Function of tonsils in the body
Tonsils serve as a barrier against external infectious pathogens
A child’s tonsils perform the function of protecting the body from attacks by pathogenic bacteria and viruses. They are located at the border of the digestive and respiratory tract. Due to this structure, the tonsils manage to timely capture pathogenic agents that enter the oral cavity during inhalation.
The tonsils take an active part in the formation of humoral and cellular immunity.
Tonsils perform a number of useful functions:
- Barrier. Prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering the human body.
- Immunogenic. Produce lymphocytes.
- Hematopoietic. The function is most important to ensure the proper functioning of internal systems in newborn babies.
In addition, the tonsils are involved in the production of enzymes that are required for proper digestion.
If a child has enlarged tonsils, there is a high probability of disruption of the functioning of this organ. For this reason, the body remains defenseless against attacks from pathogens.
Causes of enlarged tonsils in children
Enlarged tonsils in a child are caused by various reasons. Only a competent doctor specializing in such health problems can find out the true factor that led to this result.
In most cases, the cause of enlarged tonsils is infectious diseases suffered by children that have not been fully cured.
Damage to the child’s body by the following infectious agents can lead to pathology:
- Staphylococci.
- Streptococci.
- Influenza virus.
- Herpes.
- Pneumococci.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Adenovirus.
- Chlamydia.
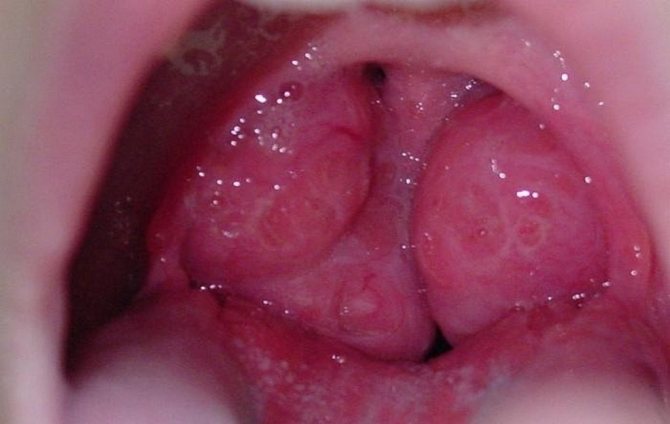
Tonsils may become enlarged if the child has an acute respiratory viral infection
After the main symptoms of the disease go away, parents begin to believe that their child is completely healthy. In fact, infectious agents continue to threaten children's safety. They can continue to conduct their life activities in the lacunae of the tonsils. At a favorable moment, viruses and bacteria will continue to actively develop, causing the tonsils to become inflamed.
The problem is usually caused by acute and chronic pathologies that affect the throat and tonsils. We are talking about the following conditions:
- Hormonal disorders and disorders of the endocrine system.
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- Chronic colds and sore throat.
- Children's infections.
- Avitaminosis.
- Deviation of the nasal septum.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Allergic reactions.
- Living in a city with poor ecology.
If the tonsil is enlarged, it means that the child’s body is actively fighting the pathogen that attacks it. If this situation does not cause discomfort to the baby, then you can do without treatment. It is enough just to observe his condition.
Causes of hypertrophy
It is not possible to say exactly why the tonsil becomes hypertrophied. However, we can say with confidence that this is a protective reaction of the body to the action of an unfavorable factor.
In children, due to the underdevelopment of the immune system, lymphoid tissue is very variable, so its hyperplasia does not require long-term exposure to a damaging factor.
Predisposing factors that cause the proliferation of lymphoid tissue, which causes hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils in children, include:
decreased immune defense; exacerbation of chronic pathology; poor nutrition; frequent infections (ARVI, influenza); the presence of infection in the throat (pharyngitis) or nasopharynx (sinusitis); chronic tonsillitis, when microbes accumulate in the folds of the mucous membrane, supporting the inflammatory reaction; heavy physical activity; dry polluted air; occupational hazards.
Note that children whose parents suffered from adenoids or had their tonsils removed, that is, with a burdened heredity, suffer more often.
Symptoms
The question of why the child’s tonsil increases in size has been resolved. Now you need to find out the symptoms that determine the painful condition.
Need to know! Enlarged tonsils are not a separate disease. Pathology is seen as a symptom of another disease.
The symptoms of the pathology directly depend on what disease it was caused by. The following signs of illness are identified:
- Fever, cough, nasal congestion and sore throat (respiratory diseases).
- Formation of ulcers in the larynx, plaque on the mucous membrane, pustules and redness of the throat (sore throat).
- White film on the tonsils, swelling of the neck (diphtheria of the pharynx).
- Enlargement of only one tonsil (syphilis, herpes).
- Congestion of the hearing organ and enlarged tonsils (otitis media).
- Presence of ulcers and necrosis on the tonsils on both sides of the throat (pernicious anemia).
- Difficulty breathing, inability to breathe through the nose (enlarged adenoids).
If a child’s tonsils are enlarged and the pathology itself occurs without fever, then he will still be bothered by accompanying symptoms. We are talking about a nasal voice, sore throat, bad breath and problems sleeping.
How does pathology manifest itself in children?
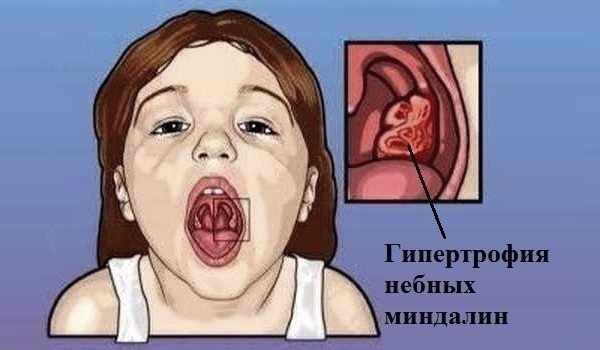
At the first examination, the doctor will determine which tonsils are affected:
- Palatine and tubal (paired) glands. The first are located on the sides of the entrance to the pharynx, the second in the hearing organs.
- Pharyngeal and lingual (unpaired) glands. The first is located on the back wall of the pharynx, the second under the tongue.
The organs of the lymphatic system protect the body from infection, dust and viruses. In a child, they cannot fully perform their functions, since they are not yet developed enough.
Formation finally ends by the age of 12, and then it is expected that the hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils will begin to decline. Not all children require mandatory treatment.
Stages of enlarged tonsils
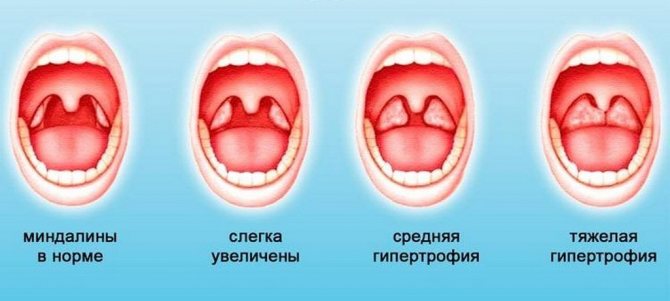
The sooner treatment begins, the greater the chance of coping with the problem using “easy” means.
There are different stages of tonsil enlargement. There are four in total:
- Initial stage. At this stage of development, the affected organ tissue covers no more than 30% of the lumen between the pharynx and the palate. Symptoms of the disease practically do not make themselves felt. The child's condition worsens mainly at night.
- Second stage. The enlarged tonsil covers half of the vomer. Because of this, even during the day, children experience problems with swallowing and breathing.
- Third stage. The patient has severe respiratory dysfunction. There will definitely be complaints of difficulty swallowing. This is because the pharynx fills with inflamed tissue.
- Fourth stage. This is the last stage of the development of the disease. By this time, the child’s tonsils have grown significantly. His pharynx is almost completely blocked by the affected tissue.
When to see a doctor?
Not every parent knows what to do if their child’s tonsils increase in size. This is an alarming symptom that should definitely be addressed to a competent specialist.
Important! Even with a slight increase in tonsils in children, you need to immediately make an appointment with a pediatrician.
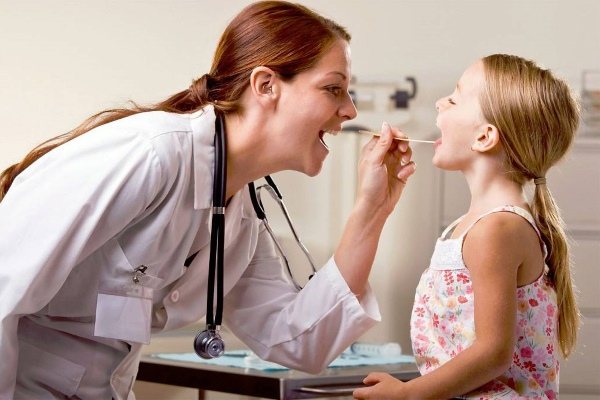
If the tonsil is inflamed on one side, then during the examination the doctor will identify this disorder. Initially, he will conduct a visual inspection of the problem area. Afterwards, tests will be required, the results of which will clarify the holistic picture of the disease.
You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if your child has the following signs:
- Organ hypertrophy.
- Redness of the throat.
- Swallowing problems.
- Increased body temperature.
- The presence of white plaque on the tonsils.
- Increased size of lymph nodes.
Depending on the disease, the patient may also experience fever, headaches and severe body weakness.
Traditional treatment
Treatment tactics directly depend on the degree of enlargement of the tonsils and the severity of the disease. If the increase is minimal and there are no serious clinical manifestations, treatment may not be carried out. The child will outgrow this, and the lymphoid tissue with tonsils will independently decrease in volume.
For grade 1-2 correction, physiotherapeutic procedures and pharmacological agents are usually used. In cases where grade 3 is observed, depending on individual indicators, the doctor may prescribe surgical intervention.
Drug treatment
This method is based on the treatment of the palatine tonsils using various antiseptic drugs. They generally have an astringent effect and are plant-based immunomodulators.

In the second degree of the disease, the tonsils can be “cauterized” with a solution of lapis or collargol, as well as hydrogen peroxide. In addition, the following medications are used:
- Tkanin. This is a solution that is used to gargle and smear onto lymphoid tissue.
- Antimorphine. This is an antiseptic that is also used for gargling.
- Silver nitrate. Widely used in medicine for cauterization.
- Lozenges. These include Faringosept, Tantum Verde, Strepsils.
- Immunostimulants. Used to support the body (Carocel, Groprinosin, Thymogen).
- drugs . If, with enlarged tonsils, the child has an elevated temperature, you can take Aspirin, Paracetamol, Metamizole or Movalis.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics : penicillin group (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Tetracycline);
- group of fluoroquinolones (Gatifloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin).
Be sure to check exactly what concentration of each solution should be for a child of a particular age, since in pharmacies all these drugs are sold undiluted. Basically, they do not have any contraindications, except for individual intolerance to one of the elements in the composition.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
This type of treatment is one of those that helps avoid surgery to remove tonsils. This is a comprehensive method that can be combined with drug treatment. The course of a particular procedure usually lasts no more than 10-12 days and is aimed at normalizing the blood supply to the tonsils and lymph nodes that are nearby.
Types of physiotherapeutic treatment can be divided into the following categories:
- Exposure to dry heat. It could be rays of light or electricity. Warming the tonsils with a laser or ultraviolet helps to destroy pathogens and destroys the harmful microbial environment. It also helps reduce sore tonsils. It is strictly not recommended to do electrophoresis for children undergoing chemotherapy.
- Impact on the tonsils by wave vibrations. It is quite an effective remedy, but it is not recommended to use the method for very young children (including infants). The main task of therapeutic waves is to destroy the structure of the cheesy mass that has formed on the tonsils.
- Steam and moist heat treatment. Inhalation has a positive effect on the healing process and is considered the most optimal treatment option for any age. The only contraindication to inhalation is the presence of high temperature.
Surgical intervention
In the most difficult cases, the doctor prescribes surgical treatment, which involves removing the tonsils. This is an extreme option, because then the person is left without one of the organs of the immune system.
Indications for surgical intervention:
- Swelling of the mucous membrane and proliferation of tissue around the tonsils.
- Progression of pathology over the course of a year, when conservative treatment has not brought results.
- Obviously expressed allergic forms of pathology.
- Complications in the form of rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, rheumatic carditis and other similar diseases.
- Exacerbations of other diseases during conservative treatment of tonsil enlargement.
- The appearance of abscesses in the tissues of the tonsils.
Contraindications to surgical intervention:
- the presence of certain chronic diseases;
- hypertonic disease;
- hemophilia;
- improper kidney function;
- caries and stomatitis;
- period of a teenager's menstruation.
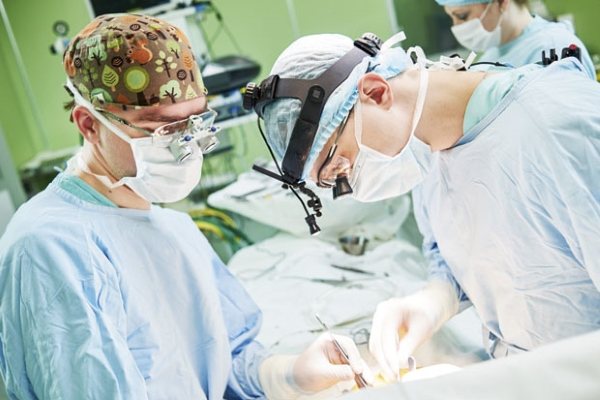
The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia. The duration of this procedure takes from several minutes to half an hour. It depends on the child's age and individual condition.
The recovery period takes 3-4 days, maximum 7. One of the main recommendations during this time is to eat food at a temperature of 25 to 30 degrees. It should be fine, without salt and sharp ingredients that can damage the surface of the larynx during its healing.
What to do if a child has enlarged tonsils
A pediatrician or a specialist who specializes in the treatment of ENT pathologies will tell you how to treat enlarged tonsils.
The course of treatment for the patient should be structured according to the following plan:
- Cleansing the tonsils from mucus and infectious agents using antiseptic solutions.
- Eliminate allergies and swelling by taking antihistamines.
- Strengthening the immune system by introducing complexes of vitamins and minerals into the course of treatment.
- Fight pathogens with antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs.
- Restoration of affected tissues using physiotherapeutic treatment.
As for the course of physiotherapy, it is recommended for patients who have managed to cope with the acute course of the inflammatory process in the throat.
Etiotropic therapy

The drug has an antibacterial effect
Etiotropic therapy can cure enlarged tonsils. With its help, hypertrophy is combated, which is caused by active reproduction in the affected area of viruses and bacteria.
Systemic medications do not allow infectious agents to continue to lead active life activities. It is suppressed until the pathogens are completely destroyed.
If the tonsil on one side is larger in size due to bacterial damage, the doctor will recommend taking the following medications:
- "Panclave".
- "Z-factor".
- "Augmentin".
- "Clarithromycin."
If there are pustules and plaque on the tonsils, you will need to use agents that cope with viruses. In the course of treatment, the doctor will introduce drugs belonging to the group of immunostimulating and antiviral drugs. These include:
- "Relenza."
- "Orvirem."
- "Viferon".
- "Kagocel".
Destroying pathogenic microflora allows you to reduce the severity of inflammation and restore the functioning of the immune system.
Symptomatic treatment

Contains large amounts of vitamin C (taken daily)
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at alleviating the child’s painful condition. It allows you to cope with pain, discomfort in the throat and other symptoms that accompany inflammation of the tonsils and their increase in size.
As symptomatic therapy, it is customary to use sprays, vitamin complexes and gargling solutions.
Children are offered therapy based on a number of medications:
- "Kameton."
- "Loratadine."
- "Stopangin."
- "Chlorophyllipt".
- «.
If the tonsils are very enlarged and conservative treatment methods do not give a positive result, then the option of removing the inflamed organ is considered.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy allows you to restore the function of enlarged tonsils. The child’s attending physician decides how to treat hypertrophied tonsils.
A physiotherapy course performs several important tasks. Its action is aimed at stimulating blood circulation in the affected area, as well as improving drainage function. Due to this, the tonsils gradually return to their normal size.
As prescribed by a specialist, children are offered a course of the following types of physiotherapy:
- Ultraviolet irradiation. The procedure allows you to quickly cope with pathogenic bacteria that provoke enlarged tonsils. Additionally, the course of treatment eliminates swelling and reduces the severity of the inflammatory process.
- UHF therapy. During its implementation, blood microcirculation returns to normal. Thanks to this, the regeneration of affected tissues is started.
- Ultrasound therapy. It is aimed at cleansing the follicles and lacunae of pus that can accumulate in them.
- Laser therapy. Using a laser, microorganisms that multiply in the affected area are destroyed.
To achieve the desired result, you must undergo a full course of physiotherapeutic treatment. It includes at least 7-10 full procedures.
During physical therapy, the child must continue to take the prescribed medications. A break in their use can adversely affect the patient's health and lead to relapse.
Possible consequences and complications

Progressive pathology, especially if not addressed, can inhibit development in children
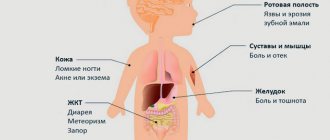
Inflamed tonsils are a source of infection that must be eliminated with adequate treatment. If this recommendation is neglected, the infectious pathogen eventually penetrates the blood and spreads to different organs and systems. It is as a result of this development of the disease that the child may experience the following complications:
- Cardiovascular diseases, in particular myocarditis and right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Joint diseases.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Anemia.
- Pathologies of the nervous system, especially urinary incontinence and tics.
- Delayed physical and mental development of the baby.
Incorrect development of the jaw bite cannot be ruled out. Also, if left unattended, enlarged tonsils often cause breathing problems due to underdevelopment of the chest.
Prevention
Enlarged tonsils in a baby are a serious symptom that requires parental attention. Various reasons lead to changes in their size, which have a detrimental effect on the child’s health. To prevent such problems, it is necessary to prevent the development of infectious diseases.
The following recommendations can help prevent health problems that are accompanied by enlarged tonsils:
- It is necessary to harden the child to increase his immunity.
- It is necessary to avoid severe hypothermia of the body. Its overheating is also not good for health.
- Do not give your babies food or drinks that are too hot or cold.
- It is necessary to promptly treat diseases that are diagnosed in a child.
- It is necessary to regularly sanitize the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
- It is advisable to maintain a healthy climate in the room where children are present for a long time.
Preventative measures help your child stay healthy. In addition, they prevent the appearance of pathologies that inhibit the function of the tonsils and lead to their enlargement.
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of treating enlarged tonsils in children can be used only in cases where there is no accumulation of pus.
Rinse
One of the main methods in the field of traditional medicine is rinsing. This can be done using the following means:
- Chamomile infusion mixed with oak bark, mint and sage.
- A solution with hydrogen peroxide (3%), which is diluted in the proportion: a teaspoon per glass of water.
- For half a liter of water, take one teaspoon each of salt and soda, as well as 3 drops of iodine.
- You can prepare a decoction of beets. To do this, you need to wash it and grate it on a coarse grater without cutting off the peel. Then add water and simmer briefly over low heat, let cool and strain. The child needs to gargle with this decoction every time after he eats.
Beverages
When fighting enlarged tonsils in children, one of the effective ways is to take various infusions. Here are several options for preparing them:
- A strong remedy is an infusion of calamus root, chamomile, wormwood, sage, St. John's wort, currant and eucalyptus. You can also add a little dill and thyme to this mixture. Fill everything with water and let it brew. Take in small doses for 3-5 days.
- Another option is to use a medicinal mixture of St. John's wort, ephedra, rose hips and horsetail.
- A decoction of calendula flowers, licorice roots, chamomile, sage and wild rosemary is considered a good remedy for relieving swelling of the tonsils.
- Drinks that help treat enlarged tonsils include hot tea with lemon and honey. Teas can also be made from mint, rose rhodiola, raspberries, blackberries and clover flowers.
- Squeeze juice from carrots, cucumbers and beetroot. Give your child this liquid once a day.