Is shape important?
As soon as a woman realizes that she is pregnant, she is required to register with a doctor so that the specialist can monitor the condition of the mother and her child. In the first trimester, various studies are required, including ultrasound.
The specialist first determines the presence of pregnancy, which will be indicated by the presence of a fetal element - this is the embryo and the various membranes surrounding it. It is diagnosed already at 5 weeks of age. Then the pathology is determined.
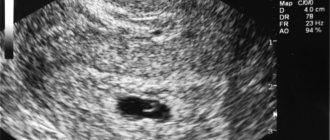
In studies, the main indicator is the average and internal diameter of the ovum (SVD). The gestational age is judged by the size of the existing fertilized egg, which in the first weeks should be oval or spherical in shape. This is the norm.
But sometimes the doctor sees it as too large or elongated; this is necessarily recorded in the history of the pregnant mother. Should I worry about this diagnosis? As practice shows, this does not apply to pathological conditions, provided that it is not accompanied by other symptoms.
Therefore, the prognosis for pregnancy in the case of a deformed fetal element is almost always positive. But it will be possible to say more accurately only after conducting certain studies.
fertilized egg
If a doctor, during an ultrasound examination, reports that he sees a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, the woman can be congratulated, because in 9 months she will become a mother. The presence of a fertilized egg can be determined already on the 7-9th day of missed menstruation. If the fertilized egg is in the uterus, then the pregnancy is normal, uterine. The specialist will immediately determine the size of the fertilized egg, its shape and location. In addition, he will pay special attention to whether there is a detachment or other pathological conditions.
What does a fertilized egg look like?
The fertilized egg is an oval or round body with a diameter of several millimeters. The diameter of the ovum is measured during the first ultrasound. Taking into account its size, a specialist can determine the gestational age. But in some cases the error in determination is 1-1.5 weeks. Therefore, when trying to establish a period, the doctor also takes into account indicators of the coccygeal-parietal size.
At 3-8 weeks of pregnancy
the fertilized egg looks like a formation in the form of a ball or oval. Already at 5-6 weeks, the yolk sac, which provides nutrition to the embryo and performs a hematopoietic function in the early stages of embryonic development, is similar to a bubble inside the cavity of the fertilized egg. The size of the fertilized egg at this stage of pregnancy is from 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters. It is already possible to examine the embryo at this time. It looks like a five-millimeter strip located next to the yolk sac. And although it is not yet possible to determine which structure and part of the embryo, the heartbeat is already being recorded. At this time, the baby’s heart beats at a frequency of 150-230 beats per minute.
In addition, the neural tube is already forming in the fetus, and the cells distribute “responsibilities” among themselves, who will create which organs.
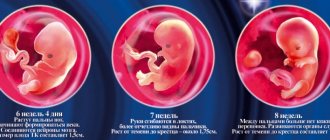
By the end of the 7th week, the embryo has already acquired its characteristic shape in the form of the letter C. At this time, it has already detached from the surface of the fertilized egg. An ultrasound can already distinguish the head, torso and tiny rudiments of arms and legs. An already formed umbilical cord is visible in the fertilized egg.
Irregular shape of the fertilized egg
Normally, the shape of the fertilized egg is oval or round. If it is flattened on the sides and looks like a bean, this may indicate the tone of the uterus. This condition should be monitored by a doctor. If nothing bothers the woman, then the deformation does not pose a threat to the pregnancy. In case of increased uterine tone, doctors prescribe a set of measures (bed rest, medication) to relieve hypertonicity and return the fertilized egg to its correct shape. This can be achieved by relaxing the muscles of the female reproductive organ.
But, if the fertilized egg has an irregular shape, and the woman experiences pain, discharge or symptoms of cervical dilatation, urgent measures must be taken. In such cases, the woman is assigned to the inpatient department of the hospital for safekeeping.
Why is this happening
Mommies are most interested in the question of why her fertilized egg may be deformed in the early stages. In fact, there may be several causes of pathology. The main one is deformation due to severe hypertonicity of the uterus. This affects the shape of the fertilized egg, which is compressed.
Other risk factors include:
- suffered stress;
- emerging infections in the reproductive system;
- viral and bacterial infections in other organs;
- hormonal imbalance.
This is not a complete list of reasons. What does this mean for a woman? A full range of studies, after which the doctor usually prescribes medication. But mommy herself will need to behave carefully, otherwise the consequences may be unpredictable.
Sizes by week
The size of the fertilized egg in the early stages of pregnancy is the main parameter by which the doctor can judge how the baby is developing. The embryo is still very small, it is not possible to measure it and its individual parts, but the growth rate of the fertilized egg is a very informative indicator of the development of pregnancy as a whole.
The size of the ovum indicates not only development, but also compliance with certain obstetric dates. The fact is that at the very beginning of pregnancy, when the embryo is just emerging, there is not much difference in height and weight. It is much later that children in the mother’s womb begin to grow differently, in accordance with their genetic program (some are tall, others are small). In the meantime, all babies develop almost identically, so the growth rate of the fertilized egg is almost the same.
Errors and range of values in diagnostic tables are associated with the likelihood of late implantation, as well as with other factors that may affect the size of the fertilized egg, but do not pose a threat to the development of the baby.
What else will the study show?
Ultrasound shows the doctor not only the shape, but also the pathologies that can be caused by this. For example, already at 6 weeks you can predict the fading of pregnancy.
Pathologies can be different:
- small ovum;
- large egg size;
- elongated shape.
We should talk about a small size if the egg does not correspond to the gestational age. But most often this is not a pathology, but an error in determining the week of pregnancy. But the same can be observed in the presence of a frozen pregnancy.
In this situation, it will be necessary to conduct additional research. But if a woman also has brown discharge, then she should rush to get tested. This may be due to a missed or ectopic pregnancy. Delay is unacceptable!
A large egg also indicates an abnormally developing pregnancy. Research shows that it develops without an embryo. But in this case, mistakes are often made during ultrasound examination, so it is best to carry it out after the 7th week of pregnancy.
Normally, the shape can be round or oval. But sometimes an ultrasound shows an elongated egg. Usually we are talking about uterine hypertonicity, which requires treatment in a hospital. An elongated egg is observed in twins and this does not indicate pathology, this is the norm.
A damaged ovum during twins often results in the loss of one embryo. The second can develop further in the absence of other pathologies.
Causes of deformation of the ovum
The approximate time of conception and a small fertilized egg at 6 weeks of pregnancy is determined using ultrasound.
The main reason for this condition is considered to be increased uterine tone. Changing shape is not always a cause for concern. More often, over time, all indicators return to normal and no additional therapeutic actions are required. The main factor influencing the tone of the uterus is stressful situations and negative emotions experienced by the expectant mother. In order for a woman’s condition to stabilize, complete rest and walks in the fresh air are necessary. Infectious diseases and harmful bacteria that penetrate the cavity along the ascending path can provoke uterine tone beyond normal. In this case, antibacterial treatment with approved drugs during pregnancy will be needed.
An elongated fertilized egg may indicate a high risk of miscarriage and spontaneous termination of pregnancy. In a hospital setting, doctors prescribe antispasmodic drugs that help preserve the baby, and also carry out diagnostic measures to determine the main causes of this condition.
From embryo to fetus
Women are often interested in why, when they talk about improper development of the egg, they don’t mention the fetus? It's simple. Until the 8th week, obstetricians do not call the new life in a woman’s body a fetus, since it is not exactly a child, but a certain substance that will very soon turn into a baby. But every week it develops, increasing in size.

This allows you to determine the shape of the developing fertilized egg week by week:
- up to 16 weeks - 1 mm per day;
- until the end of pregnancy - up to 2.5 mm per day.
The 6th week is important, at this time the digestive system and spleen are born. With a size of 16 mm - the stomach and esophagus. It is at this time that they say that a woman is carrying a child. And this is a difficult period associated not only with the restructuring of the entire body, but also with the discomfort that the woman experiences during this process.
And each of us wants to look as attractive after a successful birth as before the “interesting situation.” And mothers will be helped with this by a special cream for stretch marks for pregnant women – “Babycoccole”. The volume of 300 ml allows you to use the composition for a long time.
And its components are completely safe for a woman carrying a child. Before use, it is recommended to take a shower and apply a small amount of cream to the area prone to stretch marks. Usually this is the stomach, chest, thighs.
Deformations of the fertilized egg
A small fertilized egg in the early stages is not a reason to worry, since usually everything returns to normal after some time. It is important to initially monitor the process using ultrasound. It’s another matter when the fertilized egg has irregular outlines.
This phenomenon is a pathology and most often indicates abnormal development of the fetus. Normally, the egg should have an oval or round shape. If it is flattened on the sides, then this is the first sign of uterine hypertonicity. The patient needs to be under the supervision of a doctor for some time. If no dangerous symptoms develop in the future, then the threat is eliminated.
If a pregnant woman experiences pain or vaginal discharge appears, immediate action must be taken. Bed rest and absolute rest are prescribed. Medications to reduce uterine tone and hormonal medications are required. It is possible that the woman will have to spend the entire remaining period before giving birth in the hospital.
Consequences
The tone of the uterus is not as terrible as it is “painted”. And quite often it goes away without the intervention of doctors or taking medications. It is simply enough for a woman to change her lifestyle, calm down, stop being nervous and normalize her diet. Most women in the early stages do not feel any tone at all, and only a doctor, through ultrasound scanning, is able to determine this condition, including by the shape of the fertilized egg.

When the tone becomes noticeable and manifests itself as nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, this may be a more dangerous condition, but even with it, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, there will be no negative consequences.
This does not mean that you need to ignore the doctor’s conclusion about the deformation of the ovum. Finding the true causes of increased tone is not as easy as it seems, since they are often complex, there are several of them at once. But it is possible and necessary to take certain measures to reduce tone, if it remains stable.
Structure of the fertilized egg
The fertilized egg begins to develop immediately after fertilization of the egg: the cells begin to divide. You can see pictures of the fertilized egg already in the third week of your missed period. When the diameter of the fertilized egg is 2 mm, then you can think about pregnancy for four weeks. If the fertilized egg is 4 mm in diameter, they say that the gestation period is very short, no more than five weeks. When using a transvaginal sensor, it is visualized earlier.
The fertilized egg moves from the abdominal cavity to the uterus. Her journey lasts from one week to ten days. During its movement, the process of cell division continues. When the fertilized egg reaches the uterus, it will contain 32 cells. It needs nutrients and oxygen for normal development, so the egg is covered with chorion on top. Its surface secretes special enzymes that dissolve the uterine mucosa. On the entire surface of the egg there are villi with which it is connected to the uterus. Subsequently, they are present only at the site of attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus. Twenty days after the last menstruation, the yolk sac can be seen on ultrasound. It provides the embryo with vital substances. Its presence does not guarantee that the pregnancy is developing normally, however, in the absence of a yolk sac, it is worth considering that in this case there are problems with the development of the fetus. If the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus, pregnancy will not occur.
At the sixth week of pregnancy, a strip about five centimeters long is already clearly visible in the fertilized egg. This is an embryo. The fetal heartbeat can also be seen at this stage. The baby's heart beats at a rate of 220-240 beats per minute. Cells begin to differentiate, they determine which will be responsible for what in the future. The embryo develops a neural tube.
It separates from the fertilized egg, and parts of the body can already be distinguished in it: arms, legs and head. The umbilical cord is also visible in the picture of the fertilized egg.
After the fertilized egg has penetrated the uterine cavity, it must implant itself against its wall, that is, the stage of nidation begins. How it attaches depends on the development of the villi. The villi develop well when the egg moves at a normal speed and the chorion has fully developed. In case of underdevelopment of the chorionic layer, the fertilized egg cannot attach to the uterus and the risk of a miscarriage increases.
Low attachment of the fertilized egg
If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, the expectant mother is prescribed drugs to preserve it (Duphaston, Utrozhestan).
As we can see from what was written above, a change in the shape of the fertilized egg does not always indicate a pathology of pregnancy. Most often, deformation of the ovum can be observed with an increase in uterine tone, to normalize which you can take antispasmodics (No-spa) and Magne B-6.
During any fertilization of an egg, it must move into the uterine cavity and implant itself against its walls. But sometimes unforeseen failures occur; the fertilized egg does not reach its intended place, attaching to the fallopian tube, to the ovary, or even to the abdominal cavity.
Such a pregnancy is defined as ectopic. After a pregnancy test is performed, it is confirmed in most cases. But the test will not show whether the pregnancy is normal or ectopic.