinking water, you can offer it to the child more often. Read when you can give water to a newborn>>>
- Don't forget to ventilate and moisten the room. And before going to bed, you can slightly raise the edge of the mattress to improve the outflow of discharge and prevent it from entering other cavities.
Causes and signs of the disease
A runny nose in a newborn baby is not always a sign of a respiratory disease. The mucous surface of the nose does not yet begin to fully function after birth. Therefore, mucus begins to be produced in response to any external factors.
Physiological rhinitis in infants does not require treatment; it is enough to instill saline solutions into the nose.
There are criteria for how to determine that a baby has a runny nose due to age characteristics. With a physiological runny nose, the baby’s general condition does not worsen; he eats well and sleeps soundly. The child is active, plays, is not capricious, and there are no other alarming symptoms.
The immunity of infants is weak, so it is easily attacked by viruses and bacteria. Often, infants who are fed formula instead of breast milk suffer from colds. A viral or bacterial infection from the upper respiratory tract very quickly spreads to other organs, so do not delay treatment.
- A number of characteristic signs will allow you to understand that a newborn has a runny nose of a viral nature. The initial symptoms of a runny nose in an infant are frequent sneezing, watery eyes, and the snot is mucous and transparent (as the cold develops, it becomes white). Breathing during ARVI is disrupted, the nose sniffles, shortness of breath and cough may occur. The child refuses to suck milk, often abandons the breast, is capricious, and cries. Acute rhinitis in children is often accompanied by a high rise in body temperature.
- Respiratory rhinitis of bacterial origin in infants has slightly different symptoms: thick, green-brown snot, nasal congestion, and body temperature rises above 38 degrees. The child has difficulty breathing through his nose, he often cries, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly.

A runny nose in a baby can be caused by various allergens. The allergen enters the nasal mucosa along with air, causing swelling and congestion.
Therefore, it is important to carry out regular wet cleaning in the room where the baby sleeps and plays, and be sure to monitor the diet so that the allergen does not enter the baby’s body along with breast milk.
There are also signs that parents can use to understand that a runny nose is caused by an allergy. Rhinitis caused by allergies in a child under one year of age occurs without fever, sneezing or coughing. It is difficult for him to breathe due to nasal congestion, the snot is clear, mucous-watery, lacrimation, redness of the eyes, a rash and irritation can be observed on the body.
How many days does a viral runny nose last in a baby?
How many days a child’s runny nose lasts depends on the treatment tactics, as well as the effectiveness and timeliness of the prescribed therapy. Nasal breathing in infants is completely normalized 2 weeks after the onset of the disease. Such a long period of the disease is due to the not yet fully formed immune system.
How long does a child’s runny nose last, according to average statistics, and when should you sound the alarm? The duration of the inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract of the infant primarily depends on the type of disease. Viral rhinitis always goes away faster than bacterial rhinitis, unless it is accompanied by another infection. If the cause of the appearance of mucous discharge from the nasal cavity and its congestion is the action of allergens, rhinitis may drag on. It’s difficult even for a specialist to say how long a baby’s runny nose caused by allergens lasts. The child will be bothered by unpleasant symptoms until the contact with the allergen is eliminated, and this may take a long time. You can alleviate the baby’s condition by taking antihistamines, but they will not completely help get rid of the disease.
How many days a baby has a runny nose of viral etiology can be understood by familiarizing yourself with the characteristics of each stage of this inflammatory process:
- Reflex stage. This phase of rhinitis lasts only a few hours. When examining the child’s nasal cavity, the otolaryngologist notes the pallor of the mucous membrane. Such changes are caused by severe narrowing of blood vessels. Characteristic signs of this stage of rhinitis are dryness and burning in the nose, frequent sneezing.
- Catarrhal stage. It usually lasts 2-3 days, during which time severe swelling and inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs, as a result of which it becomes bright red.
- During the transition of the inflammatory process from the second stage to the third, the addition of a bacterial infection is noted. It is impossible to accurately answer how many days it takes for a runny nose caused by bacteria to go away. If the child is given topical antibacterial drugs, such as Isofra or Polydexa, on time, rhinitis can disappear even in 2 days. However, in advanced situations, the disease can drag on for up to 3 weeks. Such a long course of a purulent-inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses is fraught with serious complications.
If no complications arise during the course of rhinitis, all stages pass within a week, after which the child returns to full development.
Folk remedies for the treatment of runny nose in infants
When using folk recipes to treat a runny nose in infants, you should follow the same rules as in the case of medications - consult a doctor and be careful. The body of infants up to six months is so vulnerable that even the most harmless means can cause serious harm to it.
- Many parents use herbal decoctions of calendula and yarrow to treat rhinitis in children. They are prepared as follows: pour a teaspoon of herb into a glass of boiling water, steam in a water bath, cool and drop ½ pipette into each nostril.
- Another common remedy that our mothers and grandmothers used is breast milk, which is also instilled into the baby’s nasal passages. It should be noted that many doctors are skeptical about such treatment, since the nutrient medium of milk can create favorable conditions for the development of viruses and bacteria.
- To make breathing easier for a baby, freshly squeezed beet or carrot juice is instilled into the nose, diluted with water or olive oil in a ratio of 1 to 1. This product not only kills germs, but also moisturizes the nasal mucosa well. Sea buckthorn oil works in a similar way.
- Dilute aloe or Kalanchoe juice with boiled or still mineral water (10 parts water to one part juice) and drop drops into the child’s nose 5 times a day. It is strictly not recommended to use pharmaceutical alcohol tinctures for this recipe.
- Irritations that can form due to leaking mucus or because the baby rubs his nose with his fists should be lubricated with baby cream.
A runny nose is a common phenomenon that every second mother of a baby encounters, so there is no need to panic in any case. With a balanced approach to treatment, you can get rid of the problem as quickly as possible and without consequences. Read on our website for causes of pain near the navel on the left in women.
Treatment with medications
The thing is that most medications will be contraindicated for children under 3 years of age. However, there are a number of medications that can be used for them. When you need to cure a runny nose in a child of only 2 years old, it is worth remembering that it is very useful to rinse the nose. This will allow mucus to be removed from the sinuses more quickly and will speed up recovery. To do this, you can use special liquids - Aquamaris, Aqualor.
They come in a convenient container, so you can drip the product into your nostrils quickly and easily. It is advisable to carry out the procedure while the child is lying down. A few seconds after the product gets into the problem area, it needs to be removed. To do this, it is enough for the baby to take a vertical position.
You should not demand too much from a small patient. If a schoolchild can immediately blow his nose, then when the child is 2 years old, this action may not work out well. You shouldn't pay too much attention to this moment. Let the healing liquid come out on its own. You should absolutely not require your child to pass the medicine through the nose and release it through the mouth. Such washing is permissible no earlier than the patient turns 6 years old. The use of Aquamaris or Aqualor can be done quite often. They mainly contain salt water, which does not cause any harm to the body.
How to help your baby
Clogged nasal passages interfere with the child's normal breathing through the nose. Young children do not always calmly and quickly switch to breathing through their mouth, so the nose must be cleared of mucus accumulation. If your nasal passages are clogged, you should use an aspirator. When crusts have formed in the child’s nose, you must first soak them and then remove them with an aspirator or syringe. To liquefy accumulated secretions, you can use drops based on natural sea water or make a weak salt solution at home.
Vasoconstrictor drops are used only as prescribed by a doctor and in accordance with strict dosage, as they can be addictive and lead to dryness of the child’s nasal mucosa. An acute runny nose must be cured completely. Untreated rhinitis can cause chronic inflammation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
Can I help my baby on my own?
Despite the reasons that led to a runny nose in a newborn, parents will be tasked with providing timely assistance and alleviating the condition of their child. For this it is recommended:
- Regulate the temperature of the room in which the newborn is staying (the temperature should be within 23 degrees).
- The room must be ventilated.
- It is necessary to monitor the air humidity in the room (about 60%), if there is no humidifier, then during the heating period you can place a container of water on the radiator.
- The child's nose should be regularly cleared of mucus. For this purpose, aspirators and saline solutions are used to instill the nasal sinuses. In this way, the secretion will be released better.
- To help with the natural discharge of mucus, experts recommend raising the head of the crib by 40%.
Prevention
If a child has just begun to develop symptoms of a runny nose, then the mother has the power to stop this process and even reverse it with the help of simple preventive measures:

- Increase air humidity if it is below 50%. This is what humidifiers are for. If there is no humidifier, hang a wet cloth and place water-filled containers with a large evaporation area (basins, wide pots, bowls);
- In addition to mother's milk, which is food, the child should drink a lot: water, baby teas. It would also be a good idea for mom to drink plenty of water so that the milk has a higher percentage of water content;
- Constantly ventilate the room, maintaining the temperature no higher than +22° +25°, do wet cleaning at least once every 2 days;
- Eliminate all possible sources of allergies: house dust, animal hair, strong odors of household chemicals and perfumes;
- Regularly cleanse the nasal passages of mucus and crusts. To do this, you need to fix the child's head on the left side, drop 2-3 drops of saline or other moisturizer into the left nostril and press the nostril to the nasal septum. Do the same with the other nostril. Then use an aspirator to remove mucus and crusts. If you couldn’t get the crusts, you can make a gauze flagellum and moisten it in boiled vegetable oil, insert it into the nostril no more than 0.5 cm, and remove what remains with a rotational movement.
Nasal drops for babies
The modern pharmaceutical industry offers parents a large selection of all kinds of drugs for the treatment of runny nose in infants, but they can only be used as prescribed by a pediatrician and in the appropriate pediatric dosage. Nasal drops that are used in this case are divided into several types:
- saline solutions;
- homeopathy;
- vasoconstrictors;
- antiallergic drugs;
- enveloping drops.
The safest are saline solutions, but when using homeopathy and vasoconstrictor drops, great care should be taken, as they have a number of side effects and can cause allergic reactions and addiction

Treating a baby's runny nose with saline
Saline solutions
- "Aqua Maris" (analogue - "Humer"). Sterilized sea water, which can be used to moisturize the nasal passages from the first days of a child’s life, as well as to combat runny nose of various etiologies;
- "Saline." A saline solution with additional chemical components (benzyl alcohol, etc.), which makes breathing easier and clears crusts from the nose.
Vasoconstrictors
- "Nazol baby." A remedy that was specially developed for infants and is prescribed in cases where a runny nose causes great discomfort to the baby (interferes with normal sleep or feeding);
- "Nazivin." A children's analogue of an adult drug, containing a minimal amount of active substance, as well as a number of chemical components that can negatively affect the health and well-being of the baby. For this reason, it is recommended to be used only as an emergency remedy;
- "Otrivin." Another common vasoconstrictor drug that has a number of side effects and can also be addictive.
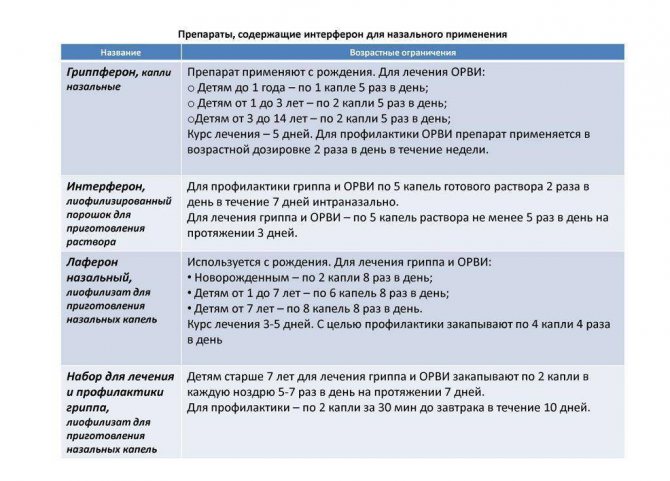
Interferon-based drugs for the treatment of ARVI and influenza
Homeopathic medicines
"Euphorbium compositum". A complex drug with anti-inflammatory, antiviral and immunomodulatory effects, which is used not only for therapy, but also for the prevention of rhinitis.
Enveloping and cauterizing drugs
"Protargol". The main component of the product is silver ions, so the drops are effective against all types of rhinitis, including purulent and bacterial (the drug is not used for runny noses of viral etiology). Incorrect and too long-term use of drops can cause the accumulation of silver in the body, which will lead to negative consequences.
Antiallergic drugs
"Allergodil." An effective remedy for combating allergic rhinitis, however, before using drops, you should make sure that the diagnosis is correct.

The most popular children's nasal drops
Snot in a 4 week old baby
Good afternoon,
Evgeny Olegovich, this is our situation. There are two children, one is 2.5 years old, he has been going to kindergarten for half a year. The girl is 2 months and 10 days old.
From the first days of September, the eldest son began to have a runny nose, because... there was no temperature and, in general, a violation of his general condition, too, then they continued to take him to kindergarten (forcing the teachers not to put socks on him, not to put on sweaters in the group, etc.), I began to pick him up early in order to walk more... at home 18 degrees, Humidity is more than 50. In the evening we still breathed into an inhaler with saline solution. We went to the pool, swam in cool water every day….
The snot has been pouring for more than a week...since September 12, the teacher says that the child did not sleep during quiet time, because... I coughed all the time... At night the situation repeated itself... in the morning I coughed up part of my dinner.
We stayed at home and within a couple of days we stopped coughing, slept normally... less snot, but still flowing...
Let's go to kindergarten... the situation hasn't changed at all...
On Monday 22 he started coughing again, the snot started flowing with renewed vigor….
We don’t go to the garden for a week... I only rinse with saline solution, do inhalations with it... I ventilate all the time... the house is cold, damp, the children are dressed. We walk a lot.
Little girl... snot since September 1... (brother loves us very much, kisses and strokes us all the time... taught him to wash his hands and wipe his nose before) We all live together and there is neither the desire nor the opportunity to completely isolate the children. During the day I am alone with both of them.
My daughter also feels good, sucks normally, sleeps normally, and walks. But my nose is stuffy, sniffling like a little train... I wash it, take out the sniffles, always when I’m at home near the inhaler with saline solution... I take out the snot again... but it feels like it’s stuck there somewhere and all my body movements lead to nothing. I've had a stuffy nose for almost 4 weeks now.
Trips to pediatricians end with a list of antibiotics, Nazivin and Protargol. The eldest child was tested, eosinophils 11, soy - 28, rod-nucleus 6, segmental nuclear 45, no young ones. The pediatrician said - inflammatory, urgently go to the hospital or take an antibiotic.
We'll get the youngest one tested next week.
Visits to ENT are not my questions; antibiotics are prescribed by the pediatrician.
Both children have liquid mucus, the older one is transparent, the younger one is white. The temperature has not risen in a month.
For 2 weeks I’ve already had snot and no fever either.
The masseuse will come next week.
In 2 weeks we will leave this cold at 26-28 for 2 weeks on vacation.
Evgeniy Olegovich,
1. What actions would you advise me to take in connection with the current situation? If I understand correctly, we infect each other in a circle. And we ourselves cannot get out of this circle. Do you need help, how can you help a 2-month-old baby, an older child with a lactose allergy, and a nursing mother?
2. How dangerous is the situation with the baby? Almost half of her life was spent with snot and rinsing. But I can't give an active, healthy baby an antibiotic. Your opinion?
3. To what extent are my thoughts correct and the masseuse will be able to help both babies get rid of phlegm?
I really don’t want to feed my kids chemicals. ...
Evgeniy Olegovich,
Thank you very much!
Prevention

Prevention of rhinitis for newborns should be carried out comprehensively. It is necessary in every possible way to increase the baby’s immunity, improve his body’s ability to resist damage from viral or bacterial infections.
Prevention of rhinitis for infants includes a number of rules:
Timely treatment or prevention of colds and other diseases reduces the risk of complications due to prolonged rhinitis. Any, even the most insignificant symptom of the disease, should not go unnoticed by parents. Treatment of the baby should be carried out according to the recommendations of the pediatrician. Self-medication threatens serious consequences for a small, fragile organism. The best food for a baby is mother's breast milk
Artificial formulas, no matter how high-quality they are, cannot compare with it in terms of the content of useful substances necessary for the formation of strong immunity in the baby. Daily walks in the fresh air and ventilation of the room help to harden the little organism. When walking in the fresh air, it is important to prevent your child from getting hypothermic. Clothes should be chosen according to the season so that the baby is neither cold nor hot
The same goes for airing rooms. The temperature in the room where the newborn baby is located should not fall below 18°C. While the windows are open, you should take the child out of the room and prevent him from being in a draft. A nursing mother should avoid highly allergenic foods. If your baby is allergic, contact with the allergen must be avoided. You should not be with your child in places with a strong smell of cigarettes, building materials, or any chemicals. The baby's nasal cavity needs to be properly cared for: moisturize daily, remove crusts. A special humidifier or a large container of water will help maintain optimal humidity in the room. The room where the baby is constantly located must be clean. Daily wet cleaning will help avoid dust accumulation and drying out the air in the room.
Children whose parents suffer from chronic rhinitis often have a predisposition to this disease. In such cases, it is recommended to strengthen preventive measures: spend more time in nature, walk.
Treatment of viral rhinitis with medications
ARVI and other infections are the most common causes of nasal congestion and runny nose. Even if it seems that this reason is excluded because the child did not have contact with sick people, this is not so. A baby can easily become infected from a carrier who is not sick.

What is viral rhinitis
The following symptoms accompanying a runny nose may indicate its viral nature:
- breathing is significantly difficult;
- mucus of a yellowish or greenish hue with a fairly thick and viscous consistency is secreted from the nose;
- body temperature is increased;
- the mucous membranes in the nose and throat are irritated and reddened;
- the baby refuses to eat or takes frequent breaks during feeding to catch his breath;
- the child behaves restlessly, cries a lot, has difficulty falling asleep and often wakes up.
In the case of viral rhinitis, it is not possible to do without medications to speed up healing and prevent complications. The doctor will examine the child and make an accurate diagnosis. If the presence of infection is confirmed, the main goal of drug therapy will be to eliminate it as quickly as possible.

Runny nose in a baby
Usually the pediatrician prescribes:
- antipyretic medications;
- saline solution for instillation into the nose;
- vasoconstrictor drops (only in rare cases when the child cannot breathe through his nose at all due to congestion);
- immunomodulatory agents (only in difficult cases when the disease occurs with the addition of a bacterial infection).
How to independently help a baby during viral rhinitis
During an infection, the baby’s already narrow nasal passages narrow even more due to swelling, and also become clogged with mucus (snot). In such conditions, the child’s breathing is blocked, he cannot eat normally, and is unable to sleep. The primary task of parents is to alleviate the baby’s condition. You can do this using the following methods:
ensure optimal humidity (60-70%) and air temperature (18-20 degrees) in the room so that the mucus dilutes and comes out easier; drop a drop of saline solution, mineral water or special preparations based on sea water (Aqua Maris) into the baby’s nostrils so that the nasal sinuses are cleared and the mucous membrane is moisturized; If the child cannot sleep at all, it is possible to use an aspirator once and carefully to suck out mucus from the sinuses.
Aspirator for suctioning mucus from the sinuses
If the air in the room is humid, the mucus thins out. Burying it in helps it come out quickly. In addition, immediately after instillation, the newborn begins to sneeze, automatically blowing out all the mucus accumulated in the sinuses with a stream of air.
Eucalyptus essential oil will also help your baby cope with a runny nose. It has antimicrobial, antiviral, antipyretic and antiseptic effects. You can arrange an aromatherapy session for your baby by dropping a drop of oil on a cotton swab placed at the head of the crib. You can also spray the oil in the room using a spray bottle, add it to an aroma lamp or a special compartment of an air humidifier. You can also drop the oil into a cup of hot water, but place it away from the child.
Eucalyptus oil for the treatment of runny nose in newborns
The doses used in the humidifier and evaporator are minimal - a drop of eucalyptus oil for every eight square meters of the room. In a spray bottle, you can use one drop of eucalyptus oil per 100 ml of plain water. Two 20-minute sessions per day are enough.
Symptoms and causes of frequent runny nose in children
Constant discharge from the nasal cavity causes discomfort, especially for young children. They become more restless, refuse food and show irritation. The symptoms and causes of frequent runny nose in children are different. The main reasons are considered:
- Allergy.
- Viral disease.
- Infection.
- Inflammatory process in the nasopharynx.
- Hypothermia.
There are many other reasons why a constant runny nose may bother you. One of them is chronic rhinitis.
The symptoms accompanying rhinitis are also different: fever, headache, burning in the nose, sneezing, coughing, soreness, increased lacrimation. Depending on the symptoms, you can make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause, and then prescribe treatment.
Constant runny nose and nasal congestion in a child
This question is worth thinking carefully about. Continuous rhinitis and a stuffy nose in a baby can be a prerequisite for serious illnesses. The main reasons for this condition include:
- Suppuration in the nasal cavity.
- Nose injury.
- Hereditary diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Adenoids.
- Atrophy of the nasal septum.
- Sinusitis.
- Sinusitis.
- Acute rhinitis.
Whatever the cause of a runny nose and nasal congestion, it must be diagnosed. The sooner a problem is identified, the faster you can find an adequate solution to it and begin a rational solution.
Frequent cough and runny nose in a child
Often the symptoms become more serious. The baby feels unwell. Frequent runny nose and cough cause him a lot of trouble. And for parents, such a condition becomes an obvious problem, since treatment is necessary. But what it should be aimed at and what it should be aimed at is almost impossible to decide unambiguously.
Increased frequency of symptoms such as cough and rhinitis in a child can be caused by the following diseases:
- Rhinopharyngitis. At the same time, the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and throat become inflamed.
- Tonsillitis. The inflammatory process actively occurs in the tonsils.
- Pharyngitis. Inflammation of the pharynx.
- Laryngitis. Inflammation of the larynx.
- Pneumonia. Active processes occur in the lungs.
- Bronchitis. The soft tissues of the bronchi are involved.
- Allergies. Inflamed mucous membrane with irritated receptors.
Each of these diseases requires immediate response. After all, frequent coughing, along with constant snot, can degenerate into a more serious condition, therefore, the sooner you begin to restore the normal functioning of the body, the faster you can alleviate the baby’s condition. The main thing is to make a timely and correct diagnosis.
Other symptoms and their causes
There are other reasons why a baby may feel very unwell. He may complain of additional pain and at the same time be constantly lethargic or, on the contrary, in a state of strong excitement.
In addition to the reasons mentioned above, it could be:
- Sinusitis. The child has a constantly stuffy nose. From time to time he may complain of headaches. Purulent exudate also comes out with clear snot.
- Vasomotor rhinitis. Constant burning in the nose and sneezing. With strong exposure to the irritant, sneezing can continue for a long time. Profuse lacrimation.
- Incorrect use of vasoconstrictor drugs. Occurs when a child is independently prescribed treatment. Against the background of severe nasal congestion, transparent discharge is actively coming out.
- Weakened immunity. A runny nose may be accompanied by a slight cough and fever. Symptoms appear and disappear.
In some cases, this condition can be caused by an unsuitable climate. Frequent runny nose appears constantly, the child feels uncomfortable. This can be tracked both in the first weeks of life and if the parents moved to a new place of residence. Literally from the first days, the baby has a runny nose, accompanied by a rare cough, and the temperature periodically rises.
Whatever the symptoms and causes, they must be eliminated and fought in every possible way. Only in this case can you help the child. There is no point in expecting the baby’s body to cope with the problem on its own.
How to cure a runny nose in a baby
The pharmacy market offers a large selection of medications to treat a runny nose. If there are no other symptoms other than a runny nose, then you can get by with local remedies in the form of drops. In other cases, treatment is accompanied by taking other groups of medications
It is important to understand what type of runny nose your baby has
- If nasal congestion is severe, the doctor may prescribe vasoconstrictor drops (Nazivin 0.01%, Nazol Baby, Otrivin Baby). Their dosage must be precise to prevent overdose. The duration of treatment of runny nose in infants with such drops should not exceed three days. If you do not follow the recommendations of your doctor regarding the dosage and duration of use, adverse reactions may develop in the form of heart rhythm disturbances, nausea and vomiting, and convulsions.
- Rhinitis in newborns can be treated with antiseptic drugs: Protargol drops (Sialor), Collargol. You can use Miramistin solution. You can reduce mucous discharge from the nose and stop the spread of germs using Albucid drops. Antiseptic agents are used only if purulent mucous discharge is observed from the nose.
- For a runny nose caused by bacteria or viruses, infants can be prescribed immunomodulators: Genferon Light suppositories, Viferon, Derinat drops, IRS-19.
- If the cold was caused by viruses, it is advisable to prescribe antiviral drugs. Grippferon nasal drops are effective and safe. They protect the body from re-infection and inhibit the growth of viruses. A baby can be instilled with one drop up to five times a day.
- If a newborn's body temperature exceeds 38.5 degrees, antipyretics are indicated: Nurofen, Ibuklin, Tsefekon.
- If you are worried about a severe runny nose, with viscous, thick snot, mucolytic expectorants (Bromhexine, Ambrobene) can be prescribed. They help thin mucus and remove it.
- In the event of a bacterial infection, treatment of a runny nose in newborns may be accompanied by antibacterial drops: Isofra, Polydex. Sometimes systemic antibiotics are prescribed: Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin.
- Treatment of a runny nose in an infant that does not go away for a long time may be accompanied by anti-inflammatory drugs: Sinupret, Pinosol, Tantum Verde.
- It is sometimes necessary to treat a runny nose in a newborn baby with the help of antihistamines. For a runny nose in a newborn, it is safe to put Vibrocil drops into the nose. Children under one year of age should be instilled one drop at a time three times a day. For oral administration, drugs such as Suprastin, Cetrin, Zyrtec, Fenistil can be prescribed.
Treatment with folk remedies is carried out with caution. Many components can cause allergies and burns to the nasal mucosa in a newborn.
The only less safe remedy for a runny nose in a 3-week-old child is chamomile. You can breathe the decoction or drop it into your nose; if there is no fever, you can take baths with the addition of the decoction. The medicine reduces inflammation, facilitates nasal breathing, and speeds up the healing process.
Among the folk remedies, Kalanchoe or aloe juice helps. After picking, it is recommended to keep the plant leaves in the refrigerator for about 10 hours so that all the beneficial properties appear. Freshly squeezed juice must be diluted with purified water in a ratio of 1:5. A newborn is instilled with one drop up to three times a day.
Why does a baby have a long runny nose?
If your baby’s rhinitis does not go away for a long time, this may be a consequence of:
- Delayed or incorrect treatment, self-medication or failure to follow instructions for the use of drugs and therapy in general.
- The contact of the newborn with the provocateur of the disease was not interrupted (in case of allergic rhinitis).
A newborn has a severe runny nose. What can be done and how to help him cope with this illness? It is necessary to urgently treat the child to avoid complications and consequences of ineffective therapy.
Consequences of a prolonged runny nose:
- Reducing the weight of the newborn. The baby's appetite decreases because snot prevents him from fully sucking on his mother's breast. In addition, the child has difficulty breathing, which is very dangerous at this age.
- Further progression of the disease and infection of the respiratory system, resulting in the formation of otitis media, pharyngitis, sinusitis, and so on. The most dangerous complication is pneumonia.
- Rashes in the form of ulcers in the nasal cavity and on it.
All of these consequences are very dangerous for a fragile child’s body and require urgent and proper treatment. You should not self-medicate as it can be dangerous. If a child’s runny nose does not go away for more than 10 days, then you should immediately consult a doctor for advice and help. It is very important not to miss the moment and take all necessary measures in time and strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. Complete all necessary research. This is the only way to help the child recover without consequences and complications.
Treatment
Most pediatricians agree that you need to understand not how to treat a runny nose in infants, but why it appeared. Rhinitis is always a reaction of the mucous membrane, which cannot be without cause: physiological is characteristic of newborn babies, whose nose is not yet accustomed to the environment. There is no point in treating a baby in such a situation, but leaving the situation “as is” is also not entirely reasonable, since this causes discomfort to the child and parents.
Treatment of a runny nose in infants regarding its prerequisites looks like this:
with physiological, be sure to wash out the nose, pump out the snot with a “pear” so that there is no congestion and breathing is not impaired; in case of allergies, it is important to use drugs that will relieve inflammation from the mucous membranes, and oral administration of antihistamines is possible (you need to consult a doctor); in case of a viral infection, especially with a high temperature and severe intoxication, you need to go to an ambulance, or, if the temperature is 37.5 degrees, call a pediatrician at home - here they are sure to prescribe drugs that kill the virus and strengthen the immune system.
What to drip your nose with
Only a doctor can advise medications for a baby, which involve internal administration, if he considers this the only effective way to eliminate rhinitis, and in most situations, pediatricians recommend trying to cope with the problem with nasal drops, which you can do yourself, using breast milk - this is the safest option, which can be used to bury the nose of even a newborn. However, this remedy will not help “break through” congestion - it will only strengthen the immune system.
Mostly doctors:
- use antiseptics (saline solution is the safest for babies);
- vasoconstrictor drops are instilled;
- use nasal immunomodulators;
- moisturizing preparations are injected into the nasal passages.
Moisturizers
Drugs that help save the mucous membrane from drying out (this is especially important for babies aged 2-3 months) are often produced as a spray, which is convenient for irrigating the nasal cavity. In most cases, they are based on a special solution of sea water, which will not provoke allergies.
Among the moisturizing drops there are also immune stimulants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
The most effective:
- AquaMaris.
- Aqualor Baby.
Vasoconstrictors
When the runny nose is profuse, the baby’s sleep is disturbed, which negatively affects the state of the nervous system of both the baby and the parents. In this situation, it makes sense to use vasoconstrictor drops, which will stop the secretion of mucus for a short period of time. However, they are used only in the symptomatic treatment of rhinitis, since they do not affect the underlying cause. It is advisable to drip them once a day, at night, since they quickly provoke addiction and dry out the mucous membrane.
For infants (even used for newborns) you can buy:
- Nazol Baby.
- Nazivin 0.01%.
- Otrivin Baby.

Antiseptic drops
Effective treatment of infectious preconditions for a runny nose should involve the use of drugs that kill viruses (only on the nasal mucosa)
However, their choice should be approached with caution: antibiotics are only prescribed by a doctor (they are almost never prescribed for infants) - it is better to focus on less “severe” options. Drops based on colloidal silver and Miramistin perform well
Use must be carried out strictly according to the instructions.
Treatment for children with viral rhinitis often includes:
- Collargol.
- Protargol.
- Octenisept.
Antiviral and immunomodulatory agents
In infants, nasal use is also acceptable for some medications that have the ability to strengthen the body's defenses. The problem with such drugs is that they do not treat chronic diseases, do not provide a quick effect, and therefore do not help during exacerbations: they are mainly used to prevent the onset of the disease. However, if the baby has noticed the first symptoms of a runny nose, the main course of therapy can be supplemented with immunomodulators.
The safest:
- IRS-19.
- Derinat.
How to distinguish physiological runny nose from other types?
The symptomatic picture of diseases in infants is usually blurred, so even an experienced pediatrician finds it difficult to determine the cause of a runny nose. One of the criteria that allows you to distinguish pathological (caused by disease) rhinitis from physiological rhinitis is increased body temperature.
But if there is inflammation, the numbers on the thermometer can show 38-39 and even 40 degrees. In addition, there are a number of symptoms that allow you to correctly diagnose a baby.

ARVI in children
| Type of runny nose | Symptoms |
| Physiological | The baby's general condition is normal, appetite and body temperature do not change. A moderate amount of mucus is released from the nose, the baby sleeps with his mouth open or snores in his sleep |
| During teething | The temperature rises to 37.5-38 degrees, the nasal discharge is clear, accompanied by swelling of the gums. Appetite is good, but there are night awakenings and irritability |
| Viral | High (from 38 degrees) temperature, poor appetite, severe malaise. Nasal discharge is abundant, clear, and there is nasal congestion, which causes severe discomfort to the baby. |
| Bacterial | Fever is present only at the beginning of the disease, after which the temperature returns to normal. The nasal discharge is thick and has a yellowish or greenish tint, but the child’s general condition is satisfactory. |
| Runny nose as a result of irritants | Appetite, body temperature and other indicators do not change, nasal discharge is clear and liquid, sometimes there is redness of the eyes, sneezing, and tearfulness. The main symptom of this type of rhinitis is that it goes away with a change of environment |
| Drying of the mucous membrane | Rhinitis is not characterized by nasal discharge, but by dry crusts that can crack and bleed. |
To summarize, we can say that if rhinitis in a two-month-old baby is not accompanied by high fever and other symptoms, most likely it is caused not by a disease, but by characteristics of the body or external factors.
Causes of persistent runny nose in a child: types of rhinitis
A prolonged runny nose in children can be caused by one of dozens of different reasons, but for ease of classification, medicine divides them into three main groups:
- infectious rhinitis;
- allergic rhinitis;
- vasomotor rhinitis;
Prolonged rhinitis in a child can be complicated by structural features of the upper respiratory tract in childhood, as well as pathologies such as deviated septum, the presence of polyps and adenoids.
In everyday terms, experts consider a wider range of etiological factors:
1
Allergy. Every year there are more and more children suffering from various types of allergies, and any smell or fine substance that gets on the mucous membrane can be a provoking factor.
The result is an overly active immune reaction to the allergen - by secreting mucus, the body counteracts the irritant, resulting in not only prolonged rhinitis without fever, but also heavy breathing, swelling, lacrimation and itching.

It is difficult for parents to distinguish allergic rhinitis from infectious rhinitis at home, but the main differential indicator is the cyclical manifestation of symptoms.
2
Sinusitis. The fact that a child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time may be caused by sinusitis (one of the types of infectious sinusitis).
Inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinus is a consequence of viral or bacterial invasion through the respiratory tract, along with blood, or due to damage to the child’s upper teeth in the periapical areas.

The characteristic symptoms of sinusitis, which causes prolonged rhinitis, are nagging pain that causes discomfort to the child when bending the body forward, and increased body temperature.
3
Vasomotor rhinitis. If a child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time, and standard methods of therapy do not produce results, the doctor may assume that the child has a pathology of neuro-reflex mechanisms of reaction to aggressive household stimuli.
Important
These factors often include strong odors from food, perfumes or household chemicals, as well as cold air.
Allergic rhinitis is also a vasomotor reaction of the body, and a common physiological feature for all types of similar runny noses is the thickening of the mucous layer in the nose and the replacement of normal epithelium with stratified squamous epithelium.
The important thing is that it is difficult to get rid of such a disease, and lack of treatment can lead to difficulty in lung function, including asthma.
4
Abuse of vasoconstrictors. Some parents, during treatment, make the mistake of abusing drugs that actively affect vascular motility.
Medicines like Naphthyzin, which constrict the microvessels in the nose and thus eliminate swelling, do not solve, firstly, the problem of the formation of secretions, and secondly, they quickly become addictive.
As a result, due to long-term use of these drugs, pathologies of an endocrine and neurovegetative nature arise, microcirculation is disrupted and capillary neurosis occurs. Source: nasmorkam.net
5
Dry indoors. In addition to the fact that dry air can cause a vasomotor reaction in the child’s nose, it also negatively affects the condition of the mucous membrane.
Normally, the mucus located there acts as a barrier against the effects of irritating and pathogenic factors, but due to the dryness of the inhaled air, the amount of natural protective secretions decreases.
For this reason, allergens and irritants more easily penetrate the mucous tissue and bloodstream, causing persistent rhinitis, which continues until the child finds himself in a more favorable atmosphere saturated with moisture.
6
Adenoids. Hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissue that is part of the nasopharyngeal tonsil leads to its growth, which is why the baby experiences problems with breathing, swallowing and hearing.
Adenoid vegetations most often occur in children aged 3 years and older (up to 7 years), and their cause is complicated processes in the following diseases:
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- flu;
- ARVI.
Despite the fact that the main method of therapy in this case is surgical removal of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the treatment of prolonged runny nose in children caused by adenoids allows the use of conservative methods.
It is important to avoid tissue inflammation, as it will lead to fever, dry cough and purulent nasal discharge.
7
Injuries or congenital pathologies. Finally, as another reason, the presence of mechanical damage or hereditary developmental pathology should be considered.
The nasal passages in children are already very narrow, which makes it difficult for the natural outflow of secretions, and if the baby has a deviated septum or other similar abnormalities, the problem can only be solved surgically.
The presence of a small injury in the nose can provoke increased secretion of mucus, as well as the entry of a foreign object into the respiratory tract - a small toy or an insect (which is typical for children aged 2 years).
In these cases, eliminating the etiological factor will quickly return all disrupted processes to normal.
Should you listen to your family's advice?
In the meantime, tons of “wise” advice from older relatives will begin to fall on the head of a young mother (a first-time mother, as a rule). Be patient, listen to everyone, and nod your head politely. Then use logic, look on the Internet or call girlfriends with older children. Self-collection of information on the topic will give greater and better results than advice like “wipe the child’s face with the inside of your own T-shirt” or sprinkling with sacred liquids. And new grandmothers can change their vector and go cook dinner for mom, wipe the floor in the nursery, or go shopping.
It is worth carefully analyzing seemingly sound advice. For example, using breast milk instead of nasal drops. The increased temperature of the mucous membrane plus increased body temperature due to illness turns the child’s nose into a small oven, where fatty milk simply bakes with mucus, forming an additional dense crust. If doubts about the adequacy of the method have yet arisen, start with yourself: express a couple of drops of milk and drop it into your nose, record the sensations.
Home healers also often advise instilling aloe or Kalanchoe juice into infants. Particularly modern healers still suggest diluting the juice with water 1:1. The idea seems great - natural biologically active substances will not harm the child’s body. Yes, they won’t cause any visible harm, but they can provoke a severe allergy that you’ll have to fight with for the rest of your life. Therefore, in the first months the child should not come into contact with plant extracts.
How to treat
Depending on the problem causing your runny nose, you may need to use medications in the form of nasal drops to increase the effectiveness of treatment. Medicines for rhinitis for infants should be instilled into the nose. Preparations in the form of sprays can be used for children aged 2-3 years, not earlier.
Vasoconstrictors

Vasoconstrictor drugs are used for infants only as prescribed by a doctor, in the precisely indicated dosage. These drugs are addictive when used for a long time, so they are used preferably at night.
The vasoconstrictor reduces swelling of the nasal mucous tissues, relieves congestion, and also slows down the process of mucus secretion. Similar preparations for infants are available in the form of topical drops. Before use, you need to carefully read the instructions, and most importantly, do not exceed the dosage. Excess of the active substance of the vasoconstrictor drug can be absorbed into the baby’s blood.
Moisturizing
Moisturizing nasal drops include saline solutions and preparations based on sea water. The main feature of this product is the absence of chemical or artificial additives. It can be used throughout the day to cleanse and moisturize the nasal passages. As a rule, moisturizing nasal drops for medicinal purposes are used 5-6 times a day (2-3 drops in each nostril). Also, these drugs are suitable for preventing drying of the nasal cavity and the formation of crusts.
You can prepare your own saline solution at home. To do this, you need to dilute a level teaspoon of salt in 1 liter of warm boiled water. For infants, pediatricians recommend using preparations based on sea water. They contain useful natural minerals such as iodine, manganese, magnesium, chromium and selenium, which have a beneficial effect on the mucous membranes of the nose: they relieve inflammation and improve immunity. Such preparations are more expensive than saline solutions, but at the same time, more effective.
Antiviral
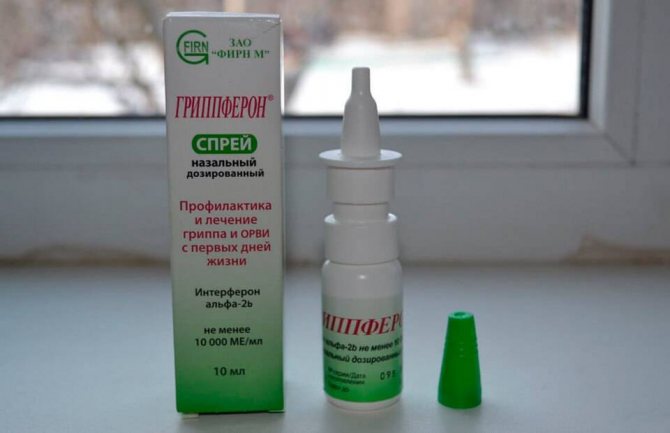
For herpes infections or viral diseases such as ARVI and influenza, antiviral drops are used. With the help of these drugs you can quickly alleviate the baby’s condition: reduce mucus secretion, relieve swelling. The main purpose of such funds is to fight viruses and prevent their spread further throughout the body through the upper respiratory tract.
Antiviral drugs are produced on the basis of interferon, a protein substance that helps reduce the susceptibility of cells to harmful microorganisms. It is advisable to use such drops for preventive purposes, or the first 3-4 days after the initial symptoms of the disease appear. Interferon-based medications are contraindicated for children suffering from protein allergies.
Antiseptics

Often viral diseases in children are complicated by a secondary bacterial infection (approximately 5-6 days of illness). In this case, to treat a runny nose in a baby, you may need antiseptic (antibiotic containing) agents in the dosage prescribed by the pediatrician. Prescribed if rhinitis does not go away within 5 days, as well as in the presence of complications. In advanced cases, they are used in combination with antiseptic medications in the form of injections or tablets.
Runny nose in babies
For any person, the period when clear liquid flows from the nose becomes unpleasant.
But while an adult can try to cope with their problems on their own, children do not have such an opportunity or skill. Therefore, parents should help their child get back to normal and get rid of the unpleasant runny nose that interferes with sleeping, eating and simply enjoying life. But first you need to establish the cause of the increased secretion of mucus from the nose. When it comes to children around 2 years of age, there can be various factors that cause a runny nose. Such babies often get sick, they may develop allergies, and there is a risk of a foreign body getting into the nose.
The latter option in curious children very often becomes the cause of discharge from the sinuses, so parents are obliged to pay extremely close attention to how and what their children play with.
A severe runny nose is called rhinitis. This is an extremely unpleasant condition that requires mandatory treatment. In addition to preventing the child from sleeping and playing normally, this problem can cause serious complications. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the cause of the baby’s runny nose, and then begin the correct treatment.
Depending on what exactly caused such trouble, one or another therapy will be used. But a doctor must prescribe medications and procedures, and only after a thorough diagnosis. When it comes to children under two years of age, self-medication is unacceptable. But even a common runny nose, as many believe, cannot be treated. Prolonged rhinitis without proper therapy can cause the development of chronic sinusitis or otitis media.
In order to cure a runny nose in a small 2-year-old child, it is necessary to determine at what stage this symptom is. At the initial stage, folk methods will also help to cope with the problem, but in advanced cases you will have to use medications and even painful physical procedures.